PHSI3010 Module 3: Muscle & Nerve
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Oligodendrocytes, like (A - example), form (B - structure)
A - glial cells
B - myelin sheath
Somatic motor neurons have cell bodies in (A - 2 areas) with a (B - type) axon to (C - target).
A - ventral horn of spinal cord OR in the brain
B - long, single
C - skeletal muscle target
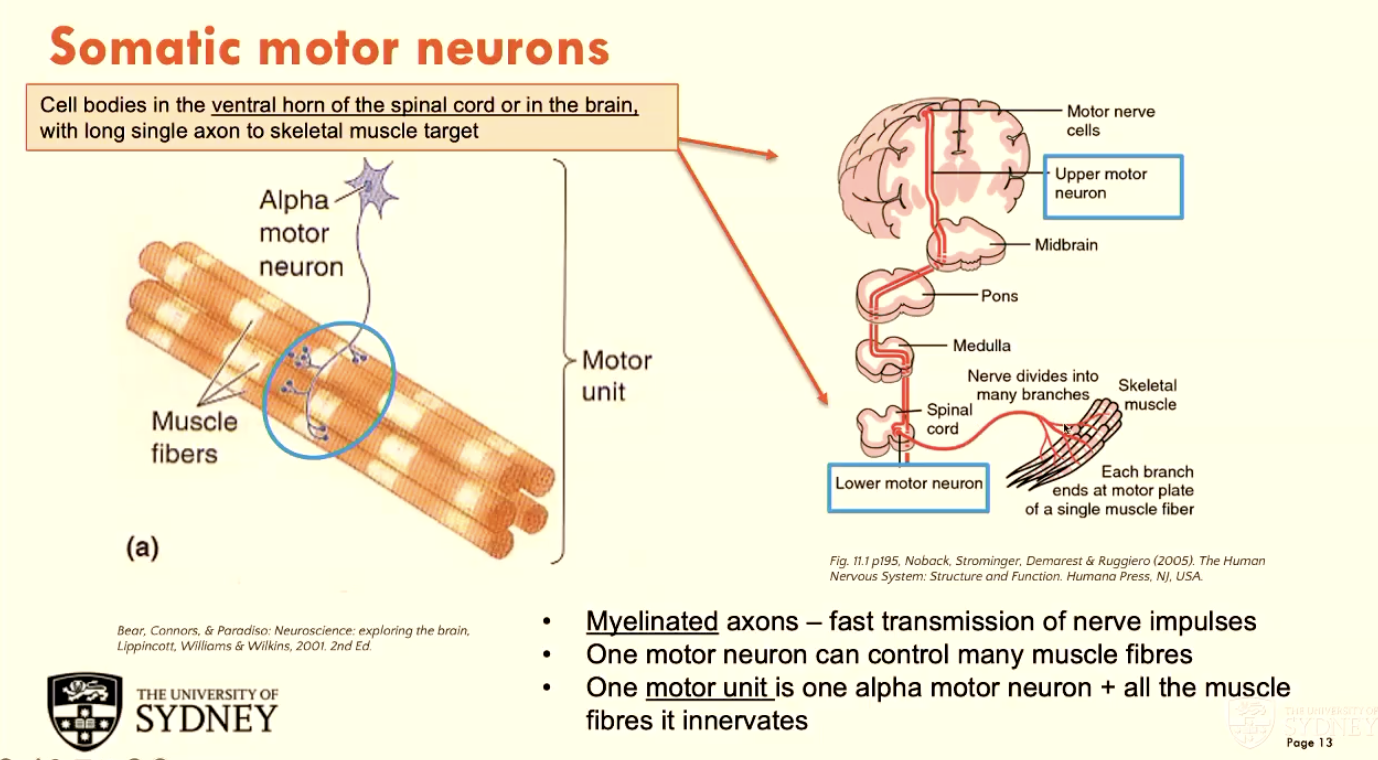
One motor neuron can control (A - how many) muscle fibres.
One motor unit refers to (B)
A - many
B - one alpha motor neuron + all the muscle fibres it innervates
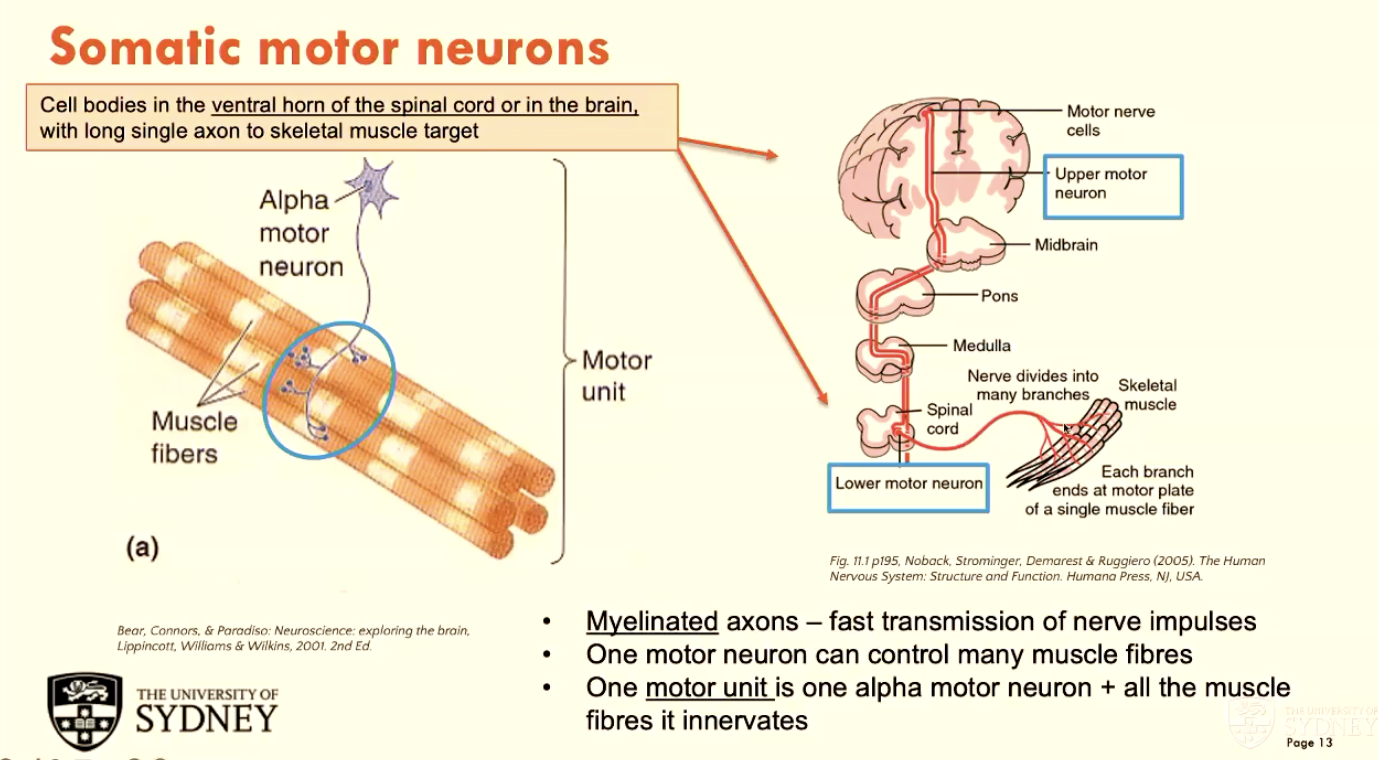
All neuromuscular junctions with skeletal muscle use (A)
A - Acetylcholine (neurotransmitter)
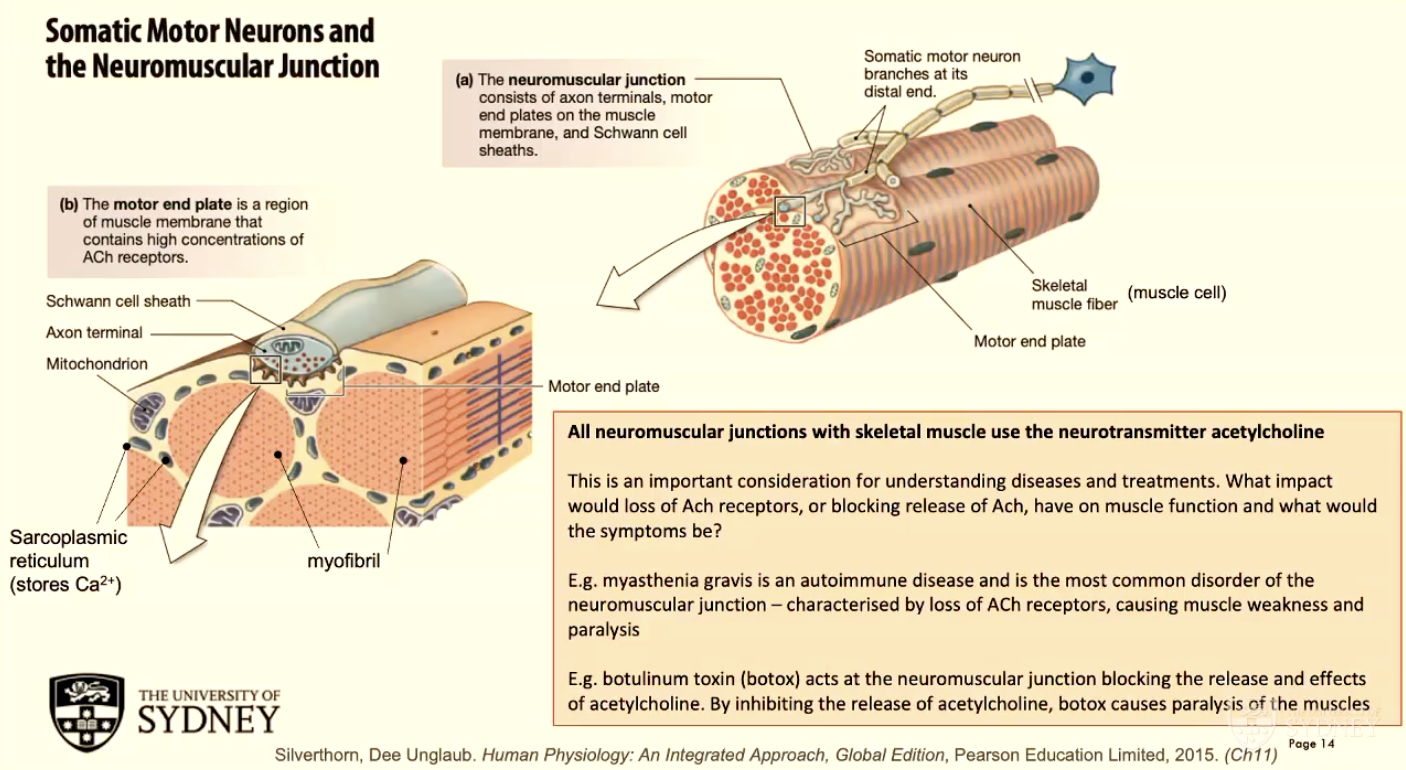
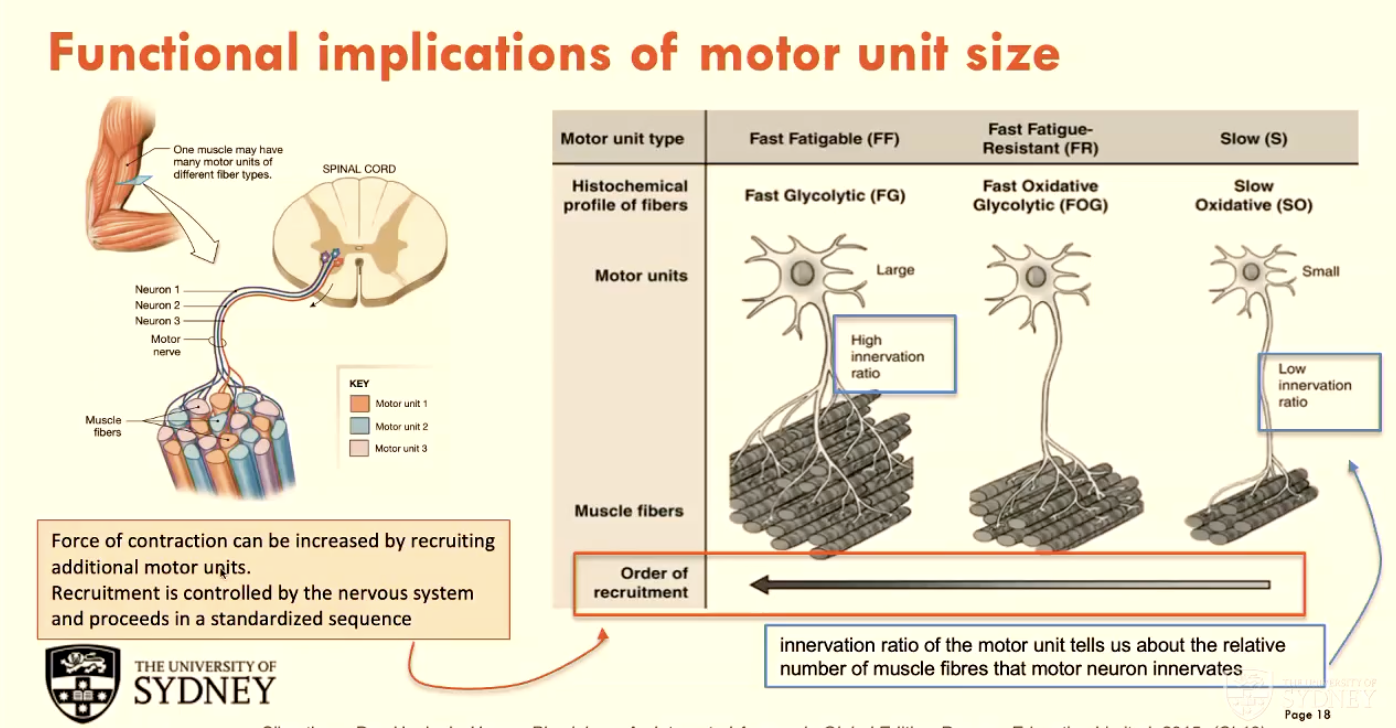
Recruiting additional motor units can increase (A - property).
Recruitment is controlled by (B) and proceeds in a standardised sequence of (C - 3).
A - force of contraction
B - the nervous system
C - slow, then fast fatigue-resistant (FR), then fast fatiguable (FF)
What are two examples of proprioceptors?
Muscle spindles (detects muscle stretch)
Golgi tendon organs (detects muscle tension)
Describe the 3 types of movements generates by motor systems
Reflexive
Involuntary, coordinated patterns of muscle contraction and relaxation elicited by specific peripheral stimuli
Circuits in the spinal cord
E.g. knee reflex
Rhythmic
Movements can occur spontaneously, or more commonly triggered by peripheral stimuli that activate the circuits
Circuits lie in the spinal cord and brain stem
E.g. chewing, swallowing, gut motility
Voluntary
Initiated to achieve a specific goal and improves with practice (feed-forward (anticipate response) and feed-back (evaluates past response) mechanisms)
Stages of nervous system maturation (7)
Neurulation
Proliferation
Cell migration
Differentiation
Synaptogenesis
Synapse pruning
Myelination