The Atom, Atoms, History of the Atom
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Atomic Number
Equal to the number of protons
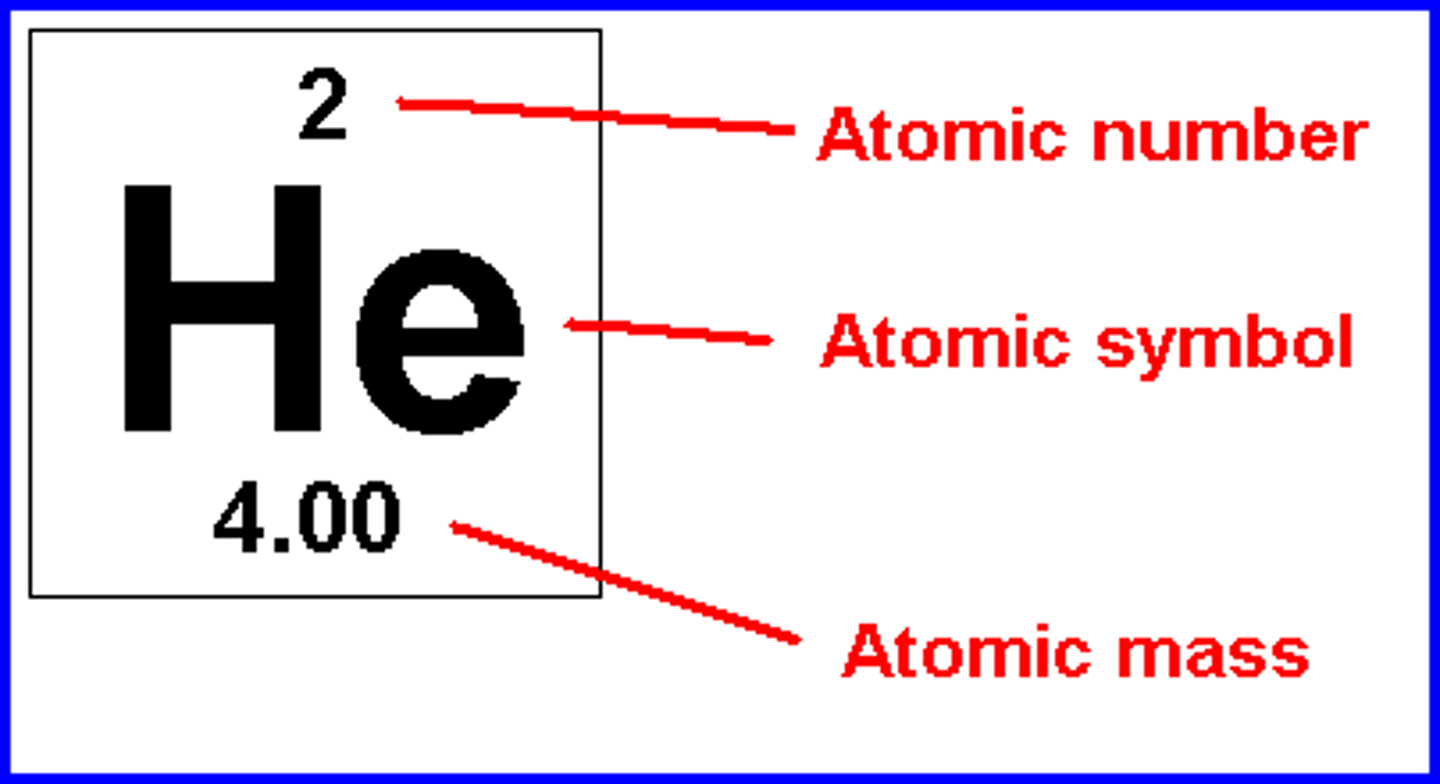
Mass Number
Equal to the number of protons + number of neutrons
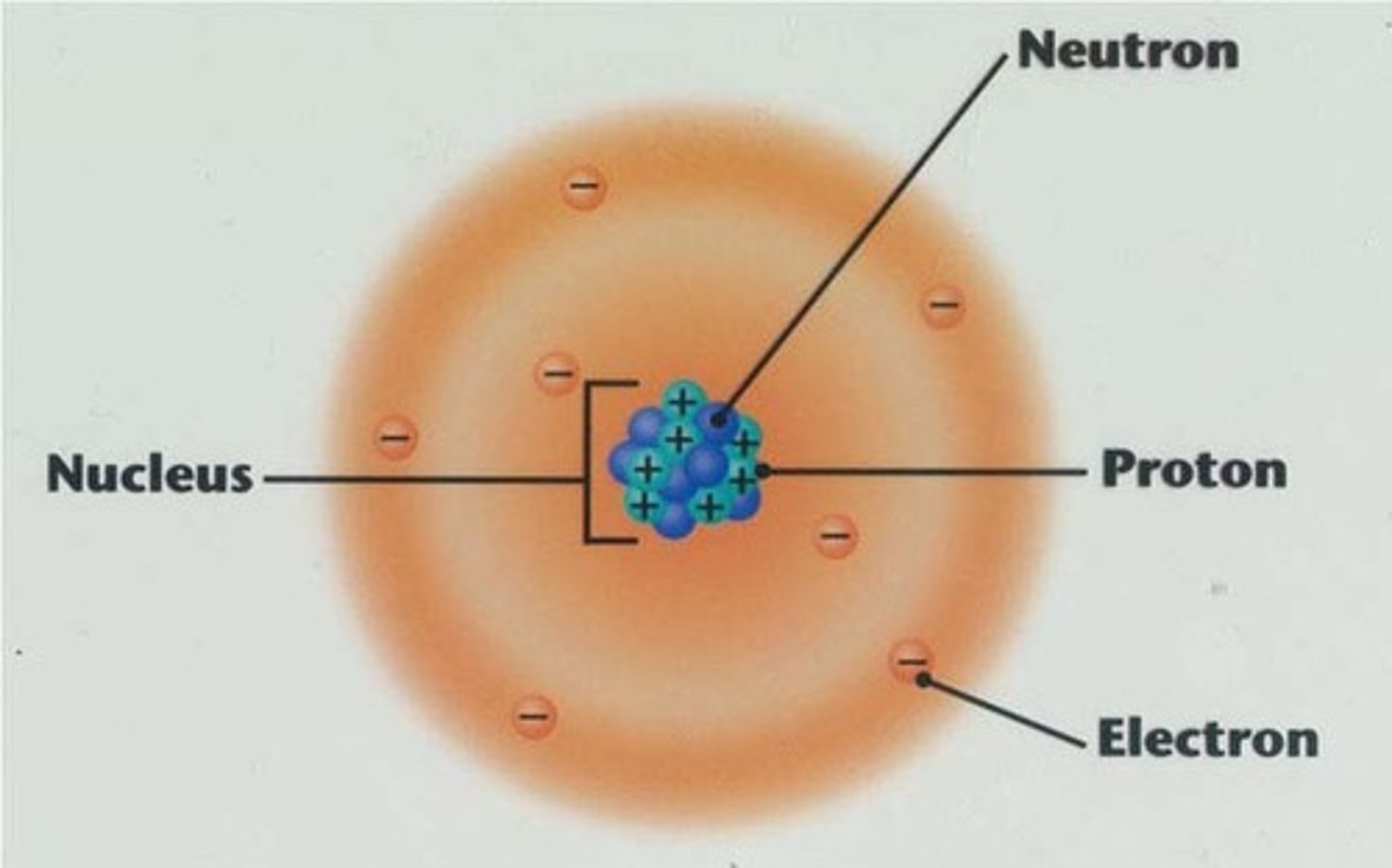
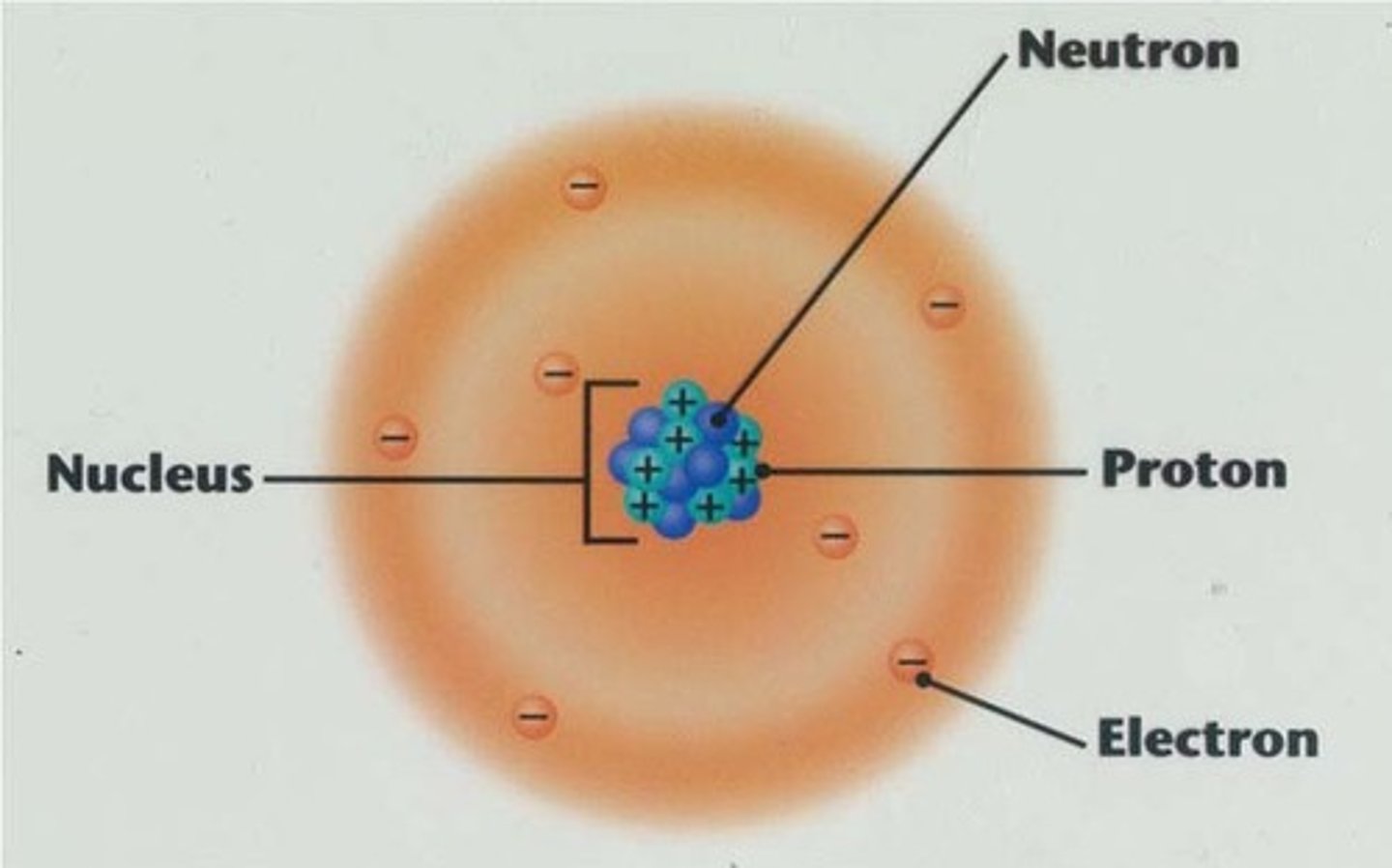
Protons
Positively charged particles located in the nucleus, responsible for the identity of the atom
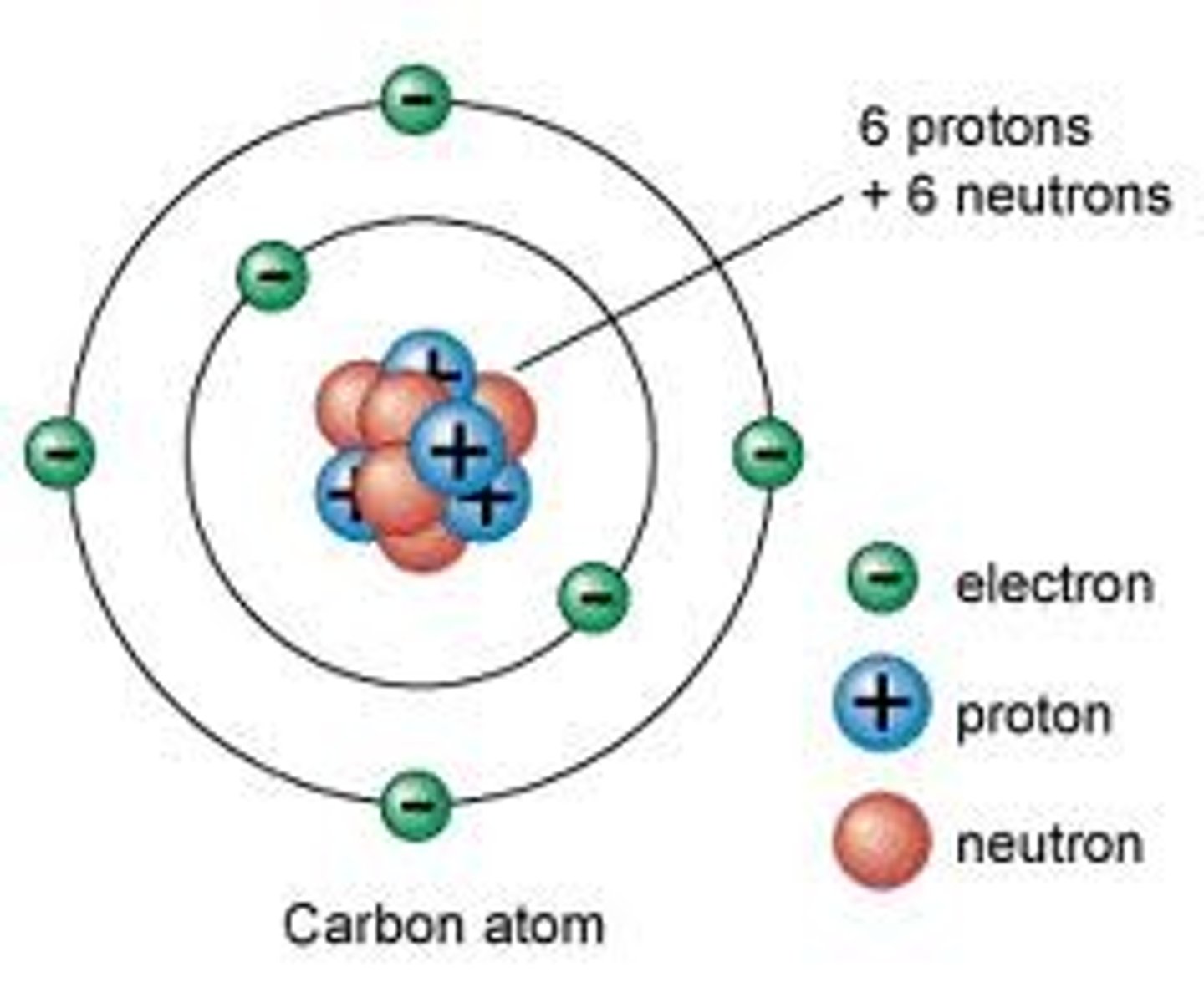
Neutrons
Neutral particles located in the nucleus, responsible for the stability of the nucleus
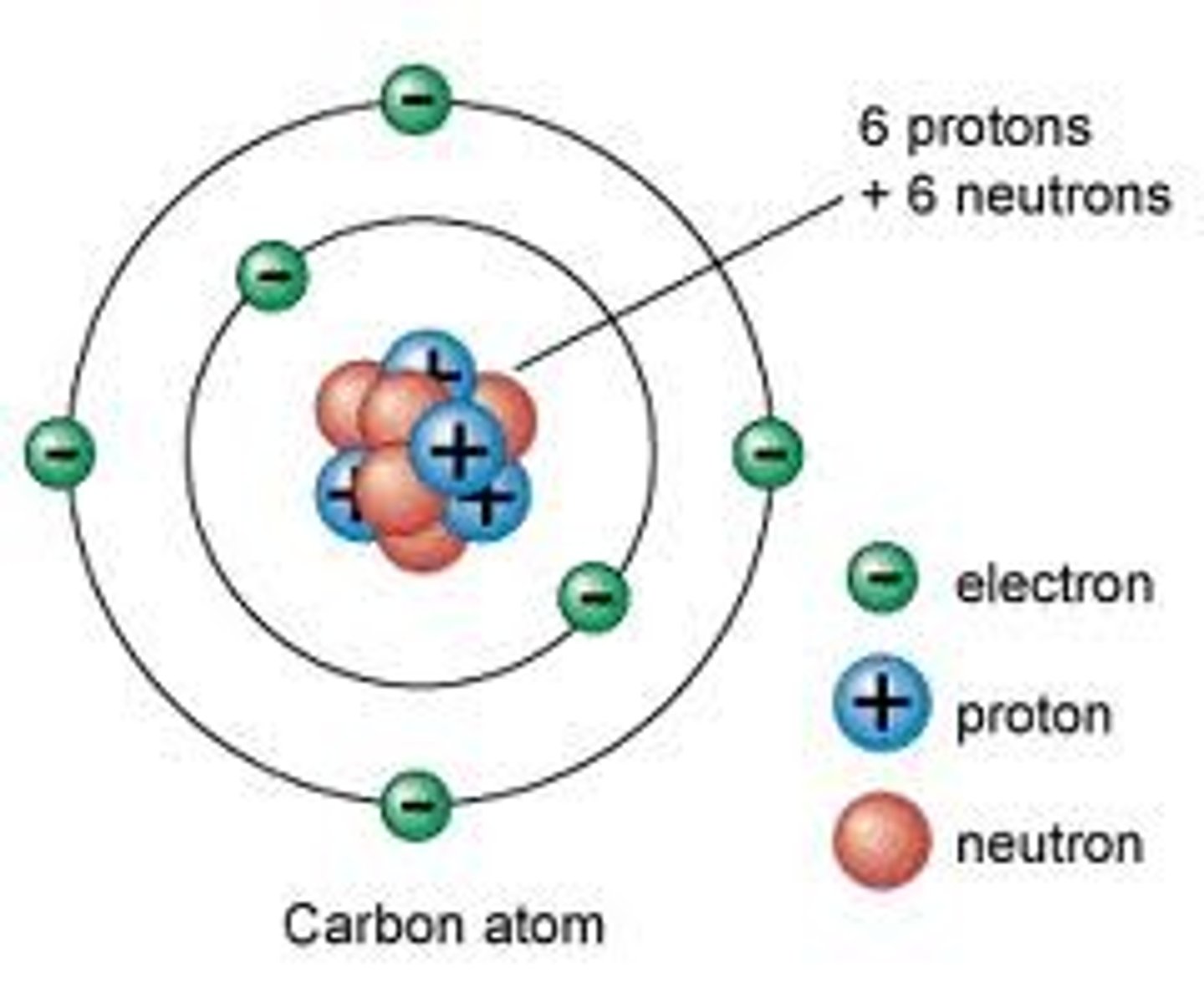
Electrons
Negatively charge particles located in the electron cloud, responsible for chemical properties
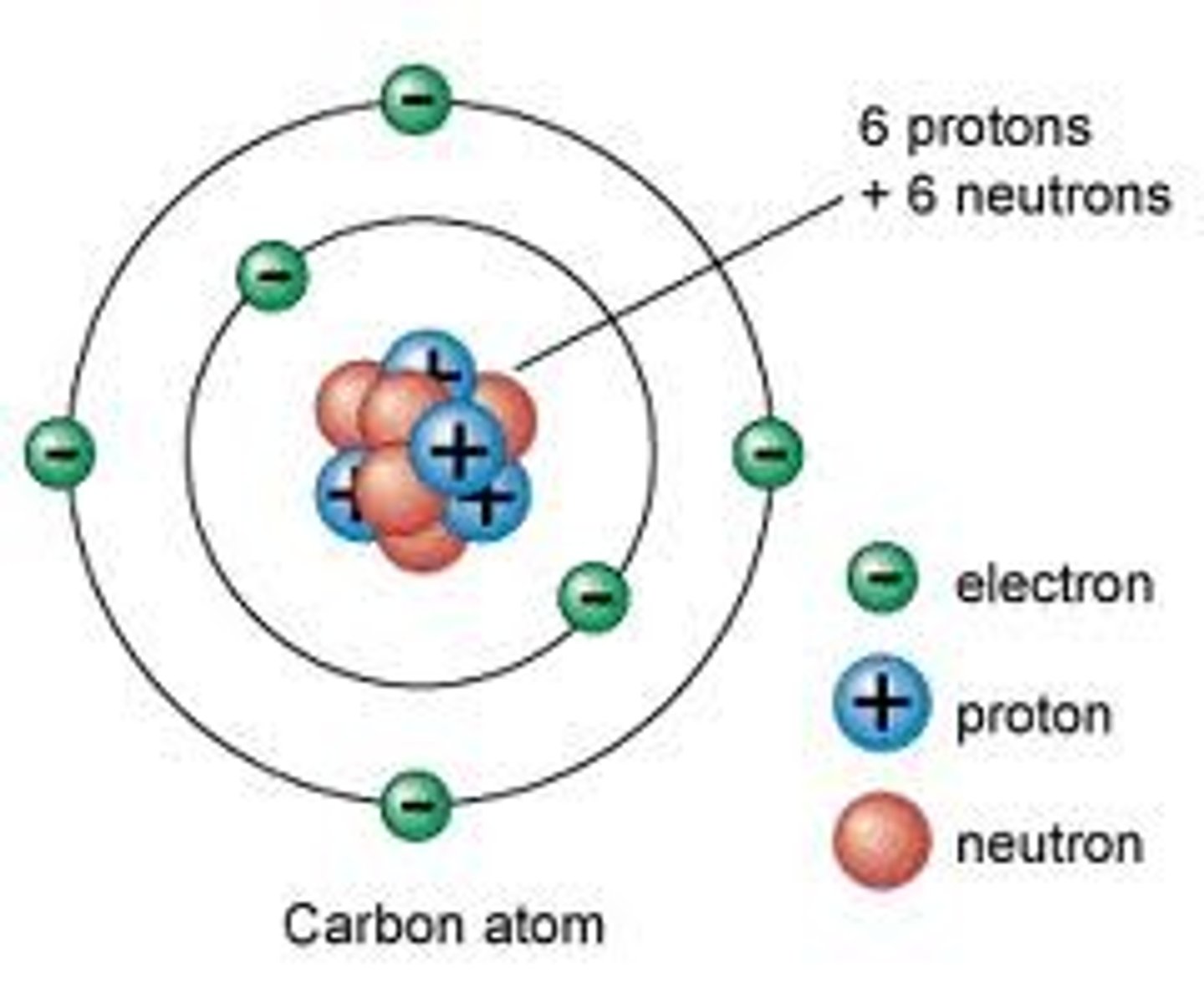
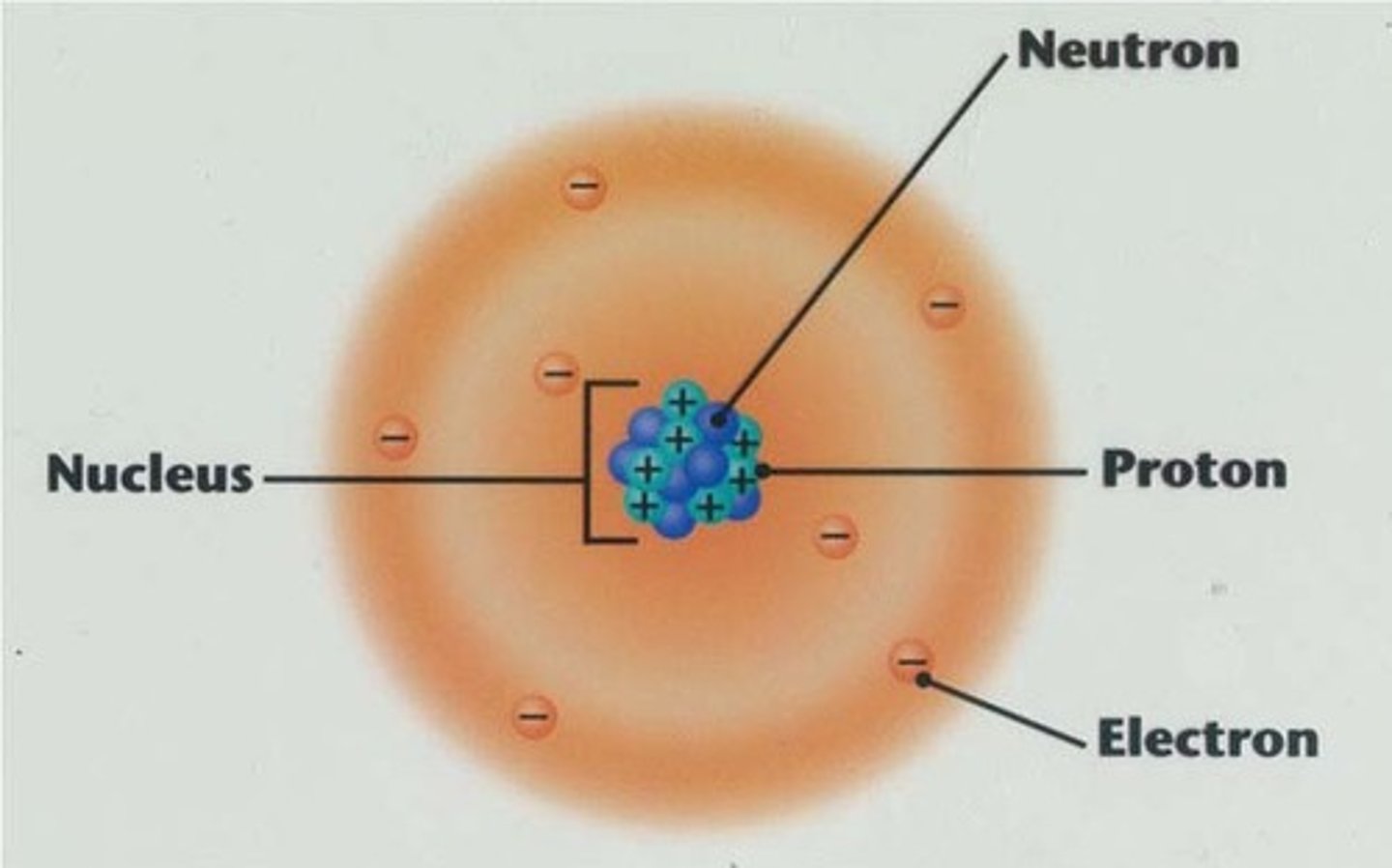
Nucleus
Located at the center of the atom, holds the protons and the neutrons
Isotope
Same number of protons, different number of neutrons
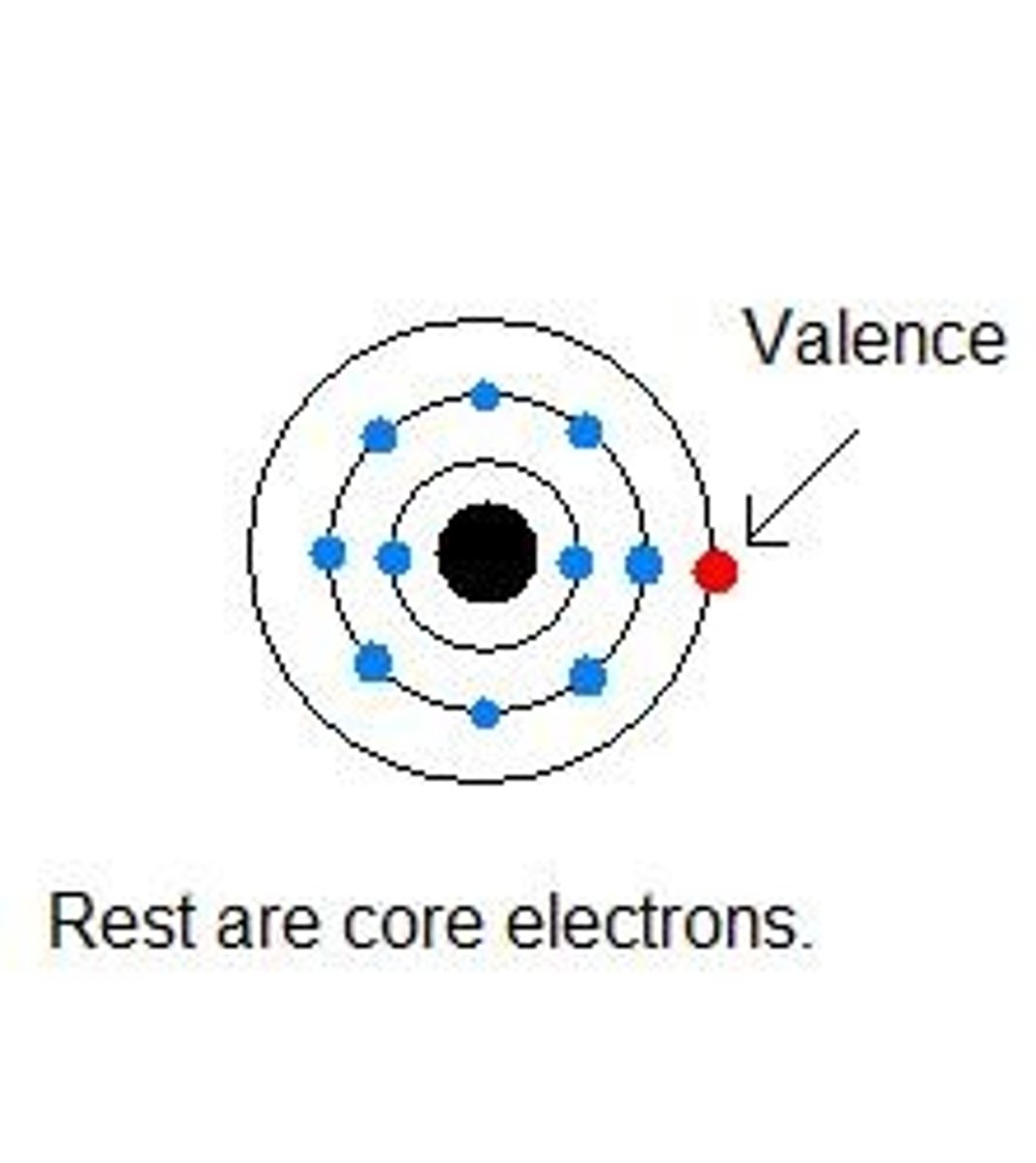
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the outermost energy level
Dalton
Atomic Theory

Atomic Number
Number of protons in an atom

Atomic Mass
total weight of protons and neutrons

atom
smallest unit of matter
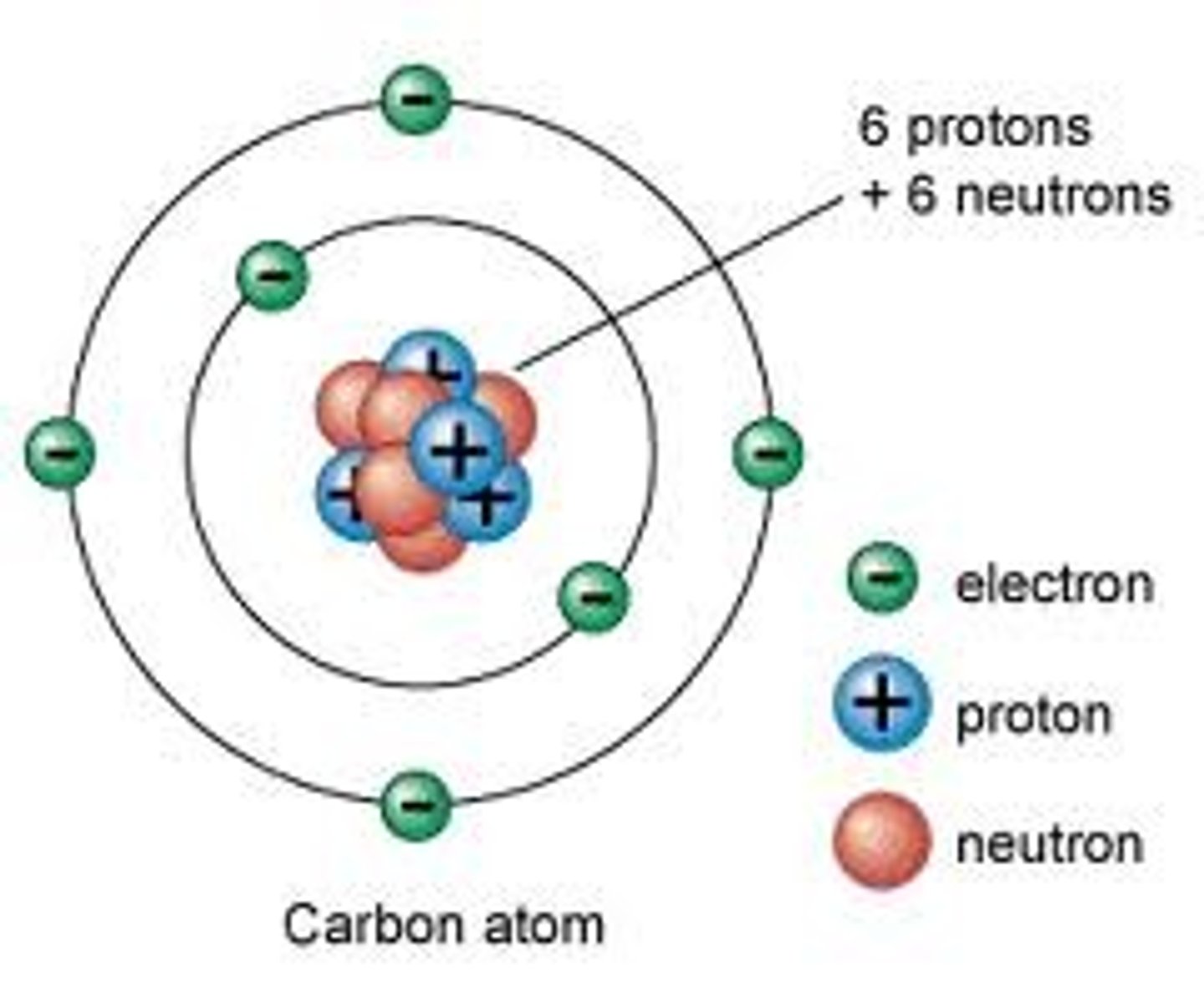
nucleus of atom
the positively charged dense center of an atom
neutron
A subatomic particle that has no charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
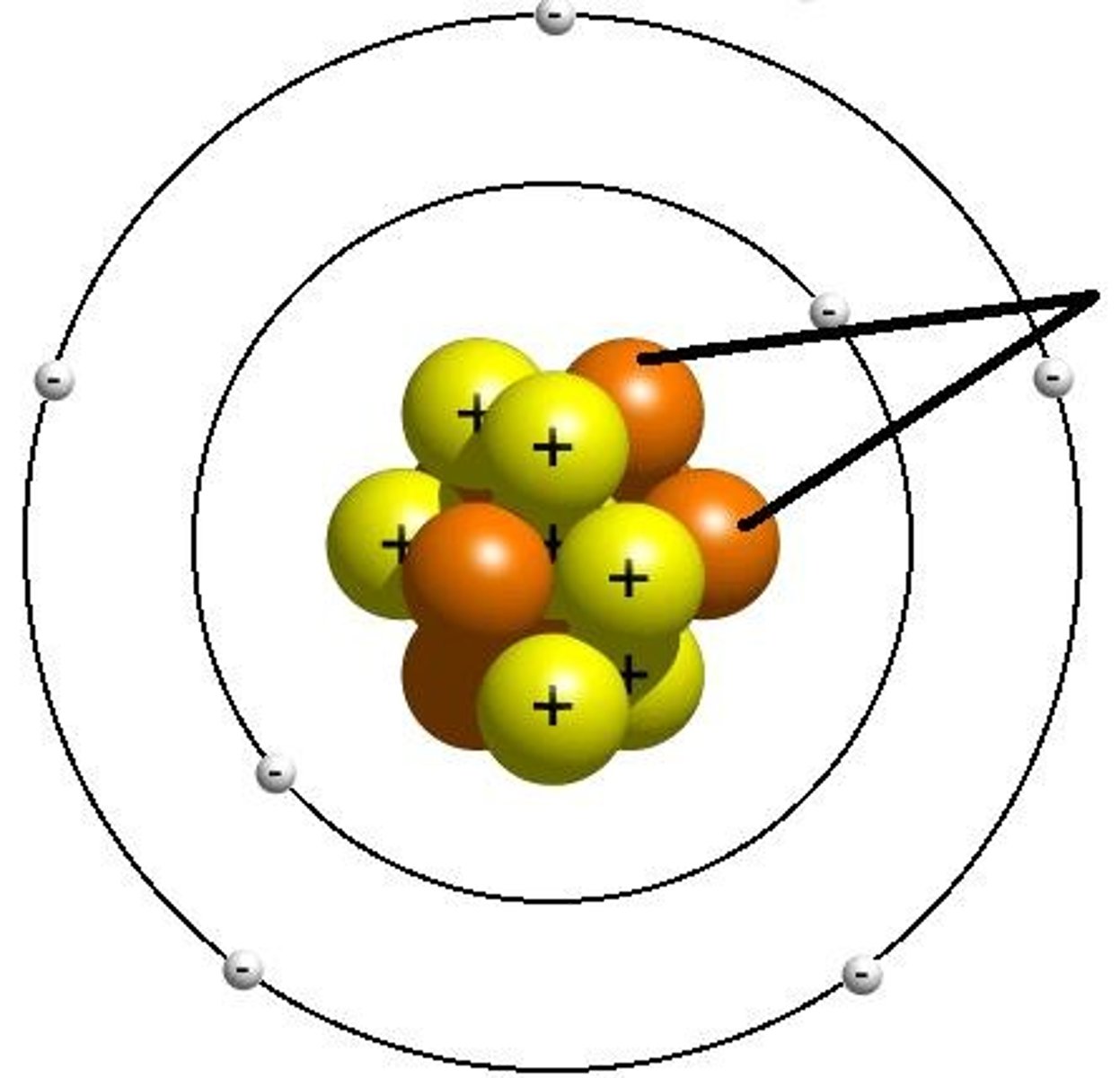
proton
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
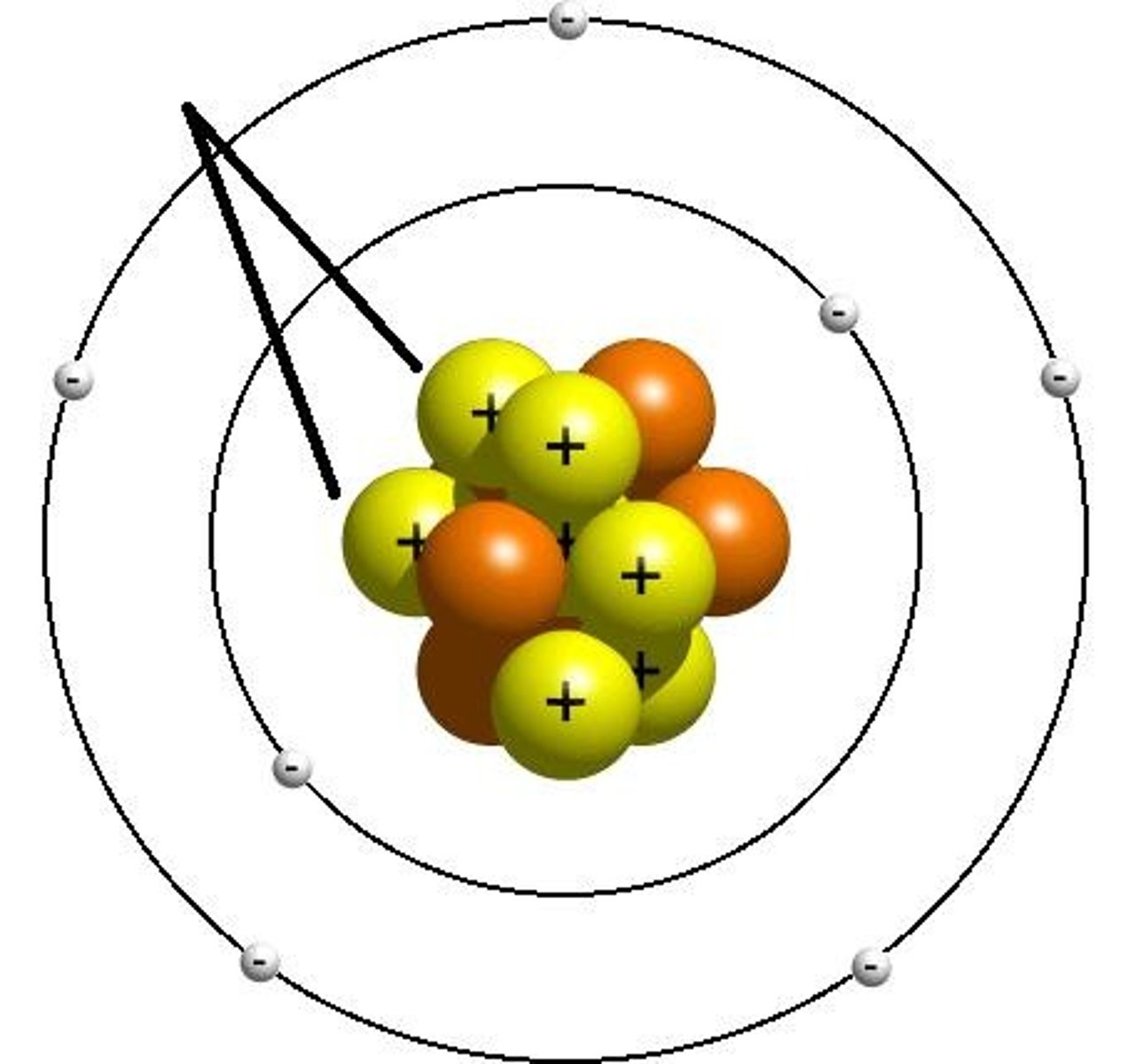
electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge
Periodic Table
A chart of the elements showing the repeating pattern of their properties
Democritus
460 BC; There is a limit to how many times one can break matter into smaller pieces; eventually one reaches the smallest particle.

Aristotle
300 BC; All matter composed of fire, water, earth, and air. Founder of alchemy.

John Dalton
1803; Atomic Theory: all matter made of atoms; all atoms of an element are alike, but are different from other elements; elements can be combined to make compounds; chemical reactions are a rearrangement of elements, but do not change the elements themselves.

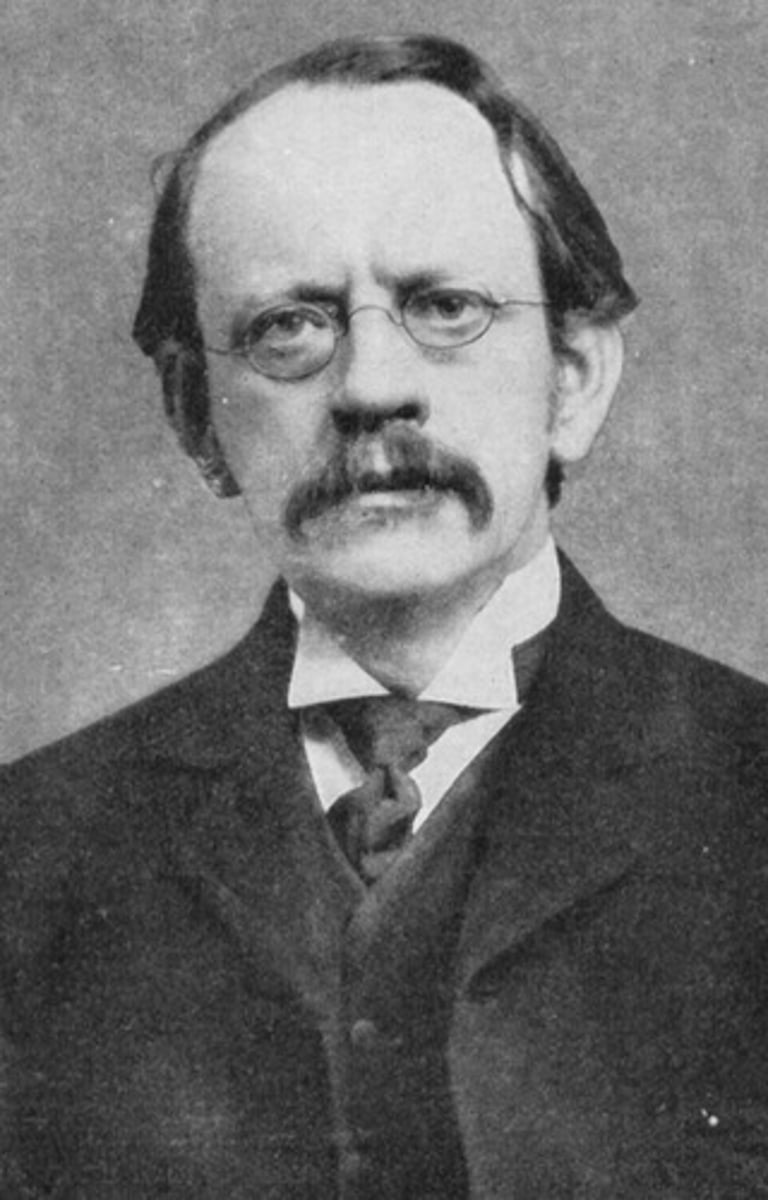
JJ Thomson
1897; finds the electron of an atom using a cathode ray tube; also said the electron must be balanced by positive charge; proposed the plum pudding model.

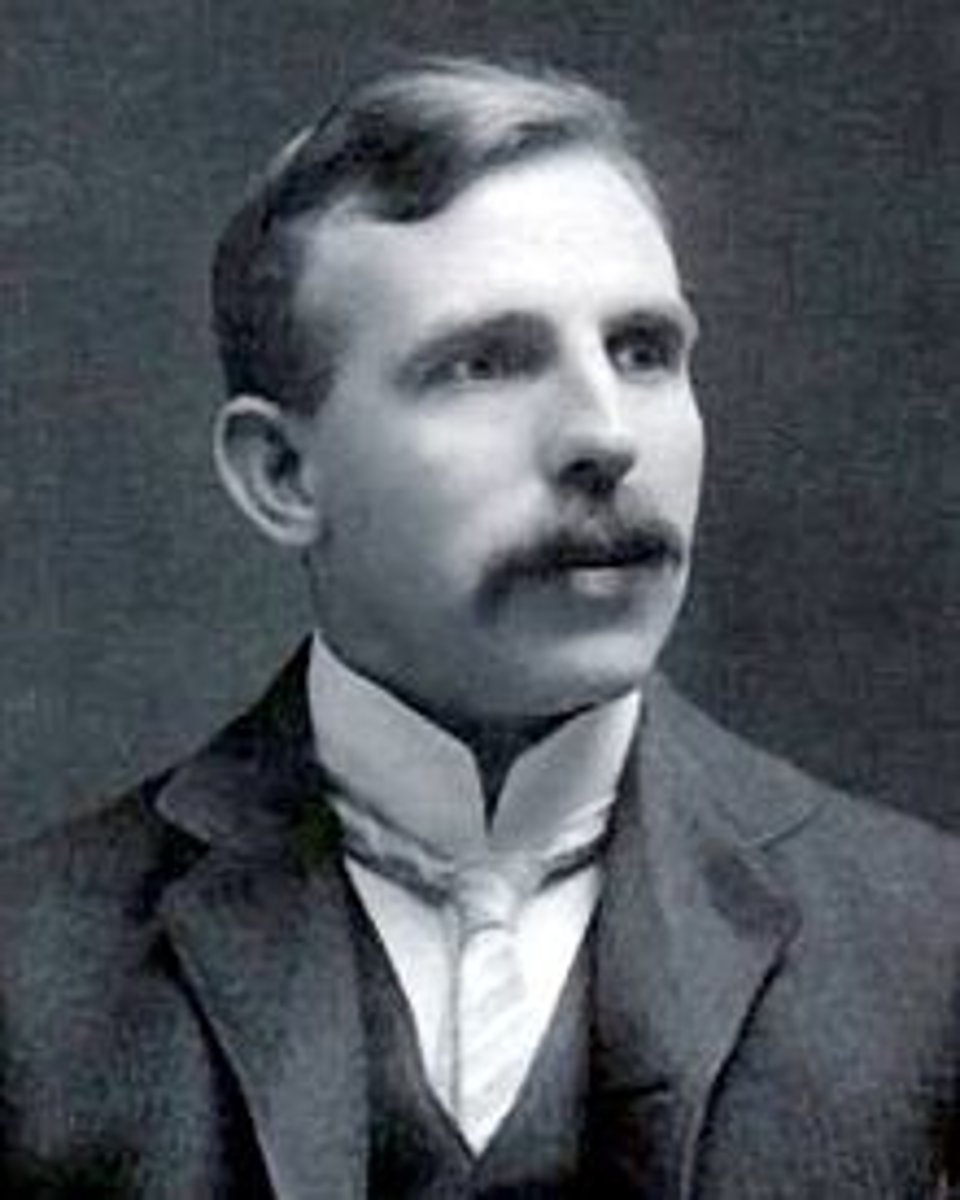
Ernest Rutherford
1911; performed the gold foil experiment; proved that most of the atom is empty space and the existence of the nucleus.

proton
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
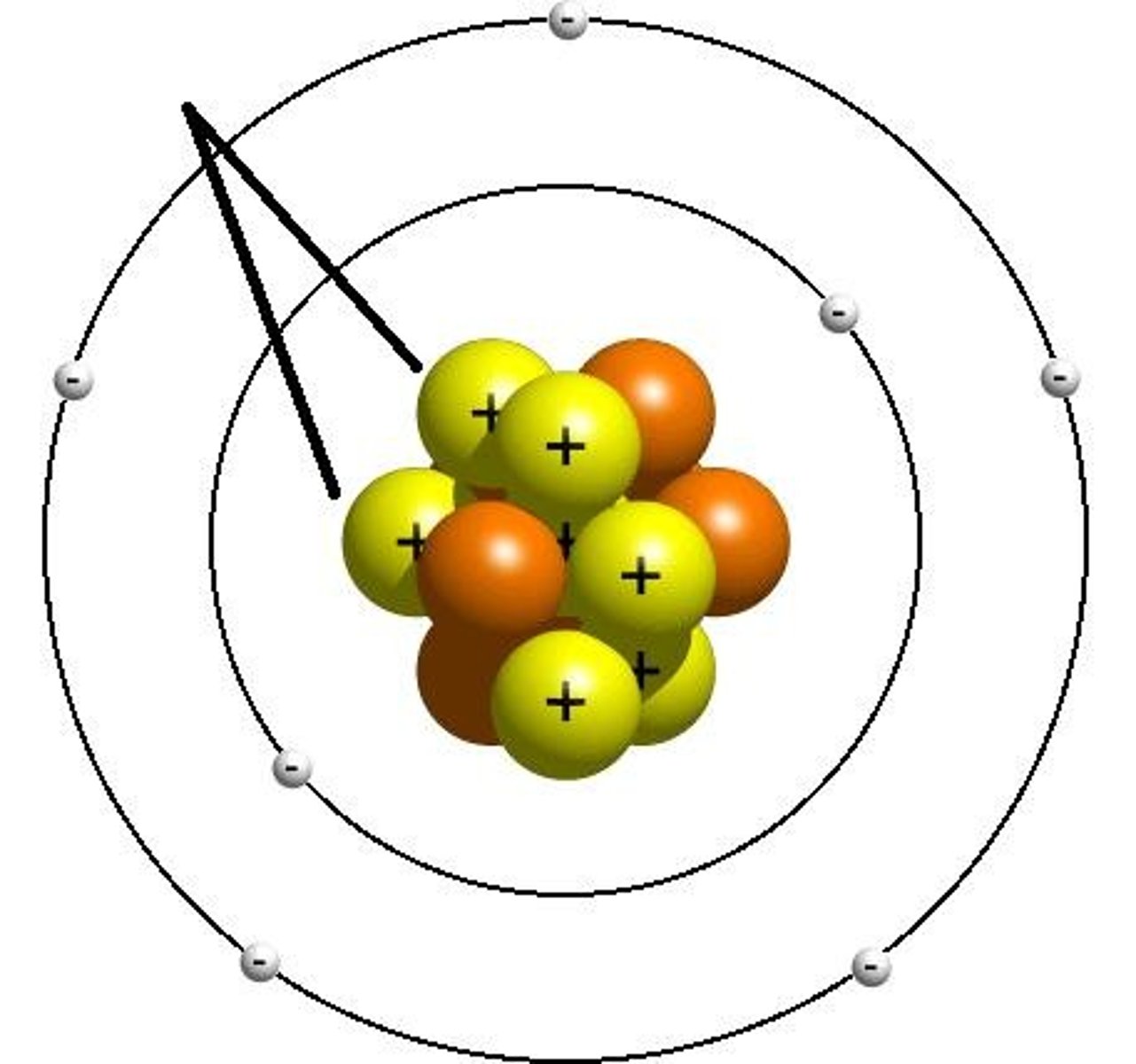
neutron
A subatomic particle that has no charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
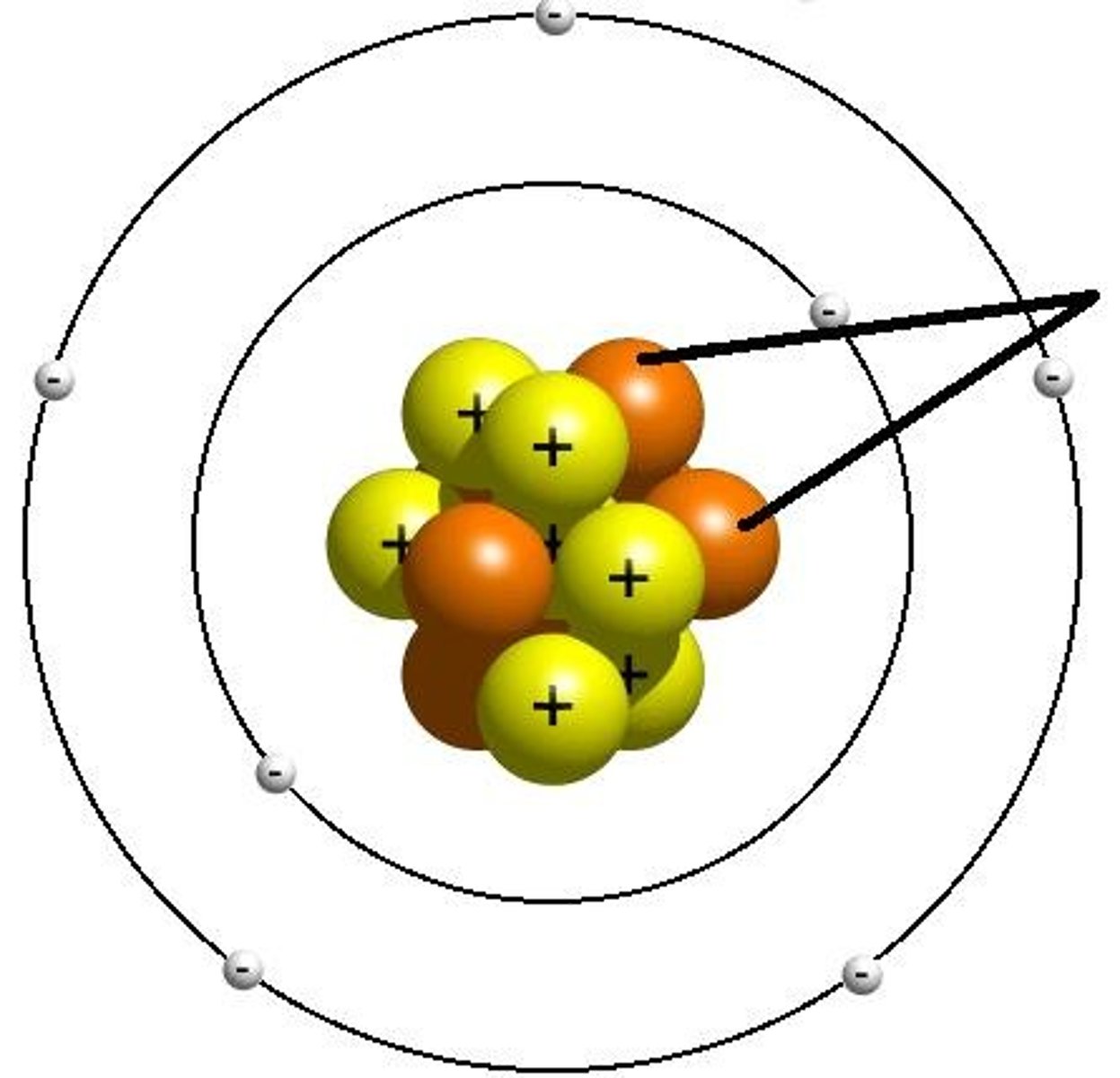
nucleus
Center of an atom
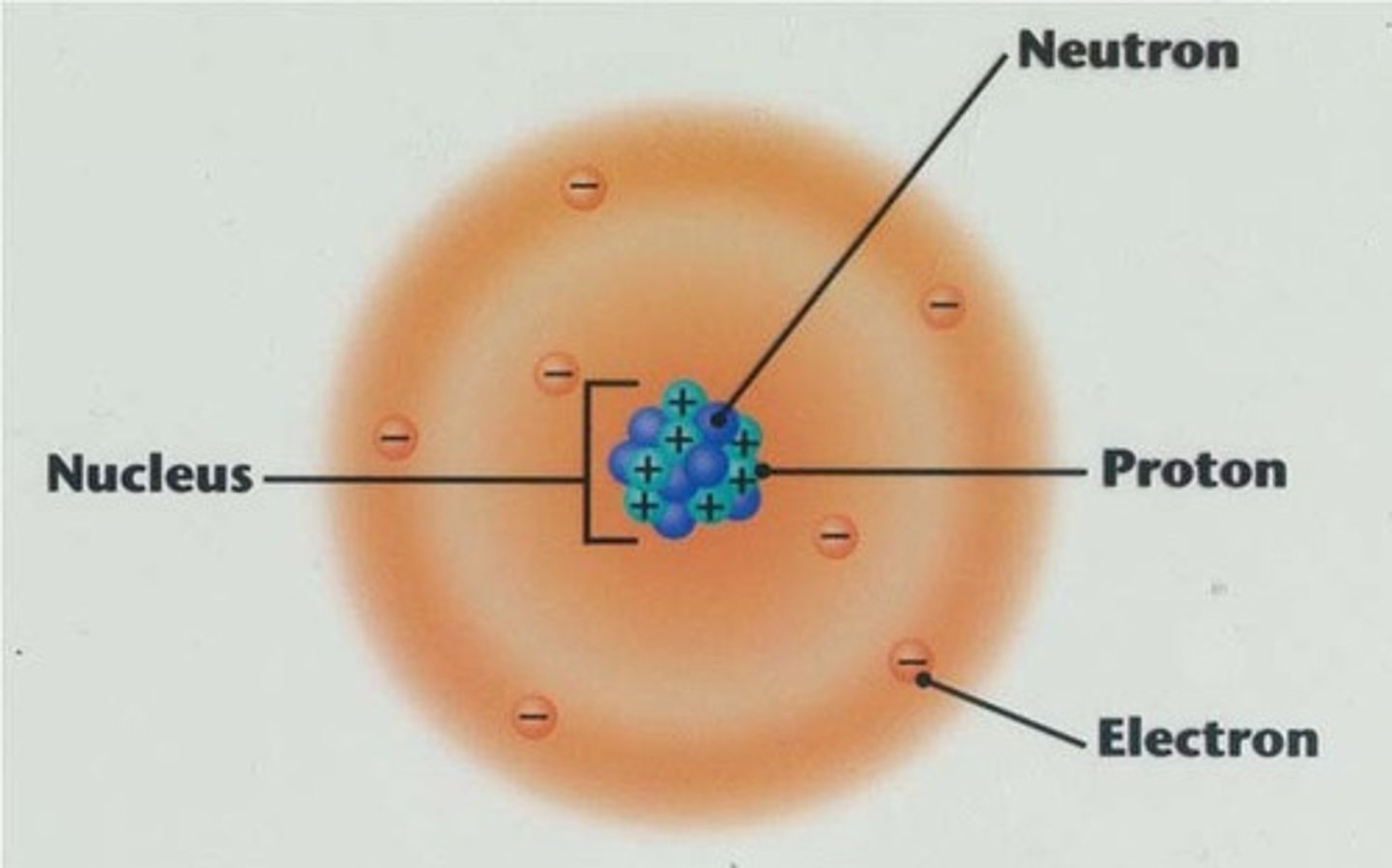
electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge
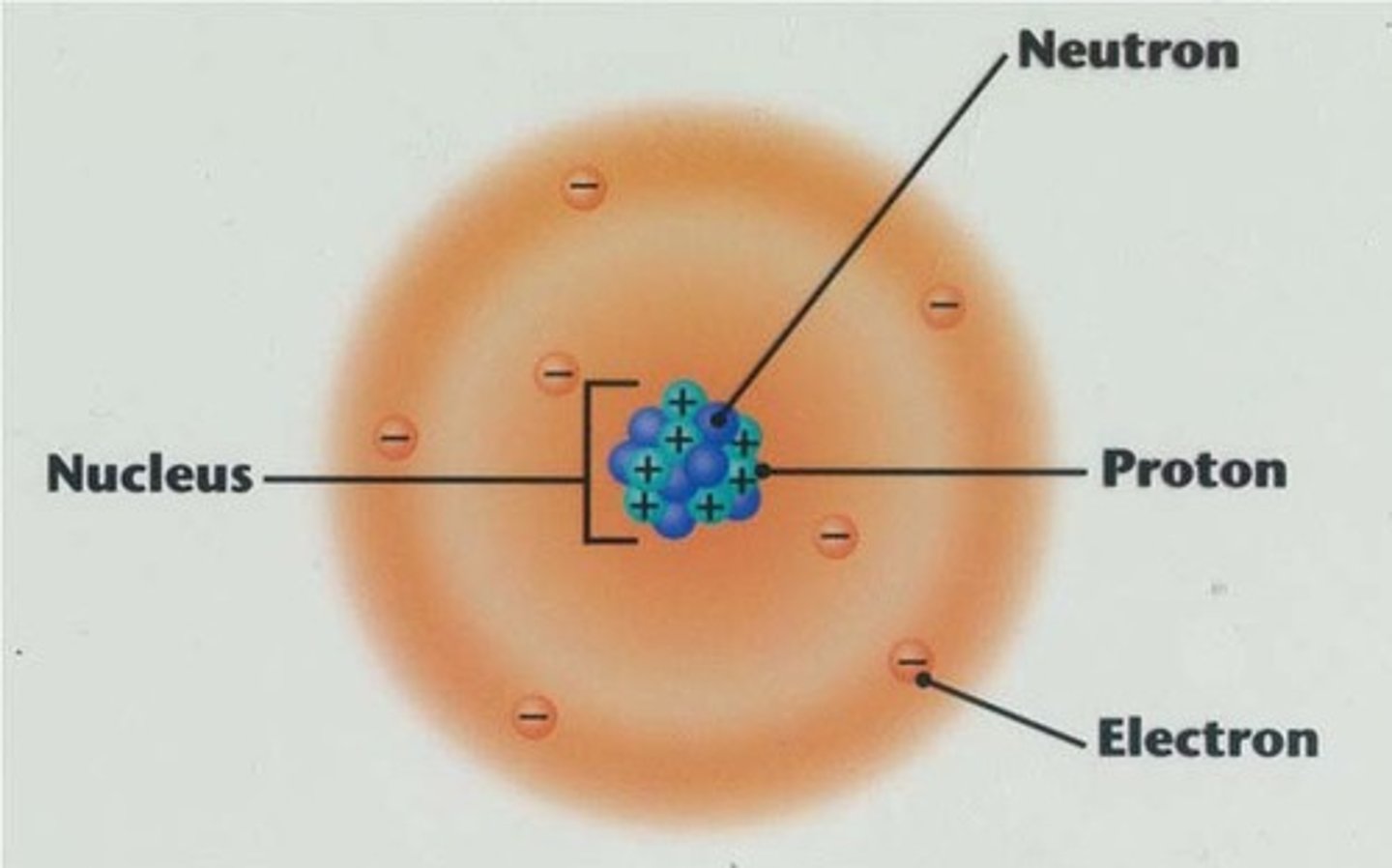
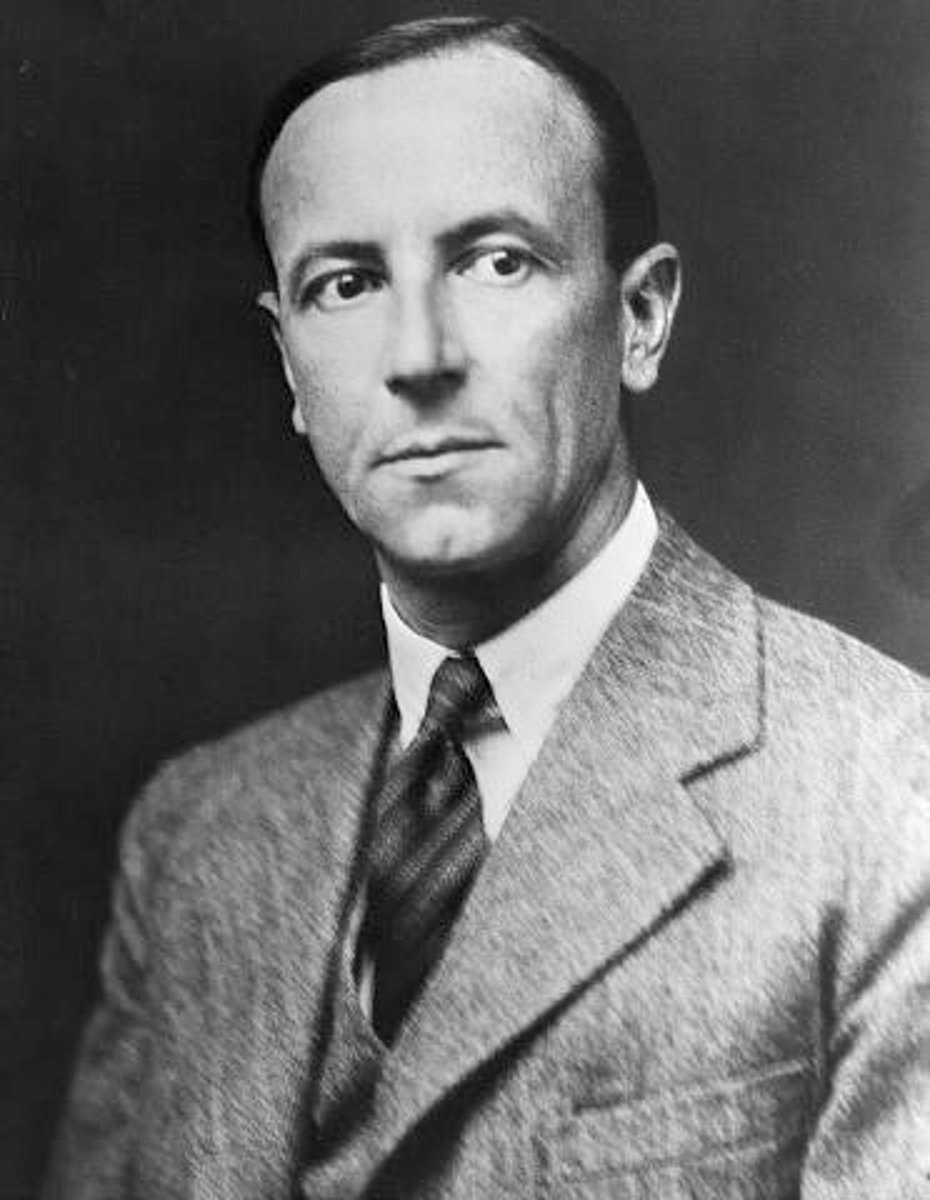
james chadwick
1932-Discovered the neutron and that its mass is the same as the proton. This led to development of atomic energy.

Niels Bohr
Electrons should move around the nucleus but only in prescribed orbits