AMINO ACIDS PROTEINS N DNA
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
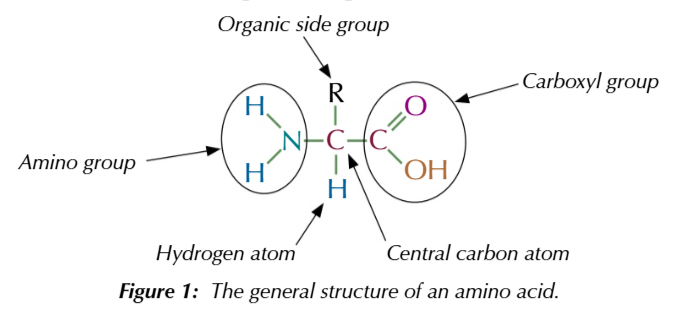
AMINO ACIDS HAVE 2 FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
amide -NH2 and carboxylic acid -COOH
amino acids are amphoteric
can act as an acid OR base
amino acids can donate protons
-COOH ⇄ -COO- + H+
amino acids can accept protons
-NH2 + H+ ⇄ -NH3+
amino acids are chiral molecules
the carbon is attached to 4 different groups
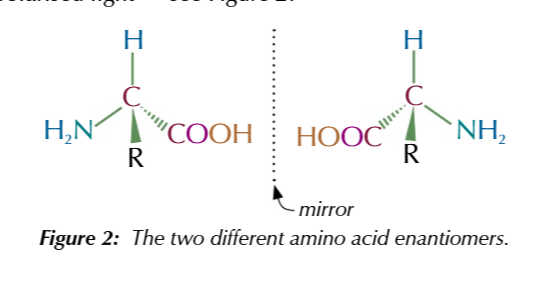
a solution of a single amino acid enantiomer
rotates polarised light
naming amino acids
find longest carbon chain w COOH
number the carbon starting w 1COOH
write down the position of -NH2 followed by AMINO
write the name of any other functional group w its position on the carbon chain

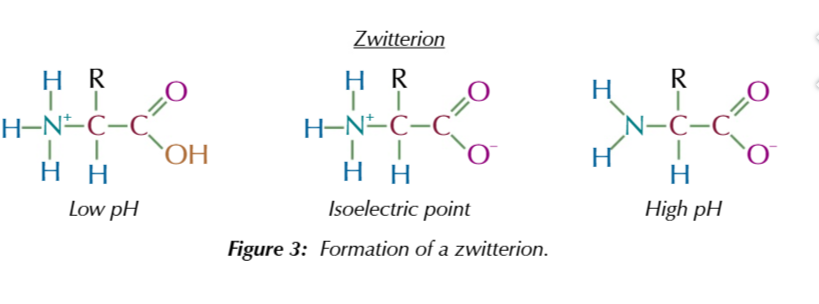
amino acids can exist as zwitterions
dipolar ions with both positive and negative parts
zwitterions only exist near an amino acids isoelectric point
when the pH gives the amino acid an overall charge of 0
amino acids becom zwiterions when the amino group is protonated -NH3+
and the COOH group is deprotonated -COO-
in acidic conditions
the NH2 group is likely to be protonated while the COOH remains the same so the amino acid molecules carried a positive charge
in basic conditions
the COOH is likely to be deprotonated and the -NH2 remains unchanged so the amino acid molecules carries a negative charge
only at or NEAR the isoelectric point are BOTH the carboxyl group and the amino group likely to be ionised forming a zwitterion
different amino acids have different R groups
therefroe they will have different solubilities to the same solvent
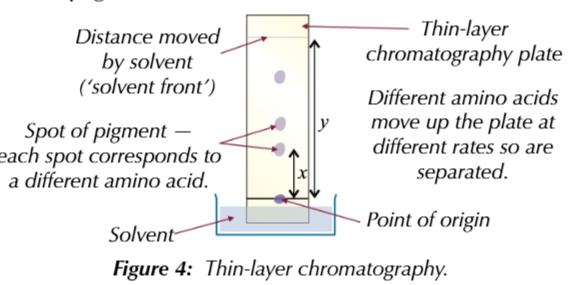
you can easily seperate and identify differemt amino acids in a mixture using
Thin layer chromatography
amino acids are colourless
you make them visible by spraying ninhydrin solution on the plate which causes amino acids to turn purple
you can use a special plate with added flourescent dye on it
the dye glows in UV light so wherever theres an amino acid the spot will appear darker
you can identify amino acids by comparing their Rf value to the databook Rf value
Rf= distance travel by spot ÷ distance traveled by solvent
protein
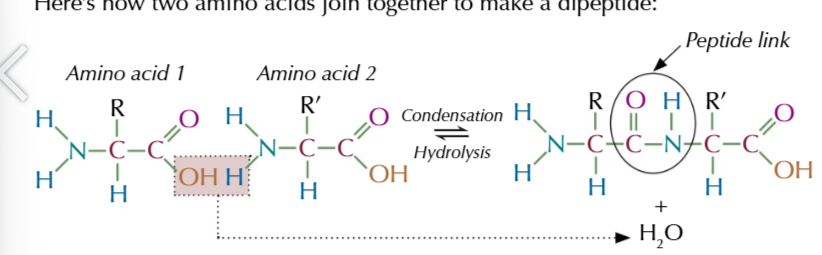
condensation polymers of amino acids joined in peptide links
amino acid 1-COOH+HHN-amino acid 2 → protein + H2O
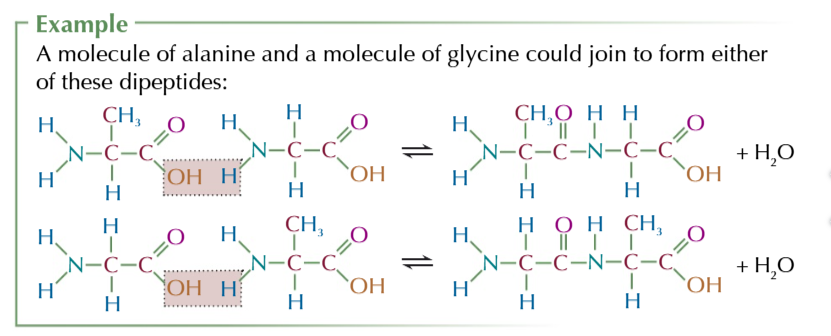
if 2 different amino acids compine then 2 different products can be formed because of chiral carbon
protein hydrolysis conditions
6 mol dm-3 HCL
heat mixture in reflux for 24hours
peptide bond
-CONH
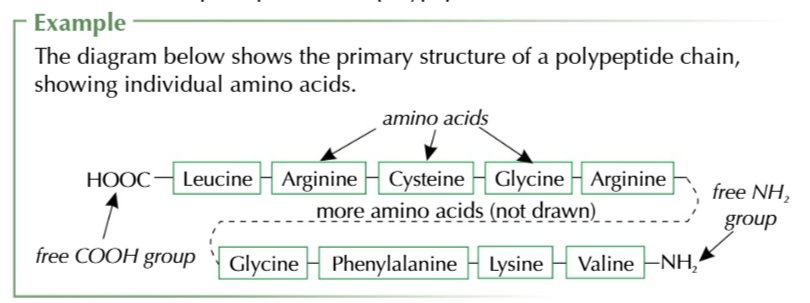
PRIMARY STRUCTURE
sequence of amino acids in long chain held together by peptide bonds
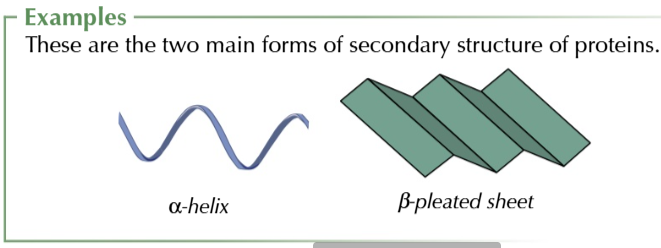
SECONDARY STRUCTURE
peptide links can form hydrogen bonds with each other so the chain is NOT straight
in fact the chain can spiral into an alpha helix structure OR fold into a beta pleated sheet structure
TERTIARY STRUCTURE
chain of amino acids itself coil and fold in characteristic ways that identifies the protein
extra bonds form between different parts of the polypeptide chain which gives is 3D shape
secondary and tertiary structures of proteins are formed by intermolecular forces
causing the amino acid chain to fold and twist
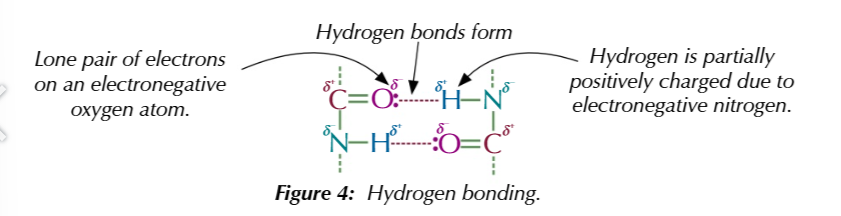
hydrogen bonding exists between polar groups like OH and NH2
these groups contain electronegative atoms which induce partial positive charges on hydrogen atoms which are attracted to lone pairs of electrons on adjacent polar groups to form hydrogen bonds
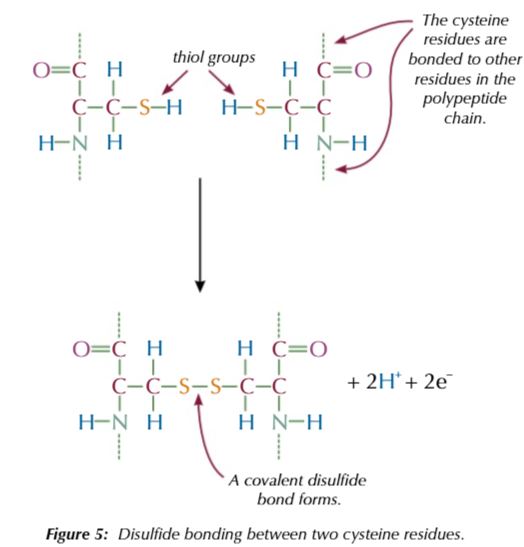
cystine
an amino acid with the thiol group -SH
the thiol group can lose its H atom and join together to form a disulphide bridge
-S-S-
these disulfide bonds link together different part of the protein chain
to help stabalise the tertiary structure
factors that affect intermolecular forces in amino acids
temperature
pH
enzymes
speed up chemical reactions by acting as biological catalysts
enzymes catalyst every metabolic reaction in the bodies of living organisms
they are proteins but have non protein components
substrates
molecules that enzymes bind to
enzyme active sites
has a specific tertiary structure for the substrate to fit into so it can interact with the enzyme
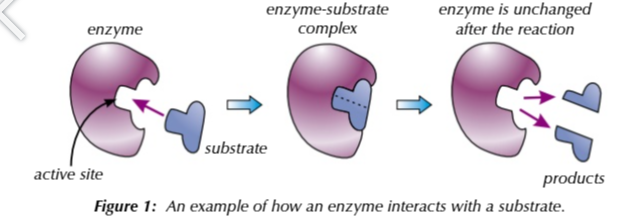
enzymes only work with specific substrates
for enzymes to work the substrates has to fit into the active site for the reaction to be catalysed
enzyme active siets are stereospecific
the active sites only work for one enantimer of a substrate (enantiomers are non superimposible so wont fit in properly)
inhibitors
molecuels with a similar shape to substrates
inhibitors compete with substrates to bind with the active site
when an inhibitor binds to the active site to reaction takes place
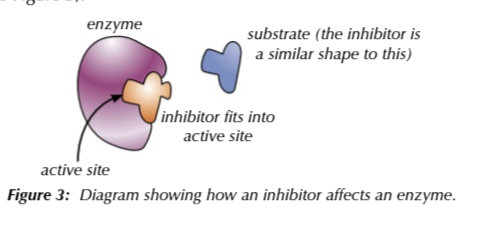
if there are more inhibitors to substrates
they will take up more active sites drastically decreasing the rate of reaction
the amount of inhibition is also affected by how strongly the inhibitor bonds
to the active site
some drugs are inhibitors that block the active site of an enzyme
to stop it from working
antibiotics block the active site of bacteria that helps make their cell wall
this causes theri cell wall to weaken till it bursts
active sites of enzymes are VERY specific
so its difficult to findd a drug molecule that will fit into the active site
DNA stands for
Deoxyribonucleic acid
DNA monomer
nucleotide
nucleotides are made up of 3 components
a phosphate group
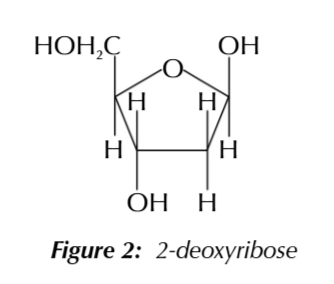
pentose sugar, 2-deoxyribose
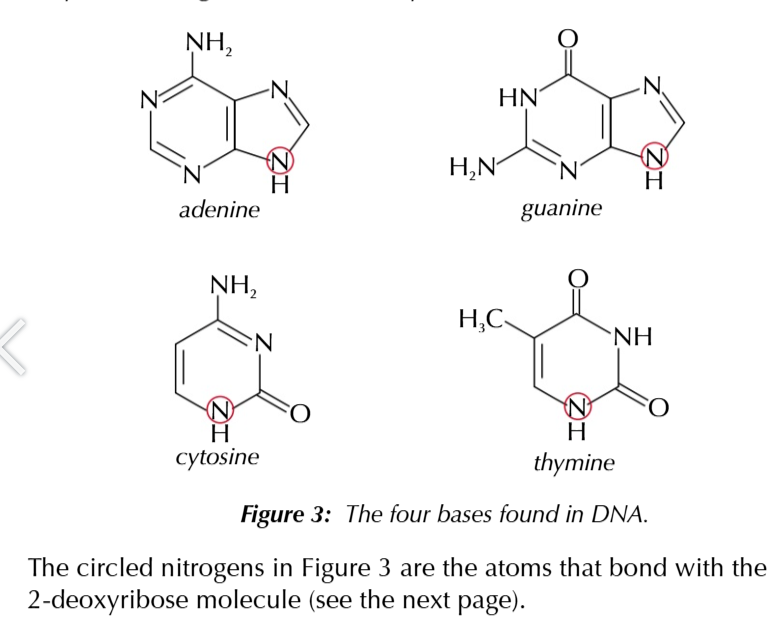
base
phosphate group is an ion with a negative charge
PO2(OH)2-
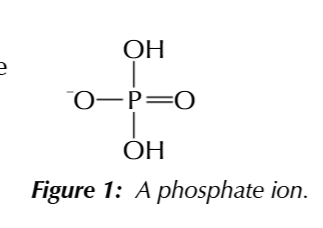
pentose sugar, sugars with 5 carbons
2-deoxyribose
bases
ADENINE N THYMINE, CYTOSIN N GUANINE
NUCEOTIDE STRUCTURE

nucleotide examples
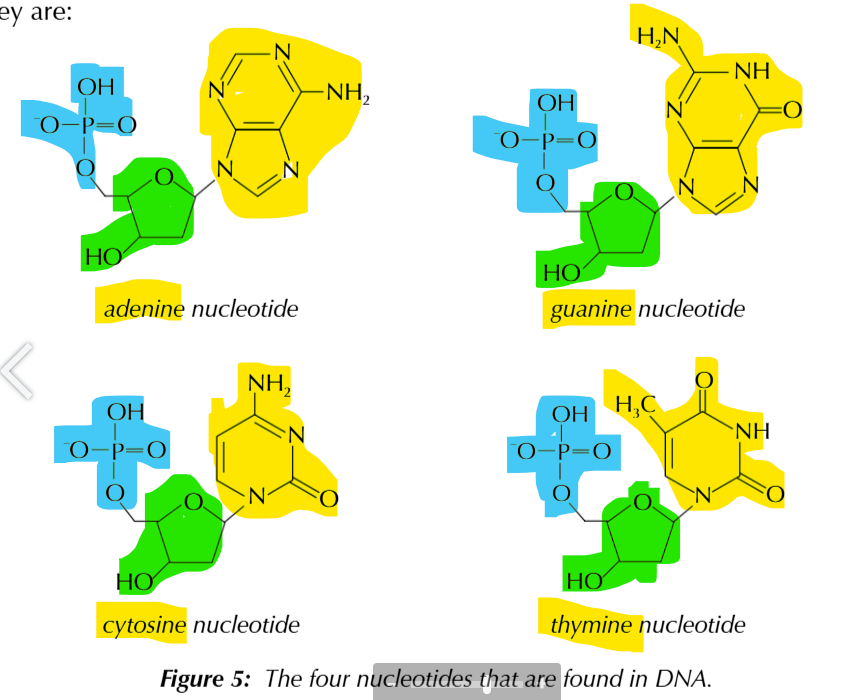
nucleotides join together to form polynucleotide chains
via sugar-phosphate backbone
a covalent bond is formed between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the sugar of another
this forms the sugar-phosphate backbone
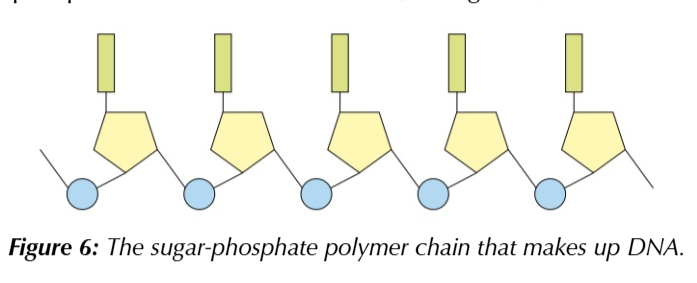
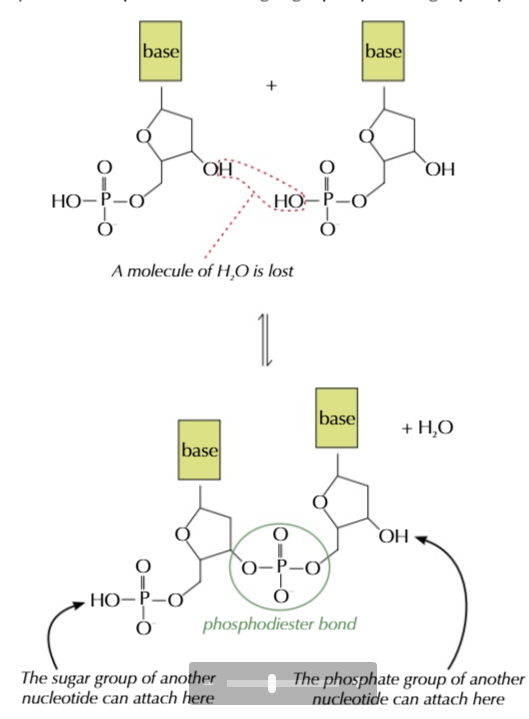
the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA is formed via condensation polymerisation
a water molecule is lost and a covalent phosphodiester bond is formed
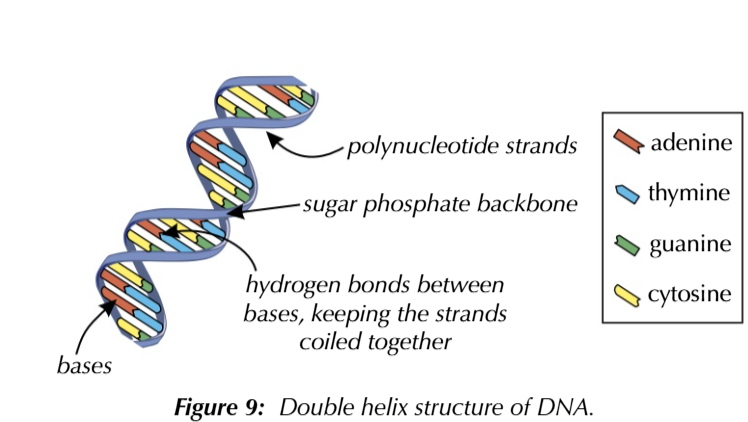
DNA is formed from 2 polynucleotide strands
they spiral together to form a double helix structure held by hydrogen bonds between bases
Adenine always COMPLIMENTARY to thymine A-T
guanine always COMPLIMENTARY to cytosine C-G
complimentary base pairing is due to the arrangement of atoms in the base molecules
which are capable of forming hydrogen bonds
hydrogen bonds
form between partial positive hydrogen atoms and partially negative oxygen/nitrogen/fluorine atoms which are the right distance apart
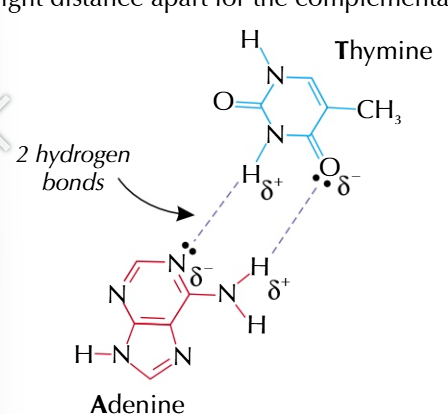
adenine and thymine can form 2 hydrogen bonds
guanine and cytosine can form 3 hydrogen bonds
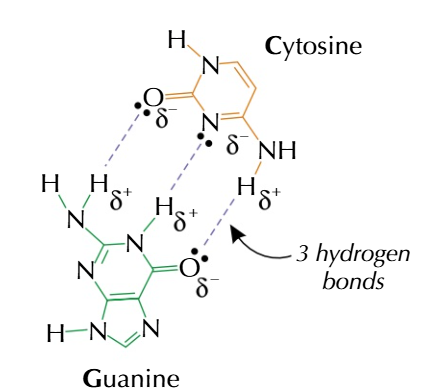
non complimentary base parings would put partialy charged atoms too close together making them repel
OR too far apart OR the bonding wouldnt line up properly
the double helix structure of DNA is important
as it twists so that the bases are in the right alignment and the right distance apart for the complementary base pairs to form
cisplatin
A platinum complex with 2 chloride ligands and 2 ammonia ligands
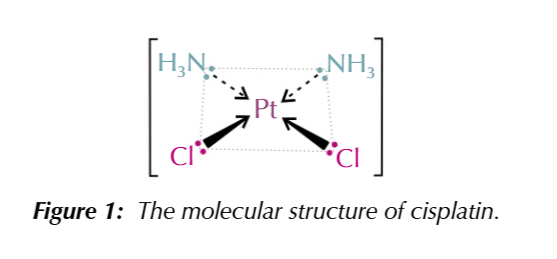
cisplatin is square planar, there are only 2 types of molecules attached ot Platinum making it CIS/TRANS
chloride ions are on the same plane to its a CIS molecule
cancer
caused when cells mutate and there is uncontrolled cell division forming tumours
inorder for cells to divide
Their DNA needs to replicate
2 strands of the DNA double helix must unwind
so they can be used as templates for DNA replication
Cisplantin stops DNA replication
thus halting uncontrolled cell division
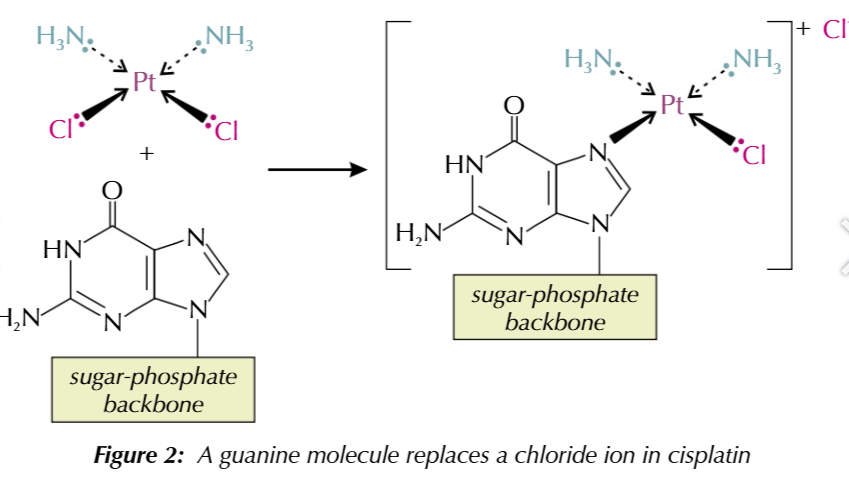
how cisplatin works PART 1:
a nitrogen atom on guanine base forms a coordinate bond with cisplatin’s platinum ion
the guanine base replaces a chloride ion ligand
this process is called ligand replacement reaction
how cisplatin works PART 2:
a second nitrogen atom on a different guanine base (from the same/opposite strand) replaces the second chloride ion in ligand substitution
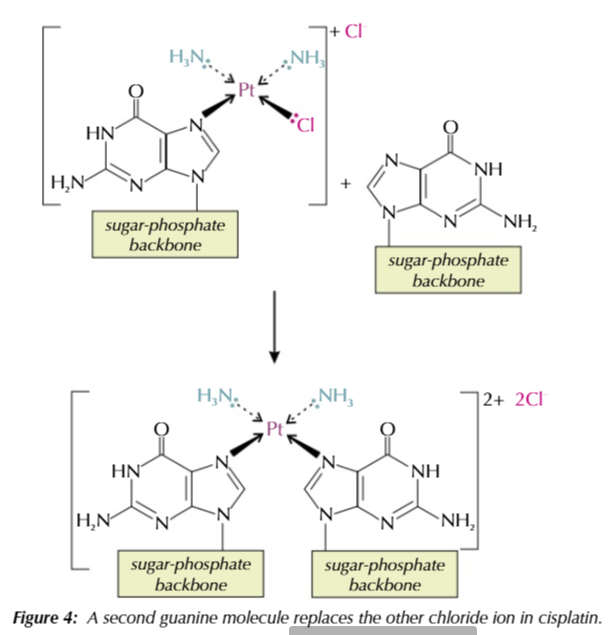
the presence of the cisplatin complex bound to the DNA strands cause the strand to kink
this means the DNA strands can’t unwind and be copied properly so cannot replicate
UNFORTUNATELY cisplatin binds to the DNA of healthy cells aswell and tumour cells
this is a problem for healthy cells that undergo replication frequently like hair cells and blood cells
cisplatin stops healthy cells from replicating the same wat is stops tumour cells
this means cisplatin can cause hair loss and supress the immune system, which is controlled by white blood cells and cause kidney damage
these side effects can be lessened by giving patients LOW dosages of Cisplatin
they can also be reduced by targeting the tumour cells directly so healthy cells aren’t attacked
cisplatin is still used as chemotherapy
because the long term advantages outweight the short term disadvantages