Forensic Toxicology - Exam 4
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
breath alcohol testing
the analysis of a person’s breath to determine the presence of and the amount (concentration) of ethanol in the sample
evidential
desk top device usually at the police department or county jail
non-evidential
preliminary breath tester, ignition interlock device
objective, easy, fast, non-invasive, available, no chain-of-custody
advantages of breath testing
alveoli
termination point of the respiratory tract
2100:1
advocated BBR (Blood:Breath Ratio)
underestimate
taking 2300:1 as the real BBR in humans predicts that using breath will __________ BAC by 9%
increase temperature, increase evaporation
effects to increase BrAC
decrease temperature, decrease evaporation
effects to decrease BrAC
1 degree change in temp
causes 6-7% change in BrAC
hypoventilation
subject induced raised BrAC
hyperventilation
subject induced lowered BrAC
2100:1 BBR, lowest reported sample, truncated results, breath temperature correction
four mechanisms to eliminate subject bias
Francis Edmund Anstie
used potassium dichromate and sulfuric acid to determine concentration of EtOH in blood, breath, and urine
Sir Edward Mellanby
first to establish blood-ethanol time course
Emil Bogen
first US scientist to correlate alcohol in breath and urine with clinical test of drunkeness
Dr. Rolla Harger
developed the drunk-o-meter in 1938
Robert F. Borkenstein
debuted the breathalyzer in 1956
potassium permanganate
substance used in drunkometer
iodine pentoxide
substance used in alcometer
Greenburg
created of the alcometer
Forrester
creator of the intoximeter
potassium dichromate
substance used in the breathalyzer
IR spectroscopy
the study of the interaction of matter with infrared radiation
Beer-Lambert Law
A=Ebc
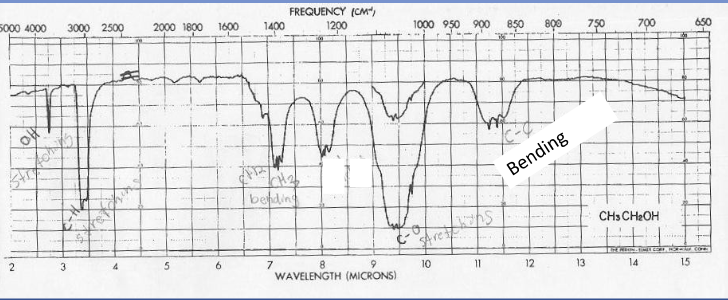
IR spectrum of ethanol
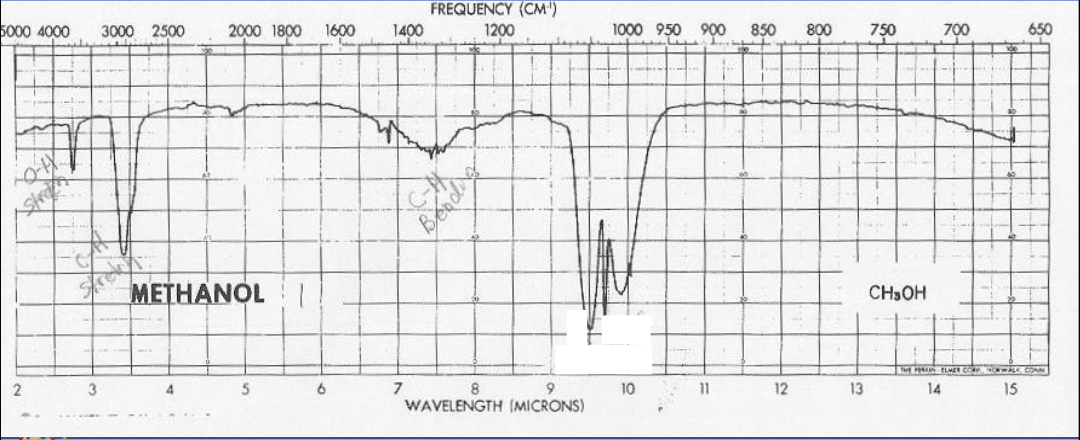
IR spectrum of methanol
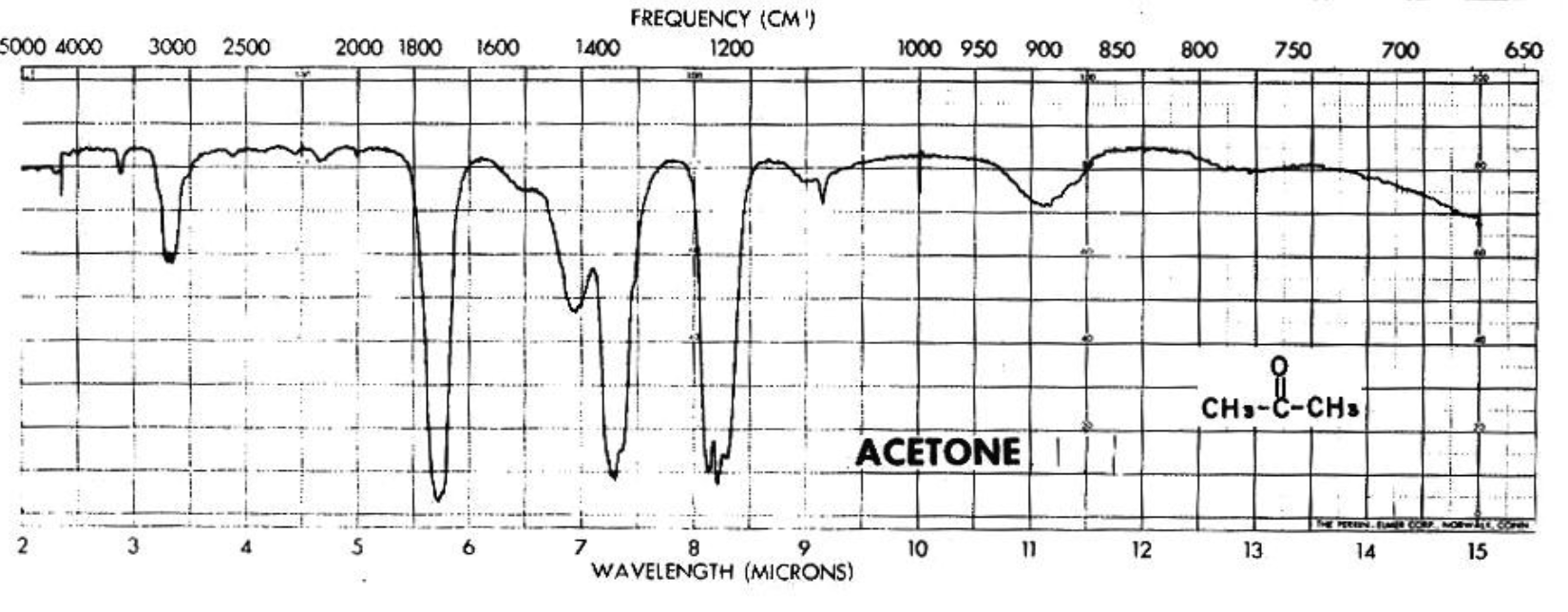
IR spectrum of acetone
electrochemical cell
a device capable of either deriving electrical energy from chemical reactions, or facilitating chemical reactions through the introduction of electrical energy
fuel cell
reversible, an electrochemical cell, which continuously transforms the chemical energy of a fuel and an oxidation material into electrical energy
cal check 0.02, subject test, air check, subject test, cal check 0.08, cal check 0.15
DUI test sequence
HGN and VGN, LOC, slow reaction to light, increase pulse, varied blood pressure and temperature, muscle tone may be flaccid
inhalant DRE characteristics
confusion, disoriented, flushed face, watery eyes
inhalant general indicators
potentiate the GABA receptor function
some inhalants _________ leading to enhanced inhibitory neurotransmission causing sedation, muscle relaxation, and anxiolytic effects
antagonist at the NMDA receptor
certain inhalants (like nitrous oxide) act as ___________ which reduces excitatory neurotransmission and contributes to the dissociative effects, altered perception, and analgesia
intoxication, disorientation, impaired judgement, hallucinations, ataxia
acute effects of inhalants
PNS and CNS dysfunction, liver or kidney failure, dementia, loss of cognitive functions, loss of coordination
chronic effects of inhalants
1,1-diluoroethane
an organofluorine compound commonly used as an aerosol propellant, commonly used in refrigerants, spray cleaners, hair spray, and spray deodorants
infrared
alcohol absorbs light at a particular IR wavelength, causing a decreased intensity of IR energy reaching the detector
multi wavelength IR detector
compares the absorption at different wavelengths and verify the ratio between wavelengths is correct for ethanol
electrochemical
alcohol from a breath sample is oxidized and a current is produced
hypnotics, anxiolytics, anesthetics, spasmolytics, anticonvulsants
types of depressants
slow reflexes, impaired social inhibitions, impaired divided attention, impaired judgment, increased risk taking, emotional instability
depressant characteristics
barbiturates, muscle relaxers, benzodiazepines, z-drugs, others
depressant classes of drugs
sedative-hypnotics, anticonvulsants, migraine therapy
barbiturate common uses
serious drug interactions, severe withdrawal, high tolerance, CNS depression
disadvantages of barbiturates
inhibition of nerve transmission in the CNS, increases affinity of GABA for its receptor
barbiturate mode of action
sedation, hypnosis, coma, death
results of CNS depression
respiratory depression
the hypoxic and chemoreceptor response to CO2 is suppressed
short acting barbiturates
used as an induction agent for surgical anesthesia and in the treatment of head injury as it lowers pressure and reduces oxygen demand
intermediate acting barbiturates
used alone as a sedative-hypnotic or in combination with ASA and caffeine for migraines
long acting barbiturates
used in treatment of seizures
absorbed orally, lipophilic, metabolized by liver
pharmacokinetics of barbiturates
meprobamate, cyclobenzaprine, methocarbamol
three common muscle relaxers
soma
carisoprodol as parent drug with meprobamate as metabolite
miltown
just meprobamate prescribed
meprobamate mode of action
works by blocking interneuronal activity in the spinal cord, but does not directly relax tense skeletal muscles
cyclobenzaprine
related to TCAs, used for muscle spasm cause by local tissue trauma or muscular strains
significant first pass effect, phase I metabolism
benzodiazepine pharmacokinetics
nordiazepam and oxazepam
diazepam and chlordiazepoxide both metabolize to _________
increase inhibition of GABA
benzodiazepine pharmacodynamics
high performance liquid chromatography
uses high pressure to force solvent or liquid mobile phases through closed columns containing fine particles that give high resolution separations
high, low
_____ polarity of stationary phase and ____ polarity of mobile phases in HPLC
adsorption, partition, ion exchange, size exclusion
four types of liquid chromatography
adsorption chromatography
separation is based on interaction between the solute molecules and the active sites on the stationary phase
partition chromatography
separation is based upon differences in partition coefficient or solubility
solvent tray, degasser, pump, autosampler, column, detector
order of LC schematic diagram
solvent tray
mobile phase bottles are placed here
degasser
used to eliminate the formation of air bubbles in mobile phases
pump
force solvent through the system
autosampler
automated injection system that is used to introduce sample onto column
column
where separation happens
detector
produce identification signals
one aqueous and one organic
two mobile phases in LC
isocratic pump
deliver constant mobile phase composition
gradient pump
deliver variable mobile phase composition
binary gradient pump
deliver two solvents
quaternary gradient pump
deliver four solvents
silica gel
usually column packing because of particle shape and pore structure that provides good separation
reversed phase, normal phase, ion pair, ion exchange, size exclusion
types of column
guard column
used to remove particulate matter and contaminant
retention time
time taken for the analyte to travel from the column to the detector
column efficiency increases
as number of theoretical plates increases, ________________
number of theoretical plates increases
as height equivalent to a theoretical plate decreases, ___________
gas chromatography
a separation technique that takes place in a column that has a continuous flow of mobile phase passing through it, usually in an inert carrier gas, maintained in a temperature controlled oven
carrier gas, flow controller, sample injector, column oven, column, detector, waste
parts of a gas chromatograph
inlet
manual or automatic injector on a gas chromatograph
septum, o-ring, inlet liner, inlet seal and washer
parts of an inlet
heated injection port
hot enough to vaporize samples, low enough to avoid thermal degradation
septum
high temperature silicone rubber, used to maintain pressure
inlet liner
deactivated tubes used to provide heating of samples and reduce column contamination, may be packed with glass wool
oven
used to maintain temperature, can run a temperature program
temperature program
ramps temperature throughout the run at a constant rate, ideal for mixtures containing compounds with a wide range of boiling points
flame ionization, nitrogen phosphorus, electron capture, mass spectrometer
GC detectors
flame ionization detector
uses an air-hydrogen flame to produce ions, can only detect compounds that are able to be burned
UV-Vis, triple quadrupole, ion trap, time-of-flight
LC detectors
single quadrupole
sorts molecules based on mass/charge
mass analyzer, collision cell, mass analyzer
order of a triple quadrupole
collision induced dissociation
fragments molecules by passing them through a field of inert gas (commonly nitrogen)
time of flight
allows us to identify a compound out to four decimal places