AP psyc unit 2 (updated for 2025) (copy)
1/117
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Perception
Involves organizing and interpreting sensory information. Brings meaning to sensation. Primarily influenced on whether one relies on external sensory information or internal prior expectations.
Bottom up processing
Relies on external sensory information. It is information processing of basic elements or features to build perception.
Ex: Learning to drive and learning when to apply the gas and brakes.
Top down processing
Relies on internal prior expectations. It is information processing that involves experience, expectations and motives to fill the gaps to complete a perception.
Ex: you have a bad reception on a phone call but can still make out what the other person is saying
Schema
Top down mental framework for organizing and understanding our world. They help guide our perceptions. Through experiences, we form schemes to organize and interpret our info.
Perceptual set
The readiness to perceive something in a particular way or having an expectation for a stimulus. We see what we expect to see.
Ex: when you were speeding and you see a flashing light, you assume you’re being pulled over.
Gestalt principles
Perceptual principles proposed by Gestalt psychology to help explain how humans organize their perceptual world.
Closure
Gestalt principle of making a hole or completed object by filling in the gaps.
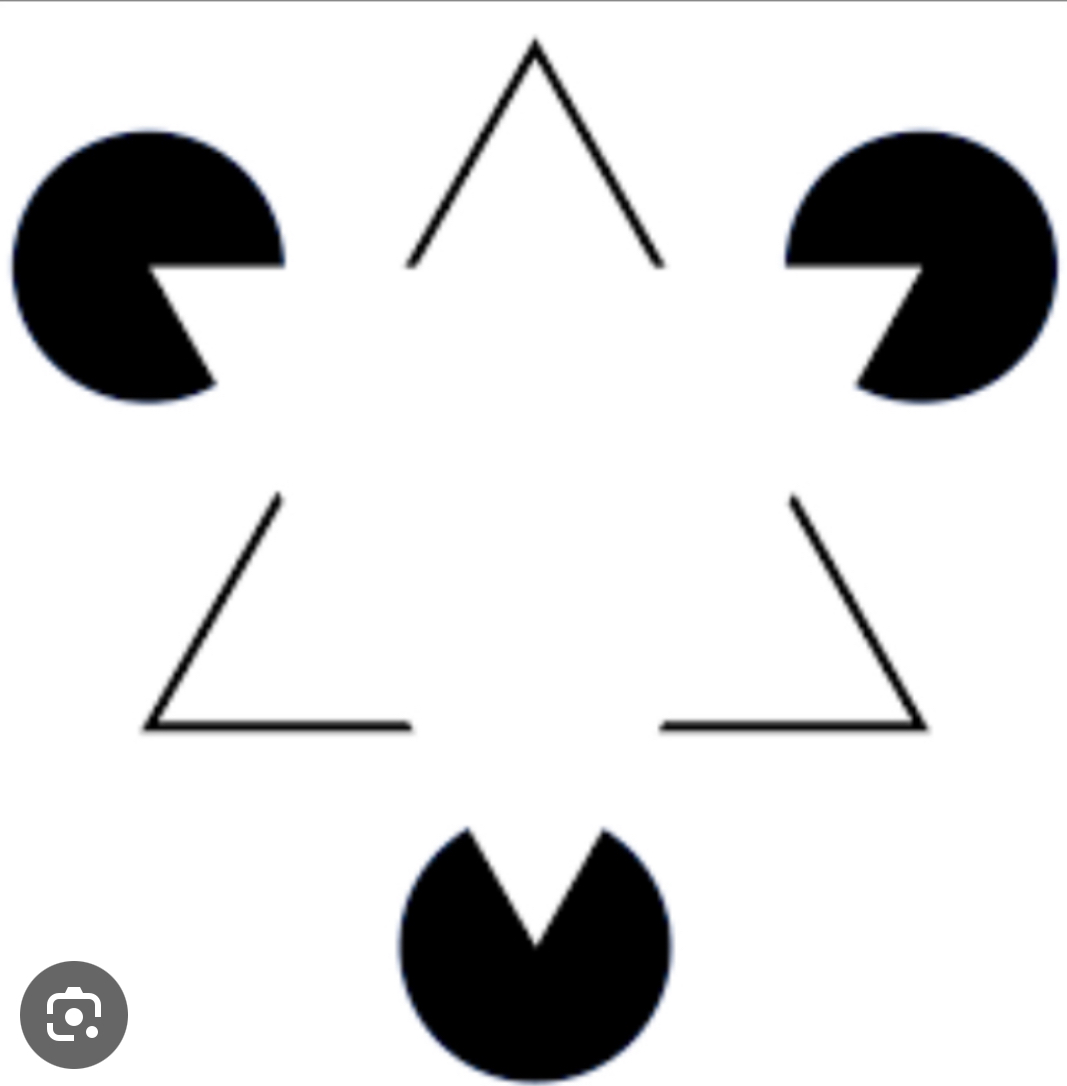
Figure and ground
Gestalt principal in which the figure is, the object in the ground is the surroundings

Proximity
Gestalt principle That items close together group more easily than items far apart.
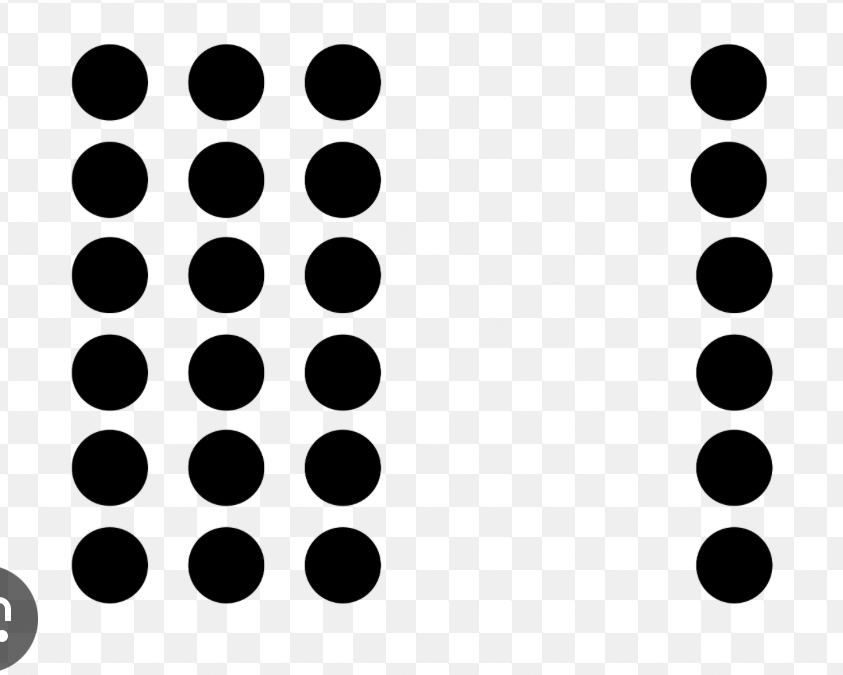
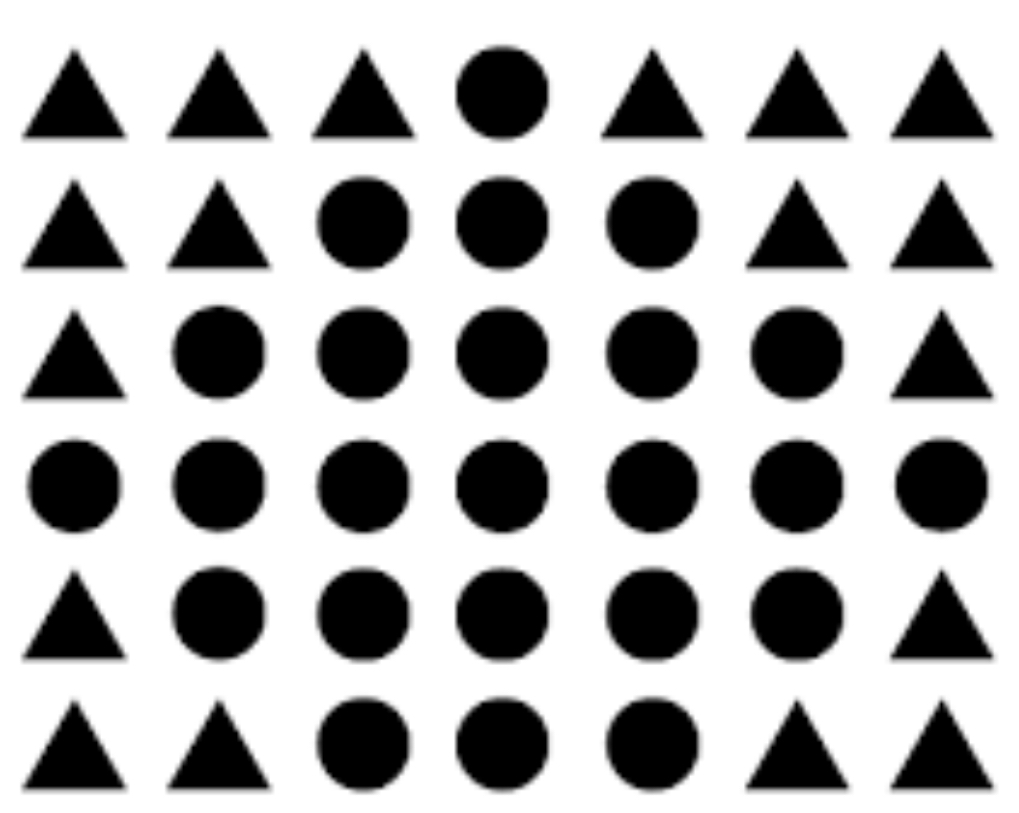
Similarity
Gestalt principle That items more alike group more easily than items that are different.

Attention
An interaction of sensation and perception that is affected by internal and external processes
Cocktail party effect
Where people attend to mentions of their names or specific topics and loud and distractive environments
Inattention
Lead to a type of blindness to aspects in the environment
inattentional blindness
Occurs when attention is focused on one part of the visual field and as a result, you may ignore or miss other parts
Change blindness
A specific type of inattentional blindness, occurs when changes in the visual field are not perceived due to inattention or brief interruption
Binocular depth cues
Retinal disparity and convergence. Two eyes to Utilize both cues to provide perception of death.
Retinal disparity
Determining depth based on the difference between what each eye sees
Convergence
Determining depth based on how much both eyes rotate inward
Monocular depth cues
Use one eye to give the illusion of depth on flat or two dimensional surfaces.
The five monocular depth cues
Relative clarity, relative size, texture, gradient, linear perspective, and interposition
Visual perception consistencies
Maintain the visual perception of an object, even when the images of the object objects in the visual field change.
Color constancy
When an object has the same brightness despite the changing amount of illumination
Shape constancy
When an object has the same dimension or shape despite the changing angle or orientation
Brightness constancy
When an object has the same brightness despite the changing amount of illumination
Size constancy
When an object has the same proportion or size despite shrinking or getting larger
Concept
Forms the mental basis of thought. They are mental groupings based on shared features, and come from experience.
Ex: fruit, dogs, furniture
Prototype
Ideal example of any given concept. What typically comes to mind. An image that represents an example from your experiences.
Ex: fruit makes you think of apples, pears, bananas, but not tomatoes
Schema
Golden blocks of intellectual development that make an organization and meaningful action possible. Schemas provide context
Assimilation
Taking a new information, but not changing the schema because of it. Placing new information into an existing schema.
accommodation
Taking a new information and changing the schema to incorporate the new info. Changing an existing schema or creating a new schema.
Algorithm
Addresses problems by attempting all possible solutions until the correct one is found
Ex: using a formula to solve math problems, instructions for a recipe, or trying all possible lock combinations
Heuristic
Addresses problems by using mental shortcuts to make judgments.
Ex: selecting a restaurant based on the reviews, guessing who’s older is based on height, choosing the best brand based on the price.
Types of heuristics
Representative, availability
Representative heuristic
Lead to an error in judgment in where decisions are made according to prior expectations or stereotypes.
Availability heuristic
lead to an error in judgment where decisions are made by recalling the first or most vivid example that comes to mind
Mental set
Using what worked in the past rather than trying something new
Framing
Alters your decision based on how something is presented to you
Gamblers fallacy
For belief that you can predict a chance event based on past chance events
Ex: you flip a coin and it’s heads five times in a row, you think there is a higher probability of it being tails
Sunk cost fallacy
A bad decision based on time, money, or effort that has already been spent.
Ex: you bought a concert ticket, but you wake up sick that day. You decide to go because you don’t want to waste your money.
Divergent thinking
Considering many different ideas or solutions to a problem. Associated with creativity since someone must break from normal problem-solving and create unusual associations.
Convergent thinking
Using knowledge and logic to narrow down options to find known solution, or single, correct answer.
Implicit memories
“Tell me how to climb a flight of stairs”
Also called declarative memories. Procedural, classically, conditioned responses or primed memories that you usually recall without conscious awareness.
Explicit memories
“ Tell me about the best birthday you ever had”
also called declarative memories. Episodic, semantic, and prospective. You recall them with conscious awareness.
Working memory
Limited information, temporarily maintained, and used for many cognitive tasks, like remembering a password, imagining how new furniture could be placed, solving a math problem, or learning to change a flat tire. It is also called short term memory.
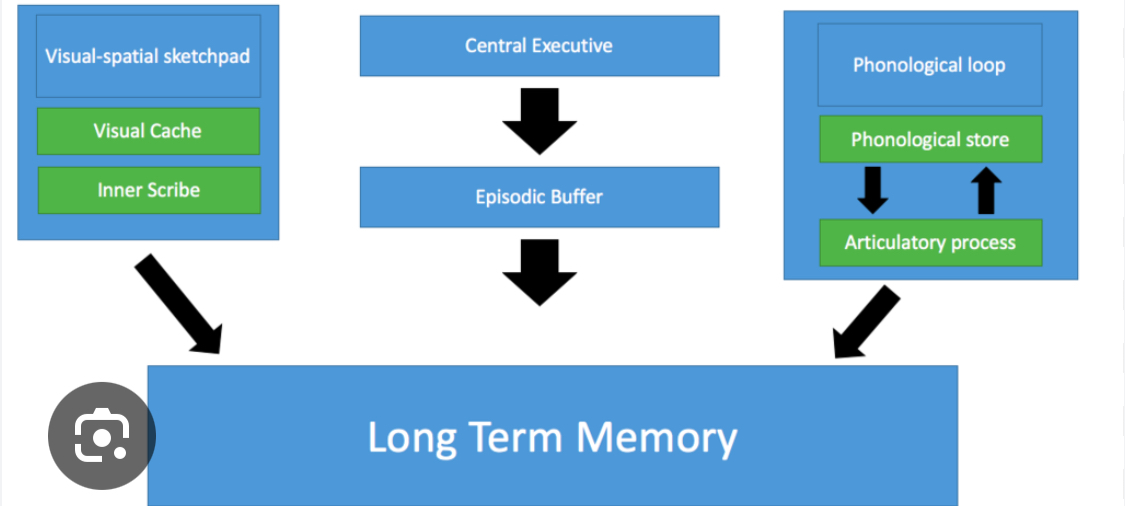
Working memory model
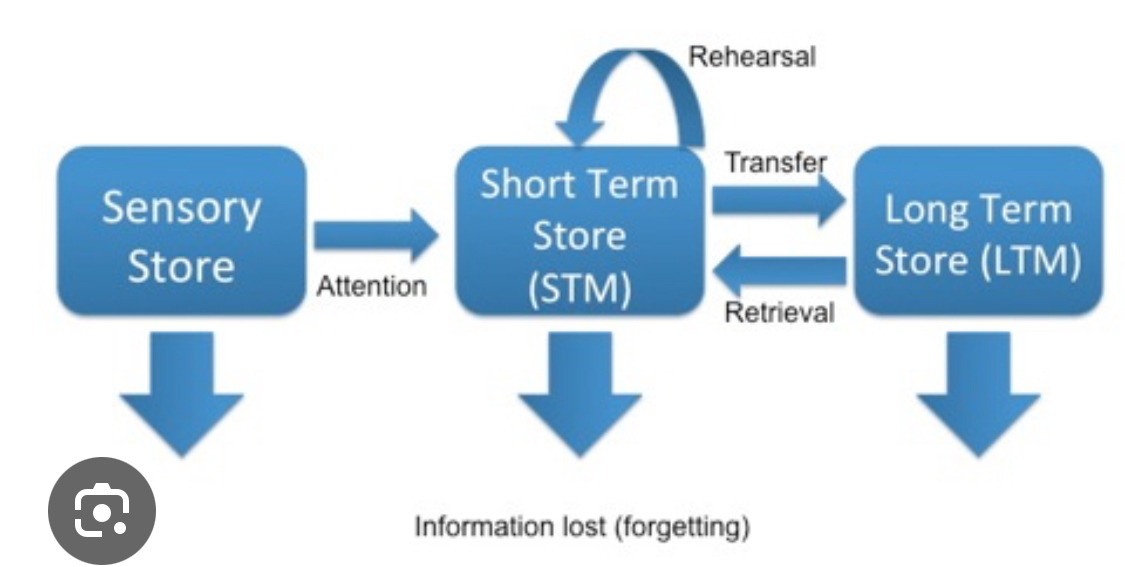
Multistore memory model
Sensory memory
a brief, automatic, and detailed record of what you see, hear, smell, taste, and feel
Iconic memory
A brief memory for visual inputs, delays quickly. Part of sensory memory.
Echoic memory
Brief memory for auditory inputs, decays quickly, but not as fast as iconic. A part of sensory memory.
Short-term memory
Temporary storage of information that we attend to from our sensory memory.
Levels of processing model
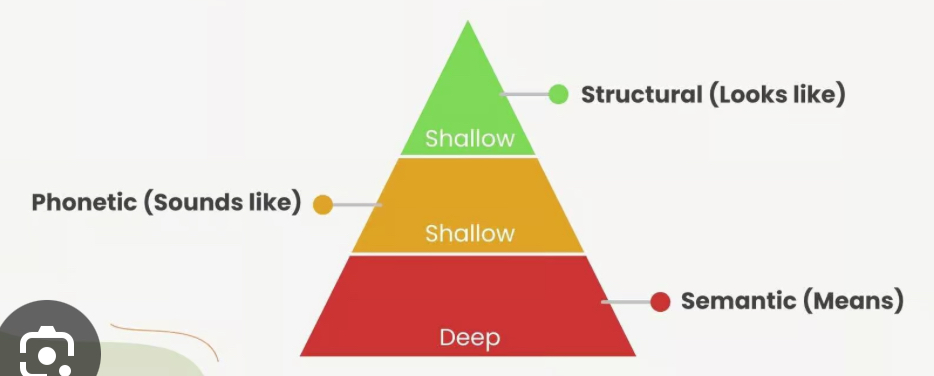
Shallow Processing: Structural
Encoding using the basic visual qualities of the word/concept. The shallowest level of processing.
“How many letters are in a word”
Shallow processing: Phonemic
Encoding is in the basic auditory qualities of the word/concept
“What does it rhyme with”
Deep processing: semantic
Encoding the meaning of the word. The deepest level of processing.
“Can you relate it to other concepts”
Method of Loci
An mnemonic device that relies on spatial relationships between locations on a familiar route or rooms in a familiar building to encode and later retrieve information
Correlational studies
Variables are not controlled, and random assignment to conditions aren’t utilized. They are different from experiments
Mode
Most frequent observation. Which course shows up the most in the data set. Can be unimodial or bimodial.
Sensory memory capacity
Untested, but thought to be unlimited
Short term/working memory capacity
5 to 9. Six letters. Five words.
Long-term memory capacity
Unlimited
Sensory memory duration
Iconic- less than one second
Echoic- less than four seconds
Short term/working memory duration
Less than 12 seconds without rehearsal
Long-term memory duration
Stable throughout lifetime
Ebbinghau’s forgetting curve
Memorized nonsense syllables, tested himself at various times after memorizing them, and data was recorded. Very rapid loss of recall after an hour. Used to test long-term memory.
Explicit memories
Stored all of the brain and semantic networks. Areas of the hippocampus are essential for new formation of this type of memory.
Anterograde amnesia
When there is a problem, moving information from short term into long-term. Can cause your memory to ”reset each day”
Retrograde amnesia
Problem, retrieving explicit memories from long-term to working memory. Damage to some part of our cerebral cortex. Can’t remember past events.
Hippocampi
Two, one in each hemisphere. In charge of explicit memory and associated with themes and schemas.
Confirmation Bias
We do not want what really happened from our memory, we want the memory that will support what we are thinking and feeling. You will remember things how they want to be remembered.
Hindsight Bias
Our current cognitive and emotional needs will “rewrite“ a memory.
Ex: If you are angry, you will have trouble accessing a happy memory
Overconfidence
Our mind is convinced that what it produces is right.
Mood-congruent memory
Our emotions influence which memory is retrieved.
Context- dependent memory
Setting (sights and smells) help retrieval.
State Dependent memory
Memory pathways are only activew when you are in the certain mental/ emotional state.
Recognition
A type of retrieval. It is like a multiple choice questions and you know the answer because you recognize it.
Recall
A type of memory retrieval. It is like an FRQ question and you are accessing all of you information in your brain to answer it.
Testing effect
The more often you take a test, or work with a certain type of question, the better you become
Meta-Cognition
Thinking about your own thinking. Being aware of your own thinking is very difficult. Noticing what might be blocking information from appearing. Noticing what happens before the aha moment.
Incubation
You can’t make a fruit tree Bloom before it is ready. You can’t you exercising without taking a break. When you won’t answer, it is best to give your mind time to find the answer.
Bar charts
Columns don’t touch and it is non-numerical data
Infantile amnesia
Can’t remember anything before age 5. Everyone has it.
Psychogenic amnesia
Memory problems without physical cause of trauma
Source amnesia
Difficulty remembering where you learned something
Anterograde amnesia
Difficulty encoding or inability to encode new memories.
Retrograde amnesia
An event blocks or prevents retrieval of old memories.
Amnesia
Associated with storing and receiving information. You can or can’t remember.
Interference
Associated with processing information. Is what you are thinking of corrupted by information that was processed at a different time?
Retroactive interference
New information, corrupts, intertwines with, or blocks information that was processed at earlier time. Self consistency bias.
Proactive interference
Old information prevents, corrupts, or intertwines with current or recent information. Can’t teach an old dog new tricks.
Reconstructive memory
Is related to memory confabulation, which means our mind blends perceptions, and images from several experiences and gives it to us as what it believes is the record of what happened
Memory confabulation
Inaccurate details are often blended with what really happened
Mental age
The level the child is operating.
Mental age/ Chronological age x 100 = IQ
Chronological age
How old the child is
Factor analysis
Factors that are similar, occurred together and can be grouped into one thing
Two factor theory
You have one general intelligence level, G and you can also have a specific mental ability, S.
Multiple intelligences
Not how smart you are, it’s how you are smart
Fluid intelligence
Speed, youth, processing power , lack of knowledge
Crystallized intelligence
Slower, can use experience to compensate
Triarchic theory of intelligence
Intelligence doesn’t exist in a test, intelligence is applied in the environment you live
General mental ability
A person‘s ability to learn and adapt to new situations