everything everywhere
1/290
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
291 Terms
alpha waves
10 hz
alpha= routing mechanism, shutting down regions actively that are not needed
By attending to something, alpha has an increase on the other side, because it's inhibited, you don't pay attention to that region, and alpha goes down on the attended side
artifact
muscle, movement, or bones that block the eeg signal
intracranial eeg
places electrodes directly into the brain
more localised signal in real time
demyelination
e.g multiple sclerosis
no swan cells or myelin sheaths for the axon
Issue; conductivity, communication of the neuron breaks down
Results in vision loss, communication issues, etc
parameters of a wave
amplitude/ power
frequency
speed
height
beta waves
13-30 hz
theta waves
4-8 hz
most commonly associated with motor cortex, but also with concentration, executive functioning, frontal cortex jobs
Specific fingerprint of highly concentrated top down thinking
delta
0.5-4 hz
slow wave sleep
spontaneous synchrony
slow oscillation= synchrony
Oscillation is when they fire in a rhythmic pattern
alpha oscillations prevent firing in a phasic manner
‘pulsed inhibition’
Rhythmic pattern that has cumulative input onto the intake neuron and post synaptic neurons, so they get enough energy to create an action potential and fire, then pass it along to the next one
TIME-FREQUENCY PLOTS.
the x axis is time
the y axis is the frequency
the increase and/or decrease is shown in the colour temperature (blue vs red)
cognitive control
overriding something well learned, replacing it with something more novel
includes:
creating an action plan
overriding learned behaviours
maintaining & mentally manipulating info
monitoring our behaviour and correcting it when necessary
managing multiple tasks
overriding learned behaviours
flanker task
when people are correct and don’t make mistakes, more activation in the inferior portions of the frontal cortex
mainly right lateralised areas
stroop task
brocas area; exert control over articulatory motor planning
lateral prefrontal cortex; important for modulating behaviour when you have to override a well learned behaviour
left lateralised
managing multiple tasks
multiple errands test
tendency for inefficiency
anterior damage; can make the plan but can’t action it. inability to flexibly manage multiple goals
creating an action plan
hotel task
very high level of task switching
involves some prospective memory; remembering to switch tasks without external cues
internal task switching whilst keeping bigger picture in mind
damage to anterior regions perform poorly here
prospective memory
the ability to keep in mind that you have to do something at a future time, often linked to a time or place
used to indicate when a switch is required from internal cues usually
monitoring behaviour
wisconsin card sorting task
analogical reasoning element
listening to feedback to guide your next decision
repeating behaviours when it is no longer advantageous to do so commonly seen in people with damage to lateral pfc
rule violations
damage to right lateral pfc
gray matter thinned in these areas
right hemisphere, and right lateral pfc implicated in tasks that involve listening to feedback or changing the course of your actions based on outside information
a simple theory (cognitive control)
lateral pfc structures maintain an internal goal state → if its not active it can no longer control your activity
bias activation away from habitual routines in favour of the goal
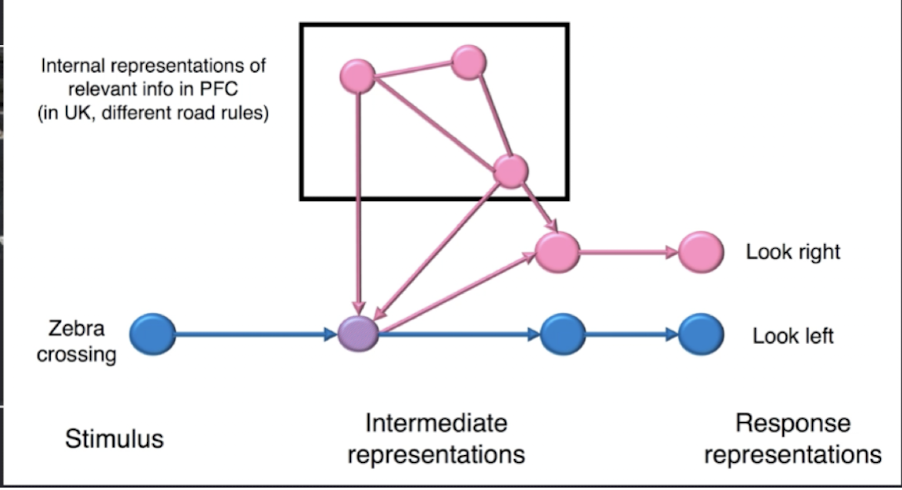
anterior pfc regions
task switching
left inferior pfc regions
control of verbal processing
right inferior pfc regions
control in nonverbal regions
koechlin & summerfield model
green; premotor cortex & sensory control = well learned response
blue; posterior pfc & contextual control = modifying behaviour based on external cues
purple; anterior pfc & episodic control = using past instructions or recent information
pink: the frontal pole & branching control = dynamic switching between multiple task sets
hierarchical models
all pfc regions work by modulation activity in more posterior areas
further up the hierarchy goes, the control becomes more abstract, less domain specific
frontal pole; controls the control systems, schematic control
lateral pfc: contextual control, domain specific. left = language, right = spatial, non verbal
motor cortex: sensory-motor control, basic control
lateral pfc
top down control of mental representations to meet internal goals
cold cognitive control
low stakes effortful situations
the frontal pole
explore vs exploit
value judgement multitasking
fmri study; signalling from frontal pole helps us decide when we want to disengage from exploiting, conservative behaviour, and explore
rostral pfc to make values based decisions
spontaneous confabulations
reporting things that aren’t true about the past and present
ventromedial pfc damage; precedes hippocampus, guides search in personal timeline
overabundance of reports of incorrect autobiographical memories
dorsomedial pfc
motivation and resource allocation
ventromedial pfc
control in high stakes situations
goal oriented behaviour
key structures in emotional processing
hippocampus
amygdala
emotion
a rapid and transient response to a stimulus with value to a person
consist of physiological changes, a behavioural response, and a subjective experience, intrinsically pleasant or unpleasant
mood
a more persistent state which shares some of the same subjective features of emotion
affect
a broader term encompassing emotion + mood
classifying emotions
positive vs negative
basic vs complex
arousal level vs valence
ekman theory of classifying emotion
core emotions biologically pre programmed
= happiness, sadness, disgust anger, fear, surprise
complex emotions draw on the same feelings, but combine them with social and cultural factors
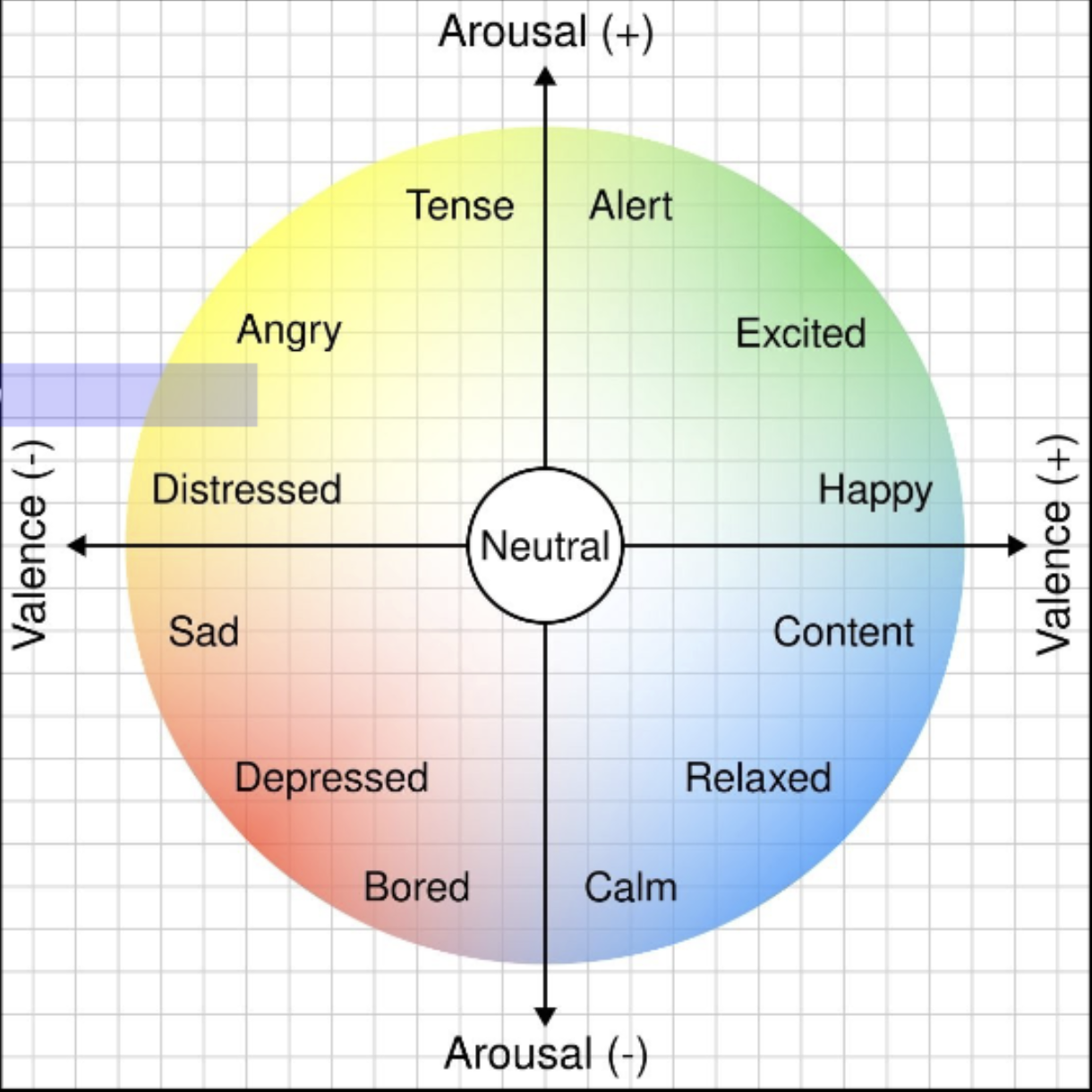
feldman-barrett theory of classifying emotion
you can put emotion on a continuum based on arousal and positivity / valence
high arousal = anger, excitement, nercousness
low arousal = sadness, contentment
physiological component of emotion
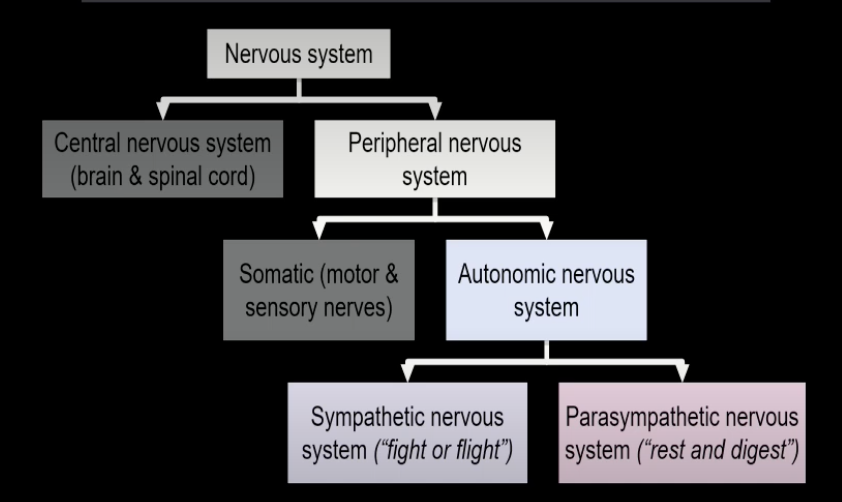
autonomic nervous system → sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
sympathetic nervous system
‘fight or flight’
up regulates respiration
dilates lungs, pupils, blood vessels
increases heart rate & perspiration
suppresses digestion
parasympathetic nervous system
‘rest and digest’
sleep rest & digestion
conservation of energy
measuring emotional responses
skin conductance response (SCR): measures change in perspiration
heart rate / heart rate variability
self report tools e.g PANAS
→ best to use the tools together so you can get a fuller picture of everything
PANAS
positive and negative affect schedule
looking at a person across a small period of time, usually a week
the amygdala: fMRI evidence
spohrs 2018
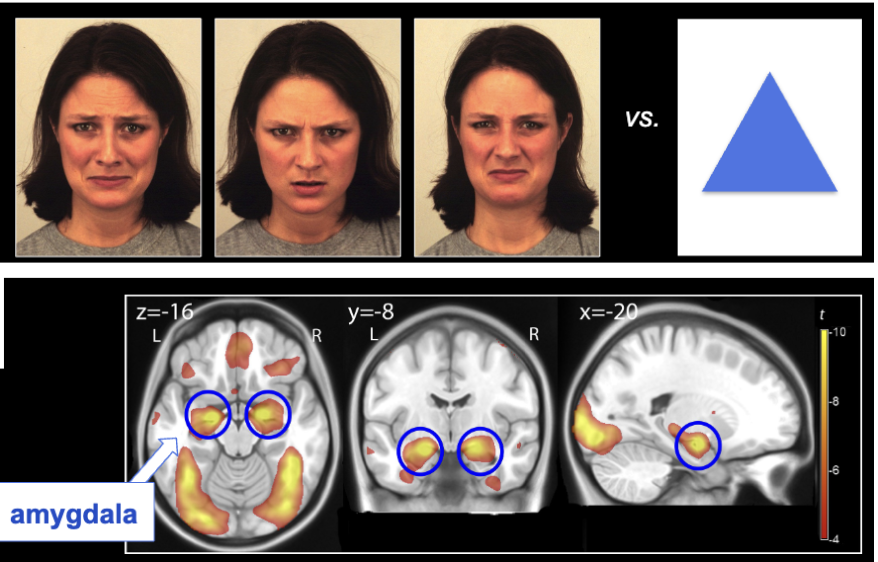
if we show people expressive faces, they respond with activity in the amygdala
→ not a great comparison between faces and shapes; lots of sites activated because faces are so different to shapes
fear conditioning paradigm
circle matched with mild electric shock on fingers
classical conditioning
when viewing shapes alon
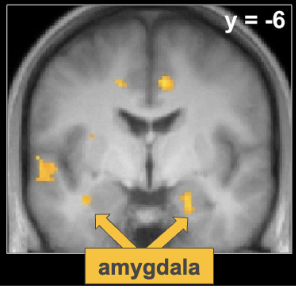
e under the scanner after learning, the circle had significantly more activation in the amygdala compared to other shapes
amygdala and memory
kensinger 2011
events eliciting higher amygdala activation in phase 1 were rated as more vivid in phase 2
BUT accuracy/details the same irrespective of amygdala activation
indicates that emotional valence enhances ability to remember, but only a more robust subjective experience
effects of damage on the amygdala
may fail to show normal fear conditioning
may fail to show a memory benefit for emotionally significant events
often poor at identifying facial expressions
SM
bilateral damage from urbach-wiethe disease
affected valence- missing negative emotions that perform a function e.g fear of snakes
overly positive & overly familiar
amygdala & story recall
phineas gage
left ventromedial prefrontal cortex damaged
impulsive, fearful, loss of control
behaviour changes around affect, inability to use good judgement for hot cognition
clinical featires of vmPFC damage
Emotional dysregulation, changes in emotional experience
philosophical calmness in high emotion situations
Diminished empathy, poor social awareness
Also true of damage to amygdala, but the problem here is somewhat higher up; can see it but cant interpret it
Poor decision-making, irresponsible behaviour, risk-taking
Specifically in hot context cases
vmPFC changes in emotional experience
increased impulsivity
increased aggression (some people get this with impulsivity, not all)
→ general disinhibition
diminished empathy / poor social awareness
NPI
neuropsychiatric inventory
designed to assess wether a person demonstrated increased impulsivity or reduced social awareness
head injury sample: significantly lower scores with right vmPFC damage
diminished empathy
tranel & damasio 1994
healthy participants; emotional picture evokes scr
damage; can describe picture in detail, but no scr
→ issue is making the perspective leap, understanding what the other person might be feeling
poor social awareness
patients score poorer than controls on the faux pas task
addresses higher level empathy than amygdala damage = perspective AND empathise
theory of mind, but for social rules and consequences
amygdala vs vmPFC
amygdala: ‘signals’ emotional valence, particularly negative valence
vmPFC: emotional regulation, cognition that relies strongly on emotion
poor decision making, irresponsibility, risk-taking
gambling game
vmPFC patients can explain the rule, but don’t act on it
difference between ability to rule detect, and ability to respond positively within the hot context
SCR: controls develop an anticipatory scr before selecting from a bad deck. patients get scr after the bad card, but don’t develop an anticipatory scr
cannot use emotional response in a proactive way to shape future decisions
left pfc crucial for this task
hot cognition
thinking and decising how to act when the emotional stakes are high
using emotional responses to guide decision making in complex high level decision making
gut instinct before verbal explanation
= winning poker
= trading on the stock market
= deciding wether or not to have cake
cold cognition
stroop task
thinking out a difficult mental problem
dividing a large goal into sub goals
gambling fMRI
people who did well on the iowa gambling task showed increasing activity in the left vmPFC as the trial progressed
right insula also activated= operate as a network
somatic marker hypothesis
vmPFC: binds memories and their emotional and physiological associations
creates an index of the way you’ve felt in similar situations in the past, which you can revoke in future to guide your actions
facilitates fast decision-making
limitations:
does it consider empathy or social awareness
does it consider causal vs association with bodily sensations
descartes error
damasio: we are not thinking machines that feel, we are feeling machines that think
it is not enough for us to be rational, that would be weird. we do a lot of things based on feeling and gut instinct
white matter fibres / tracts
arcate fasciculus= key language tract
white matter tracts helps us understand the anatomical interconnections between regions
structural connectivity
the roadways of the brain = cant have good communication without good ways to connect areas
diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)
tracks the direction of movement of water molecules
systematic flow in one direction indicates a large white matter tract
DTI clinical applications
identifying diseases that affect long axons e.g multiple sclerosis
psychologically; if basic scans down show anything but there are cognitive problems
diffuse axonal injury in head injury and concussion, twisting and tearing large white matter tracts
know a lot more from these methods about structural problems that underlie amnesia
corpus colosseum
people experiencing significant amnesia tend to have lower white matter fibre volume
corpus colosseum damage itself is occurring, but also predictive of greater amnesia, along with many other areas
functional connectivity
the crosstalk between interconnected regions during a particular activity
traffic on the road
degree of cross talk between regions varies depending on the task
can measure the degree of synchrony between activity in different regions - how does the bold signal change over time to map connection and communication between areas
dynamic networks
Lots of large scale networks operate as inhibitors of each other, so the networks will ebb and flow as the brain moves between thought and focus
default mode network
‘day dreaming’ network
active at rest
active when focused on internal thoughts
deactivated when focus shifts to external stimuli
inner reflection exploring ideas / solutions
super portion of the
prefrontal cortex
number of lateral structures, but lots of key ones on the medial surface
temporoparietal cortex, hippocampus, ventromedial PFC, posterior cingulate cortex
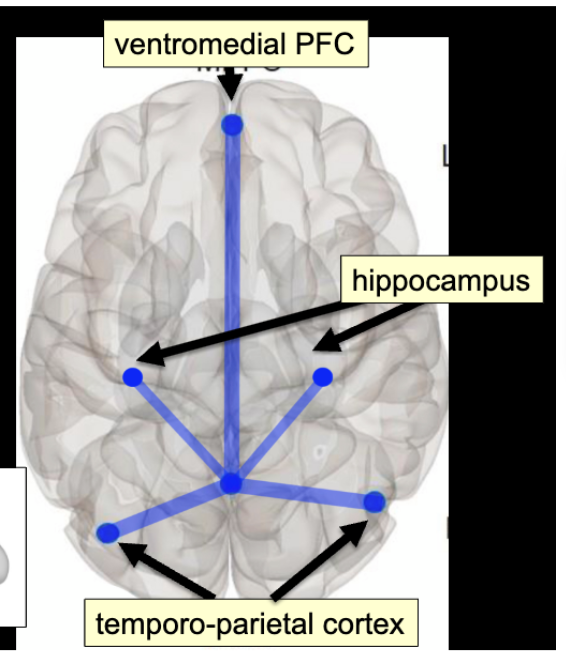
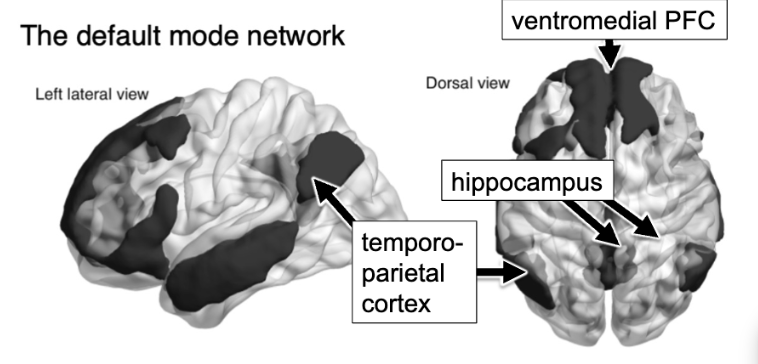
DMN activities
retrieving memories for past experiences, reliving mentally (hippocampus)
making judgements about themselves relative to others (VMPFC, social cognition and judgments on others)
mind wandering
mind wandering
button press tasks
greater activation of the DMN when day dreaming
able to measure beyond activities that require an external focus
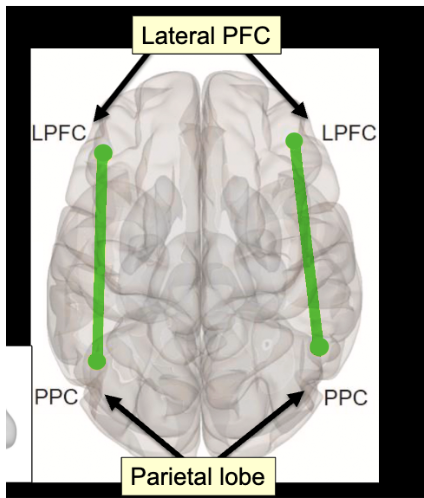
frontoparietal control network
activated when performing a demanding task
highly externally focused cognitive control & effortful tasks
controlling behaviour to achieve a goal
large portion of the lateral PFC
parietal lobe
interparietal sulcus
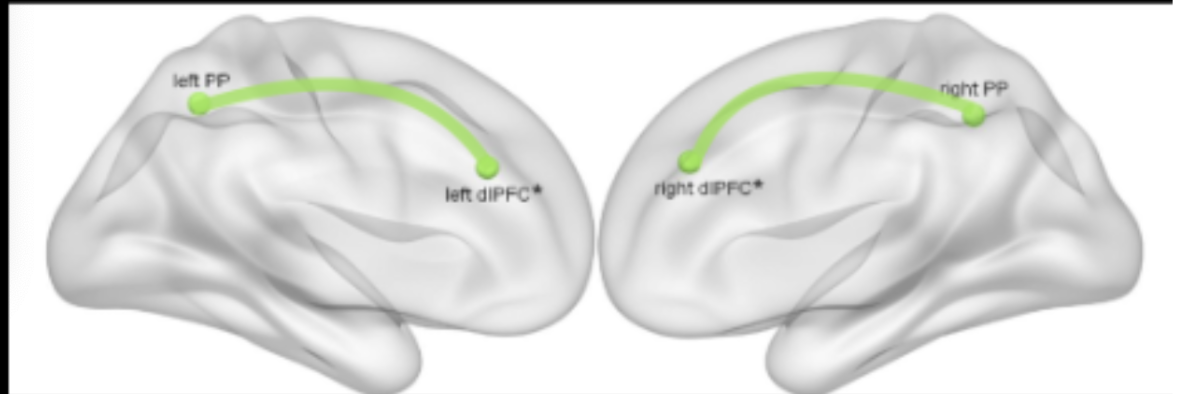
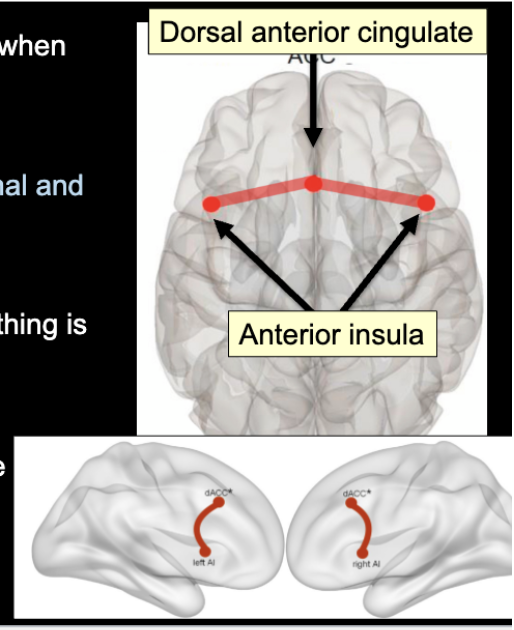
the salience network
signals when something is aversive or emotionally salient
can respond to a thought or emotion
helps to initiate rapid switches between networks
dorsal anterior cingulate= signals when we need to exert effort on a task
anterior insula= evaluates emotional and bodily states
anterior PFC
the hotel task & complex problem solving
real life problems & multi tasking involve dynamic switching between modes
damage to the anterior PFC; people get fixed in one network and then cannot switch to the other one
depression
increased connectivity, synchronicity, and overall activation within the default mode network
more time being introspective, more time ruminating
unclear as to wether cause or effect
creativity in healthy people
high scorers: tightly synchronised activity in parts of the default mode and fronto parietal control networks
low scorers: primarily posterior cross talk
suggests that creative thought involves flexible interplay between;
1. Default mode network (internal thoughts, reflection, imagining, remembering)
2. Frontoparietal control network (goal directed top-down control of cognition, evaluation of ideas, etc.)
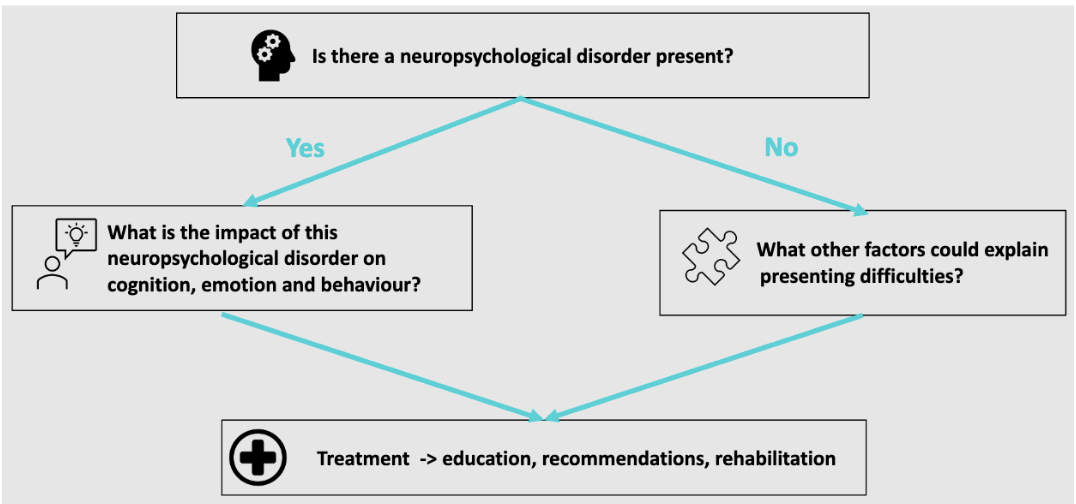
clinical neuropsychology
Aims to understand and help treat people who are experiencing nervous psychological difficulties, as a result of some type of brain disorder
steps
is there a neuropsychological disorder present
what is the impact of this neuropsychological disorder on cognition, emotion, and behaviour
what other factors could explain presenting difficulties
treatment = education, recommendations, rehabilitation
TBI neuropsychological manifestations
cognitive impairment
impaired alertness / arousal
slowed cognitive processing
attentional impairment
learning and memory impairment
executive functioning impairment
aphasia
social functioning impairment
TBI and cognition
pathophysiology = what happens
injury severity n the brain as a result of the injury
mechanisms of the injury
mechanisms of injury
direct impact
external forces colliding with neck or head= tsunami
acceleration - declaration
forces of body movement have been so strong that it moved your brain
blast injury
penetrating injury
an external object has penetrated through the skulls and into the brain
direct impact vs penetration
penetrating can be debilitating if its penetrated into critical areas of the brain
BUT
can also be less severe than direct, because the injury is localised rather than generalised
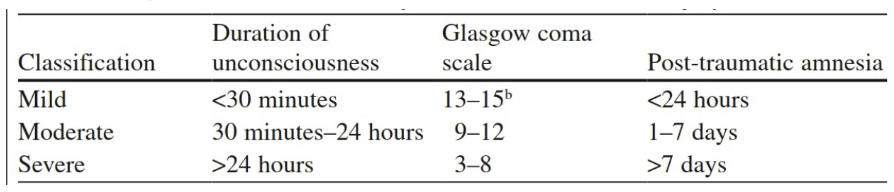
rating severity of TBI
duration of loss of consciousness
glasgow coma scale (gcs)
post traumatic amnesia
glasgow coma scale
rates verbal responses, eye opening behaviour, and motor responses
3 to 15 point scale
how alert a person might be
post traumatic amnesia
anterograde memory loss for events occurring immediately follow the injury
retrograde for events immediately piror
assessment; remembering objects a day apart
severity classification
if one classification trumps the others, you move into that category
mild TBI
concussion
any period of LOC
any loss of memory for events immediately before or after the accident
any alteration in mental state at the time of the accident
focal neurological deficit which may or may not be transient
pathophysiology - focal
contusion (bruise)
more for direct impact
contrecoup contusions
intracranial bleeding
contrecoup contusions
onion in liquid in a jar
brain hits the back and front of the skull
intracranial bleeding
if forces in the brain are significant enough to rupture a blood vessel
areas vulnerable to contusion
prefrontal cortex
results in issues with cognitive control, executive functioning, emotional control
anterior and inferior temporal lobe
located in the cavities
results in difficulties with memory
less common;
cerebellum
superior parietal region
pathophysiology; diffuse
diffuse axonal injury
shearing of neural axons
tearing of bridging veins resulting in intracranial bleeding throughout brain
white matter has lower density, so more likely to be impact by forces from an injury
happens at a very micro level
more common injury than focal injuries
impacts more areas and bigger functions like memory due to them using a large number of regions
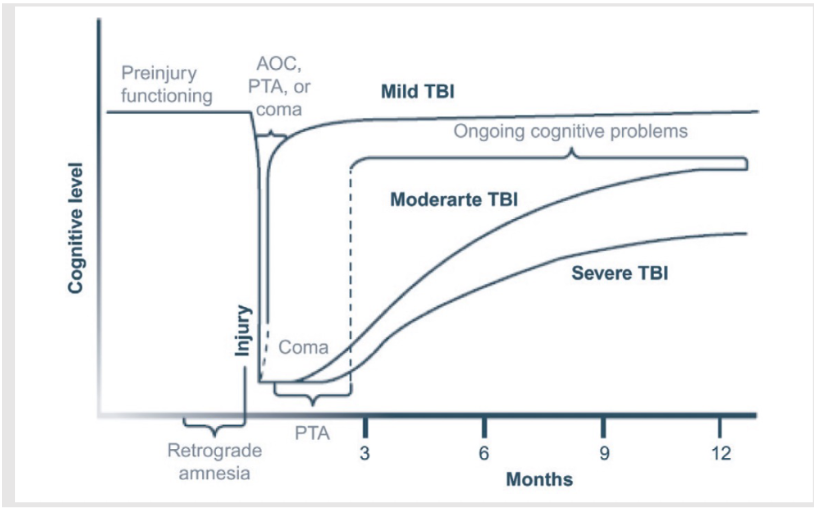
cognitive recovery
typically experience transient cognitive, emotional, and physical
recovery often within 1-3 months post-injury and expected to have favourable long-term outcomes
prolonged or atypical recovery associated with acute injury conditions (LOC), severity of initial symptoms, preexisting or comorbid psychiatric, medical, or psychosocial factors
moderate and severe TBI
chronic impairments that limit ability to return to previous levels of functioning
cognitive functioning typically improve over time with the most recovery seen in the first 6 months
improvements in basic cognitive skills (attention, orientation) precede improvement in more complex cognitive skills
recovery usually plateous at 18-24 months
recovery
stroke (CVA)
defined as a sudden onset of impairment in neruological functioning due to severe decrease of blood supply to the brain
blood ocntains oxygen and important nutrients for proper functioning. if brain cells do not get enough of this, they die (infarct)
ischemic stroke
starved
most common in adults
neuronal damage or infarct caused by inadequate blood supply to a particular part of the brain due to an obstruction
anterior circulation most frequently affected, 80% of cases
types of ischemic strokes
embolic= a blood clot forms elsewhere in the body, breaks loose, and travels to the brain via the blood stream
thrombotic= a blood clot develops in the blood vessel inside the brain
vasospasm= the narrowing of intracranial arteries, which can lead to hypo perfusion (reduction in the amount of blood flow)
the tree
dimensions of blood vessels reduce as they circulate through the brain
smaller blood vessels are more vulnerable to blockages, but will impact less of the brain
if the blockage is in the trunk, it will effect the whole tree
haemorrhage stroke
less common → 12% of all strokes
caused by a weakened vessel that ruptures and bleeds into the surrounding brain
associated with higher mortality
intracerebral haemorrhage
bleeding within the brain tissue itself
subarachnoid haemorrhage
bleeding within the subarachnoid space
spaces where the cerebrospinal fluid is has a rich blood supply
if theres a rupture here it causes a change in pressure due to extra fluid, which compresses brain tissues
mortality of 50% in the first 6 months after stroke