Week 9- DMS 212 Fetal Age and Size 2nd/3rd Trimester and Placenta
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
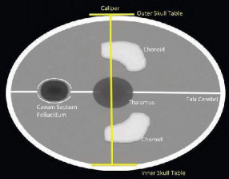
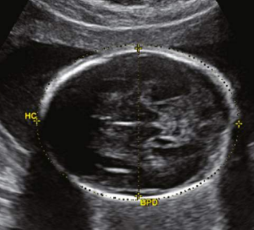
biparietal diameter (BPD)
diameter measurement of skull
how is BPD measured
from leading to inner edge of parietal bone
outer calavarian margin to inner calvarium margin
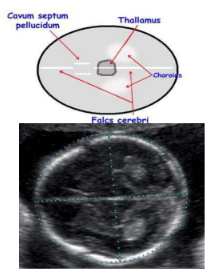
what brain structures should you see when measuring BPD, HC, and OFD
thalamus!!!, cavum septum pellucidum, falx
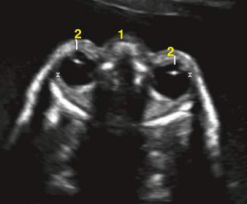
binocular distance (BOD)
measurement from outer orbit to outer orbit of the lenses
interocular distance (IOD)
measurement from inner orbit to inner orbit
cephalic index (CI)
ratio of BPD to OFD
occipito-frontal diameter (OFD)
outer to outer measurement from the frontal bone to the occipital bone
head circumference
circumference of the transverse skull
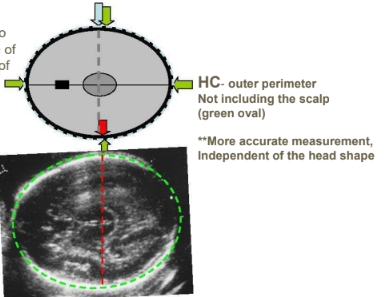
how is head circumference measured
outermost perimeter not including the scalp
macrosomia
fetus weight over 4000g or 8lb 13oz
how is OFD measured
outer to outer
at same level as BPD
the ___________________, _____________________, and __________________ can all be measured in the same image
cerebellum
cisterna magna
nuchal fold
other fetal brain structure measurements
lateral ventricles: no more than 10 cm
cerebellum: 1 mm
cisterna magna: 3-10 mm
nuchal fold: 6 mm
list the standard routine measurements
BPD, HC, CI, cerebellum, cisterna magna, nuchal fold
binocular/interocular, AC, FL, HL
measurement accuracy can be achieved by
multiple measurement average
the nuchal fold measurement can no longer be taken after _________ weeks
24
what structures you should see when measuring abdominal circumference
portal vein, umbilical vein, stomach
list the anatomic landmarks for abdomen measurements
junction of umbilical vein/portal vein, stomach, AO, spine, circular shaped abdomen
list the long bones
femur, humerus, tib/fib, radius/ulna
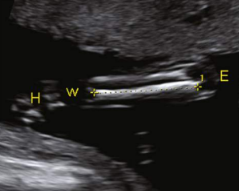
when measuring long bones only include the
echogenic part
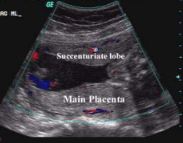
succenturiate lobe
extraplacental lobe smaller than the placenta
braxton-hicks
uterine contractions that do not lead to labor
cotyledons
subdivisions of the maternal placenta containing fetal vessels, chorionic villi, and intervillous spaces
decidua
functional layer of the endo post-ovulation/during pregnancy
retroplacental
vascular area between the myometrium and placenta
wharton jelly
Mucous tissue surrounding the umbilical cord
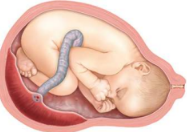
central insertion
cord inserts into middle of placenta
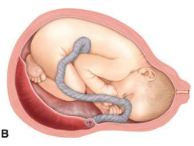
marginal insertion
cord inserts near the edge of the placenta
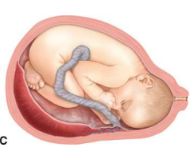
velamentous insertion
cord inserts into chorioamniotic membranes
marginal insertion is also called
battledore
velamentous insertion increases the likelihood of _______________________
vasa previa
vasa previa
umbilical cord crosses over the internal os
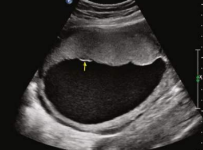
Grade 0 placenta
no calcs
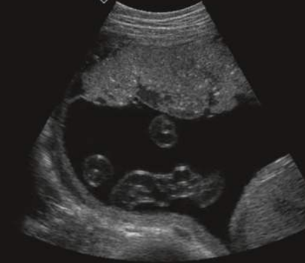
Grade 1 placenta (31-36wks)
scattered calcs
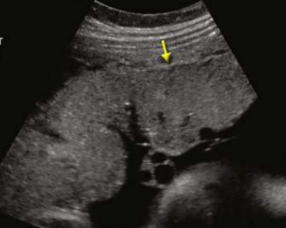
Grade 3 placenta (36-38wks)
basal calcs with increased lobulations
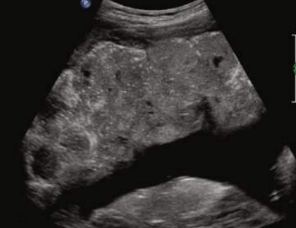
Grade 4 placenta (38wks-term)
basal and interlobar septal calcs
the placenta matures considerably after the ___________ week
40th
Most term pregnancies have grade ___ or ___ placentas
1 or 2
only about 10-15% of term pregnancies are grade _____
3
what must be evaluated when examining the cervix
cervical length
incompetency
funneling
what is the correct way to measure the cervix
from internal os to external os
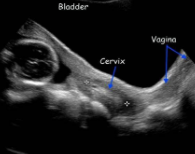
normal cervical length
2.5 to 3 cm
what is the gold standard for measuring the cervix
TV
clinical findings of cervical incompetence
painless dilation
premature rupture of mems
vaginal bleeding
cervical length less than 3cm
funneling
funneling of the cervix
list some indication for cervical evaluation
hx of premature labor/birth
multiple gestation
Premature rupture of mems
uterine anomaly
DES exposure
funneling
premature opening of the internal os
PROM
premature rupture of membranes
cerclage
procedure where circumferential suture closes the cervix
what are the two most common cerclage techniques
shirodkar and McDonald
what is placenta
vital support organ for the fetus
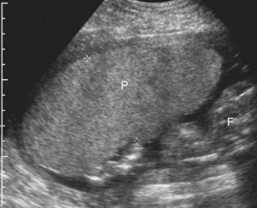
normal measurement of placenta
2-3cm should not exceed 4cm
how is placenta formed
from trophoblastic cells that make up chorion
chorionic villi
functional units of placenta
maternal portion of the placenta
decidua basalis/basal plate
fetal portion of the placenta
chorion frondosum
what is a cotyledon?
consists of a chorionic villi from the fetus and a caruncle from the mother
genetic material in the chorionic villi is the same as the __________________
fetal cells
caruncle
maternal tissue that anchors the cotyledon to the uterine wall
list the functions of the placenta
respiration
nutrition
excretion
hormones
storage
protection
how does the placenta facilitate respiration
oxygen from maternal blood passes through placenta into fetal blood and carbon dioxide returns to maternal blood
how does the placenta produce hormones
synctiotrophoblast cells produce estrogen, hCG, and progesterone
sono appearance of placenta
solid
homogenous
medium gray
smooth borders
list the locations of the placenta
fundal anterior
posterior
fundal posterior
right or left lateral
causes of premature maturation of the placenta
maternal HTN
smoking
IUGR
multiple gestation
causes of delayed maturation of the placenta
maternal diabetes
obesity
fetal congenital heart disease
fetal chromosomal abnormality
placentomegaly
enlarged placenta
AP over 4cm
causes of placentomegaly
maternal diabetes
isoimmunization
fetal-maternal hemorrhage
intrauterine infection
non-immune hydrops
chromosomal anomaly
uterine anomaly
twin-twin transfusion
congenital neoplasm
triploidy
placental insufficiency
placenta under 1.5cm
causes of placenta insufficiency
placental infarction
chromosomal anomaly
intrauterine infection
diabetes
IUGR
preeclampsia
polyhydramnios
toxemia
placenta previa
placenta covers the internal os of the cervix
if the placenta is low lying in the second trimester is is often...
self correcting and is pulled up as the uterus grows
complete previa
placenta totally covers internal os
partial previa
partially covering internal os
marginal previa
small edge extends to the margin of internal os
low lying
not considered previa but need monitoring
placental edge is less than 2cm away from internal os
what is the most common cause of painless bleeding in the 2nd and 3rd trimester?
placenta previa
risk factors for placenta previa
multiple gestations
multiparous women
prior C-section
hx of abortion
advanced maternal age
closely spaced preg
abnormal fetal position
hx of fibroids
maternal anemia
hx of uterine infection
an __________________________ can cause the illusion of placenta previa
overdistended bladder
_________________ can mimic low lying placenta
uterine contraction
succenturiate placenta
bilobed placenta/accessory lobe connected to placenta by vessels
succenturiate placenta can increase likelihood of ________________________
vasa previa
placental lakes
enlarged spaces in the placenta filled with maternal blood
Placenta accreta
superficial invasion of the placental villi into decidua
placenta increta
deeper invasion of villi into myometrium
placenta percreta
invasion of villi through myometrium and often into bladder wall
placenta 'cretas can cause __________________ due to _______________
maternal death, exsanguination
sono eval of placenta 'cretas
assess placental/myometrial borders
use high res TDR
ID borders
___________ may be useful in identifying placenta 'cretas
MRI
abruptio placenta
placenta tears away from uterine wall before birth; can be life threatening to fetus and mother
abruptio placenta is known as
placental abruption
retroplacental abruption
Rupture of spiral arteries and high pressure bleed
sono appearance of retroplacental abruption
thick placenta
possible clot in area of abruption
marginal placental abruption
rupture of marginal vein and low pressure bleed
sono appearance of marginal placental abruption
anechoic or hypoechoic bleed in subchorionic area usually at edge of placenta
placental abruptions are an ______________________
OB emergency
placental abruptions may result in...
premature labor or delivery
fetal demise
symptoms of placental abruption
vaginal bleeding
painful contractions
sudden onset of severe abdominal pain
chorioangioma
benign vascular tumor of the placenta
what is the most common placental tumor
chorioangioma