Unit 1 pt 2: Cell Basics & Membrane
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Cell Theory |
All living things are made of cells, cells are the basic unit of life, and all cells come from pre-existing cells.
Cell Structure |
Determines the function of the cell and contributes to overall activity. |
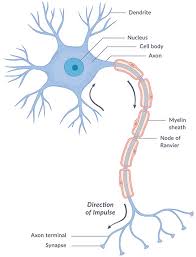
Irregular-shaped Cells
Example: nerve cells; shaped for communication
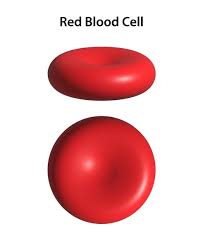
Biconcave Disc
Example: red blood cells; shape increases surface area for gas exchange.
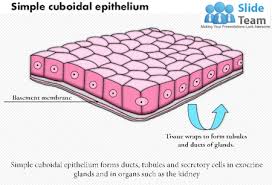
Cube-Shaped Cell
Example: kidney tubule cells; suited for absorption and secretion.
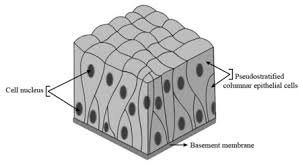
Column-Shaped Cell
Example: intestinal lining cells; specialized for absorption.
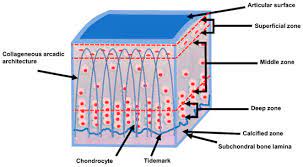
Spherical Cell
cartilage cells; round shape for cushioning.
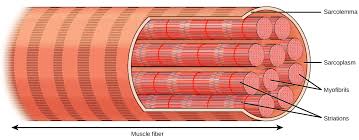
Cylindrical Cell
Example: skeletal muscle cells; elongated for contraction.
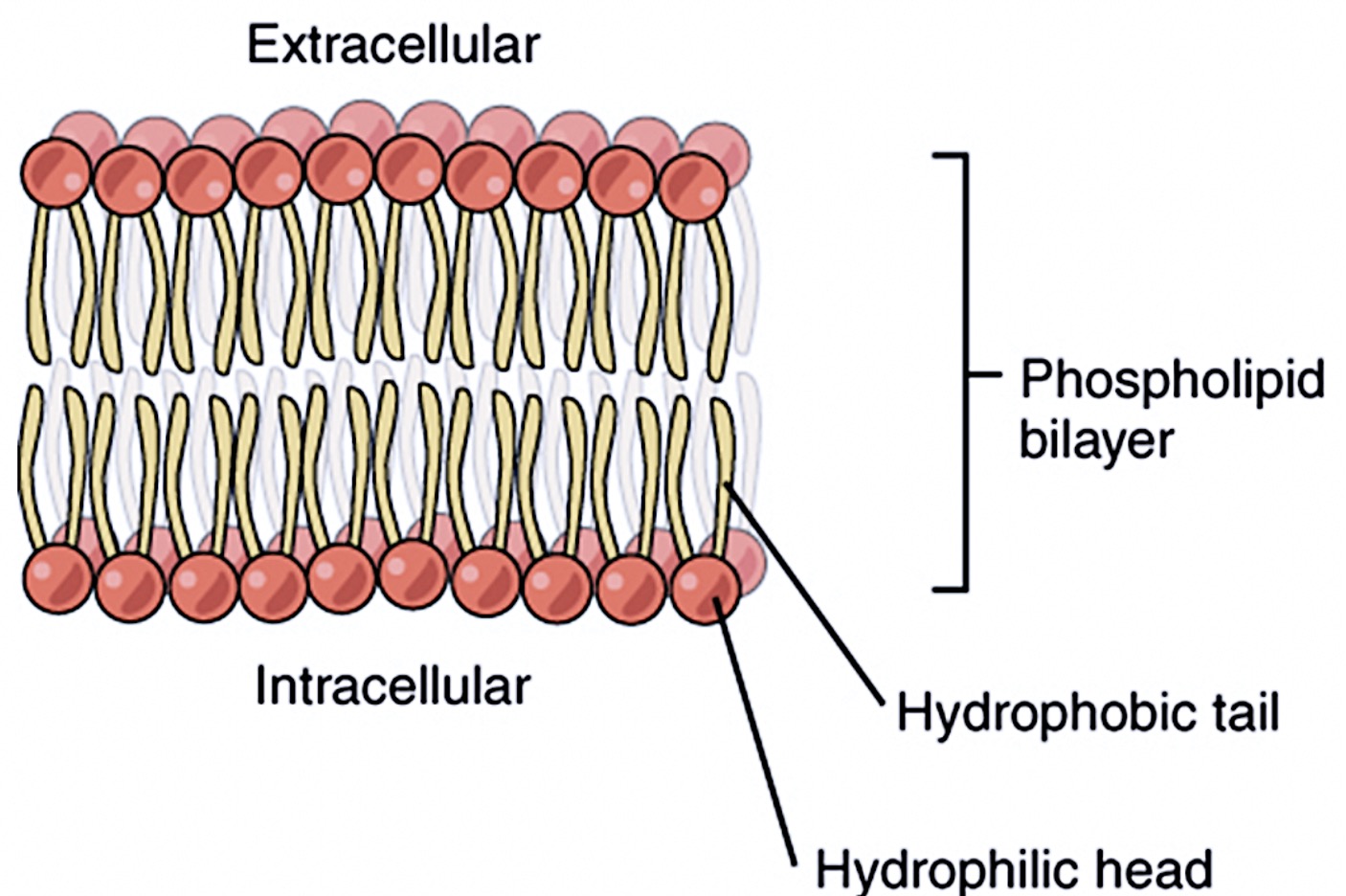
Phospholipid Bilayer
Double layer of lipids; forms the basic structure.
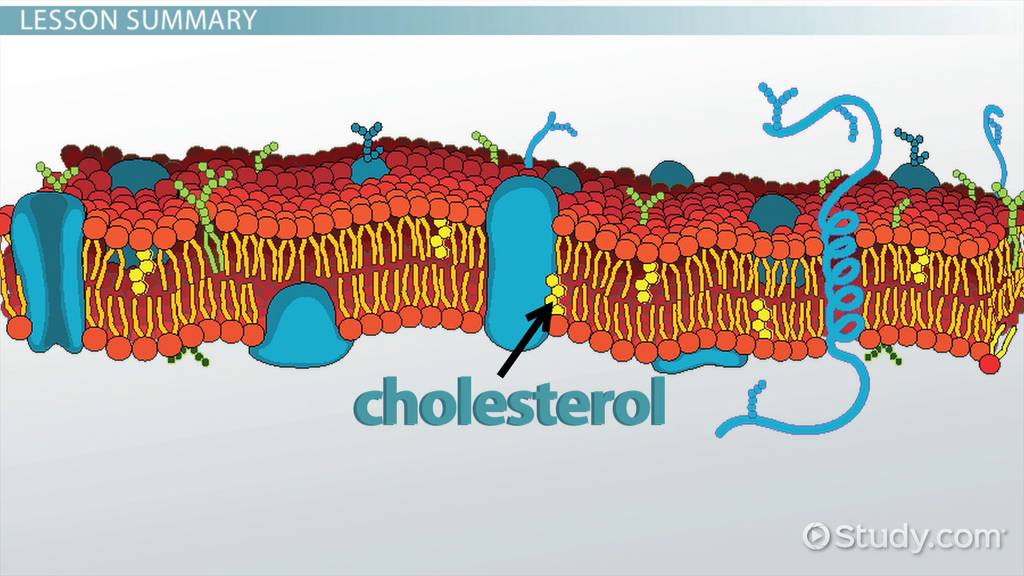
Cholesterol
Stabilizes membrane fluidity and structure.
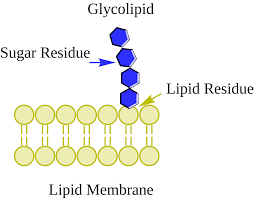
Glycolipids
Lipids with carbohydrate chains; cell recognition.
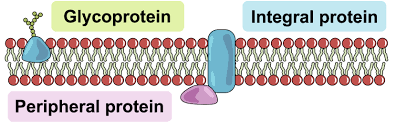
Integral Proteins
Embedded in the membrane; transport & signaling.
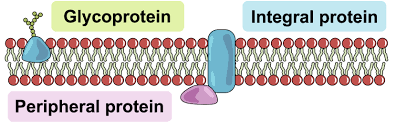
Peripheral Proteins
On membrane surface; support & signaling.
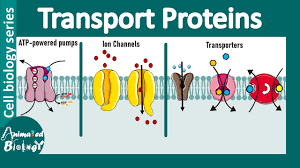
Transport Proteins
Move substances across the membrane.
Cell Surface Receptors
Bind signals and start responses.
Binds molecules called Ligands
Identity Markers
Allow cells to recognize each other.
Enzymes
Catalyze chemical reactions at the membrane.
Anchoring Sites
Attach cytoskeleton for stability.
Cell-Adhesion Proteins
Help cells stick together in tissues.