CHW3M - Intro + Human Evolution
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Intro to civilizations Human evolution
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What are the elements of a civilization?
Centralized government (laws, taxes, military)
Specialization in occupations (jobs)
Agricultural intensification (farming, food supply)
Science and writing (inventions, historical records)
Merchants and trade (economy, currency)
State religion (culture)
Class structure
Rivers and civilization (water source, food supply)
Centralized government
Laws to regulate society
The pre-civilized societies, individuals took it upon themselves to correct a wrong they suffered
Small scale warfare and raids carried out
Eventually, leaders were appointed to solve disputes and prevents chaos
Specialization in occupations
Surplus food and leisure time supports people to engage in other pursuits
Increasingly complex society needs specialists: tax collectors, record keepers (inventory and food), judges (ensure law is obeyed)
Trades developed: weaver, carpenters, coppersmiths, goldsmiths, tanners, bakers
In leisure time, arts and architecture also developed
Agricultural intensification
Planning and coordination of irrigation projects, building dikes to reclaim land, and development of a calendar system to plan planting and harvesting
Dramatic increased in agricultural productivity
Secure year-round food supply
Creates leisure time
Development of science and writing
Medicine, math, architecture
For practical reasons or curiosity, people explored the natural world and how it works
Made advancements in metallurgy
Led to invention of the wheel, baked bricks, mortar, simple machines, and specialized tools
Needing to note inventory of how much food was needed to feed the population and animals required writing
Recording religious texts also required writing
Merchants and trade
The nature of trade changed
Before it was raw materials such as obsidian, amber, and shells
With specialized trades, trades shifted to manufactured goods, and luxury items prized by the wealthy: rare dyes, ivory carvings, precious stones
Merchant class developed, leading to shops and markets, leading to the development of currency
Long distance trade developed, leading to more movement of people between civilizations
State religion
Some argue religion is not an essential for civilizations
Strong link between religion and authority of the government
Religion legitimized government, and government protected and promoted religion
Concept of God gives a reason for authority
Class structure
Equality was lost as specialized trades emerged
Private ownership of land developed
Desire to own more land and hire others to work at the land, leading to slavery
Unequal wealth distribution leading to formation of classes
Nobles and commoners had sharp division
Wealthy people were educated, being in jobs like scribes, priests, advisors, military commanders, and government leaders
Rivers and civilization
Most common characteristic of early civilizations is they developed along river valleys
Mesopotamia = Tigris and Euphrates rivers
Egypt = Nile river
India = Indus River Valley
China = Yellow River
Rivers provide steady water source, fertile soil, and fish
Facilitated communication, trade, exchange of ideas
Young-earth creationism
The belief that the God of Judaism or Christianity created the Universe
The earth is around 5,700 and 10,000 years old
Humans were created as they are now

Old-earth creationism
The belief that God created the universe, but does not follow the history of the Torah/Bible
Believes the events of Genesis should be taken figuratively
Humans were created as they are now
Theistic evolution
The belief of evolution set in motion by God

Atheistic evolution
The belief of evolution being a cause and not set in motion by any god
Natural selection & survival of the fittest
Environmental changes cause species to adapt in order to survive.
The species that is most fit for that environment lives longer than those without, therefore they can live long enough to reproduce offspring with those features.
What is prehistory?
Period before written records appeared, which occurred approximately 3500 BCE
Includes the stone age (Paleolithic and Neolithic)
Early societies maintained history through oral stories and art
Without written records, primary sources are used to research early hominids: skeletal remains provide clues such as diet (teeth), speech (jaw), walking upright (hinged foot, straight backbone, hip), size, age, appearance

What are examples of man-made artifacts, and what can they indicate?
Tools and weapons
Remains of settlements
Artwork
Indicates basic way of life, cultural development, clothing, religion, and social organization

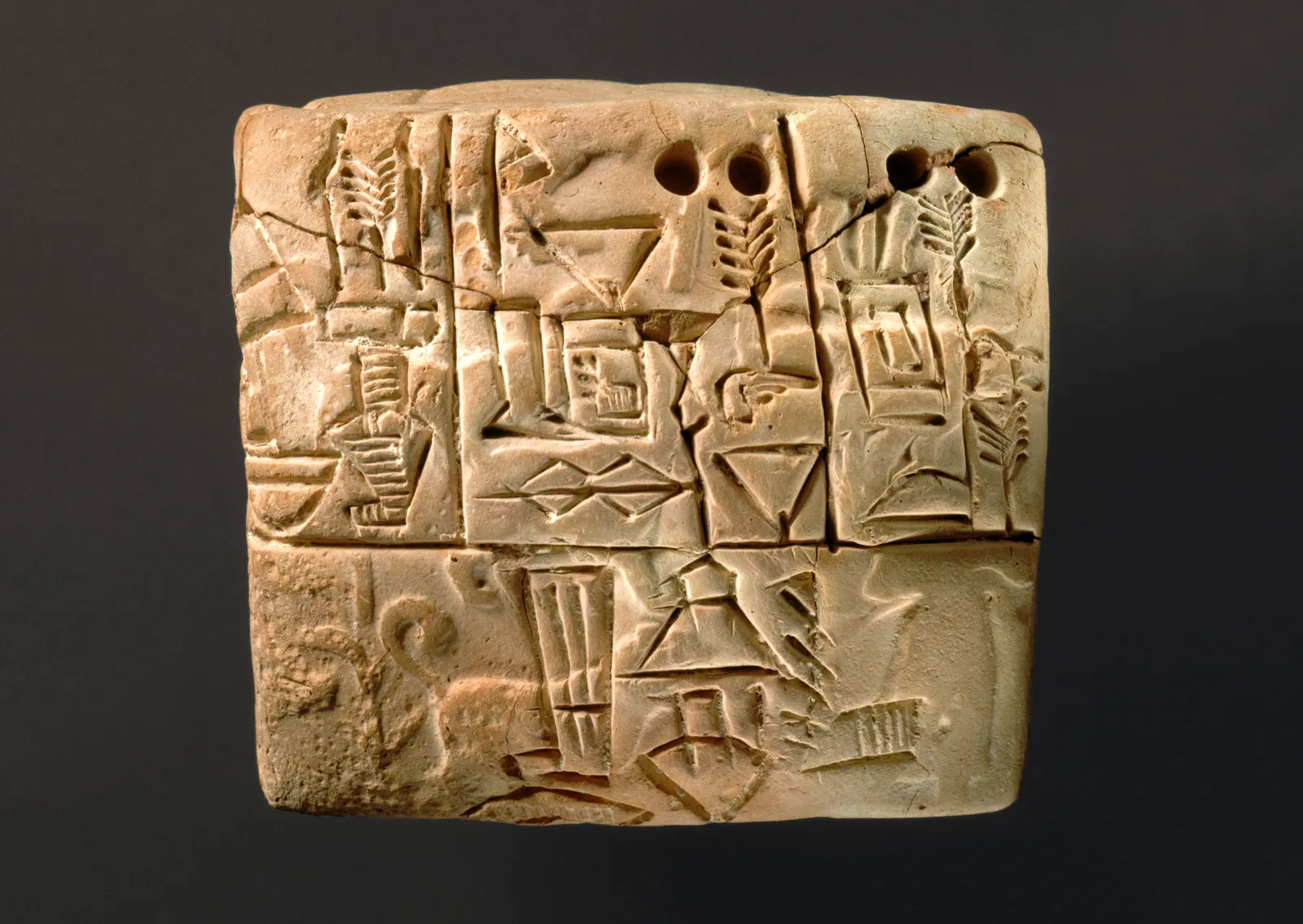
What is cuneiform?
One of the oldest forms of writing known
Means "wedge-shaped”
Written on baked clay tablets

What is hominid biped?
Known as australopithecus (“Ape people”)
Primates that walk on two feet
6 mya (this is when humans diverged from apes)
Brain capacity 350-500 cc
Had no language or home
Curved spine
Ape from waist up, biped from waist down
Used tools like bones, twigs, and rocks, but could not make tools

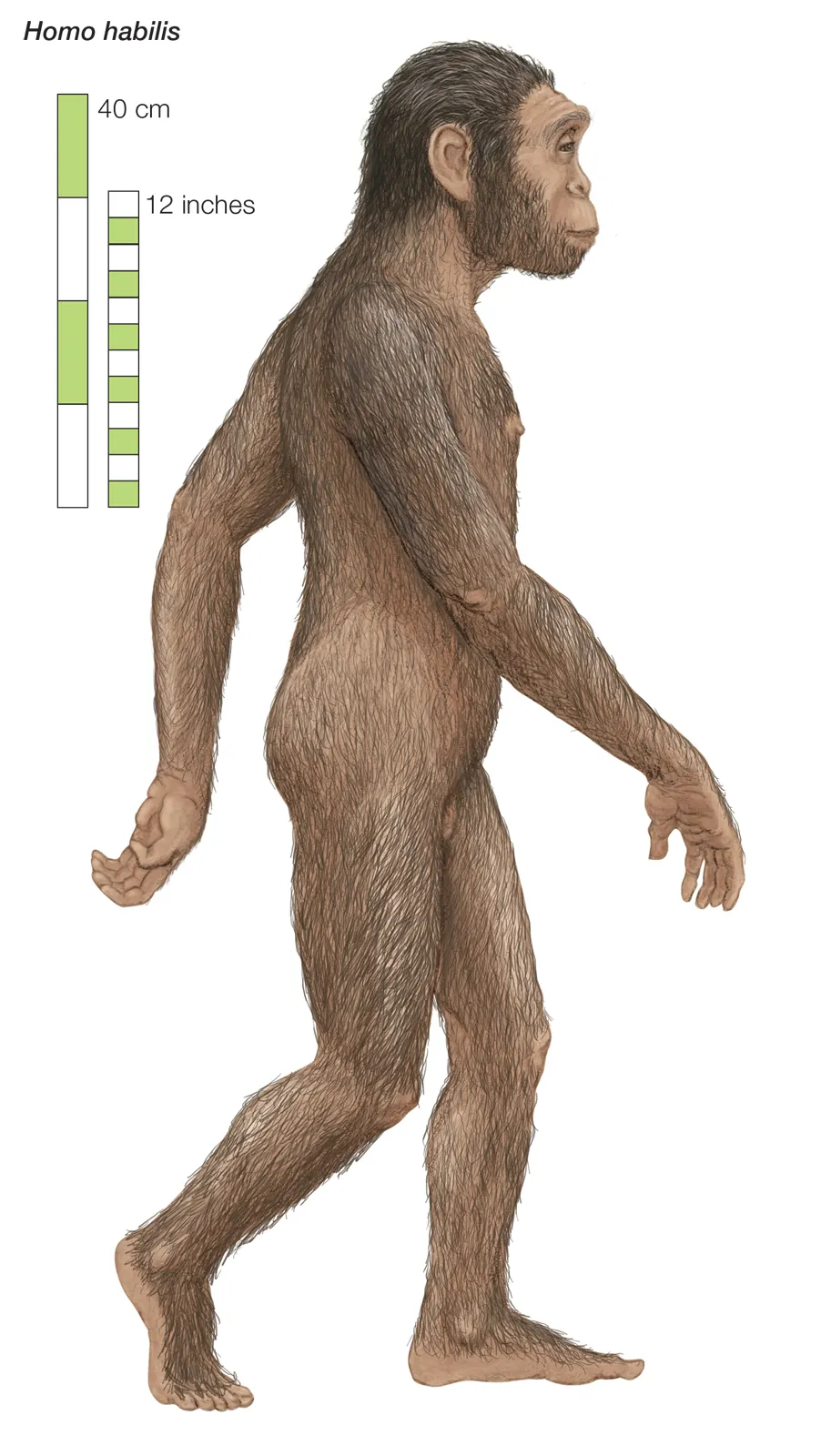
Who is homo habilis?
“Homo” aka genus “human”
2.5 mya
Nicknamed the “handy man”
Ate a lot more meat
Used a lot more tools
Same height as australopithecus, but had double the brain size
More human, less ape
Rapid climate change challenged homo habilis to adapt for survival, which doubled the brain size
Began to make tools

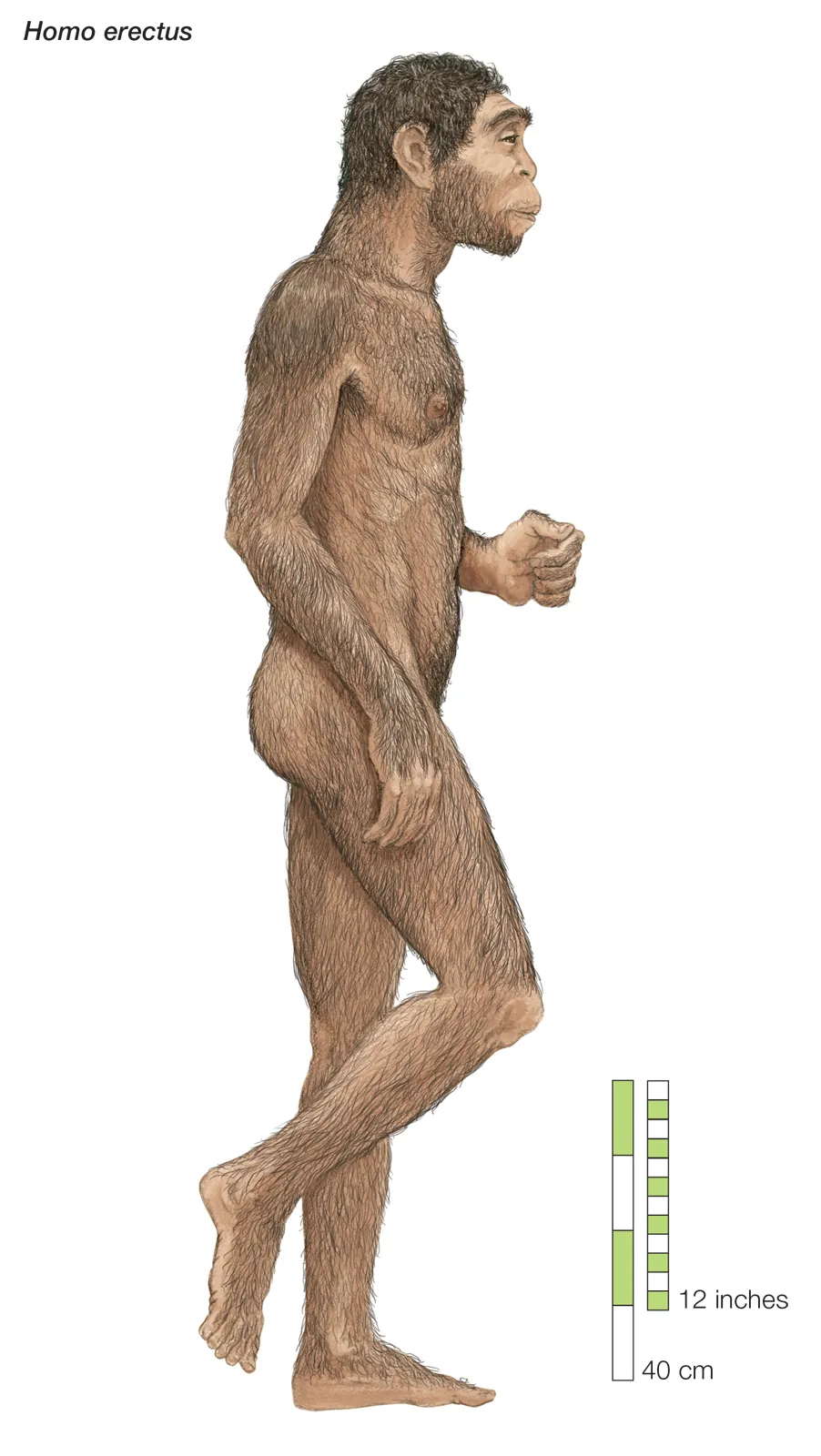
Who is homo erectus?
First to leave Africa
Had no language or home
Probable use of fire
Made primitive tools
First creature that started to look like us

Who is homo sapiens?
Homo sapiens neanderthalensis (“Neanderthals” named after Neander Valley in Germany)
“Wise man”
Originated in Eastern Africa
Known as “Cradle of Man”
Found caves to make homes out of
Had a language of repetitive sounds
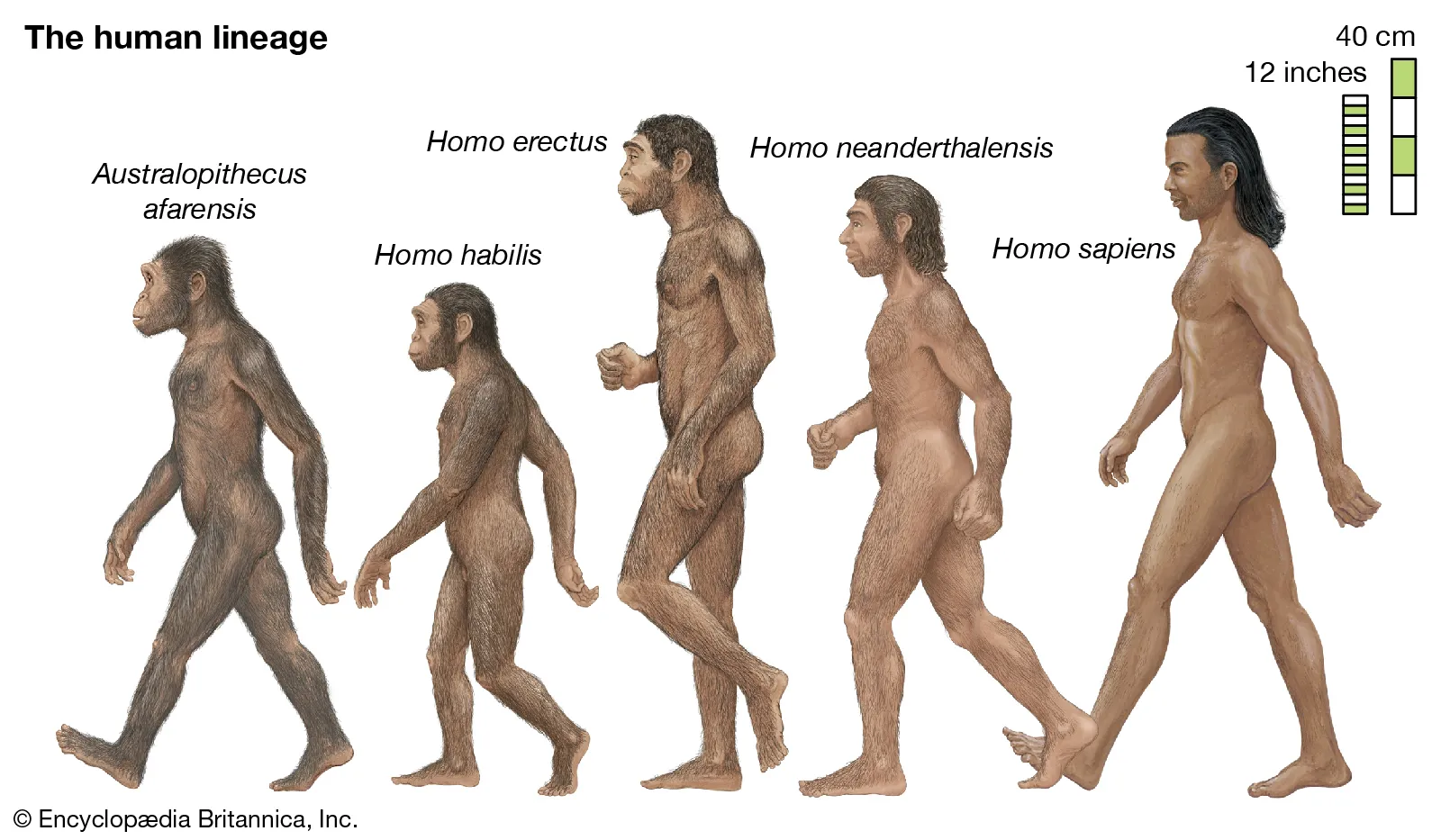
What was neanderthal society like?
Hunted and scavenged
Males lived separately from women and children
Women and children gathered plants near caves
No evidence of society
Mating was random
No interaction between groups
No laws, with only a primitive religion
Most children died in childbirth
80% of adults died before age 40
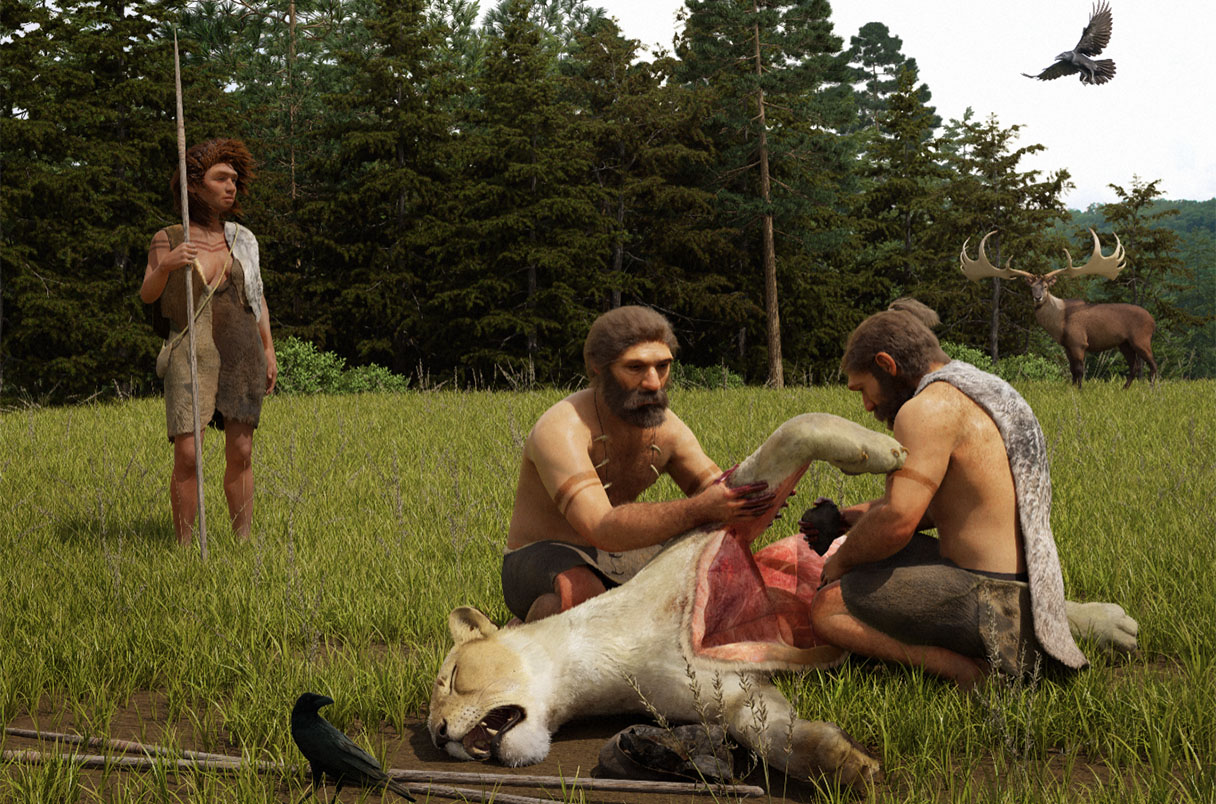

Who is shanidar I?
Estimated to have been in his 40’s at time of death
100 000 – 50 000 years old
Buried with flowers in Iraq, all serving medicinal purposes
Severely disabled individual with atrophied arm and blind eye (since birth)
Would have been impossible for this Neanderthal to have survived on his own
Thus, Neanderthals took care of their elderly and sick individuals, and performed burial rituals
His teeth indicate that he contributed to group by procuring hides for clan.
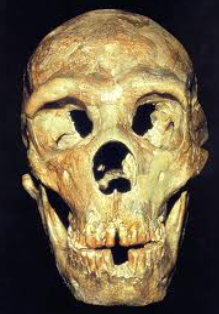
Who is homo sapiens sapiens?
“Wise wise man”
Made save drawings and elaborate tools
Found and created shelters, and lived in huts
Developed a language
Led to extinctions and/or mixing of neanderthals
Theories of warfare between us and neanderthals, but still no one knows why the neanderthals went extinct
Why did humans become bipedal?
The most important reason was to save energy
Ability to carry food long distances
The body is more energy efficient on two feet
Standing upright, 50% more heat is eliminated from body, thus less water is required to replenish the body
40% of the body is only exposed to the sun if walking upright
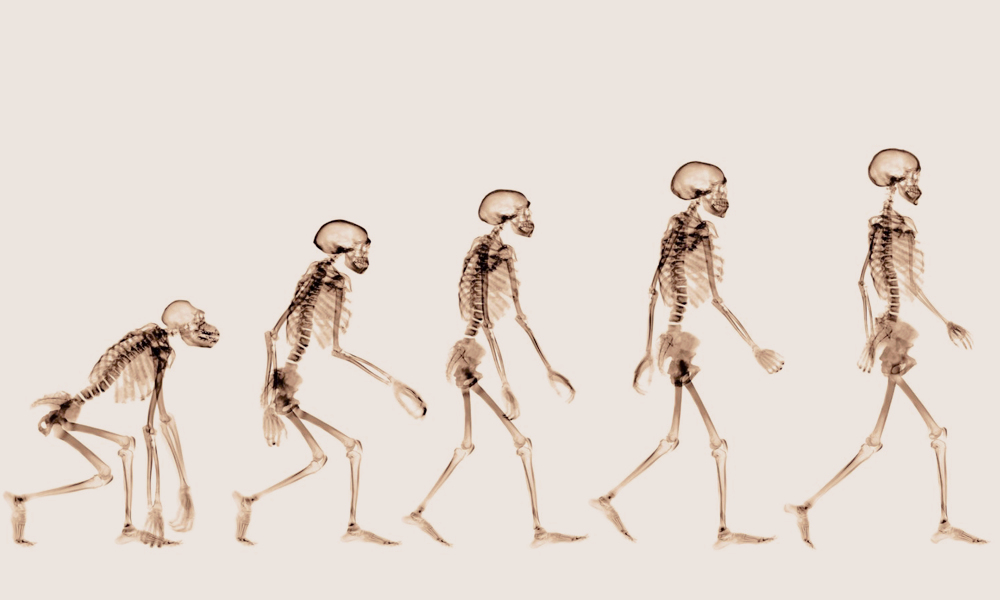
Who was the first hominin to walk on two legs?
Australopithecus Afarensis
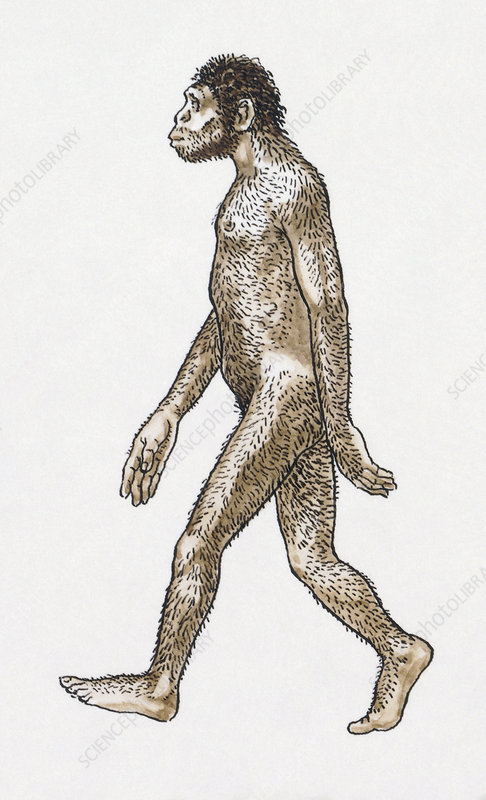
Who is Toumai?
Sahelanthropus Tchadensis
Found in the Sahara desert in Chad
The earliest skull found in human evolution so far
Believed to have walked on two legs, but there are many doubts
Thigh and femur which resembled an ape were suspiciously discarded by the founder, potentially to hide the fact Toumai was not biped

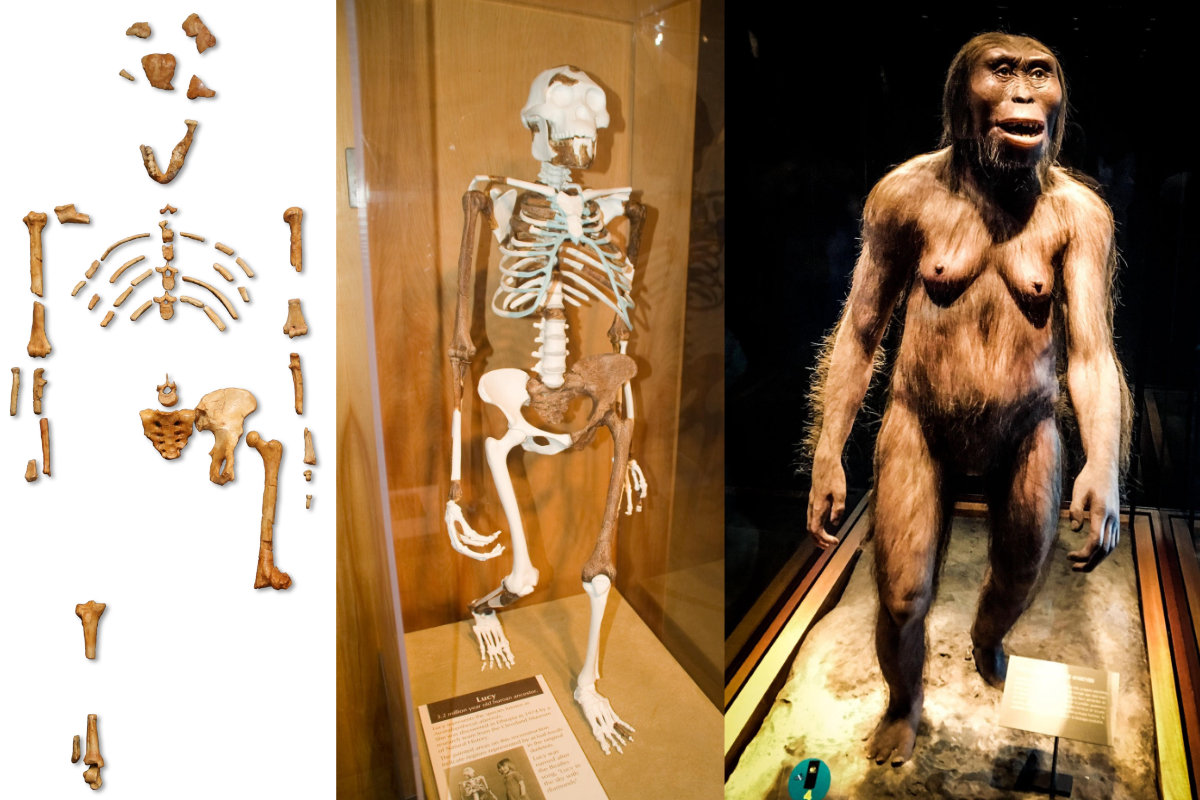
Who is Lucy?
Australopithecus afarensis
Around 3.2 mya
Found in Tanzania by Don Johanson
One of the oldest known and most famous human ancestors
11-12 years old, but is still an adult
Who is Selam?
3 year old body of australopithecus afarensis
Around 3-4 mya
Found in Ethiopia
Selam’s brain at age 3 was only 75% of how much a chimp’s brain should be at that age, indicating that her brain was growing at a much slower rate (slow growth rate is related to humans)
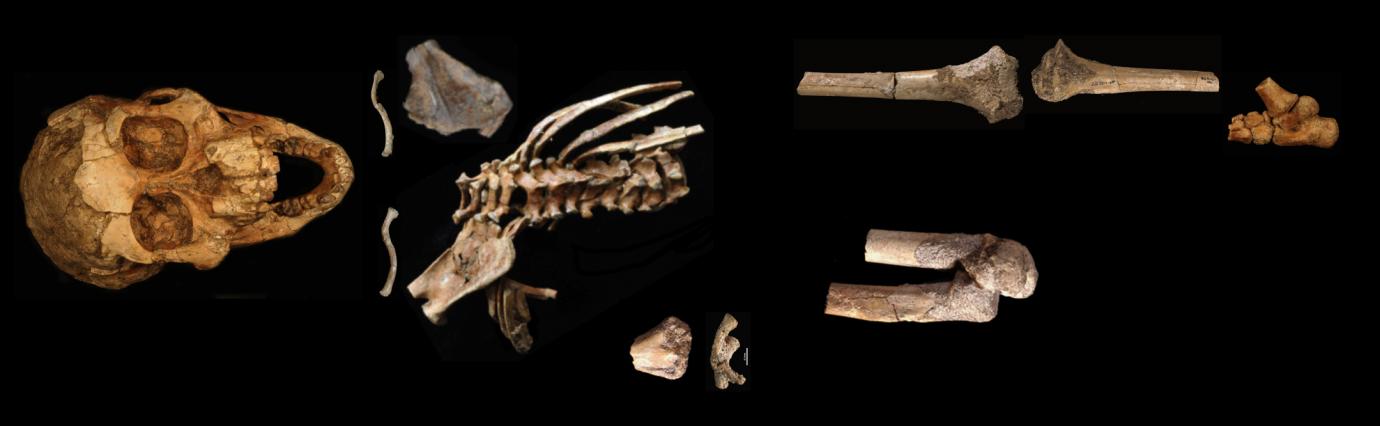

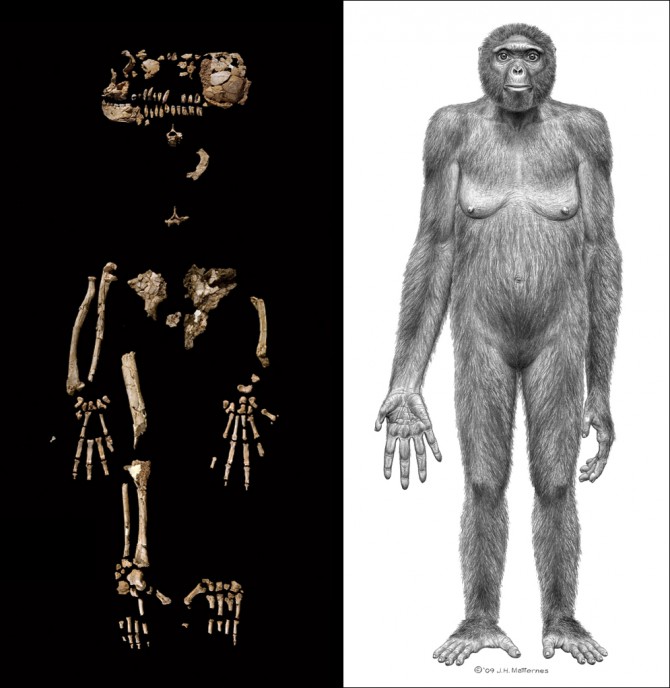
Who is Ardi?
Found after Lucy, but is dated to be older than her
Around 4.4 mya
Found in Ethiopia
4 feet 110 pounds
What are Laetoli footprints?
Set of footprints found to be 3.6 mya
Found by Mary Leakey
What is the order of age of the popular ancient human findings?
Toumai
Ardi
Laetoli footprints
Selam
Lucy
What are the benefits of a fire?
Protection from predators
Source of light
Kills toxins/parasites in food
Warmth (which, in turn, allows migration farther north to colder areas)

Soil stains are caused by…
Middens (garbage pile)
Hearths (fire)
Decaying wood
Best organic artifacts are found in…
Dry, waterlogged, or cold areas
What preserves human bodies in peat bogs?
Acid
What is the first thing looked for when analysing human remains?
Age and sex
Mental baggage
Preconceived ideas leading people to draw conclusions in a way that meets their expectations.
Written records mostly deal with…
The wealthy class
Liberal historian
Tend to see history as unfolding in a progressive manner, each generation building on the accomplishments of previous generations for the greater good
Marxist historian
Tend to focus on the struggles of the common people against the tyranny and oppression of those with power
Post-modern historian
Celebrates diversity and rejects monolithic world views like liberalism, marxism, etc.