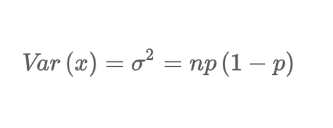Statistics Chapter 5: Discrete Probability Distributions
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is a random variable?
Numerical value/description that is assigned to each possible experimental outcome
What is an example of a random variable?
Assigning 10 emails recieved to numbers (0,1,…8,9)
What is a discrete random variable?
Assumes a finite number of values or infinite sequence of values
What is a continuous random variable?
Assumes any numerical value in an interval/collection of intervals
ex: 0<x<12
How do you determine if a random variable is discrete or continuous?
Think of the variables as a number line. Pick two points, if the entire line segment is denoted by what’s in-between, then its continuous.
What is probabibility distribution?
Describes how probabilities are distributed over the values of a random variable
What is a probability function
For discrete random variable x, f(x) denotes the probability for each value of the random variable
What is an empirical discrete distribution?
Discrete probability distribution where relative frequency method assigns toe probability
What are the required conditions for a discrete probability function?
f(x) cannot be negative and the sum of f(x) for all random variables must equal 1.
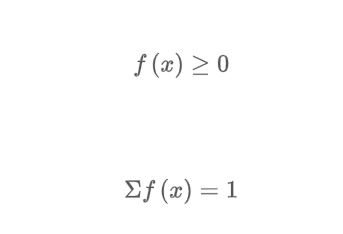
What is the discrete uniform probability distribution?
Probability distribution where each possible value of the random variable has same probability (equal chance of happening for all outcomes)
What is the discrete uniform probability function?
where n is the number of values the random variable may assume
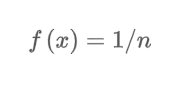
What is the expected value of a random variable?
The weighted mean of the random variable
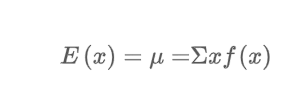
What is the variance of a discrete random variable?
Summarizes variability in the values of a random variable
RECALL: Standard deviation is square root of???
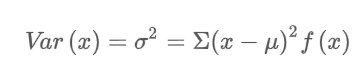
What is a bivariate probability distribution?
Probability distribution that involves two random variables.
What is the covariance of two random variables (x and y)?
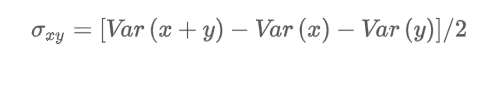
What is the correlation between two random variables (x and y)
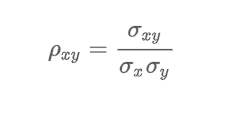
What is the expected value of linear combination of two random variables?
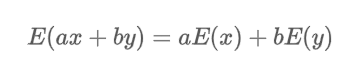
What is the variance of a linear combination of two random variables?

What is a binomial experiment?
Experiment consists of sequences that have n identical trials
There are two possible outcomes per trial: a failure or a success
Probability of success is p, probability of failure is 1-p
Trials are independent (do not impact one another)
What is a binomial probability distribution?
Probability associated with the random distribution of a binomial experiment.
Probability of x successes in n trials
What’s the expected value equation for a binomial experiment?
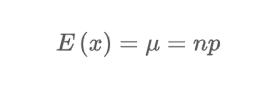
What is the variance equation for a binomial experiment?