EM E2: Topic List
1/451
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
452 Terms
What are sx of Chilblains?
pruritus, burning paresthesia, local edema, erythema, cyanosis, nodules, rarely -ulcers, vesicles, bullae
What is the tx for Chilbains?
supportive → rewarm skin, oral Nifedipine, Pentoxifylline, topical corticosteroids
What are the sx of Trench foot?
tingling, numbness, pale mottled, pulselessness → rewarming = severe burning pain, regain proximal sensation; edema & bullae form, paresthesia
severe: tissue sloughing, gangrene
What is the tx for Trench foot?
prophylaxis; keep warm, ensure boots fit, change wet socks frequently
What are the supportive measures for Trench foot post injury?
maximize efforts to warm, dry, & elevate; oral Pentoxifylline or Limaprost, monitor for infection
Which frostbite zone:
most severe usually distal, irreversible
Zone of coagulation
Which frostbite zone:
severe, but possibly reversible, cell damage, tx may have benefit
Zone of stasis
Which frostbite zone:
more superficial, proximal w/ the least cellular damage, generally recover w/o tx in < 10 days
Zone of hyperemia
How does Frostbite typically present?
usually on nose, ears, face, hands, feet or burn pts w/ prolonged ice tx; keratitis if snowmobilers or skiers
How does frostnip present?
superficial freeze injury in the absence of progressive tissue loss, sx resolve on rewarming
What is the tx for Frostbite?
rapid rewarming; aspiration of clear blisters (do NOT drain hemorrhagic ones), cover w/ aloe vera, PCN G
What is hypothermia?
core temp < 95 F resulting from loss of body heat > body heat production
What are the sx of Hypothermia?
intense shivering → CNS dysfunction, can’t sense cold, lethargy, clumsiness, confusion, hallucinations/coma → resp & HR slow, death
How does hypothermia present on an EKG?
sinus bradycardia, slow afib → V fib or asystole
What is the tx for hypothermia?
prevent further heat loss (remove wet clothes, wrap in blankets); inc core temp by 1 C/hr
supportive: O2 and IV fluids, intubation, glucose if low, warm fluids, thiamine
What is the tx for heat syncope?
rehydrate, remove from heat, evaluate for serious dz
What is the tx for heat cramps?
replace fluids (oral or IV), do NOT use salt tablets
What is the tx for heat exhaustion?
NS 1-2 L IV
What are sx of heat exhaustion?
high HCt, Na or BUN; normal neuro, orthostasis, hyperthermia
What is a heat stroke?
classic: pts w/ compromised homeostatic system
exertional: healthy pts over do it in hot environment
What are the hallmark sx of heat stroke?
cerebral dysfunction w/ impaired consciousness, high fever, absence of sweating
What is the tx for heat stroke?
O2, NS IV, immediate cooling, AVOID ASA & Tylenol, caution if temp of 102-104 to avoid over-correction
What are sx of 1st degree burns?
erythema, pain
What are sx of 2nd degree burns?
blistering, new skin can regenerate, some dermis remains, heal in ~2 wks
What are sx of 3rd degree burns?
painless, slow healing via periphery w/ scarring and contracture, total destruction of dermis/epidermis
What are sx of 4th degree burns?
involves SQ tissue, muscle, fascia, bone
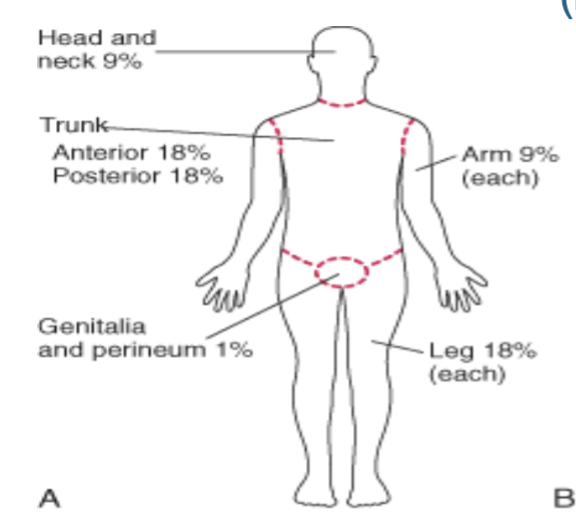
Rule of 9s
review 🙂
What type of fluid is most commonly used in US EDs for burns?
Lactated ringers
Parkland formula to calculate fluid requirements in burn pts
4 mL x kg x TBSA = total fluids in first 24 hrs
*give ½ in first 8 hours; ½ in the next 16 hours
Parkland formula: 70 kg pt w/ 40% TBSA
11 L (5.5 in 1st 8 hrs)
What should urine output be in a burn pt?
30-50 mL/kg/hr
What is the burn tx?
skin: remove FB, charred or necrotic skin debrided, leave blisters intact
Topical Silver sulfadiazine
What is the criteria to admit burn pts?
2/3rd degree > 15%
> 50 yo w/ > 10%
burns to hands, feet, face, perineum
CO poisoning
inadequate support or abuse
severe medical dz (COPD, CAD, DM, renal insufficiency)
What is the burn center criteria?
2/3rd degree > 25%
> 50 yo > 20%
3rd degree: hands, feet, face, perineum
major chemical or electrical burn
respiratory tract injury
major trauma or electrical burn
What are the most frequent cause of immediate death d/t electrical injuries or lightening?
cardiac arrhythmias & respiratory arrest
What are sx of electrical injuries or lightning strikes?
AMS, coma, paralysis, seizures, resp arrest, cataracts 6 mo-1 yr post exposure
What is the tx for electrical injuries and lightening strikes?
BLS, hydration, clean, debride, and dress burns; massive fluid replacement w/ LR
What is the MC fish envenomation?
Stingrays
What are sx of a Stingrays sting?
severe pain -peaks in 30-60, min lasts 48 hrs; weakness, N/V, HA, diaphoresis, syncope, cramps, edema, hypotension, paralysis, arrhythmias, death
What is the tx for Stingray stings?
irrigate, hot water soak x 30-90 min, pain control, XR, abx & Td, no sutures, wound exploration/debridement
What are sx of Sea Urchin stings?
immediate, intense pain, burning pain that evolves into severe muscle aching, erythema & edema near site; synovitis, N/V, paresthesias, paralysis, abd pain, syncope, resp distress
What is the tx for a Sea Urchin sting?
immerse in hot water (113 F x 30-90 min), remove embedded spins, XR, corticosteroids, abx
What are sx of a Portuguese man-of-war sting?
intense pain, burning, throbbing, pruritus, radiates centrally, reddish brown “whiplike” lesions, multiple, linear, very painful, urticarial lesions
Severe: neuro, CV, resp, MSK, GI
What is the tx for a portuguese man-of-war sting?
immediately rinse w/ sea water, 5% Acetic acid (vinegar) will inactivate venom, shave area to remove nematocysts, topic creams, Benadryl or steroids, Td
What are sx of Seabather’s eruption or itch?
vesicular or morbilliform pruritic dermatitis after saltwater, involves covered areas, itching, stinging, or burning, HA, chills, night pruritis
What is the tx for Seabather’s itch?
Benadryl, Calamine lotion, topical steroids
What is the tx for high altitude illness?
descent & O2
What are sx of acute hypoxia?
dizziness, light-headedness, tunnel vision, LOC, unconsciousness
What are sx of Acute mountain sickness (AMS)?
rapid ascent over 6600 ft, insufficient acclimation, HA, N/D, fatigue weakness, pulm edema, dyspnea, cerebral edema, alt consciousness, death
What is the hallmark sx of Acute Mountain Sickness?
fluid retention, peripheral edema, especially face
In addition to descent & O2 what can be given for acute mountain sickness?
Diamox (acetazolamide) carbonic anhydrase inhibitor -diuretic
*can also give as prophylaxis
What are sx of high altitude pulm edema (HAPE)?
onset w/in 6-36 hr after arrival, incessant dry cough, SOB disproportionate to exertion, HA, fatigue → wheezing, orthopnea, hemoptysis, tachy, rales, patchy infiltrates
What is the tx for HAPE?
rest, semi-Fowler position, 100% O2 mask, immediate descent at least 2000 ft essential, Procardia, Decadron if CNS sx
What are the sx of high altitude cerebral edema (HACE)?
progress neuro deterioration w/ HAPE or AMS, hypoxemia, cerebral edema, ataxia, alt consciousness, coma w/in 12 hrs w/o tx
What is the tx for HACE?
immediate descent at least 2000 ft, O2 mask, Decadron
What snakes are venomous?
Eastern diamondback rattlesnake, Canebreak rattlesnake, Pigmy rattlesnake, Cottonmouth, Copperhead, Coral snake
What are sx of snake bites?
fang marks, soft pitting edema, bullae, streaking, erythema, contusions, hypotension, petechiae, epistaxis, hemoptysis, paresthesias
What is the tx for snake bites?
identify snake, immobilize limb, Antivenom ASAP = mainstay -give w/in 4-6 hrs, Antivenin or Crofab (do NOT give in field), Td booster
*can stop antivenom when edema stops or S&S improve
What is the tx for a snake bite w/ no signs of envenomation?
clean wound, Tdap, observe > 6 hr, consider abx (Augmentin)
What are sx of envenomation?
mild: local pain, edema, no systemic signs, normal labs
mod: severe local pain; edema >12 in, systemic toxicity, N/V, alt lab values
severe: generalized petechiae, ecchymosis, blood-tinged sputum, hypotension, hypoperfusion, renal dysfunction, changes in PT/PTT
What do you need to do before giving antivenom?
intradermal skin test to check for allergic rxn
(+) = wheal > 10 mm diameter
What are the 5 P’s of compartment syndrome?
Pain, Pallor, Paresthesia, Paralysis, Pulselessness
What is the best tx for compartment syndrome and coagulopathy secondary to snake bites?
antivenom
What are sx of Brown recluse bites?
local, soft tissue destruction; initial stinging sensation replace by severe pain and pruritis, erythematous halo around lesion
systemic: 1-2 days post bite, rash, fever, chills, N/V, arthralgia, myalgia, petechiae, hemolysis, renal failure, seizures, DIC, coma, death
What is the tx for a Brown Recluse bite?
elevation, immobilization, cool compress, selective debridement, Td prophylaxis, analgesics, antipruritics, abx; admit if systemic sx or hemolysis
What are sx of Black Widow bites?
bite may go unnoticed, systemic effects w/in 1 hr; muscle cramping that progresses, N/V, HA, anxiety, diaphoresis, severe pain that wax & wanes, muscle weakness, neuro sx, mimics peritonitis
What is the tx for a Black widow bite?
O2, IVs, monitor, pain meds or benzos, Td prophylaxis, possibly administer antivenom
*antivenom may cause resp difficulty, HTN crisis, Rhabdo, priaprism
How does type 1 diabetes frequently present?
DKA w/ acute infection or other significant stress
How does Type 2 DM present?
asx for yrs, present w/ complications of the disease (candida vaginitis or balanitis, recurrent UTI)
What are sx of T2DM?
visual changes, neuro sx, numbness, dizziness, weakness, GI/GU sx, inc thirst, slow wound healing, paresthesia
What is considered prediabetic?
fasting plasma glucose >110 but < 126
What is the tx for acute hyperglycemia?
volume restoration, tx underlying cause
What is the criteria of HHNS?
serum glucose > 600 mg/dL, plasma osmolality > 315, serum bicarbonate > 15, arterial pH > 7.3, negative or few ketones
What are sx of HHNS?
weakness, anorexia, fatigue, cough, dyspnea, abd pain, poorly controlled T2DM, CNS sx
What is the tx for HHNS?
correct hypovolemia (IV NS), tx precipitating causes, correct electrolyte abnormalities, gradual correction of hyperglycemia and osmolarity (insulin)
What are sx of DKA?
BG > 250, ketones, wide anion gap, metabolic acidosis, inc ventilatory response, N/V, abd pain, AMS, coma
What is the tx for DKA?
aggressive fluid (1-3 L isotonic saline w/in 1st hr), fix volume first, then insulin ± potassium, phosphate, magnesium, bicarbonate
What complications can arise from tx DKA?
hypoglycemia, hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia, ARDS, cerebral edema
What is wide-anion-gap acidosis most often associated w/?
acute cessation of alcohol consumption after chronic use (alcoholic ketoacidosis)
What are sx of AKA?
N/V, abd pain, gastritis, pancreatitis, tachycardia, rarely mental status changes
What are lab findings of AKA?
elevated anion gap (essential for dx), alcohol levels low or undetectable, mild hyponatremia, hypokalemia; elevated LFTs, bilirubin, BUN, Cr
What is the tx for AKA?
fluid of choice is D5NS, administer gluocse, bicarb if pH < 7, multivitamins, IV Thiamine
What is the MCC of hyperthyroidism?
Grave’s disease
What medications can induce a thyroid storm?
iodine, lithium, thyroid meds
What are classic markers of a thyroid storm?
fever, tachycardia out of proportion to fever, GI sx, changes in normal mental status (confusion, delirium, coma)
What scale is used for thyroid storm?
Burch-Wartofsky Point scale
What is the tx for a thyroid storm?
stabilize, ABC’s IVFs → BBs (propranolol), PTU or methimazole, electrolyte replacement, do NOT administer iodine until later
Euthyroid → radioiodine
What causes primary hypothyroidism?
AI -Hashimoto’s, idiopathic, iodine deficiency, after ablative therapy
What is the tx for hypothyroidism?
thyroxine
What is a myxedema coma?
rare clinical state d/t long-standing preexisting hypothyroidism w/ life-threatening decompensation
What are sx of a myxedema coma?
AMS, hypothermia, bradycardia, hypoventilation, CV collapse
*usually follows infection or cold exposure, drugs (sedative, lithium, amio), trauma, stroke, CHF, inadequate thyroid replacement
What is the tx for a myxedema coma?
ABCs, IVFs, correct hypothermia, IV levothyroxine (alt T3), glucocorticoids, hyponatremia → hypertonic saline
How much adrenal gland must be destroyed for insufficiency to occur?
90%
What causes primary adrenal insufficiency?
AI (Addison’s)
What are sx of an adrenal crisis (life-threatening)?
hypotension resistant to catecholamine and IVF, hemorrhage or thrombosis of glands → abd and flank pain w/ hypotension; may mimic ruptured AAA
What AM cortisol levels rule in/out adrenal insufficiency?
rule in: < 83; rule out: > 525
*use short corticotropin test to exclude AI
What is the tx for an adrenal crisis?
rescue dose of corticosteroids (mandatory) → IV hydrocortisone
What are sx of Pheochromocytomas?
severe HTN, palpitations, HA, sweating, anxiety
What lab tests for Pheochromocytomas?
24 hr urine catecholamine, plasma metanephrines
What is the tx of a Pheochromocytoma?
pre-op: alpha blockers (phenoxybenzamine) & BB → adrenalectomy