MCAT Physics Module I: Newton's Laws
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
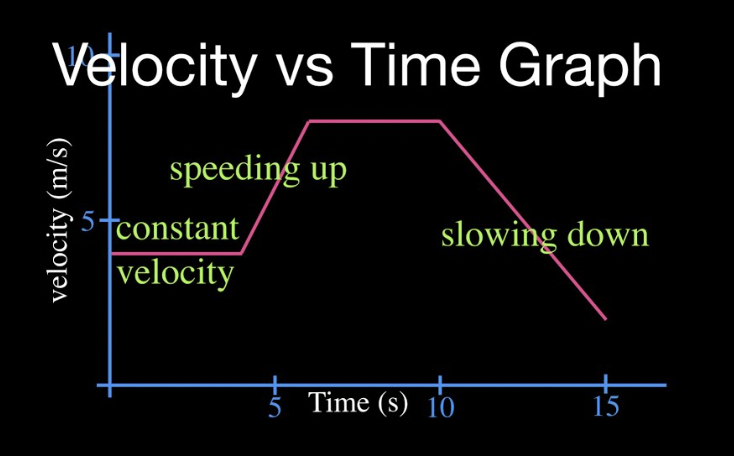
How do you find the displacement from a velocity vs time graph?
The displacement can be found by calculating the area under the velocity vs time graph. The area represents the total distance traveled, taking into account the direction of the velocity.
T/F: If you are just given the acceleration and initial conditions for a given situation, can you plot the velocity vs time on a graph?
True, use the acceleration as the slope of the plot and initial conditions to guide you.
Under constant acceleration, how do you compute displacement Δx\Delta xΔx using initial and final velocities?
Δx=((vi+vf)/2)Δt
A car starts at 5 m/s and accelerates at 2 m/s² for 4 s. What is its final velocity?
A) 11 m/s
B) 13 m/s
C) 18 m/s
D) 21 m/s
B) 13 m/s
Explanation: vf=5+2×4=13 v_f = 5 + 2 (4) =13 m/s.
A velocity-time graph shows a straight line from 5 m/s to 13 m/s over 4 s. What is the total displacement?
A) 24 m
B) 32 m
C) 36 m
D) 72 m
C) 36 m
Explanation: Area = rectangle (5 × 4 = 20 m) + triangle (½×8×4 = 16 m) → 36 m total.
Under constant acceleration from 5 m/s to 13 m/s over 4 seconds, what is the average velocity?
A) 5 m/s
B) 8 m/s
C) 9 m/s
D) 13 m/s
C) 9 m/s
Explanation: Average velocity = (vᵢ + v_f)/2 = (5 + 13)/2 = 9 m/s.
How far does the car travel if its average velocity is 9 m/s over 4 s?
A) 9 m
B) 18 m
C) 36 m
D) 72 m
C) 36 m
Explanation: Distance = average velocity × time = 9 m/s × 4 s = 36 m.
Newton’s First Law
An object at rest stays at rest, and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by a net external force.
A hockey puck slides across frictionless ice at constant velocity. What must be true about the net force acting on it?
A) It is non-zero and directed forward
B) It is non-zero and directed backward
C) It is zero
D) It decreases over time
C) It is zero
Explanation: According to Newton’s First Law, if an object moves at constant velocity, the net force on it must be zero.
An astronaut in deep space throws a wrench. Ignoring gravity and drag, what happens to the wrench after it leaves the astronaut’s hand?
A) It slows down and eventually stops
B) It continues at a constant velocity
C) It speeds up
D) It rotates in place
B) It continues at a constant velocity
Explanation: In the absence of net external forces, the object continues with constant velocity (Newton’s First Law).
Which of the following situations best illustrates a case where an unbalanced force changes direction but not speed?
A) A box sliding to a stop on rough ground
B) A satellite orbiting Earth
C) A car accelerating from a red light
D) A rocket launching vertically
B) A satellite orbiting Earth
Explanation: The gravitational force acts as a centripetal force, continuously changing the direction of velocity but not its speed.
In everyday life, moving objects tend to slow down because:
A) Their inertia weakens
B) Gravity pulls them down
C) Unbalanced forces such as friction act on them
D) Energy is destroyed over time
C) Unbalanced forces such as friction act on them
Explanation: Friction and air resistance are unbalanced forces that cause deceleration in daily life.
Which of the following statements is correct regarding unbalanced forces?
A) They always change the object’s direction
B) They always change the object’s speed
C) They always change the object’s velocity
D) They only act when an object is at rest
C) They always change the object’s velocity
Explanation: Velocity includes both speed and direction; an unbalanced force must change one or both, thus changing velocity.
Newton’s Second Law: Law of Inertia
If no net force acts on the object, that object will remain in current state of motion.
If an object is more massive than another, how will this affect the acceleration of the more massive object?
A more massive object will have less acceleration for the same force applied.
If an object’s displacement vs time curve plateus… what will this mean for acceleration?
The object’s acceleration is zero, indicating it is at resting or moving at a constant velocity.
T/F: An object in motion will slow down unless acted upon by unbalanced forces in the direction of the motion.
False; an object in motion will continue its motion with constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced force
T/F: An object in motion will maintain it’s speed and direction forever unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
True; according to the first law, an object will maintain its course unless acted upon by an external force.
T/F: An object at rest will stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
True
Newton’s Third Law
Every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
Based on Newton’s Third Law of motion, would a person walking on the ground not be able to move because the forces acting on each other?
No, the person is able to walk on the ground and move because the 2 forces act on different objects and not the same (like in box sitting on a table). These 2 forces would never sum together.
A gymnast performs a maneuver where her legs are extended outward and her torso leans backward. What happens to her center of mass?
A) It shifts toward her legs
B) It shifts toward her head
C) It remains stationary
D) It shifts upward and outside her body
B) It shifts toward her head
Explanation: The center of mass depends on the distribution of mass. As she leans back, more mass is redistributed upward, shifting the center of mass in that direction.
A uniform horizontal beam of mass 10 kg is supported at both ends. A 40-kg child stands one-quarter of the way from the left end. Where is the center of mass of the system relative to the left end?
A) At the midpoint of the beam
B) Closer to the child than to the midpoint
C) Directly under the child
D) At one-quarter of the beam’s length
B) Closer to the child than to the midpoint
Explanation: The child contributes significantly more mass and shifts the system's center of mass toward their position but not all the way. You’d use a weighted average to calculate the exact location.
A person attempts to balance a broom horizontally on their palm. The broom has a heavier bristle end and a lighter handle end. Where should they place their palm?
A) At the midpoint of the broom
B) Closer to the bristle end
C) Closer to the handle end
D) It doesn't matter; either end will balance
B) Closer to the bristle end
Explanation: To balance the broom, the support (palm) must be under the center of mass. Since the bristle end is heavier, the center of mass shifts toward it.
If we know the direction of acceleration, we intuitvely know….
the direction of force
During a test crash, a 500 kg car is driven at a constant velocity of 50 mph until it hits a wall without braking. Apply all three Newton’s laws to this situation:
in the absence of any forces, or when the net force is zero, there will be no change in velocity
acceleration results from the sum of force vectors
for any two interacting objects, all forces acting on one object have an equal and opposing force acting on the other object
A projectile is fired from ground level with an initial velocity of 50 m/s and an initial angle of elevation of 37 deg, as shown below. Assuming g=-10m/s² find the a.) projectile’s total time in flight b.) total horizontal dist traveled
Voy= Vosin37= (50)(0.6)=30m/s
Fg||=
Fg_|_=
mgsino, mgcoso
What are some easy formulas to use to find acceleration and normal force when given an object sliding on a frictionless inclined plane?
a=gsintheta
Fn= mgcostheta
How do the forces acting in free fall and projectile motion differ?
the only force acting in both is gravity
At what angle of launch is a projectile going to have the greatest horizontal displacement? What angle will result in the greatest vertical displacement assuming a level surface?
greatest horizontal: 45 deg ; this is because the product of sin and cos are maximized when the angle is 45. Becuz horizontal relies on both measurements.
greatest vertical: 0; objects return to starting point
4) An elevator is designed to carry a maximum weight of 9800 N (including its own weight), and to move upward at a speed of 5m/s after an initial period of acceleration. What is the relationship between the maximum tension in the elevator cable and the maximum weight of the elevator while the elevator is accelerating upward?
A.) the tension is greater than 9800N
B.) the tension is less than 9800 N
C.) the tension equals 9800 N
D.) it cannot be determined
A) the forces on the elevator are the tension upward and the weight downward, so the net force on the elevator is the difference between the two. for the elevator to accelerate upwards, the tension in the cable will have to be greater than maximum weight so that there is net force directed upwards
7) A 10 kg wagon rests on an inclined plane. The plane makes an angle 30 deg with the horizontal. Approximately how large is the force required to keep wagon from sliding down the plane (Note: sin30= 0.5, cos30= 0.866)
A.) 10 N
B.) 49 N
C.) 85 N
D.) 98 N
B.) the static force of friction acts parallel to the plane and is in the opposite direction from the parallel component of gravity in this setup. because the wagon is in equilibrium, these two forces are equal in magnitude. remember that gravity is often split into components inclined plane problems. Gravity split into parallel and perpendicular. Parallel is mgsintheta. Plugging in the values from the question, both the parallel component of gravity and static force of friction must be equal to (10)(9.8)sin30= 49 N.
A 30 kg child sits on a seesaw at a distance of 2m from the fulcrum. Where must the child’s parent sit to balance the seesaw if the parent has a mass of 90 kg?
A.) 67 cm from the child
B.) 67 cm from the fulcrum
C.) 133 cm from the child
D.) 267 cm from the fulcrum
B.) torque equations set equal to each other rFsintheta
12) A physic major builds a potato launcher and tests it in an open field. The student launches a potato with a velocity of 12 m/s at an angle of 30. The potato is found 60 m from the launch site. Which of the following represents the maximum height achieved by the potato?
A.) 0.3m
B.) 1.8 m
C.) 5. m
D.) 18 m
B.)
Centrifugal force is an apparent outward force during circular motion. It has been described as a reaction force according to Newton’s third law. Which of the following is most likely to be correct regarding centrifugal force?
A.) Centrifugal force exists only for uniform circular motion, not nonuniform circular motion
B.) Centrifugal force exists only when tension or a normal force provides centripetal acceleration
C.) Centrifugal force always acts antiparallel to the centripetal force vector
D.) Centrifugal force is result of repulsive electrostatic interactions
C.) because the stem indicates that centrifugal force is reactionary and acts outwardly away from the center of rotation, we can draw the conclusion that it is a reaction to the centripetal force. according to Newton’s third law, these forces must have equal magnitude and opposite direction
Which of the following statements is true of movement on a plane with friction? 1. A is a function of applied force 2. more force is needed to accelerate a stationary object than an identical moving object 3. the force of friction is independent of the mass of objects
a.) I only b.) II only c.) I and II only d.) I and III only
B.) the presence of friction does not change the impact of newton’s laws. a net force must still be applied to cause motion. This net force is not necessarily equal to an applied force, as friction and gravity also act on an object; thus I is eliminated. Static friciton opposes the movement of stationary objects, and is necessarily greater than the force of kinetic friction; thus, II is correct. III is false because the normal force is related to mass, and friction is related to normal force.