Lecture 11: Transcription
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What is the core promoter?
Sequence of DNA that is recognized and binded by RNA pol.
What is the CRM?
Cis regulatory module which is recognized and bound by transcription factors
True or False: CRM are always located upstream
False
What is the coding region made up of?
Introns which are spliced out and exons which are expressed in mRNA
Downstream sequences can determine
Stability of mRNA and the transcription stop site
Bacteria core promoter vs Eukaryote core promoter
In bacteria, the core promoter is a TATA box located from -10 to -35
In eukaryotes, the core promoter is a TATA box located from -25 to -80
Transcription is completed by RNA polymerases (RNAPs), what are the 3 classes of RNAPs in animals and what are they responsible for?
RNAP 1- Ribosomal RNA
RNAP 2-mRNA, microRNA, lncRNA
RNAP 3-tRNA
What are the three stages of transcription?
Initiation, Elongation, Termination
What is initiation?
When RNAP binds to the core promoter
In bacteria, what binds to the core promoter?
Sigma factor which recruits 2 alpha and 2 beta subunits to form a Holoenzyme
There are many sigma factors and each recognize a sequence in which each nucleotide is the one that occurs most frequently at the site also which is also known as a
Consensus sequence
-35 and -10 consensus sequence, why?
None of the sequence is incorporated into the RNA
In eukaryotes, which sites are recognized by binding proteins?
A-T rich sites
A binding proteins bonds to an … which is a sequence necessary for general transcription factor recruitment
Initiator element
What is the TATA box?
TATAAA initiator element recognized by TBP (TATA-Binding Protein)
TBP is a subunit of what enzyme?
TFIID which is a general transcription factor that recruits other general transcription factors to from the pre initiation complex with RNAP
TFIIB function
Promotes binding of RNA pol 2 to the core promoter
function of TFIIH
Acts as helicase to form an open complex
General transcription factors vs Sequence specific transcription factors
GTF are necessary for transcription, do not regulate transcription, recognize the same general consensus initiator elements
Sequence specific TF bind to elements in the CRM or TRM for transcriptional regulation
What two parts make up a transcription factor?
DNA binding domain and protein interaction domain
a mutation of the CRM of which gene can lead to legs growing on the head of a fly?
Antp
One major mechanism for chromatin remodeling is
Acetylation and deacetylation
What enzyme aids in acetylation and what enzyme aids in deacetylation
Acetyltransferases and deacetylases
Acetyltransferase makes chromatin into …. And deacetylases makes chromatin into….
Euchromatin (loose) and Heterochromatin (tight)
What is another mechanisms for gene expression regulation?
CG islands
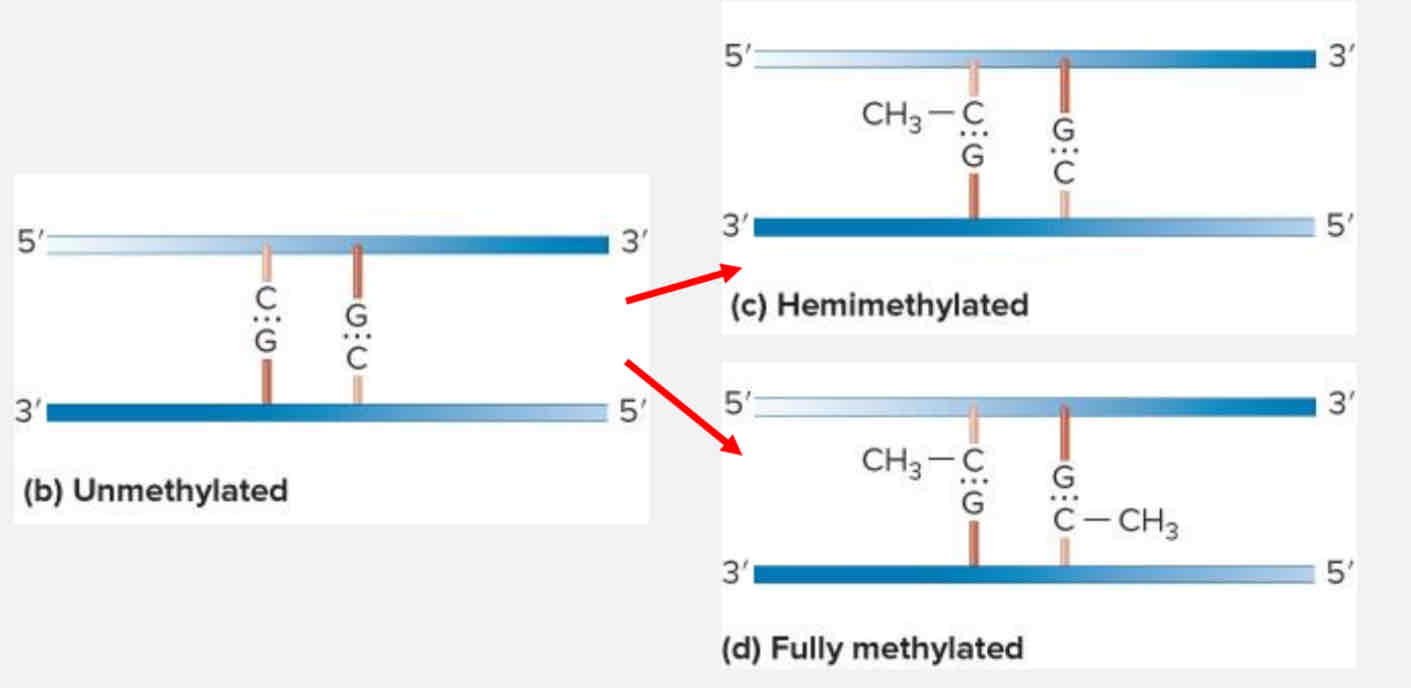
CG islands are methylated by
DNA methyltransferases
DNA methyltransferases add a methyl group to
Cytosines
Hemimethylated vs Fully Methylated
What is the mediator?
The mediator is essential for transcription in nearly all genes transcribed by RNAP 2
Transcription takes how many nucleotides per second in prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
50-60 nucleotides per second in prokaryotes
15-20 nucleotides per second in eukaryotes
Splicing in bacteria vs eukaryotes
Bacteria: Very rare;self splicing
Eukaryotes: occurs in protein encoding pre-mRNA via spliceosome (protein and RNA complex)
Splicing involves 3 consensus sequences
5’ splice site
3’ splice site
Branch point adenine
Most mature mRNAs have a … attached at their 5’ end in an event known as capping
7-methylguanosine
Most mature mRNAs have a string of adenine nucleotides at their 3’ ends known as
The poly-A tail
What is RNA editing?
Exon sequence is alter after transcription