Chapter 22 - Anxieties and Experiments in Postwar Europe and the United States
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
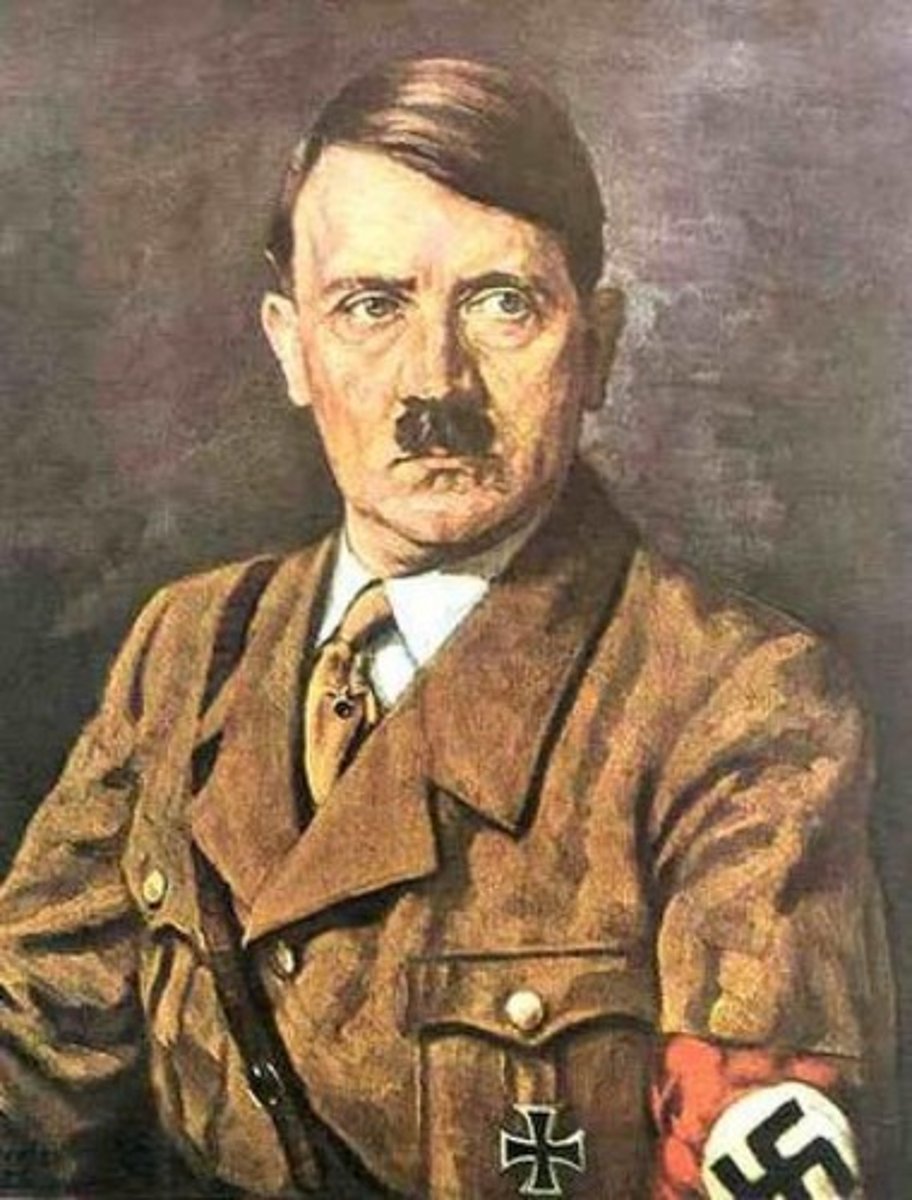
Adolf Hitler
1889-1945 C.E. German politician and leader of the Nazi Party, who came to power in 1933. He initiated the European theater of World War II by invading Poland in 1939 and oversaw the establishment of death camps that resulted in more than ten million deaths.

Albert Einstein
1879-1955 C.E. German-born physicist who developed the theory of relativity and whose ideas had profound influence on the development of science in the twentieth century.

Antisemitism
Term coined in the late nineteenth century that was associated with a prejudice against Jews and the political, social, and economic actions taken against them.
Benito Mussolini
1883-1945 C.E. Italian politician and journalist who led the National Fascist Party and ruled as prime minister from 1922 to 1943.
Black Thursday
October 24, 1929; stock market crashes and almost 13 million shares are sold that day alone
Chauvinism
an aggressive form of nationalism
Collectivization of Agriculture
Process beginning in the late 1920s by which Stalin forced the Russian peasants off their own land and onto huge collective farms run by the state; millions died in the process.
Dadaism
An artistic movement that had a purposely nonsensical name. Between 1916-1920 in places like Zurich, Paris, and New York the Dada artists used any public forum to express its total rejection of nationalism, materialism, and rationalism, which they believe contributed to a senseless war.

Economic Nationalism
Economic policies pursued by many governments affected by the Great Depression in which the nation tries to become economically self-sufficient by imposing high tariffs on foreign goods. The policy served to exacerbate the damaging effects of the Depression around the world.
Eugenics
A late nineteenth- and early twentieth-century movement that sought to improve the gene pool of the human race by encouraging those deemed fit to have more children, and by discouraging those deemed unfit from reproducing. The movement was deeply tied to racism, and was eventually adopted by the German Nazi regime to justify the extermination of "undesirable" populations.
Fascism
Political ideology and mass movement that was prominent in many parts of Europe between 1919 and 1945; it sought to regenerate the social, political, and cultural life of societies, especially in contrast to liberal democracy and socialism; fascism began with Mussolini in Italy, and it reached its peak with Hitler in Germany.

First Five-Year Plan
Set targets for increased productivity in all spheres of the economy but emphasized heavy industry - especially steel and machinery - at the expense of consumer goods.

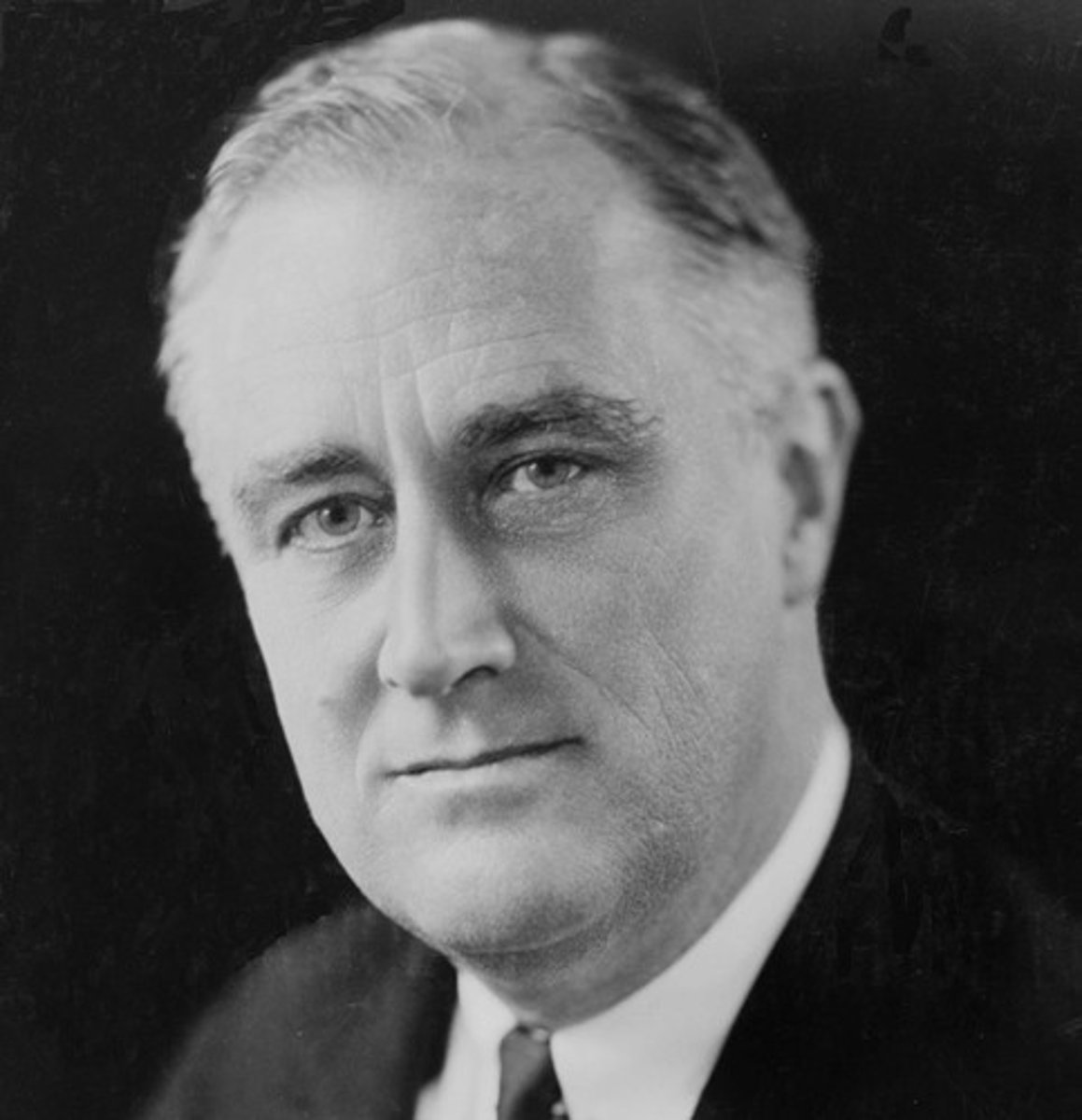
Franklin Delano Roosevelt
1882-1945 C.E. American politician who served as the thirty-second president of the United States from 1933 until his death.

Great Depression
the economic crisis beginning with the stock market crash in 1929 and continuing through the 1930s

Great Purge
(1934), Stalin cracked down on Old Bolsheviks, his net soon widened to target army heroes, industrial managers, writers and citizens, they were charged with a wide range of crimes, from plots to failure to not meeting production quotas.
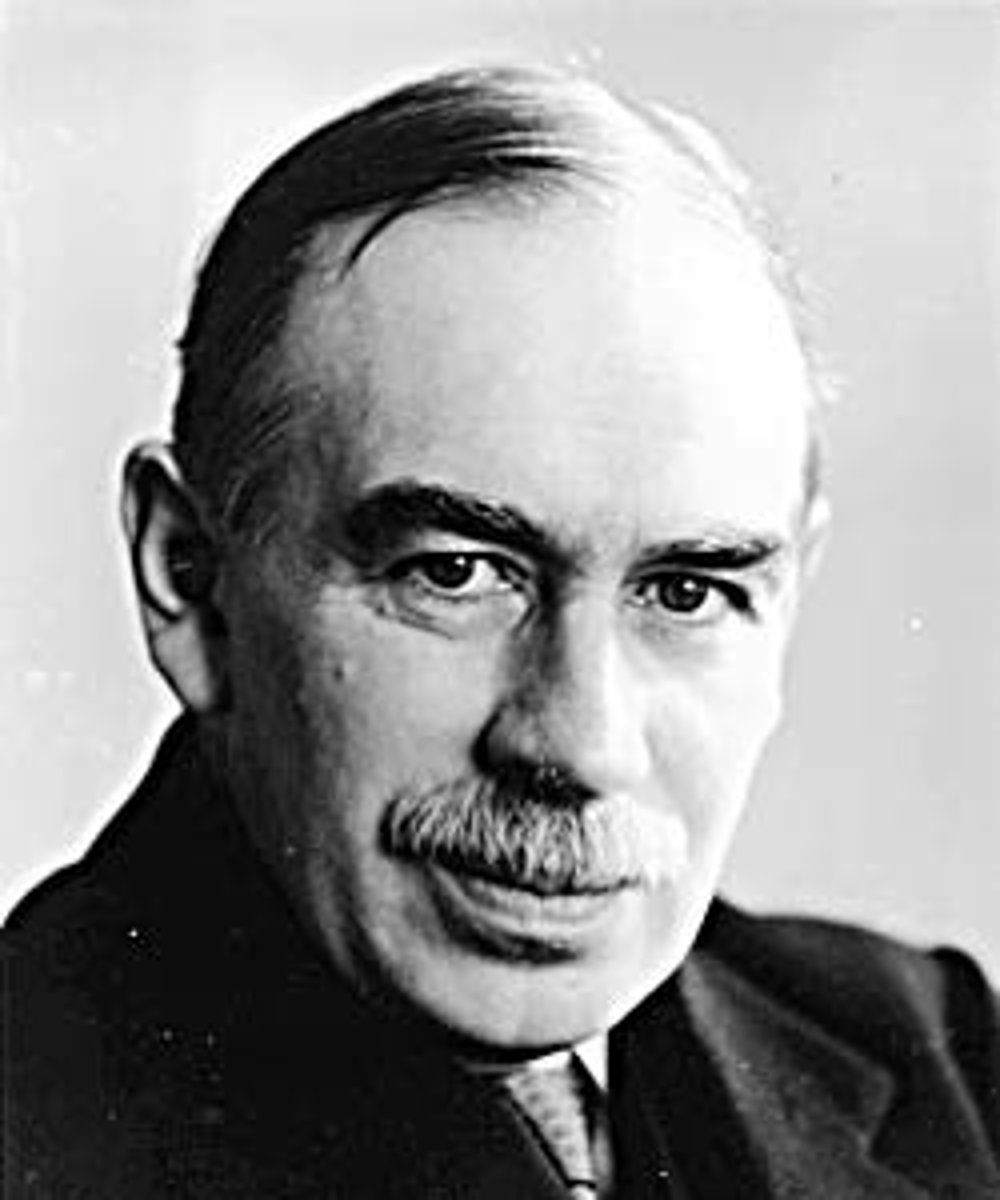
John Maynard Keynes
English economist who advocated the use of government monetary and fiscal policy to maintain full employment without inflation (1883-1946)

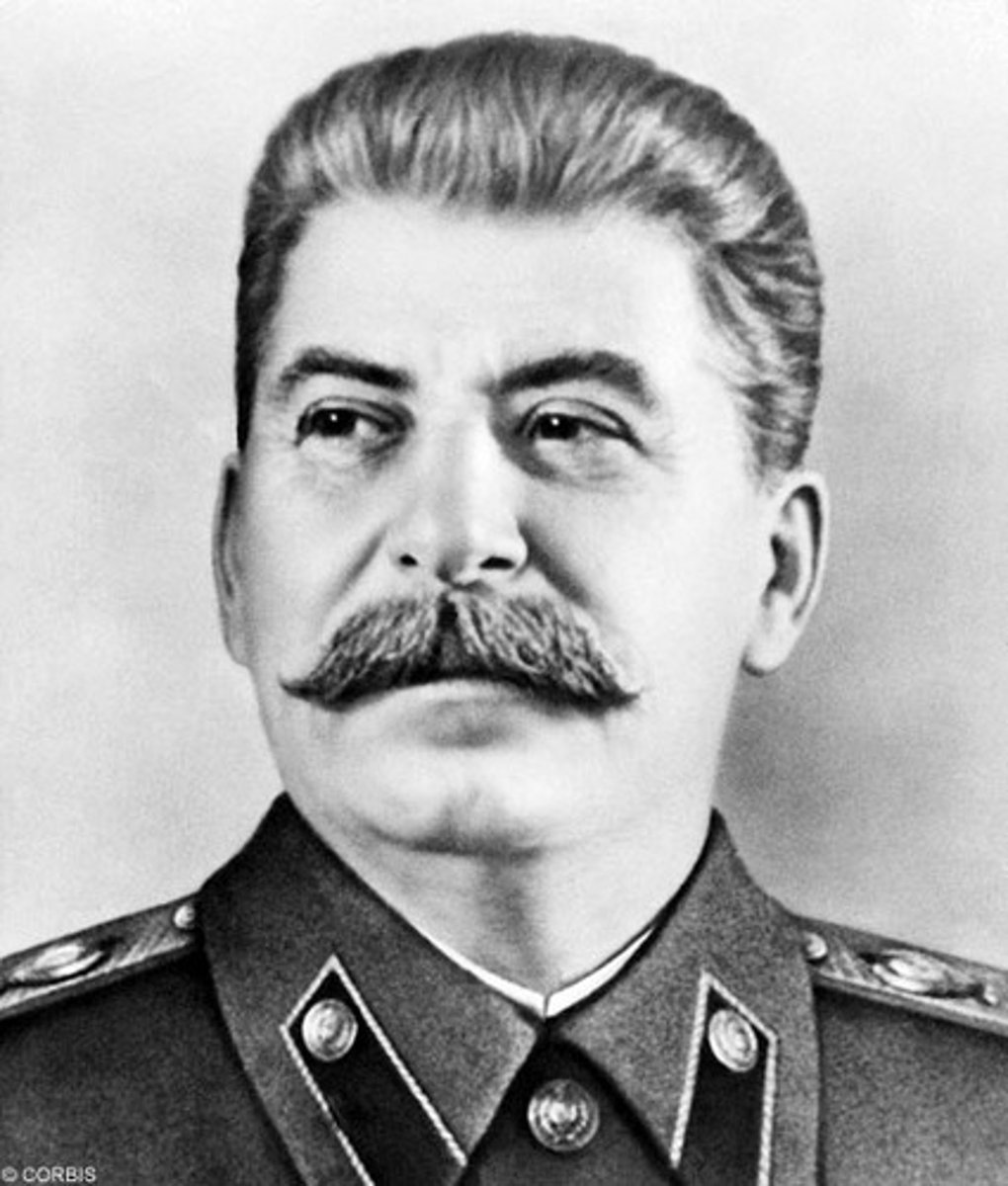
Joseph Stalin
1878-1953 C.E. Soviet revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from the mid-1920s to his death, whose policies resulted in the deaths of twenty million people.

Kristallnacht
(Night of the Broken Glass) November 9, 1938, when mobs throughout Germany destroyed Jewish property and terrorized Jews.

Kulaks
Land-owning Russian peasants who benefited under Lenin's New Economic Policy and suffered under Stalin's forced collectivization.
Lost Generation
Artists who expressed through poetry and fiction, the malaise and disillusion that characterized U.S. and European thought after World War I

National Socialism
the ideology and practices of the Nazi party, which included national expansion, state control of the economy, the totalitarian principle of government, and anti-Semitism.

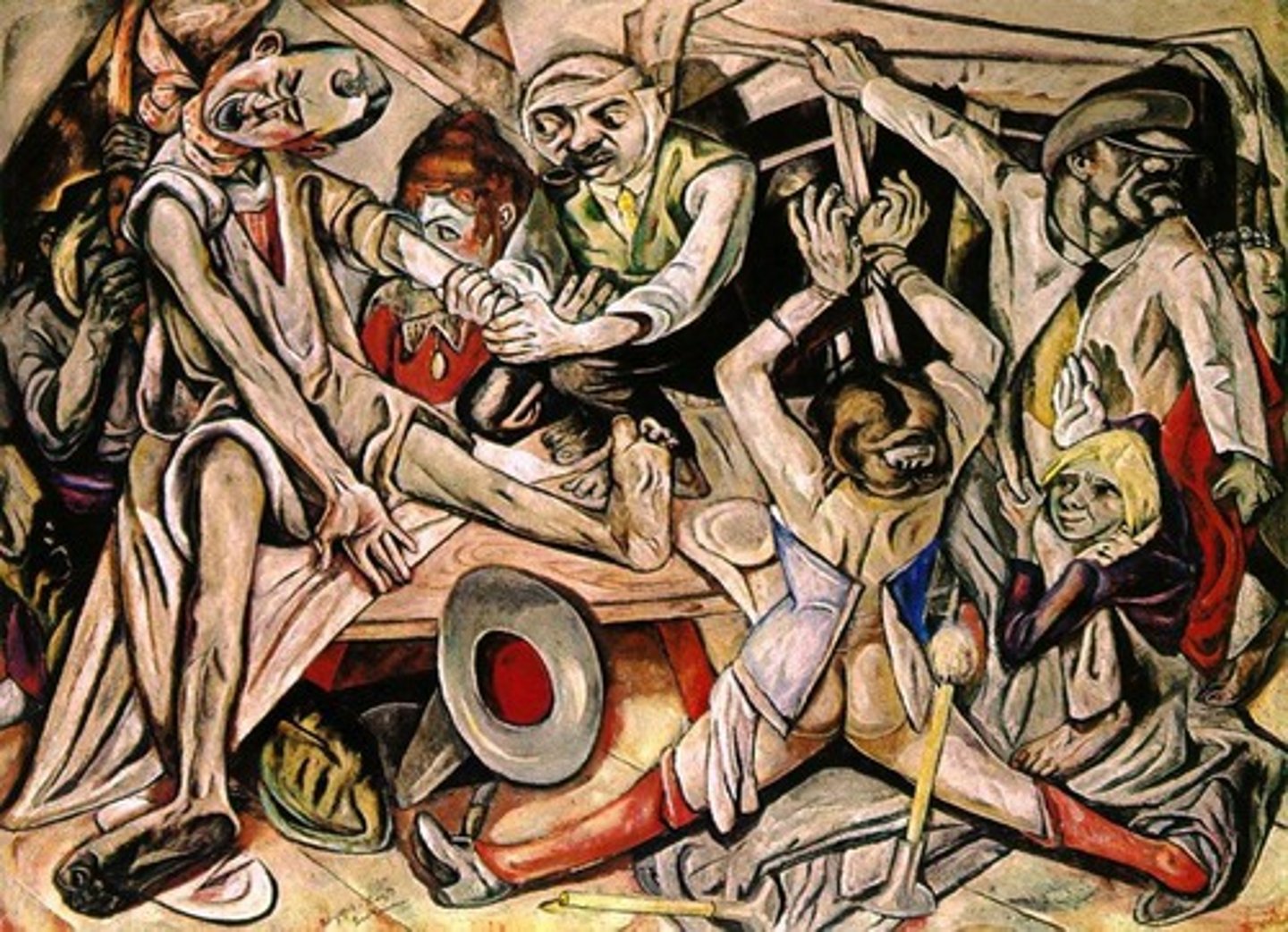
Neue Sachlichkeit (New Objectivity)
this genre was characterized by a realistic style of painting that reflected a very cynical and highly critical attitude toward war. Many proponents of the Neue Sachlichkeit aggressively attacked and satirized the evils of postwar society, especially as symbolized by those in political power, all the while illustrating the devastating effects of the Great War

New Deal
The name of President Roosevelt's program for getting the United States out of the depression

New Economic Policy (NEP)
Plan implemented by Lenin that called for minor free-market reforms.

Nuremberg Laws
Placed severe restrictions of Jews, prohibited from marrying non- Jews, attending schools or universities, holding government jobs, practicing law or medicine or publishing books.
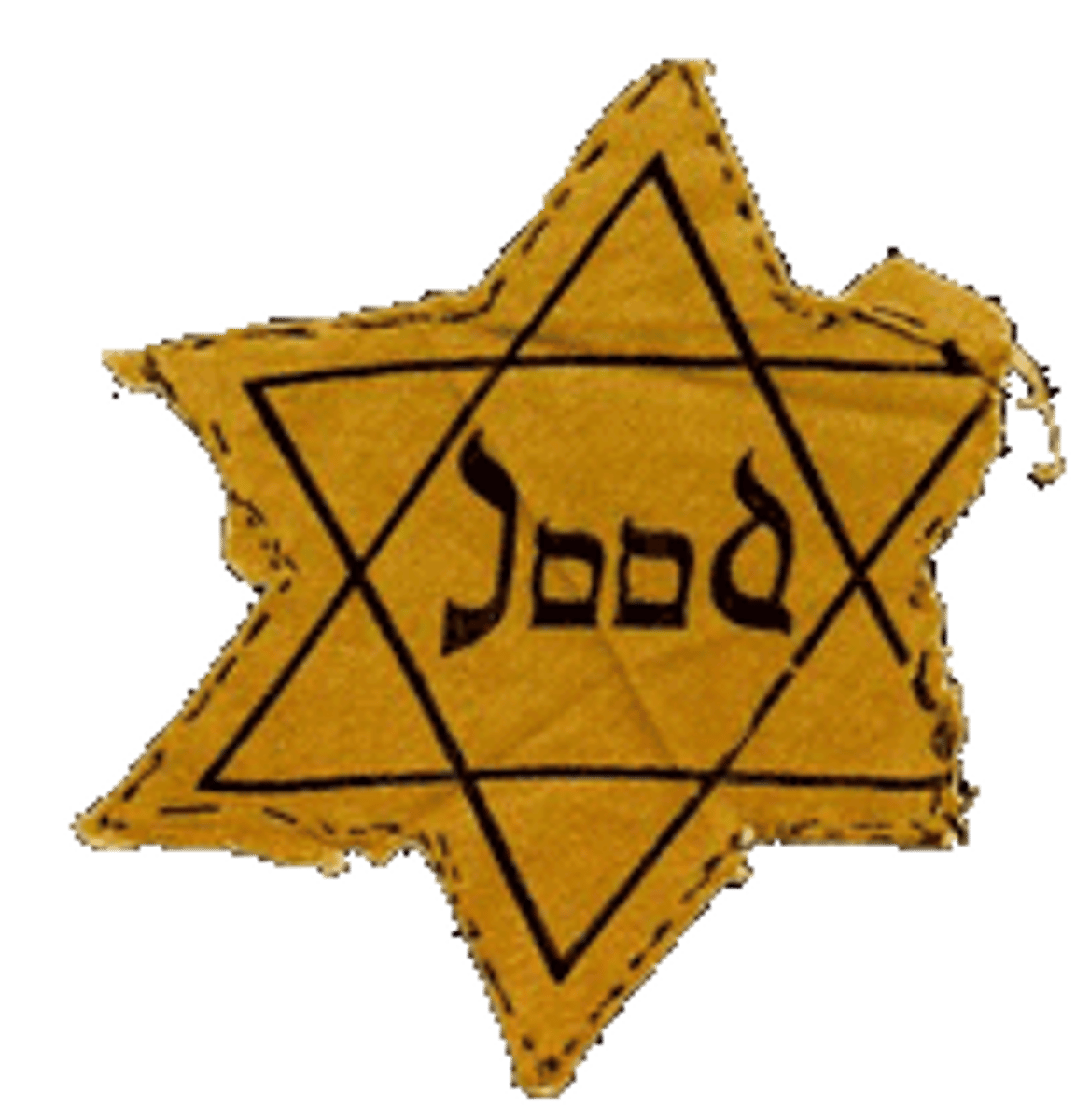

Pogrom
Yiddish word meaning "devastation," referring to an organized massacre of a particular ethnic group—especially Jews in Eastern Europe.

Psychoanalysis
Sigmund Freud's therapeutic technique. Freud believed the patient's free associations, resistances, dreams, and transferences - and the therapist's interpretations of them - released previously repressed feelings, allowing the patient to gain self-insight.
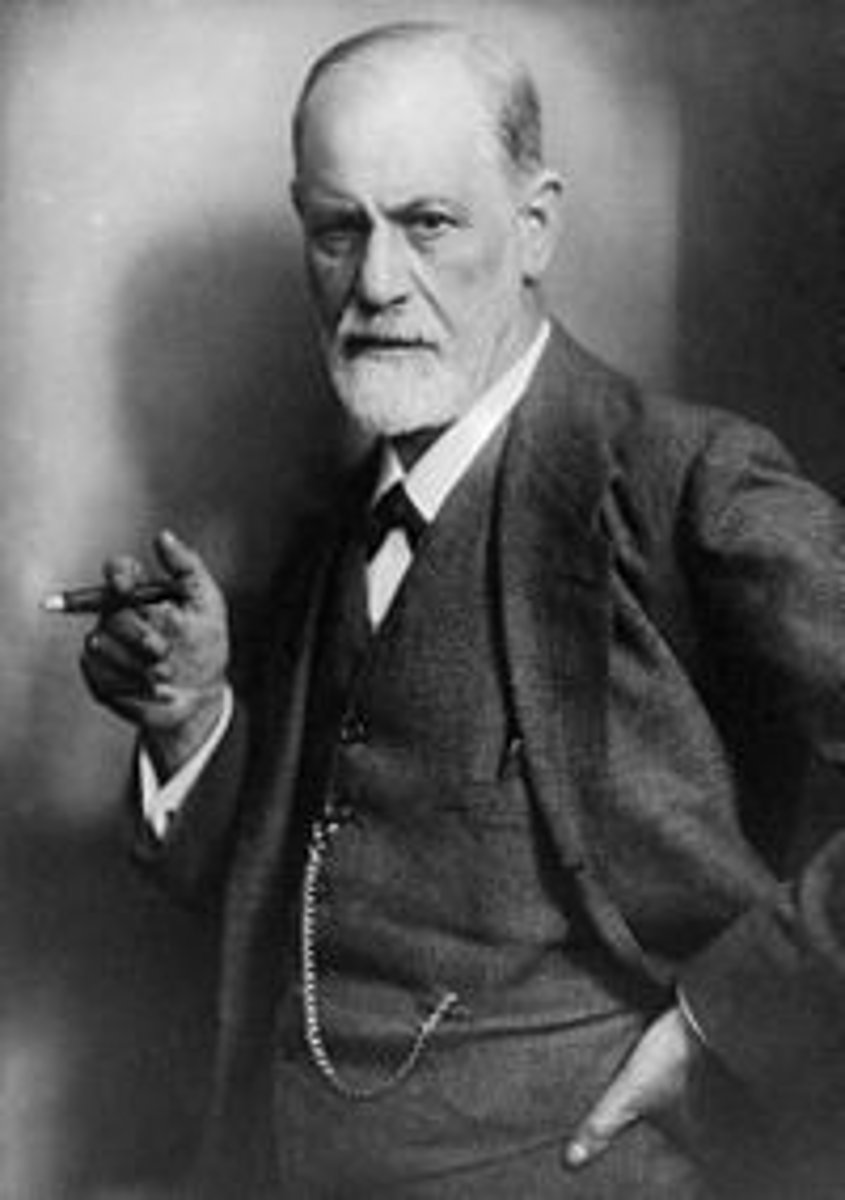
Sigmund Freud
1856-1939; Austrian.
Austrian physician whose work focused on the unconscious causes of behavior and personality formation; founded psychoanalysis.
Contributions: id/ego/superego, reality and pleasure principles, ego ideal, defense mechanisms (expanded by Anna Freud), psychoanalysis, and transference.

Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act
high tariff law that contributed to a global economic downturn in the 1930s
Uncertainty Principle
The idea that it is impossible to know the exact velocity and location of a particle; this principle becomes important when studying electrons. By Warner Heisenberg
War Communism
The Bolshevik policy of nationalizing industry and seizing private land during the civil war.

Xenophobia
a fear of foreign people
Still learning (8)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!