general science
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
physical change
change in shape, size, or physical state of matter but not its composition
chemical change
change in the composition of matter as a result due to chemical reaction
physical change
change of phases or states
dissolution process
change in physical properties
chemical change
formation of new substances
evolution of gas (formation of bubbles)
change in temperature
evolution of energy
chemical reaction
a process where reactants are transformed into other substances called products
indication of chemical reaction
change in color
change in temperature
formation of an odor
formation of a gas
formation of a solid/precipitate
chemical equation
is a written representation of a chemical reaction
chemical reactions are represented by this
left = reactants
right = products
separates reactants or products

separates reactants from products; produces, forms, yields

reversible reactions

substance is in solid state

substance is in liquid state
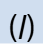
substance is in gaseous state
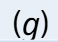
substance is in aqueous state
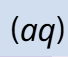
evolution of gas instead of (g)

formation of precipitate instead of (s)

application of heat

catalyst used in the reaction

combination reaction
synthesis reaction
involves 2 or more reactants forming a single product
A + B > AB
A + B > AB
combination reaction
decomposition reaction
reverse of combination reaction
compound is broken down into two smaller substances
may be initiated by heat, light, electricity of catalysts
AB > A + B
AB > A + B
decomposition reaction
monoatomi
carbonates
are decomposed to carbon dioxide (CO2) and metal oxide
chlorates
are decomposed to oxygen gas (O2) and metal chloride
single replacement reaction
an element replaces another element in a compound
the reaction yields a compound and a replaced element
A + BC > AC + B
single replacement reaction
double replacement reaction
occurs when two compounds react to from two new compounds
the reactants are ionic compounds that simply exchange ion partners
AB + CD > AD + CB
AB + CD > AD + CB
double replacement reaction
AC are positive ions, BD are negative ions
combustion reaction
when fuels (hydrocarbon) reacts in the presence of oxygen gas (O2) producing an immense amount of energy causing its products, carbon dioxide and water, coexist in steam from creating smoke
CH + O2 > CO2 + H2O
combustion reaction
solution
homogenous mixture of two or more substances
composed of solute and solvent
solute
minor component
solvent
major component
solid solutions
solvent is in solid state
mostly found in alloys
liquid solutions
solvent is in liquid state
gaseous solutions
solvent is in gas state
globally harmonized system of classification and labelling of chemicals ghs
classifies chemicals based on the type of hazard they pose with the use of universally recognized symbols
oxidizers

flammable

explosives

acutely toxic (severe)

burns skin

gases under pressure

carcinogen

toxic to aquatic environment

acutely toxic (harmful)
