Chemistry 2024
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Write a symbol equation for the combustion of ethane
Unbalanced: C2H6+ O2 → H2O + CO2
Balanced: 2C2H6+ 7O2 → 6H2O + 4CO2
What is combustion?
Combustion reactions occur when a fuel burns in oxygen.
When a hydrocarbon undergoes combustion the products depend on how much oxygen was available
For combustion to occur ...
you need oxygen
Incomplete combustion produces
carbon monoxide and water
Durning combustion the following 3 things occur ....
•Carbon and hydrogen are oxidised
•Energy is given off
•Waste products are made and released into the atmosphere
complete combustion equation
hydrocarbon + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water
Write a symbol equation for the combustion of methane
Unbalanced: CH4 + O2 → H2O + CO2
Balanced: CH4 + 2O2 → 2H2O + CO2
Write a symbol equation for the combustion of glucose
Unbalanced: C6H12O6+ O2 → H2O + CO2
Balanced: C6H12O6+ 6O2 → 6H2O + 6CO2
Organic compunds contain
Carbon
Examples of organic compounds
methane
ethane
propane
pentane
glucose
diatomic molecule examples
hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine
Write a symbol equation for the incomplete combustion of methane
Unbalanced: CH4 + O2 → + CO + C + H2O
Balanced: 4CH4 + 5O2 → + 2CO + 2C + 8H2O
Write a symbol equation for the incomplete combustion of ethane
Unbalanced: C2H6 + O2 → CO + C + H2O
Balanced: C2H6 + 2O2 → CO + C + 3H2O
Write a symbol equation for the incomplete combustion of butane
Unbalanced: C4H10+ O2 → H2O + CO + C
Balanced: C4H10+ 3O2 → 5H2O + CO + 3C
Write a symbol equation of hydrogen (H2) being oxidised to make water (H2O)
H2 + O2 → H2O
Write a symbol equation of sulphur being oxidised to make sulphur dioxide
S + O2 à SO2
Human activities increase the amounts of ...
Carbon dioxide
-Burning fossil fuels for electricity/running cars
-Deforestation. Cutting down trees reduces the amount of CO2 absorbed from the atmosphere by photosynthesis
combustion is the scientific word for...
burning
Incomplete combustion occurs when ...
there is not enough oxygen
Complete combustion produces ...
carbon dioxide and water
Most fuels are compounds of ____ and _____. Some of these also contain ____
hydrogen, carbon, sulfur
Oxidised
to combine chemically with oxygen
complete combustion
This happens when something burns in plenty of oxygen. It produces the waste products carbon dioxide and water.
Write a symbol equation for the combustion of propane
Unbalanced: C3H8+ O2 → H2O + CO2
Balanced: C3H8+ 5O2 → 4H2O + 3CO2
Incomplete Combustion example
hydrocarbon + oxygen → carbon monoxide + carbon + water
incomplete combustion
This happens when there is little oxygen.
- Releases less energy then complete combustion
- The products can be a mixture of carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and carbon as well as water
- Carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas
- Carbon is released as soot
Ethanol fermentation
C6H12O6 → 2 C2H5OH + 2 CO2

Hydration of ethene
C2H4 + H2O → C2H5OH

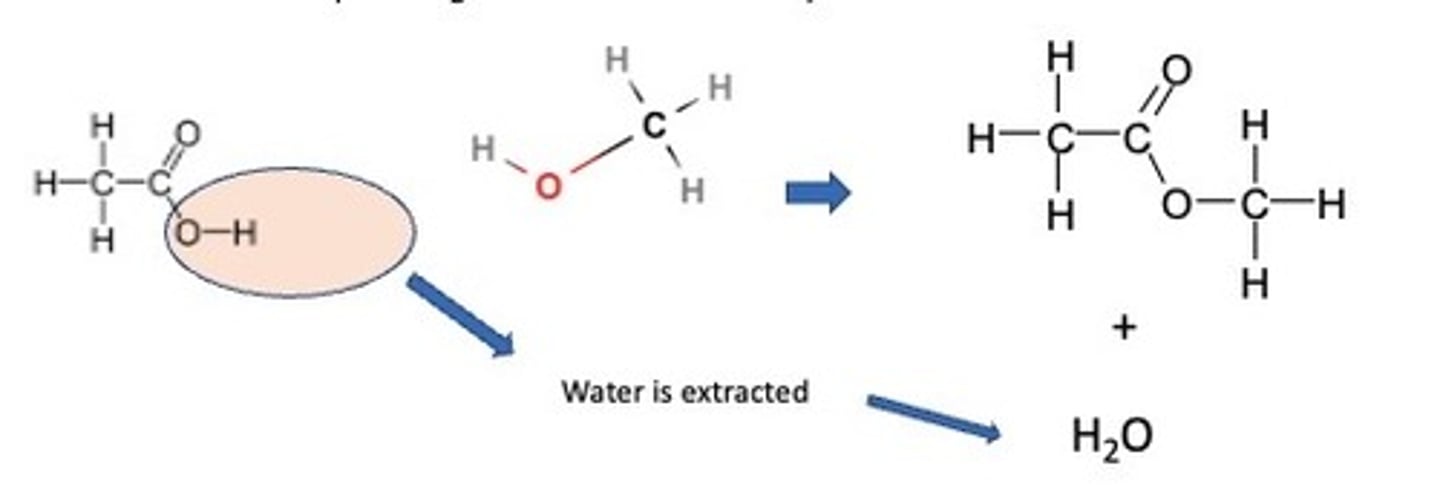
Esters
Esters can be made by reacting carboxylic acids with alcohols. A chemical which can extract the water is concentrated sulfuric acid
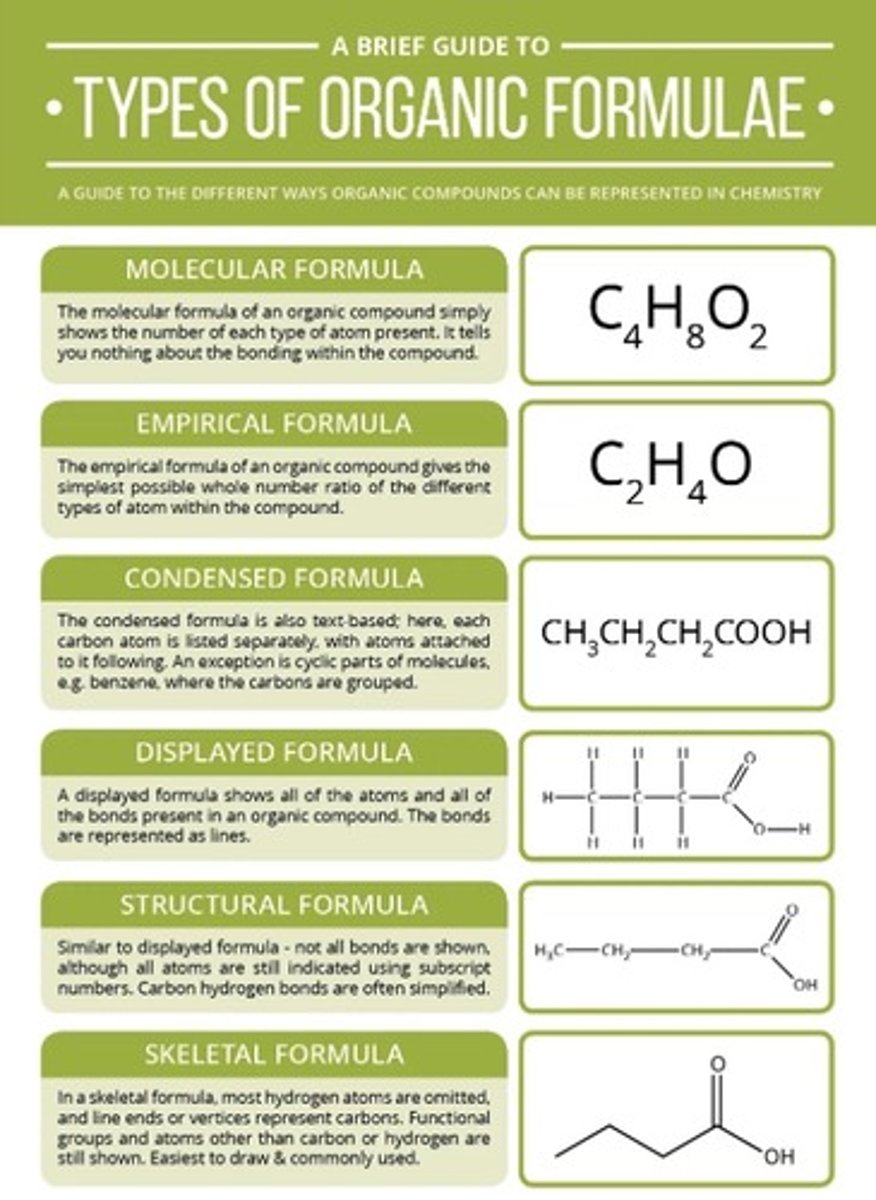
condensed formula
The condensed formula of a compound shows how the atoms are arranged in a molecule and, in particular, shows which functional groups are present.
Unlike displayed formulae, structural formulae do not show single bonds, although double/triple bonds may be shown.
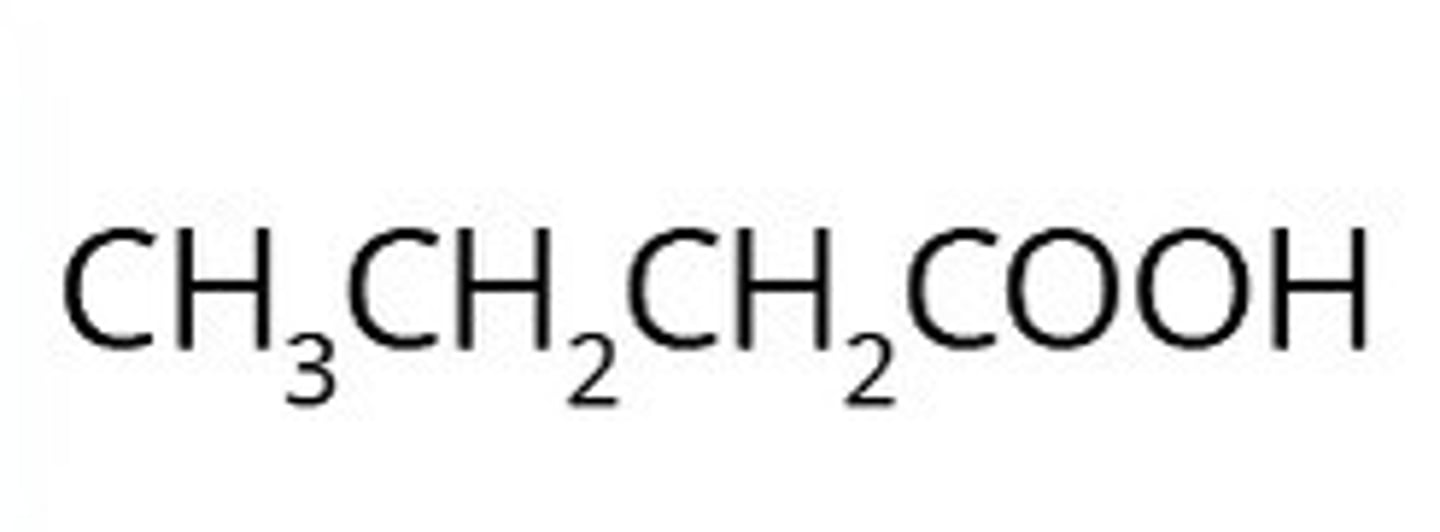
structural formula
A structural formula uses groups of atoms to show structure. Often the bonds between the carbons are drawn but the others are not.
skeletal formula
The skeletal formula of a compound shows the bonds between carbon atoms, but not the atoms themselves. Hydrogen atoms are also omitted, but other atoms are shown.
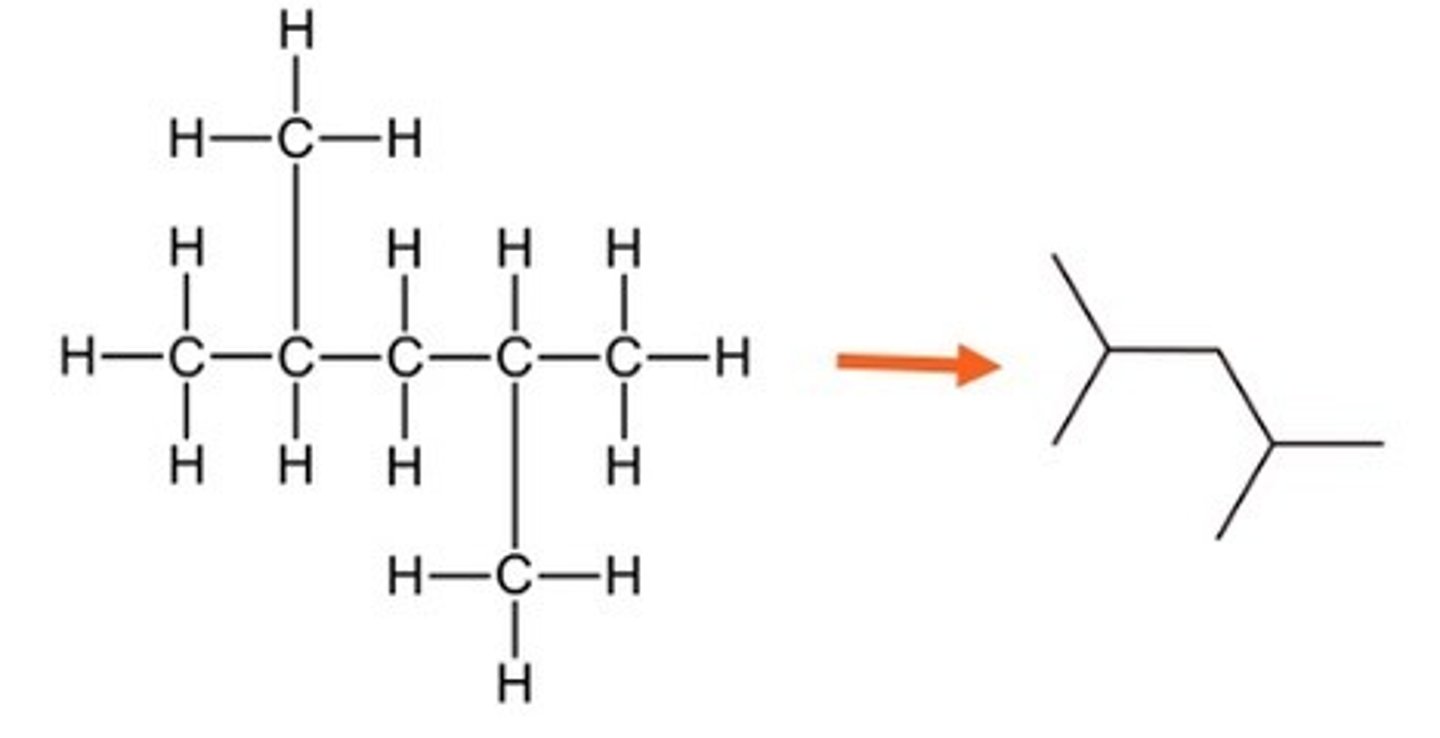
Saturated Hydrocarbons
Alkanes - Saturated means contains only single bonds, hydrocarbon means contains hydrogen and carbon only. This family of chemicals are called alkanes and this is used in the names.
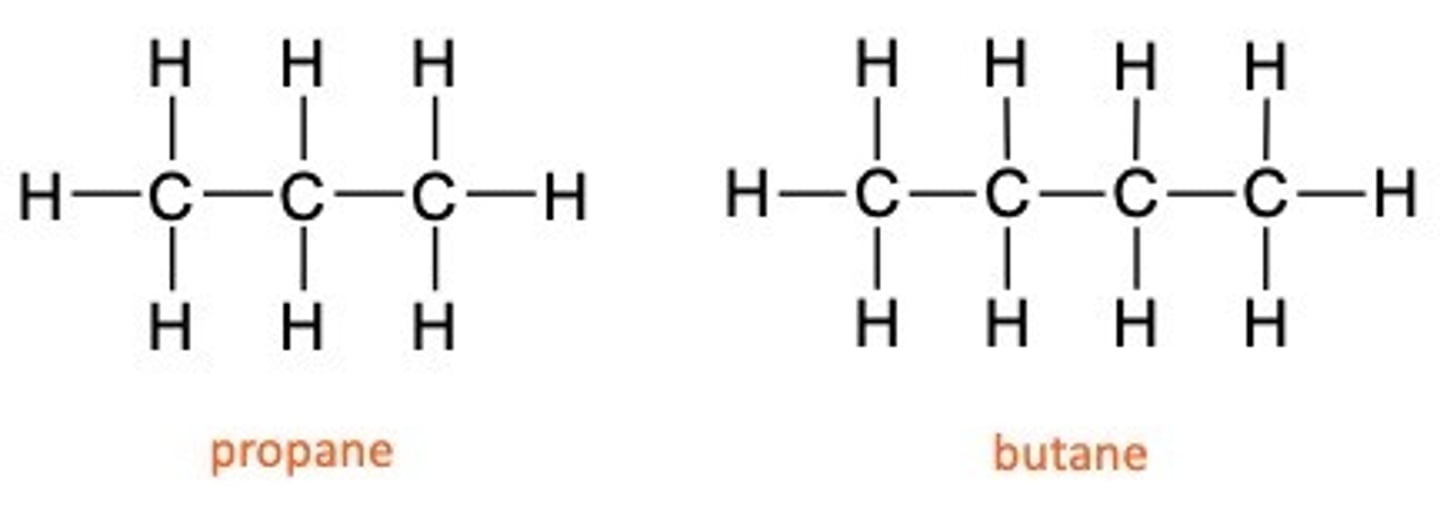
Homologous series
•All the compounds fit the same general formula
•The chain length increases by one each time
•The chemical properties show a gradual change as the chain get longer (e.g boiling point increases with chain length)
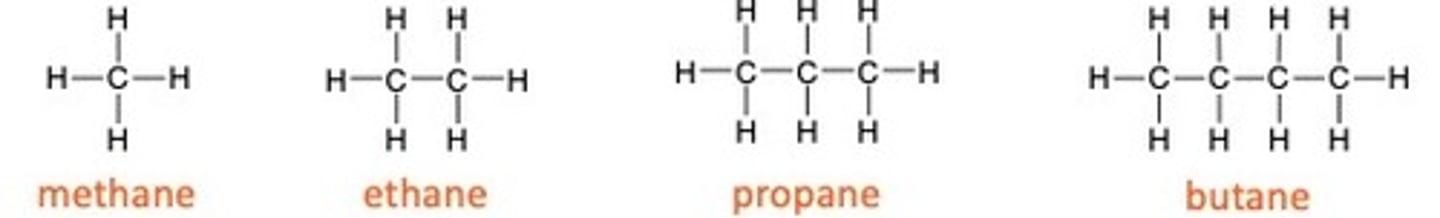
General formula for alkanes

Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
Alkenes have one (or more) carbon to carbon double bonds.
These hydrocarbons are said to be unsaturated
The name follows the parent chain prefix again
This time followed by -ene
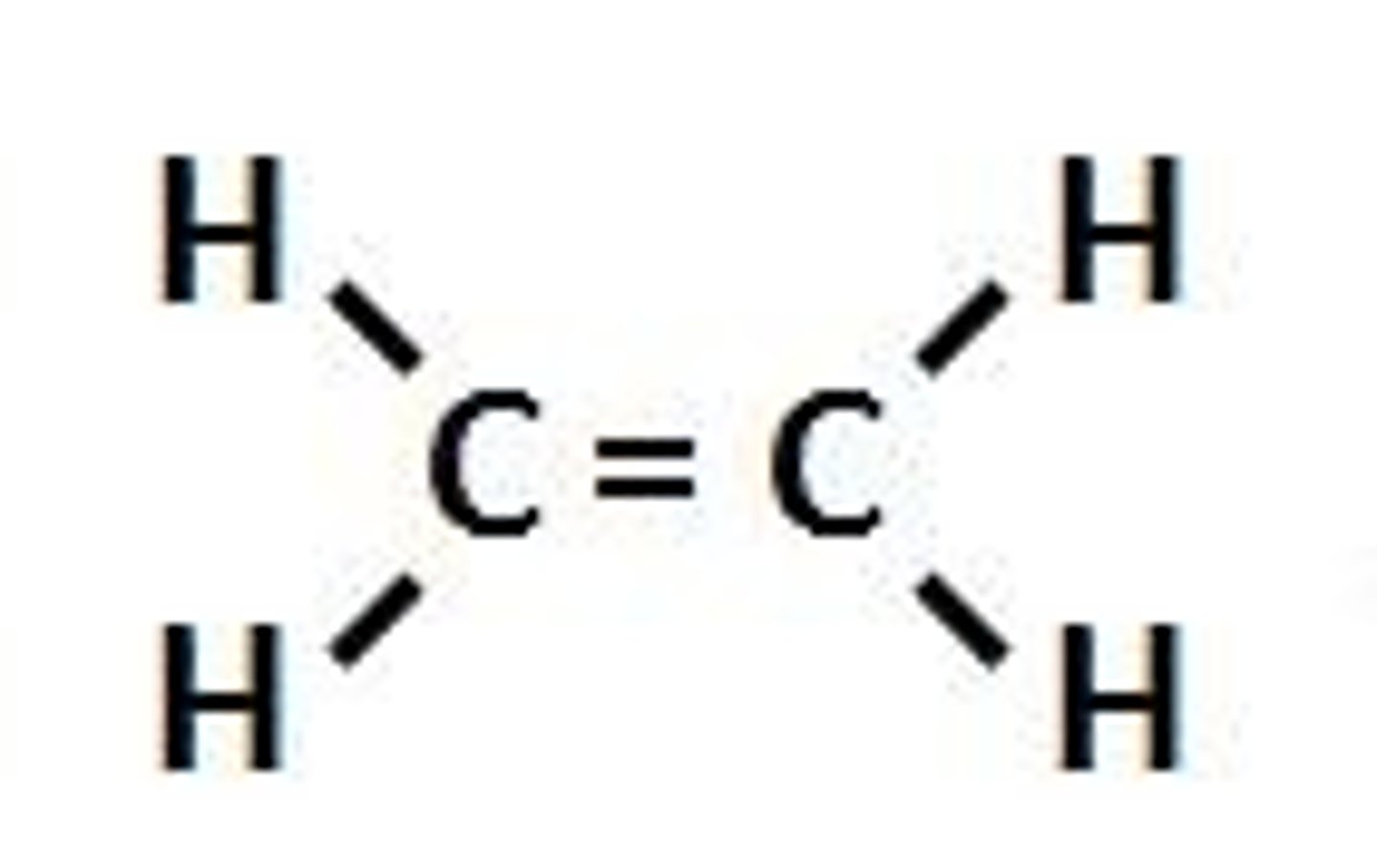
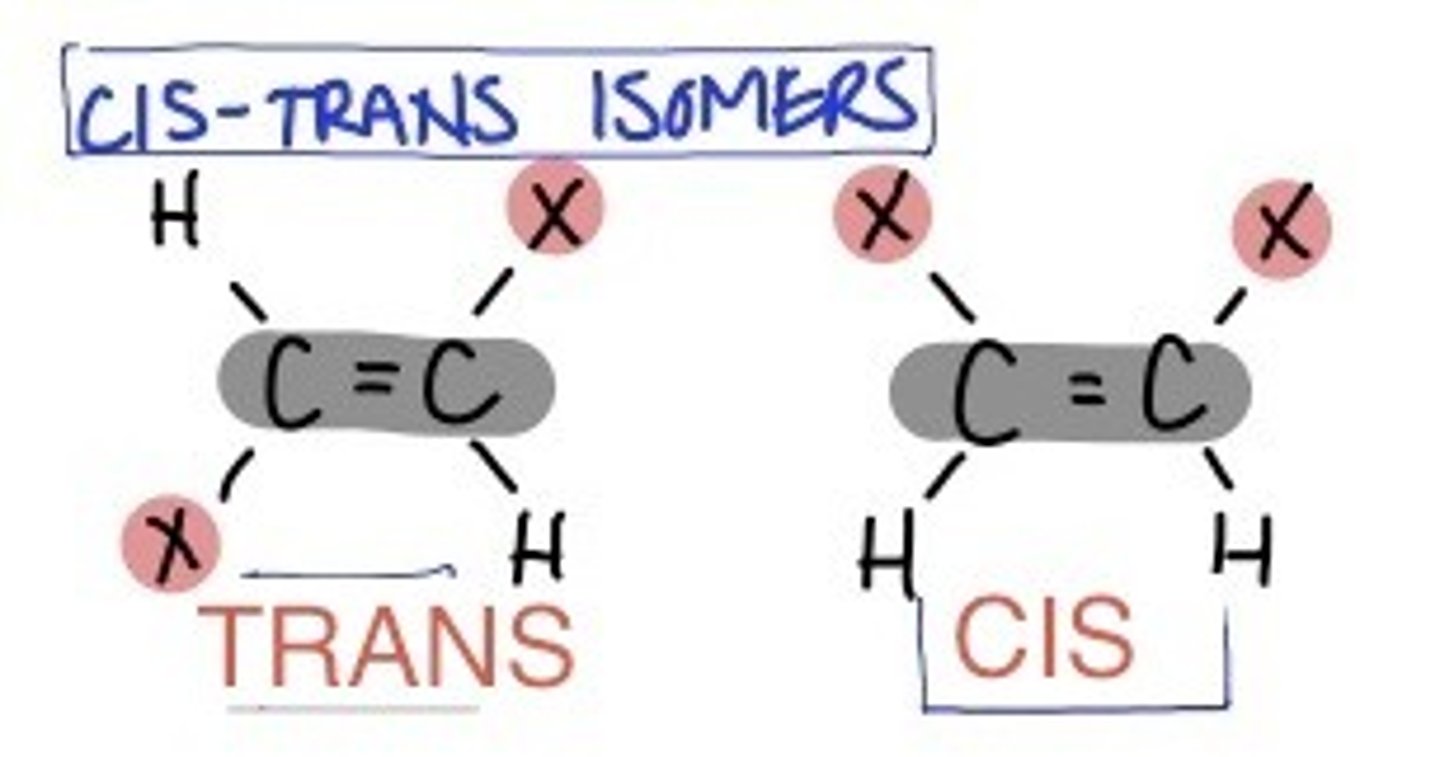
Cis and Trans
A single carbon bond allows for rotation
A double bond stops this rotation from taking place
This means the arms of the molecule are locked in position
Therefore, if the chlorines are on the same side we call this cis and if the chlorines are on opposite side we call it trans
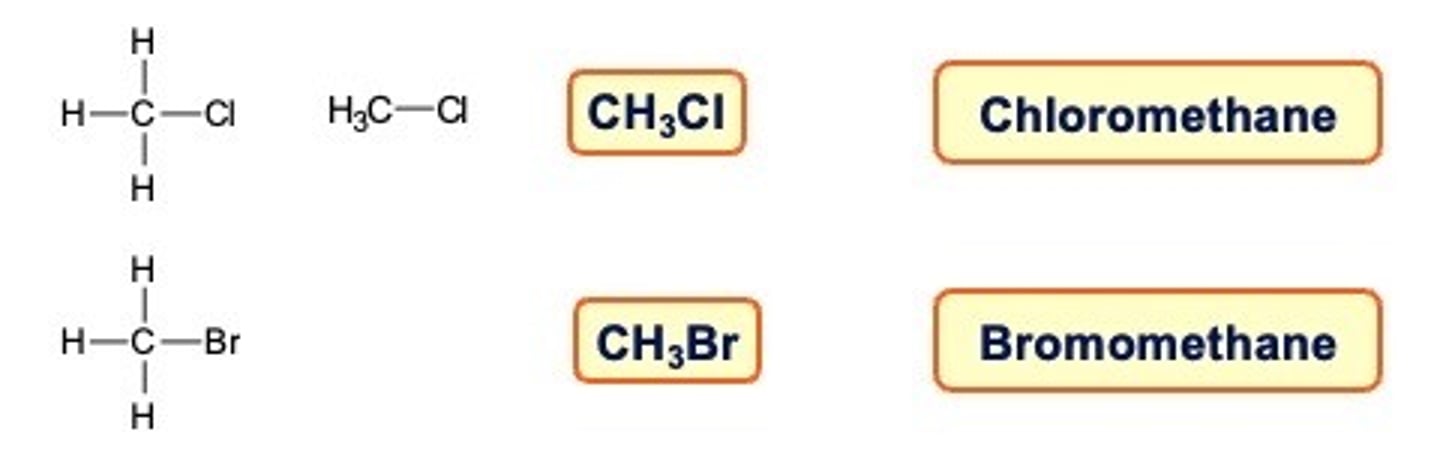
Halogenoalkanes (haloalkanes)
In halogenoalkanes a halogen atom replaces a hydrogen atom in the structure
The name is based on halogen prefix alkane name
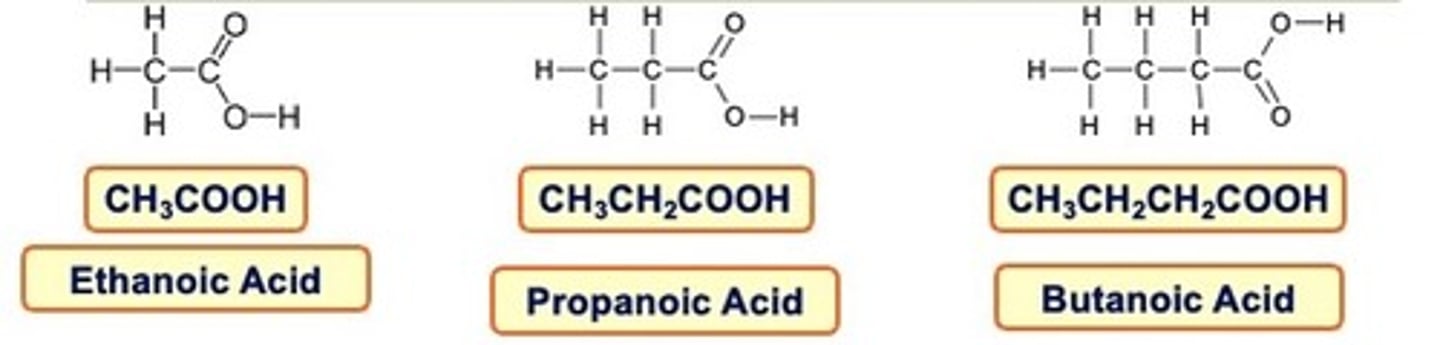
carboxylic acids
In carboxylic acids a carbon chain is ended in a carboxyl group.
This is often written as -COOH
When naming carboxylic acids don't forget the carbon in the carboxyl group is counted in the name.
Naming esters
1. Find the carboxyl group - this is the carbon with the double bonded oxygen
2. count the length of the chain away from the oxygen, in this case 2 carbons, so this ester is an ethanoate
3. count the number of carbons on the other side of the oxygen, in this case 1 carbon, so this ester is a methyl.
4. Join the two names together.
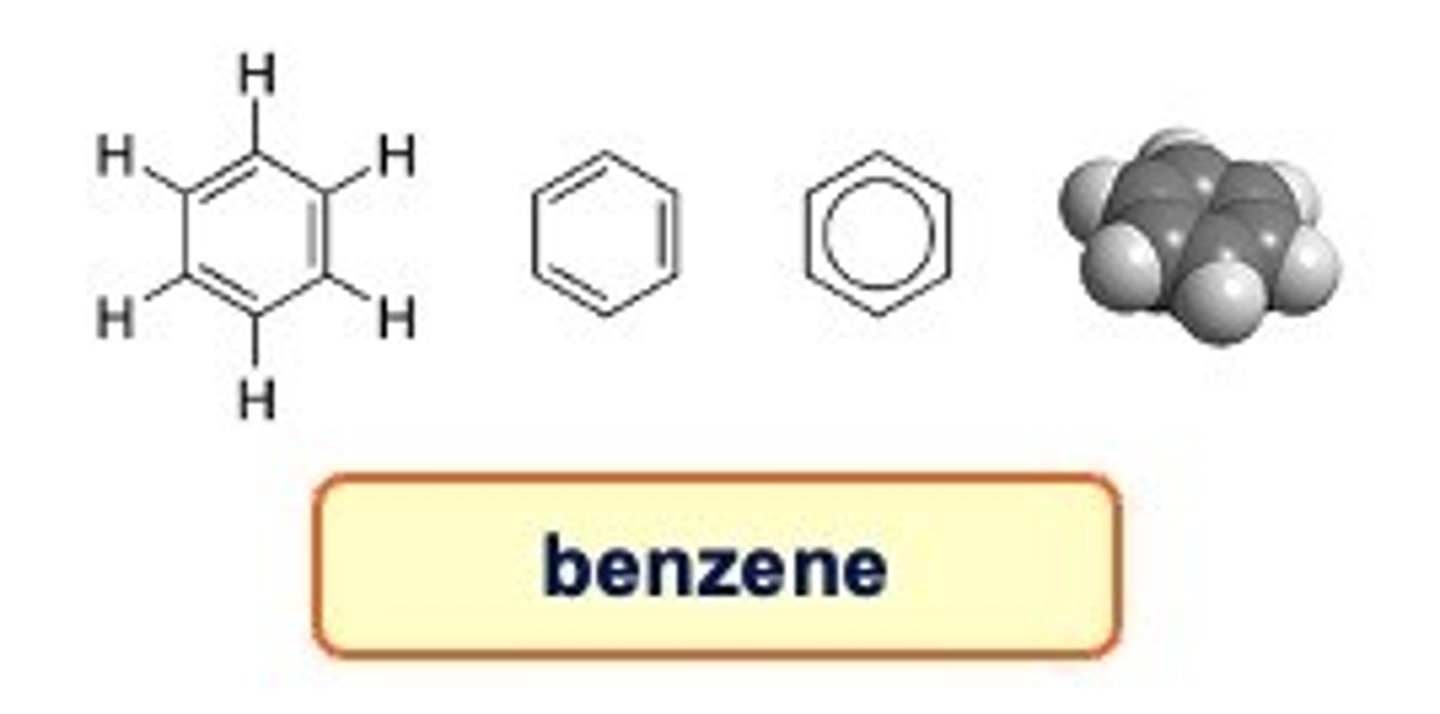
Aromatics
Aromatic chemistry is characterised by ring structures.
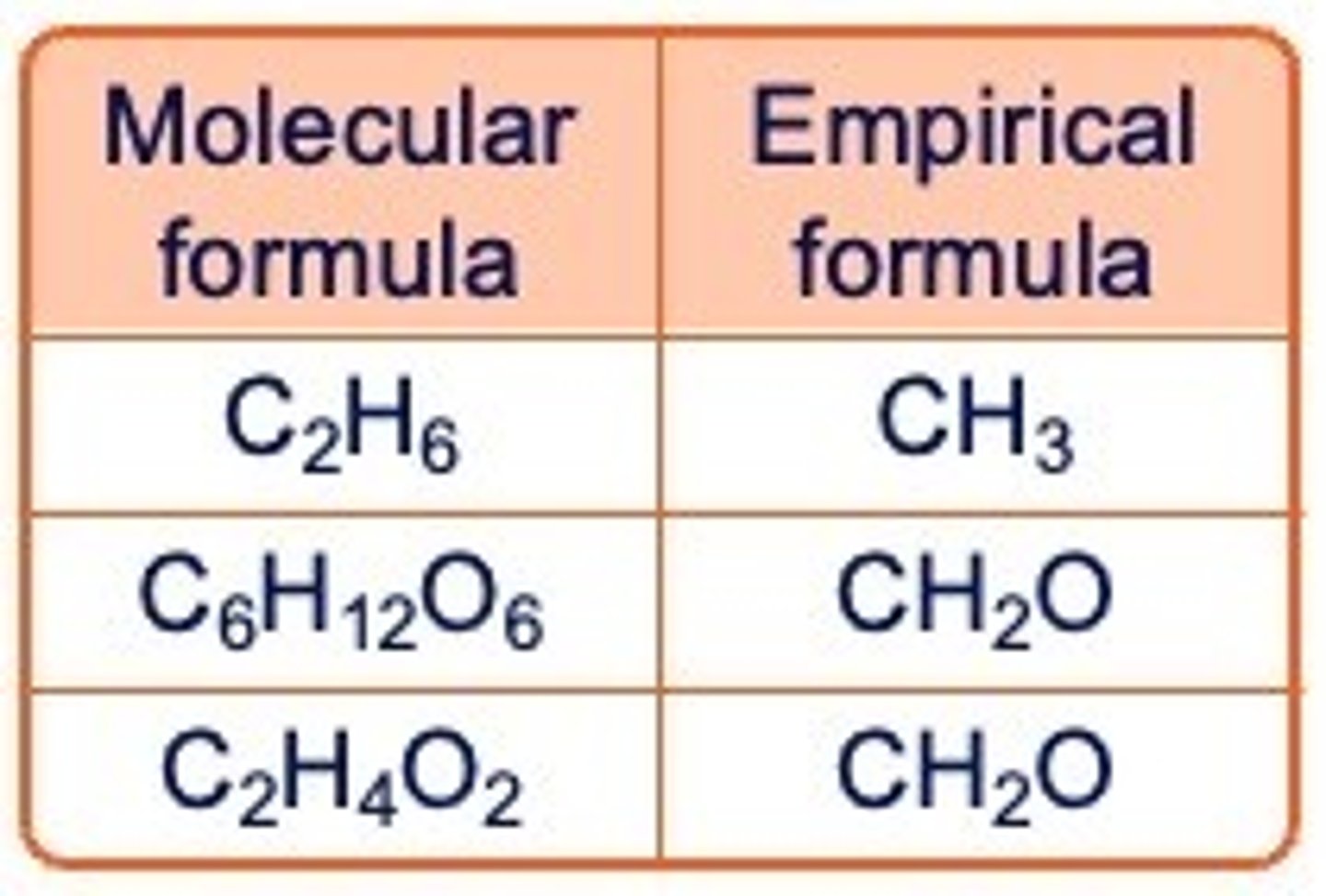
empirical formula
The empirical formula of a compound shows the simplest ratio of the atoms present
empirical formula vs molecular formula
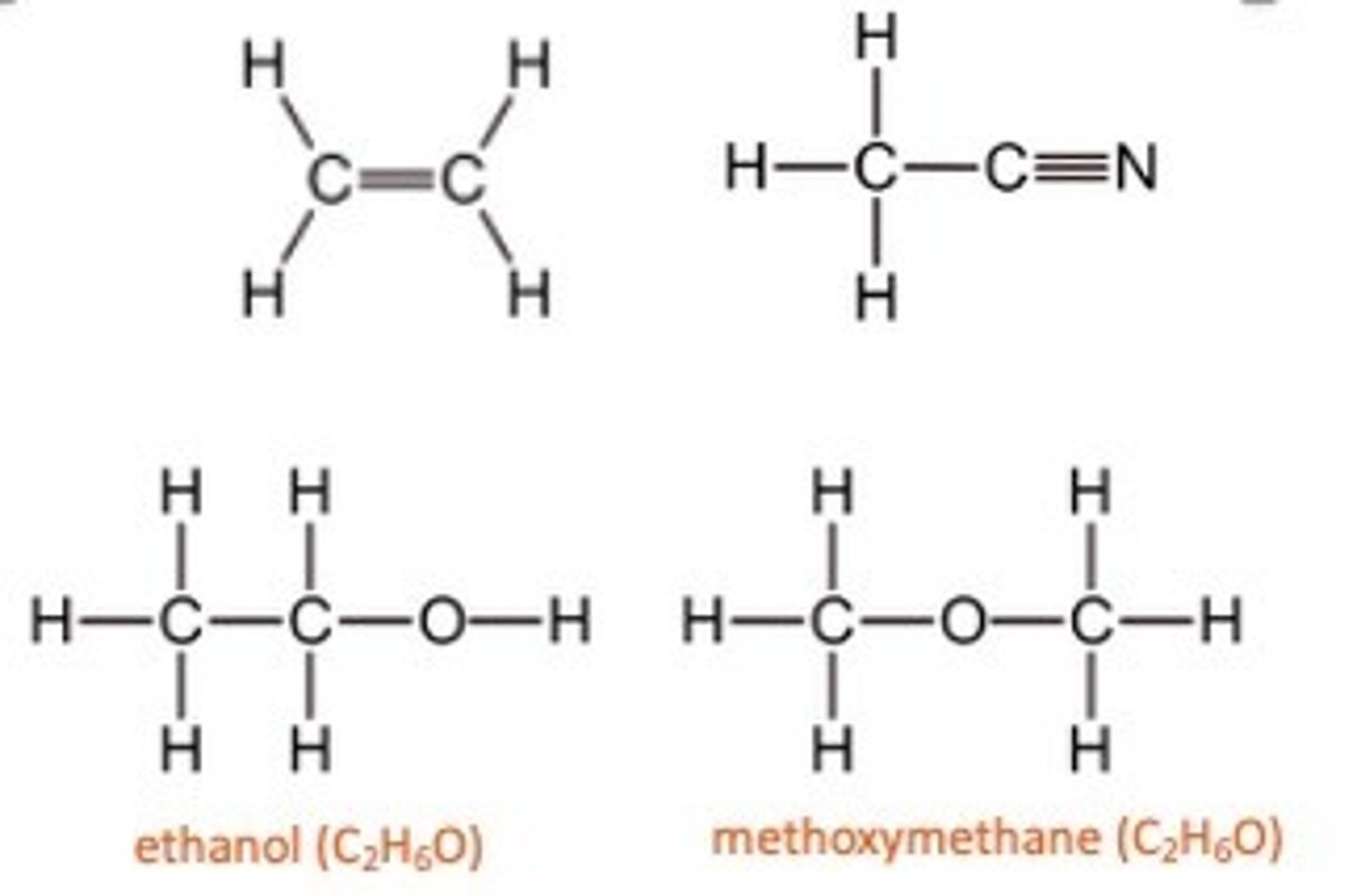
displayed formula
The displayed formula of a compound shows the arrangement of atoms in a molecule, as well as all the bonds.
Single bonds are represented by a single line, double bonds with two lines and triple bonds by three lines.
The displayed formula can show the different structures of compounds with the same molecular formulae.
IUPAC Names
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemists (IUPAC) developed a system for naming organic compounds.
This system eliminated many of the ambiguities that plagued earlier naming systems
Isomers
Isomers have the same formula, but different structures
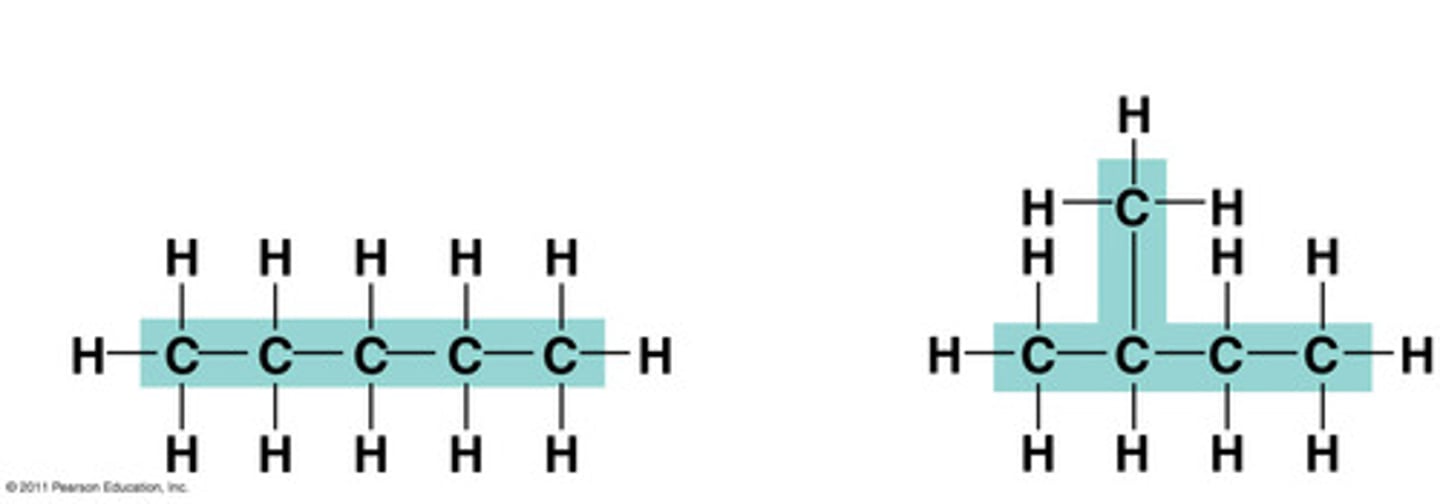
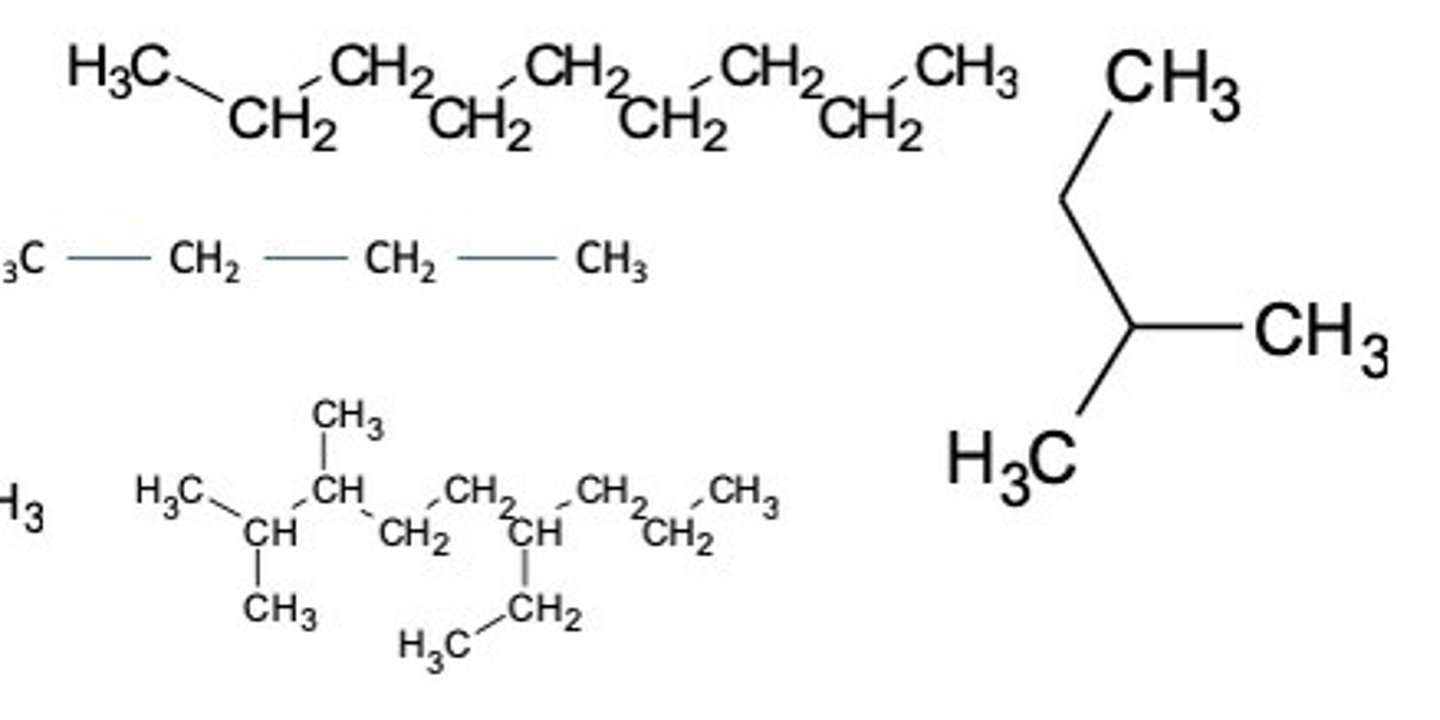
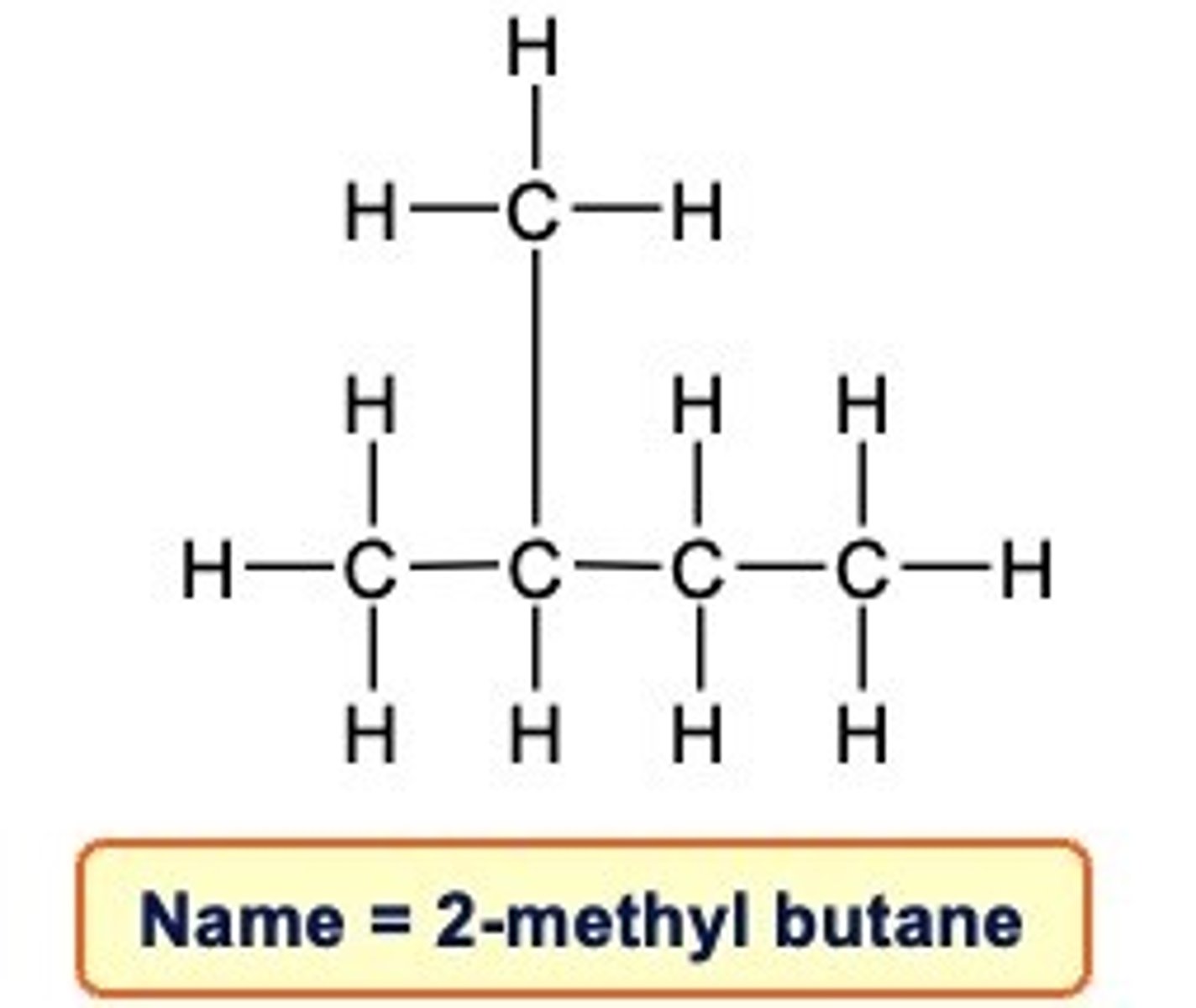
Steps to naming branched structure
1.Find the parent chain (the longest chain in the molecule).
2.Number each carbon, starting from the end closest to the branch
3.If necessary, write the number if the carbon atom in the parent chain the branch is attached followed by a hyphen.
4.Write the name of the branch, using the prefix corresponding to the number of carbons in the branch followed by the suffix -yl.
5.Write the name of the parent chain, according to the number of carbons in it, as if it were a simple alkane
Naming Alkenes
When there are 4 or more carbon atoms in a chain, the location of the double bond is indicated by a number.
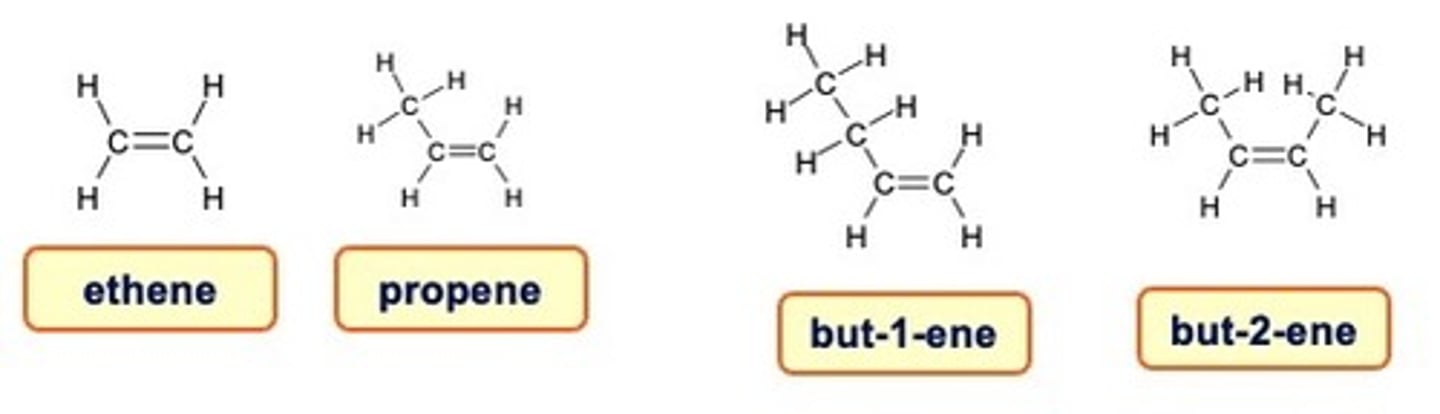
General formula for Alkanes

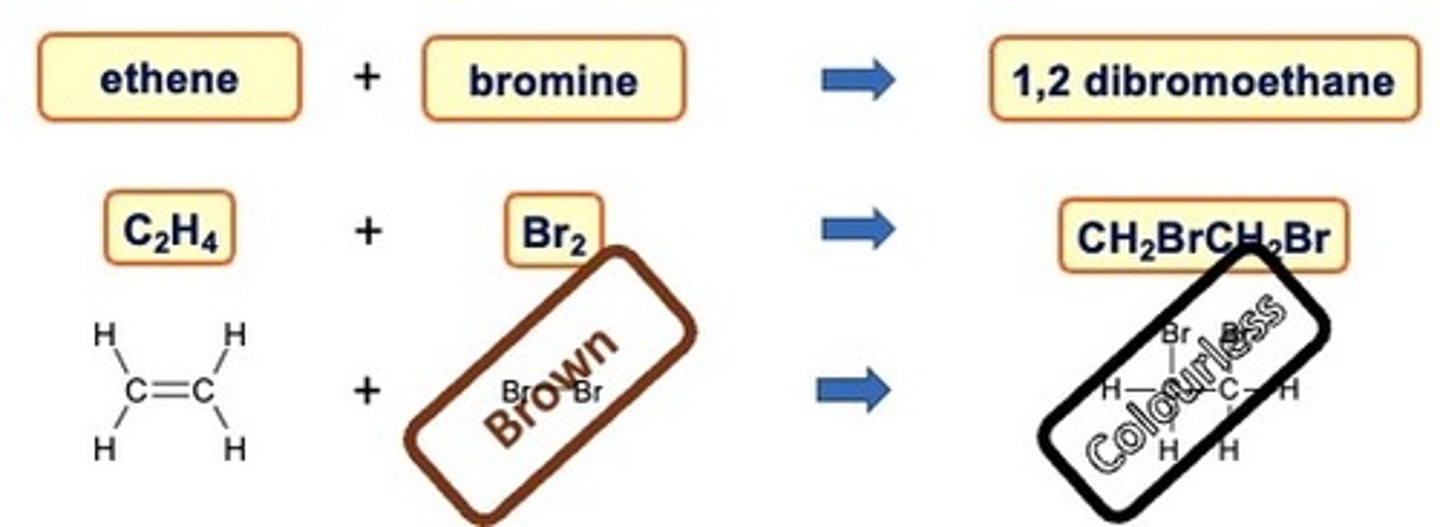
How can you test for Alkenes?
As alkenes are unsaturated they can react with bromine water.
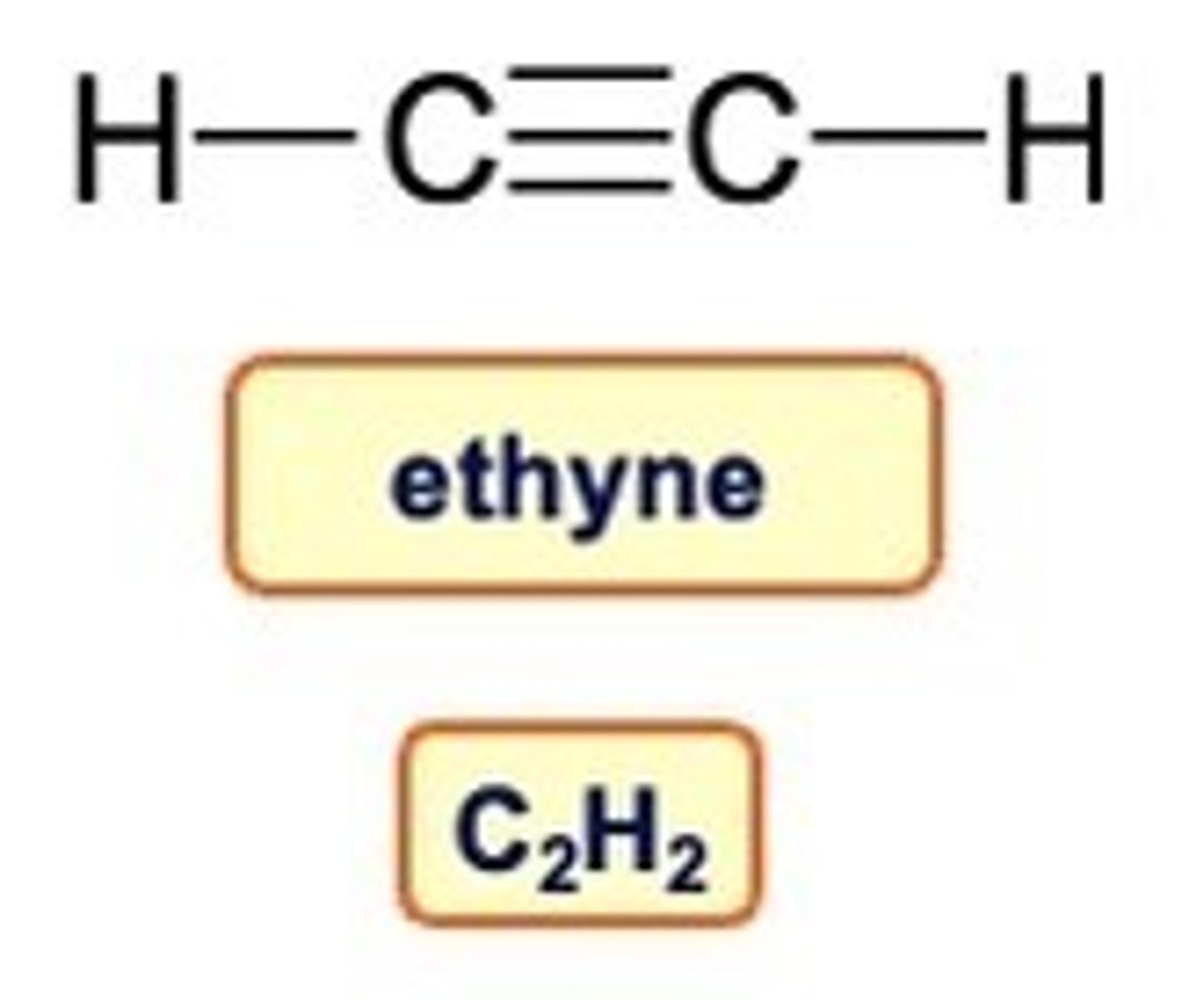
Alkynes
The family of hydrocarbons which contain triple bonds are called alkynes
The name ends -yne
Ethanol
the chemist's favourite alcohol
Ethanol is the alcohol found in alcoholic drinks, but it is also used as an industrial solvent.
For drinks ethanol is made by fermentation and then maybe distillation
For industrial use ethanol is made by the hydration of ethene
molecular formula
The molecular formula of a compound shows the number of each type of atom present in one molecule of the compound.
full list of organic formulae
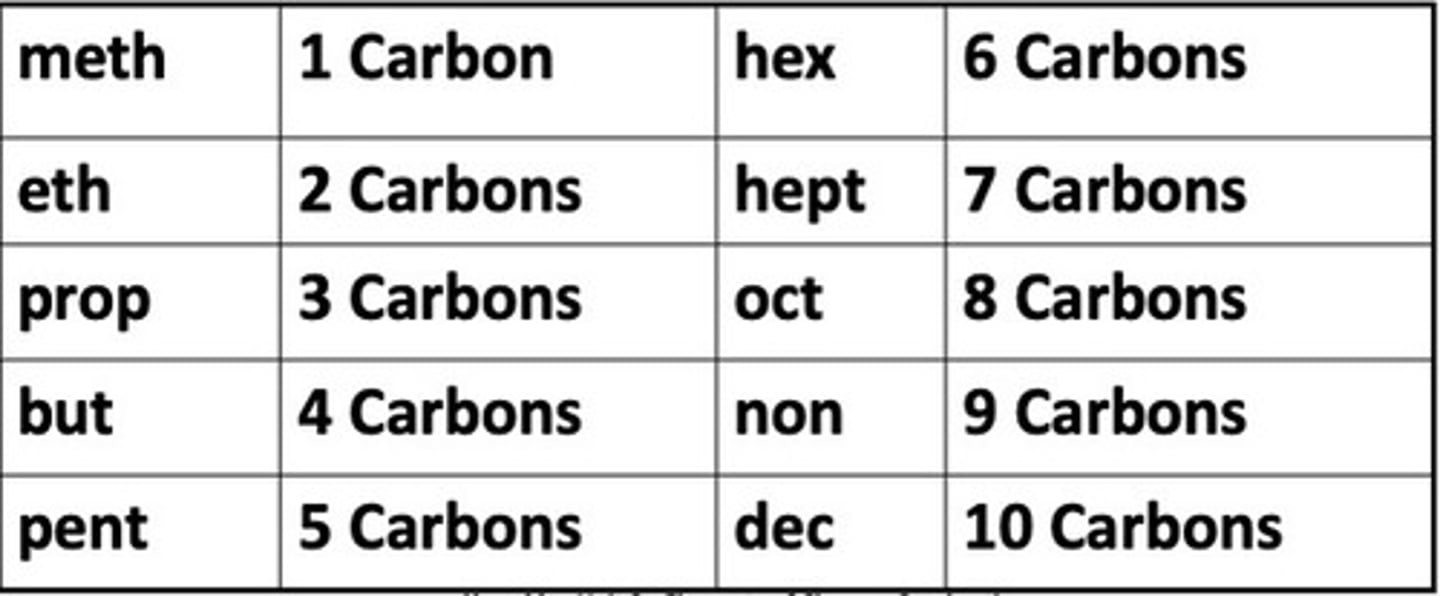
A series of prefixes are used to designate the number of carbon atoms in a carbon chain ...
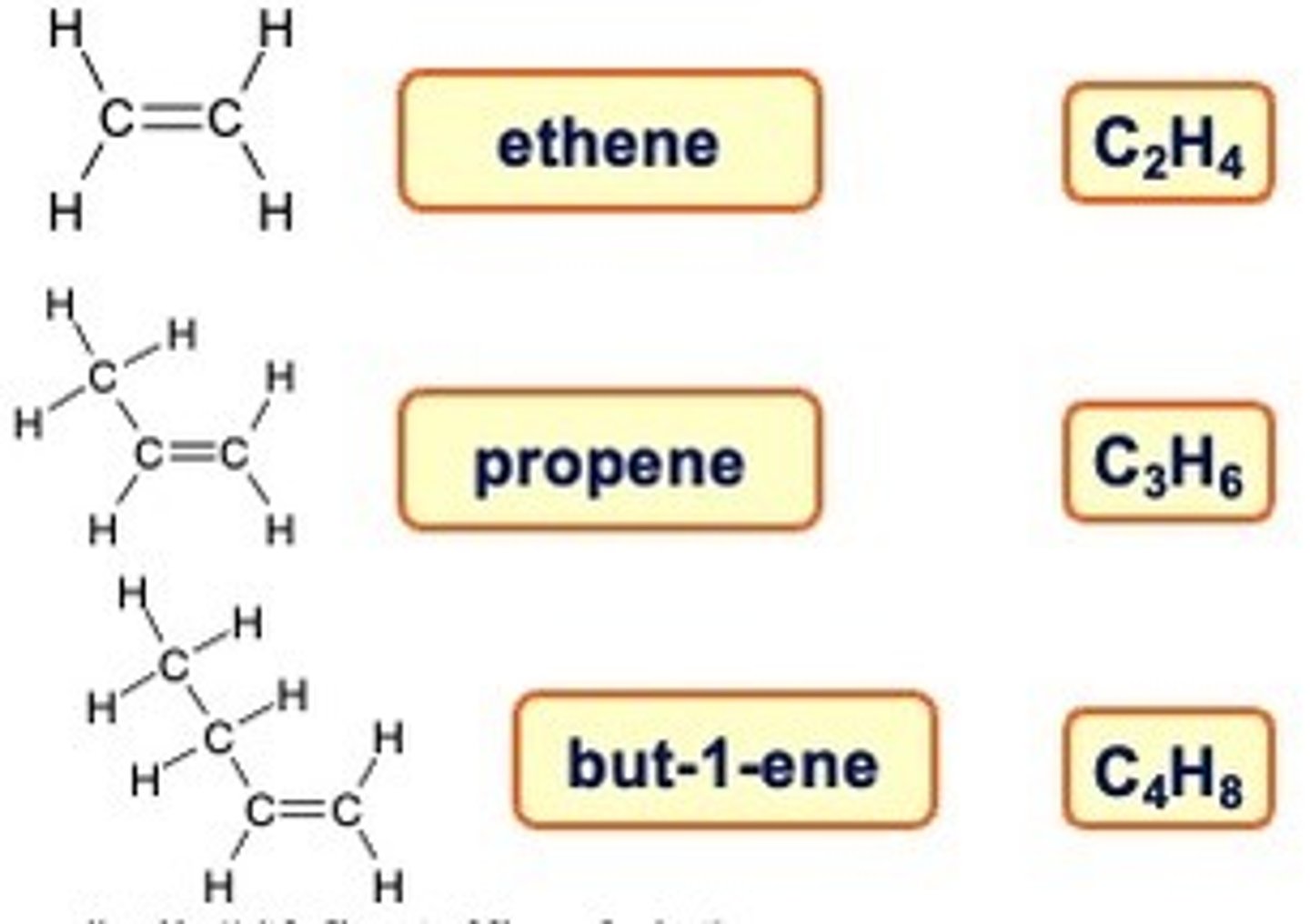
Alkenes are a ______ series
homologous
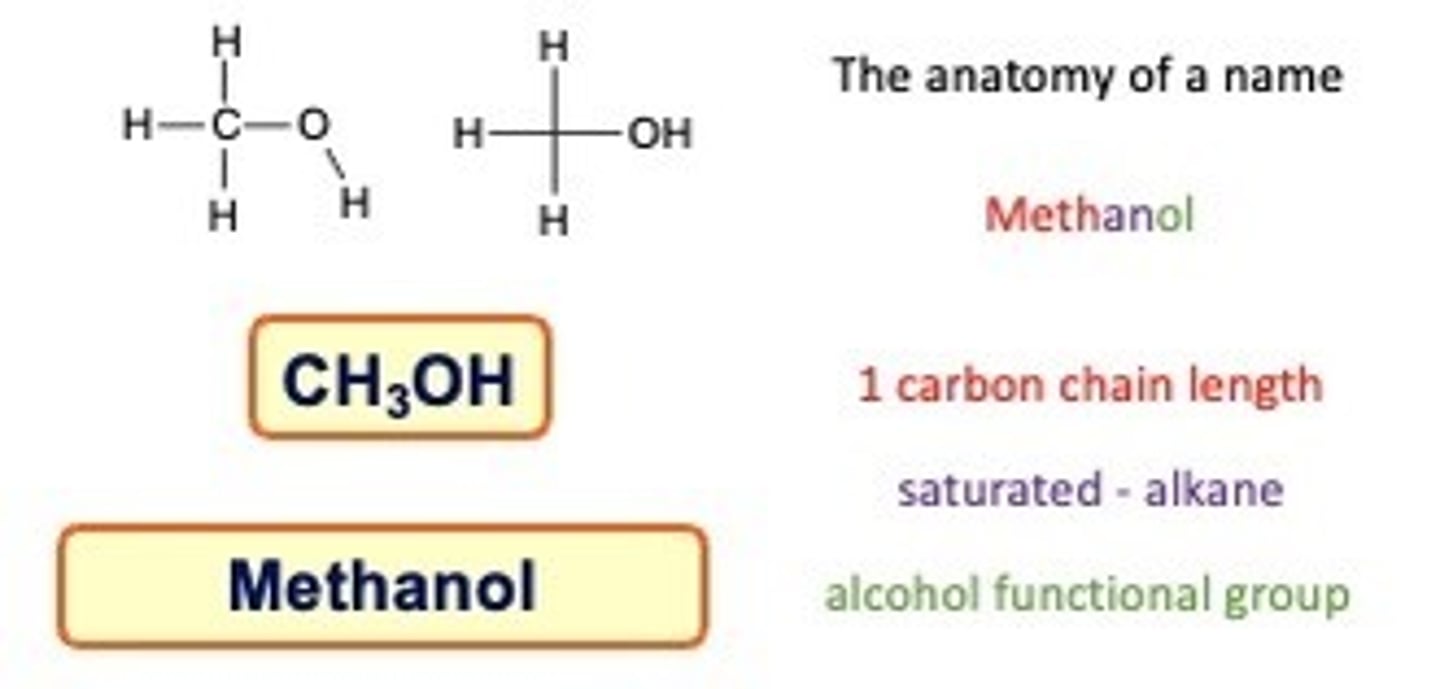
Alcohols
Alcohols are a classification of organic molecules contain a hydroxyl group attached to a saturated carbon atom.
The suffix -ol is used to name alcohols