All Things Covalent
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
QUIZ Topics: Lewis Structures, Resonance Structures, Formal Charge and Properties of Covalent Molecules
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Central atom
Atom in the center of the lewis structure, forms most bonds, is the least EN (NEVER H)
How to know a central atom in a lewis structure
USUALLY the first element listed in the chemical formula OR look for least EN
exceptions:
- diatomic compounds (2 atoms)
-Hydrogen is the starting element
Single dots (lone e-) on a Lewis structure show…
Bonding sites & if you count them up the ideal # of bonds
Can you reduce the formula of a covalent compound
NO, NEVER.
Formal charge equation
FC= VE-CB-NE
The # of valence electrons (from periodic table) - # of covalent bonds on the atom (on the LS) - # of non-bonded e- (on the LS)
-Do this for each atom in the compound and then add up their charges to see the compounds overall charge
-Most stable is zero UNLESS it’s a polyatomic in which case it would be the charge of the polyatomic that is most stable
Polyatomic ions
Polyatomic’s have both ionic and covalent character (covalently bonded cluster of atoms with an ionic charge)
How to show polyatomic ions lewis structure
Put the compound in parentheses and put the charge on it’s upper right corner
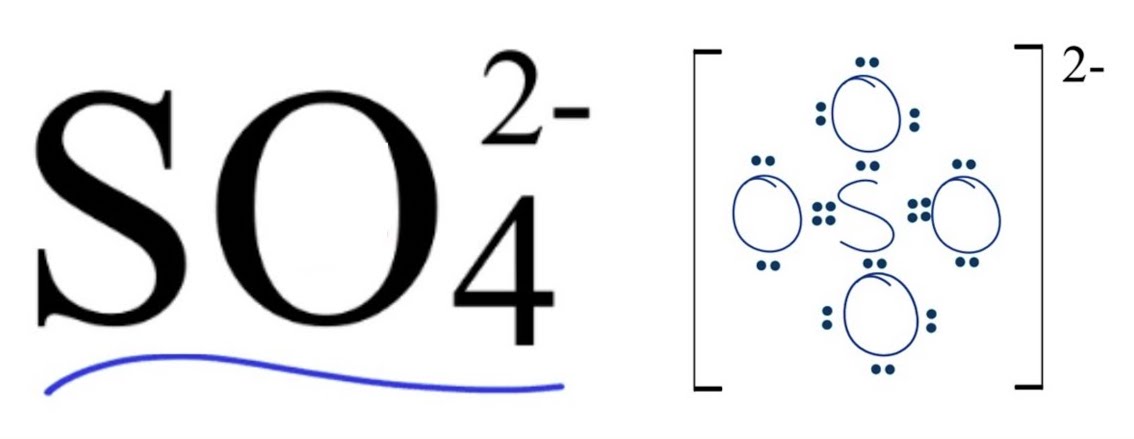
Things that have multiple bonds are more ___ than single bonds
Conductive
this is bc the transfer of e- is quicker & more efficient
Resonance structures
Resonance structures show the multiple ways bonding can occur in a compound
Why are resonance structures caused
They are caused when there is more than one way to place double bonds and lone pairs on atoms
Coordinate bond
When both bonding e- are donated by a single atom
ie. this happens when one atom is satisfied and another isn’t, the satisfied atom will share 2 of it’s e with the other atom, forming a bond, to satisfy it so the whole compound can be more stable
Multiple bonding
Double or Triple bonds
-these occur to satisfy atoms that do not fulfill the octet rule
Why are excess atoms theorized to happen
The D sub-level acts like a trunk where extra e- can be stored if need be, this is why we can fit 10 e- on some atoms instead of only eight, bc 2 would be in the “trunk”
The bonds are SPD hybrids when this happens
How many e- can Sulfur hold?
12*
*only when acting as a central atom!
How many e- can Phosphorus hold?
10*
*only when acting as a central atom!
How many e- can Hydrogen hold?
2
How many e- can Boron hold?
6*
*only when acting as a central atom!
How many e- can Beryllium hold?
4*
*only when acting as a central atom!
*Note, this is a metal but it’s EN is close to NM so it can covalently bond
What are the deficit atoms
Atoms that are stable with less than 8 e-
These are H, B, Be
What are the excess atoms
Atoms that can hold 8+ e- but can be stable @ 8
These are P, S, Noble gases & Halogens (NG and Halogens are VERY rare)
Why are covalent bonds NOT conductive
Bc they do not have charged particles capable of transporting e-
Melting and boiling point increases with…
Molar mass
more mass= more substance to melt
State of matter @ room temp for covalent bonds
Can be solid, liquid, or gas
Why do covalent bonds have low MP/BP
Bc they have weak forces of attraction btwn them. Since covalent bonds form btwn NM’s there is no opposite charges & therefore no coulombic attraction, this makes the force weaker. The e- are also shared, not transferred, making a weaker bond which is easier to break and therefore a lower MP/BP
Properties of covalent bonds
-low melting/boiling point
-soluble (dissociates in water)
-non-conductive
-share e- to achieve octet
How does e- sharing work
Covalent bonds share e- via. orbital overlap
-more overlap (ie. double & triple bonding) = stonger bond
Covalent bonds occur so that…
They can act like noble gases (and be stable)
What is the rep. particle name for covalently bonded atoms
Molecule
Covalent bonds are formed btwn…
Non-metals only*
They share electrons
*Some metalloids bond with nonmetals and tend to form covalent bonds
Lone pair/unshared pair
pair of e- that are NOT shared btwn atoms
Where does hybridization occur
ONLY on the central atom