Overview of the Nervous System and Its Functions
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms

Capable of dividing.
Glial Cells
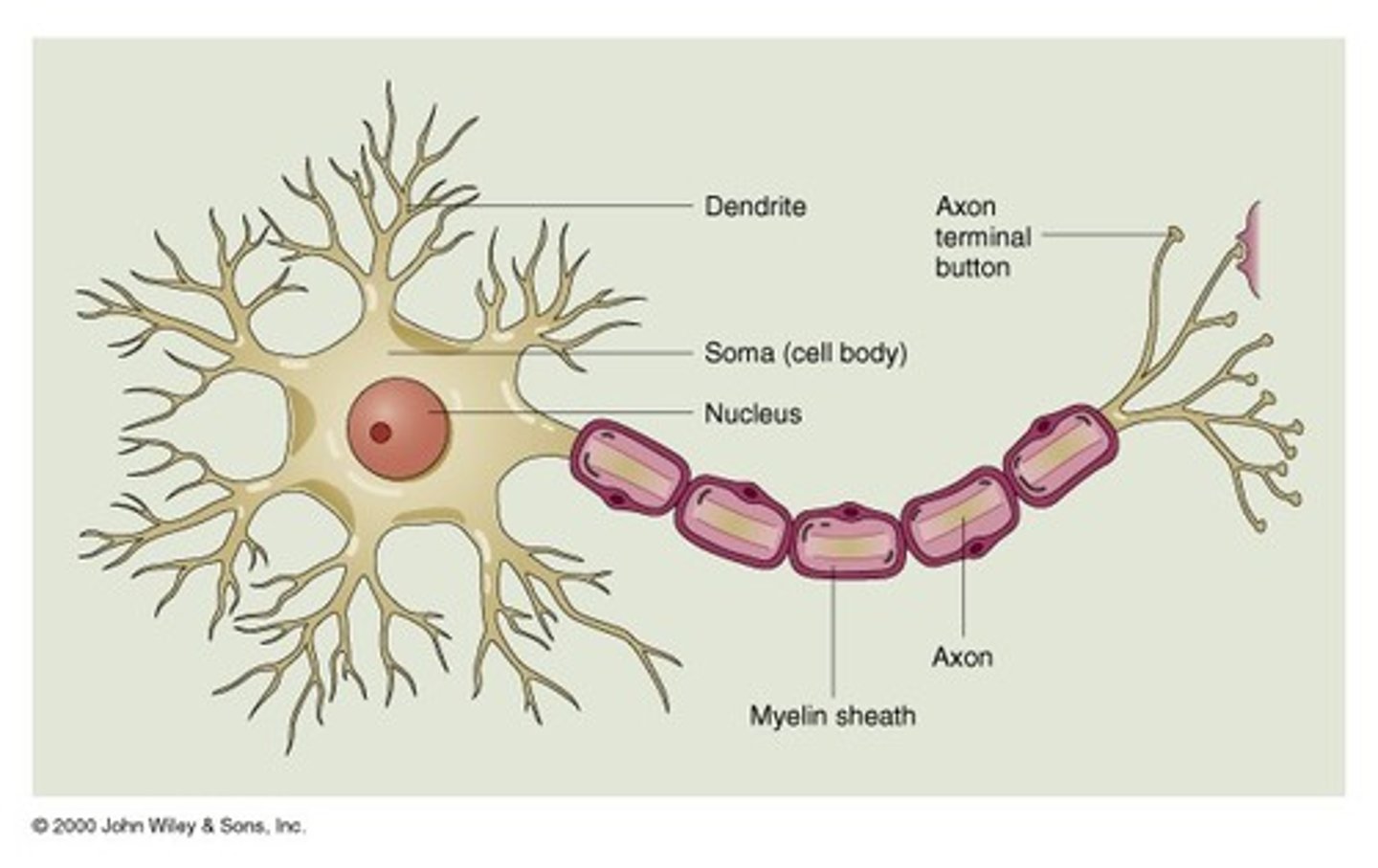
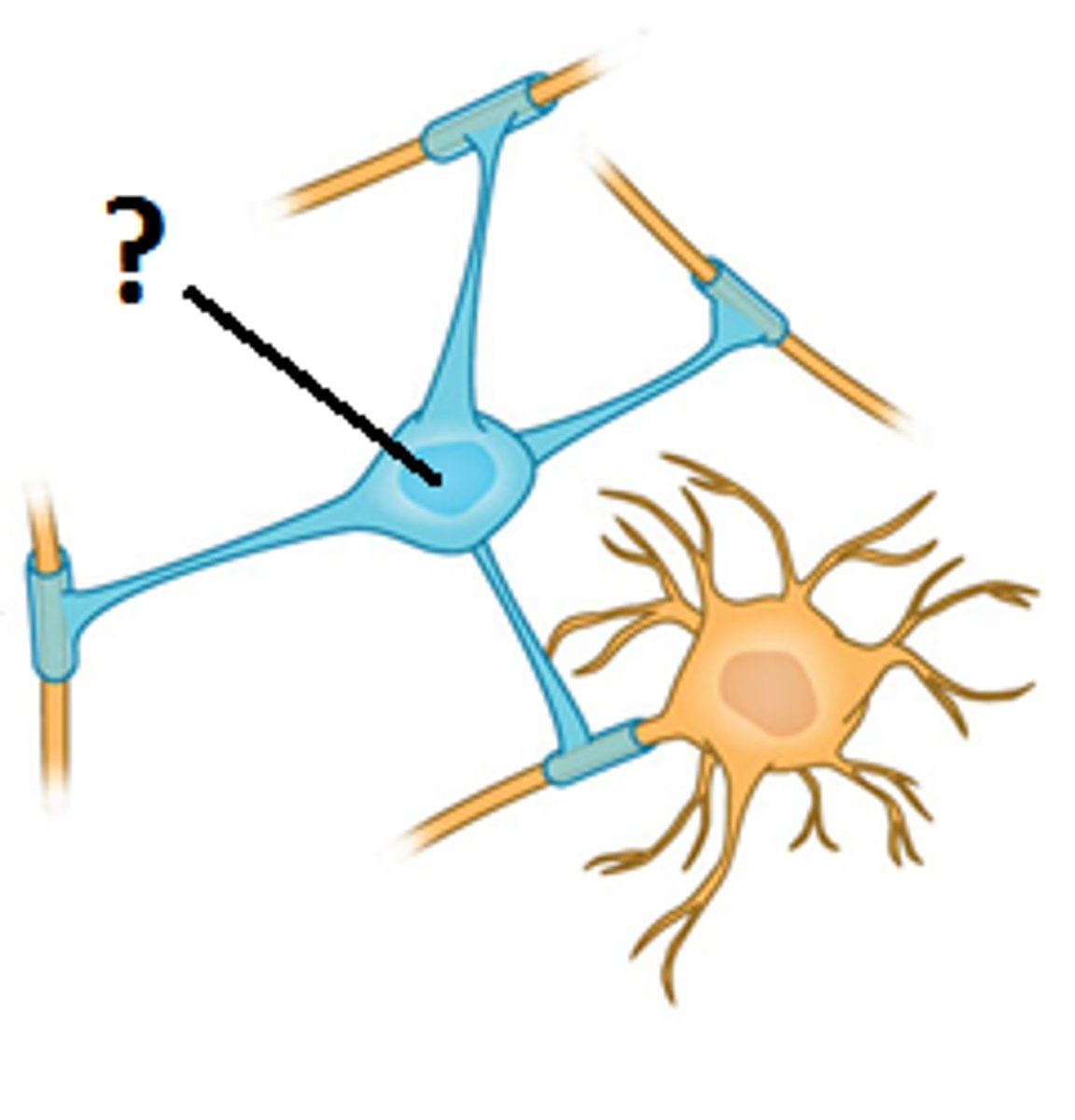
Consists of several dendrites, single branched axon, and cell body (soma) - cannot divide.
Neuron
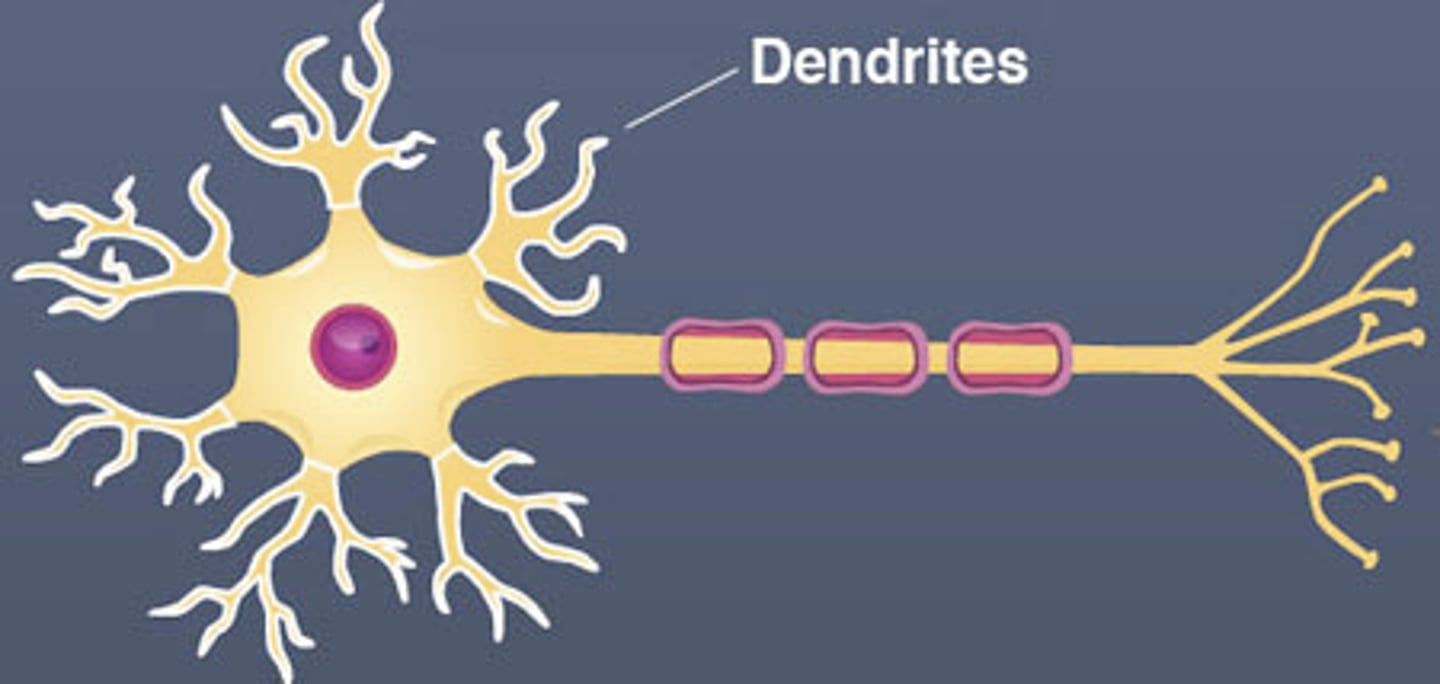
Receive information to transfer to cell body.
Dendrites
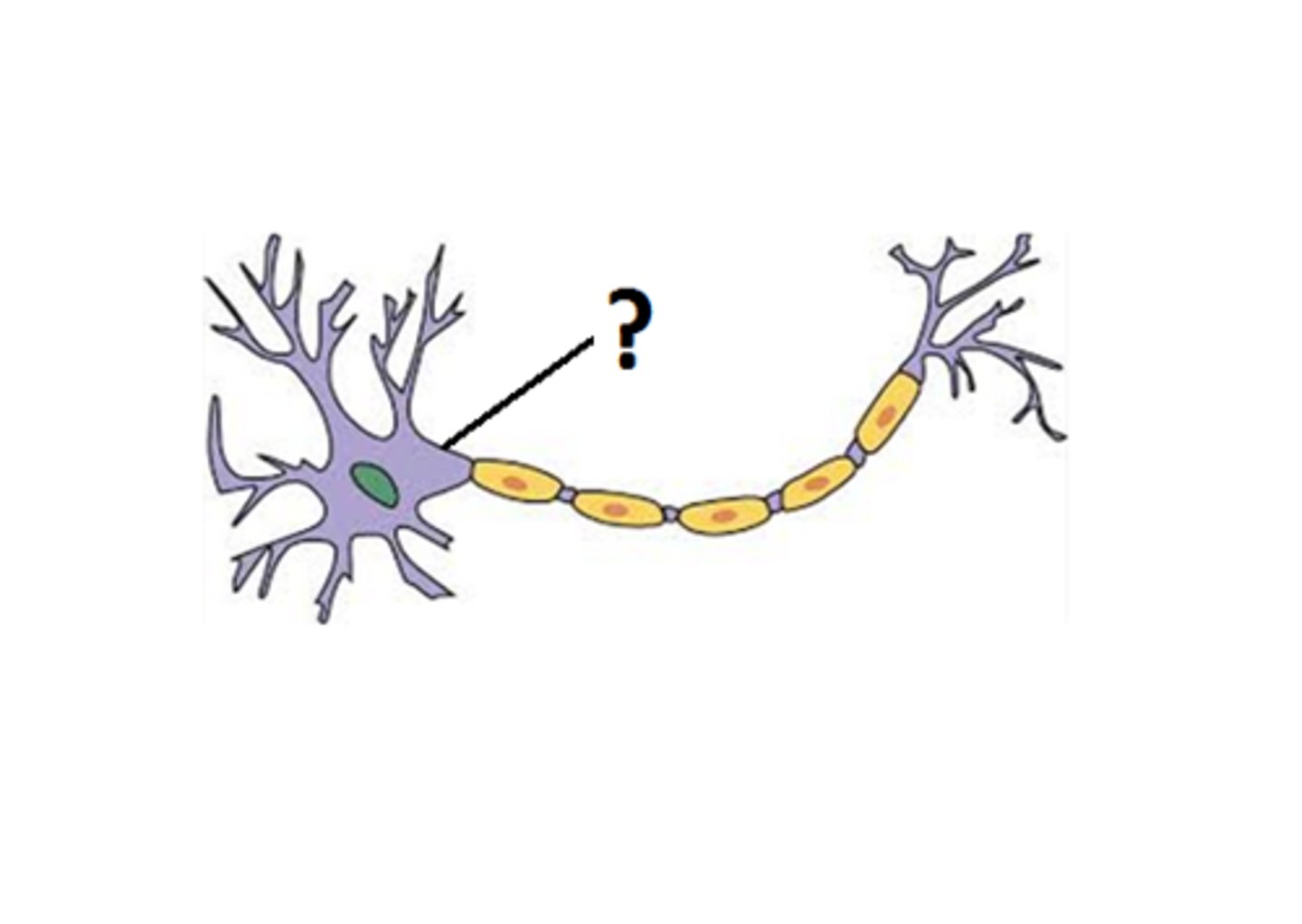
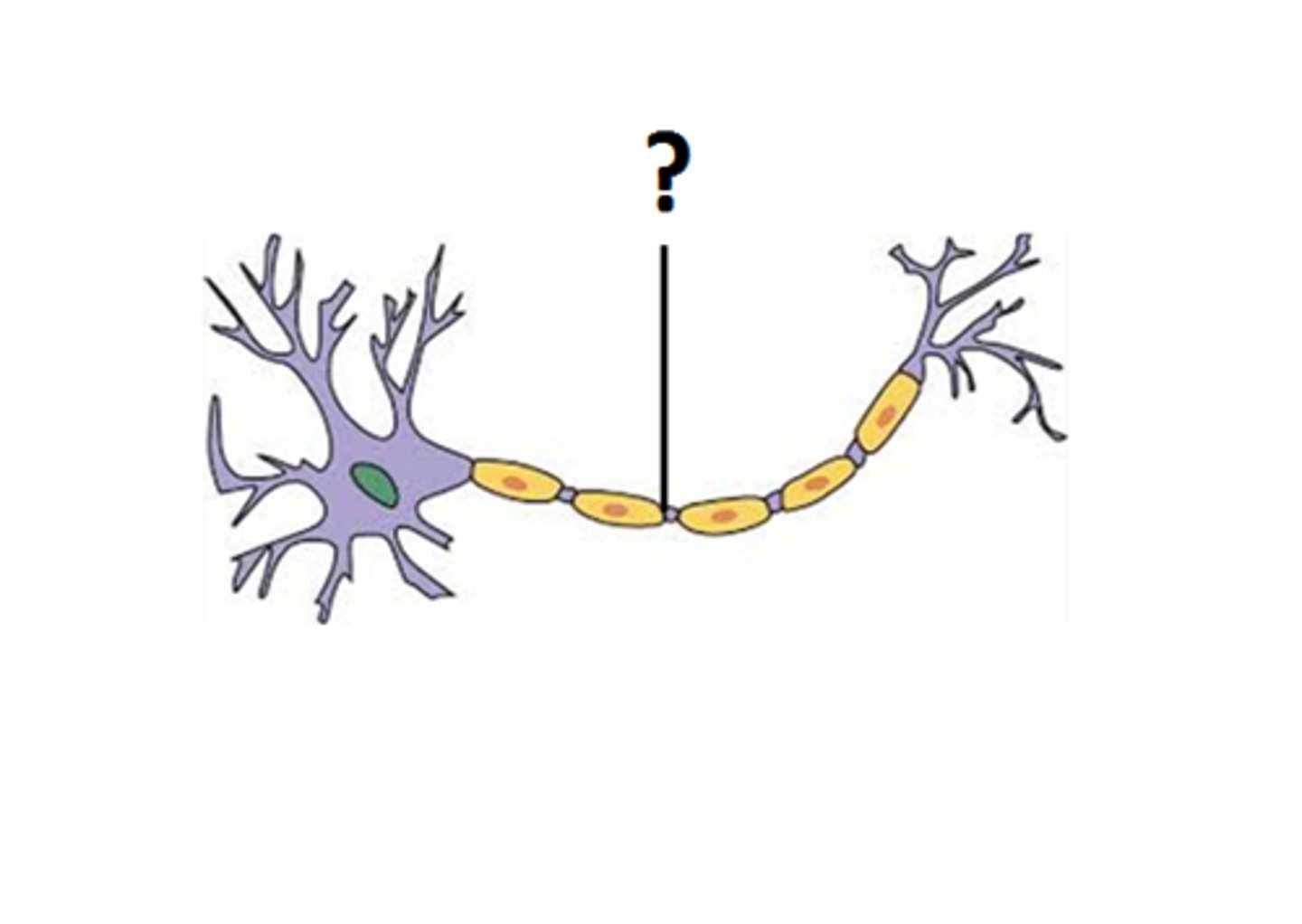
Site of action potential generation.
Axon Hillock
Transfer impulses away from cell body.
Axon
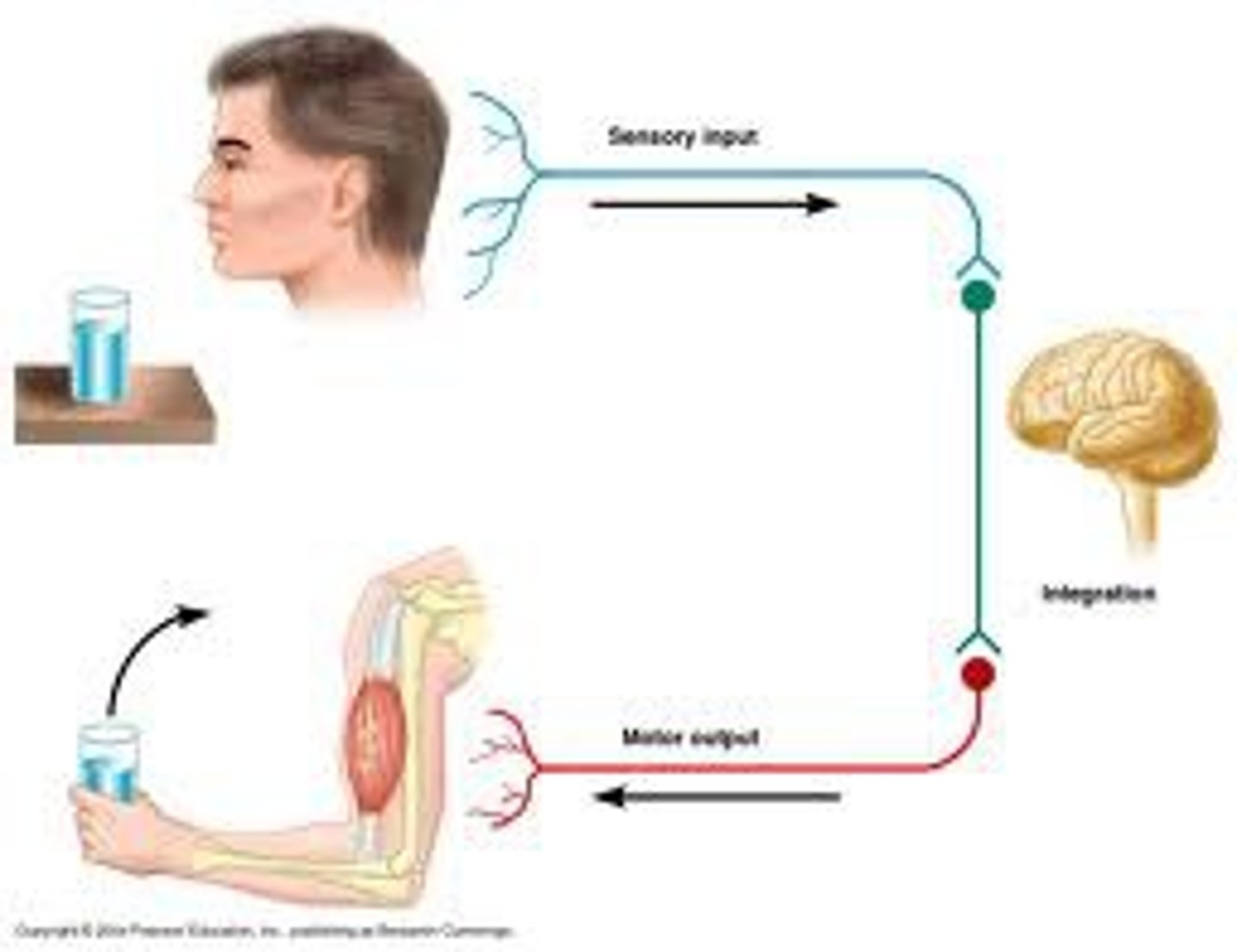
Receive initial stimulus from environment.
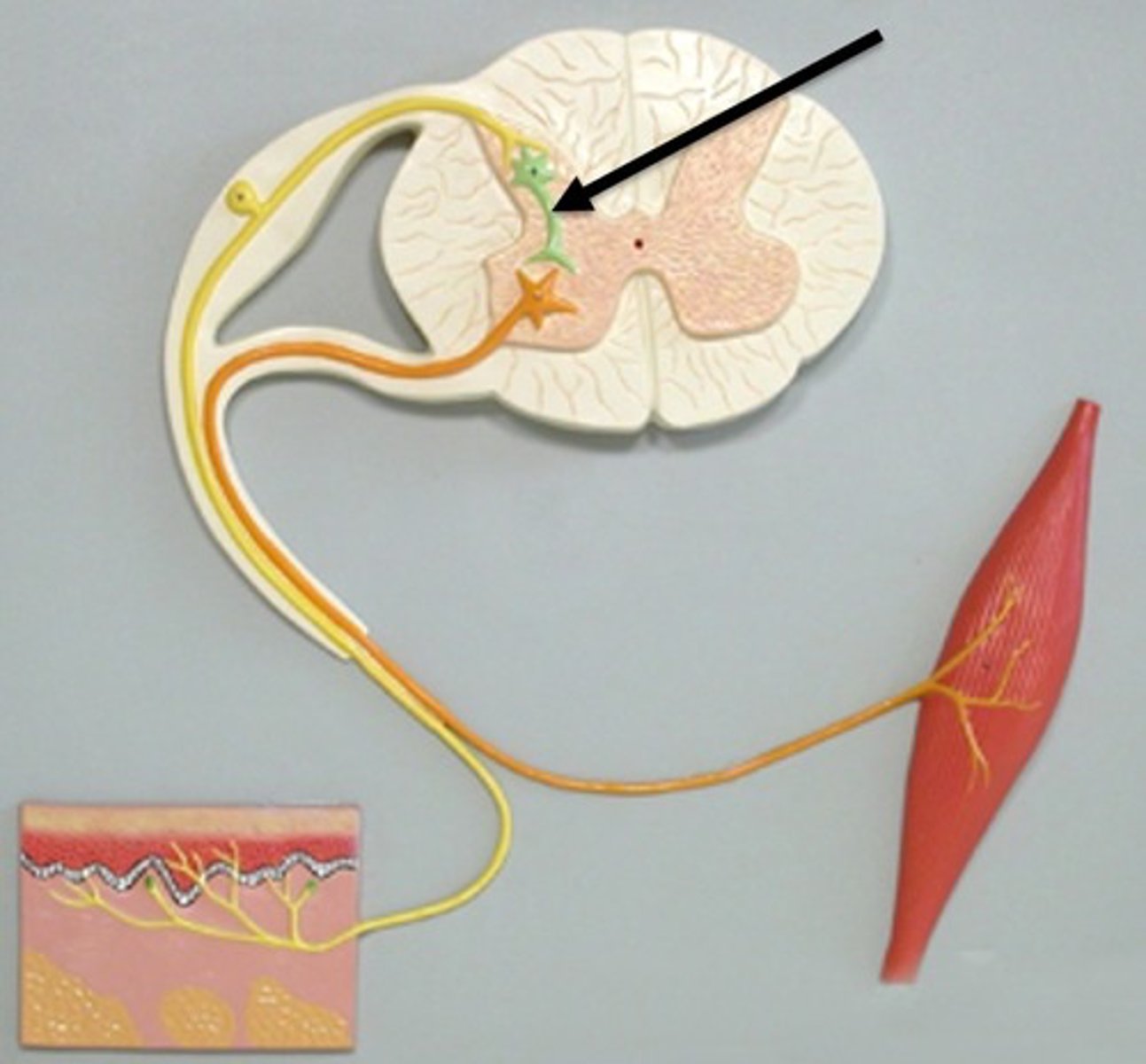
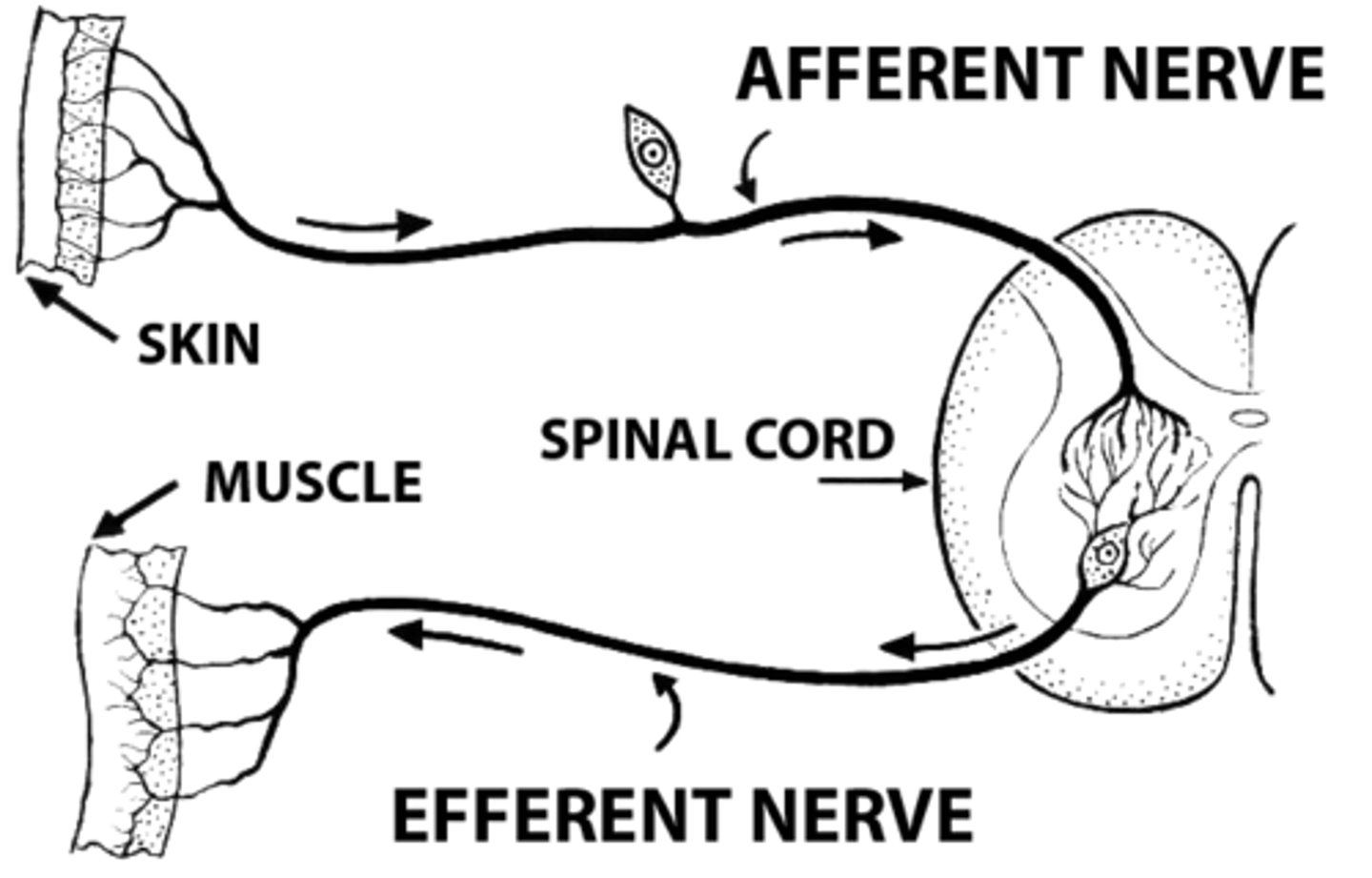
Sensory (Afferent)
Receive input from sensory and send to motor neuron - Make up 99% of the body's neurons.
Association (Interneuron)
From brain, stimulate target cells (effectors) to elicit response.
Motor (Efferent)
Produce myelin in CNS.
Oligodendrocytes
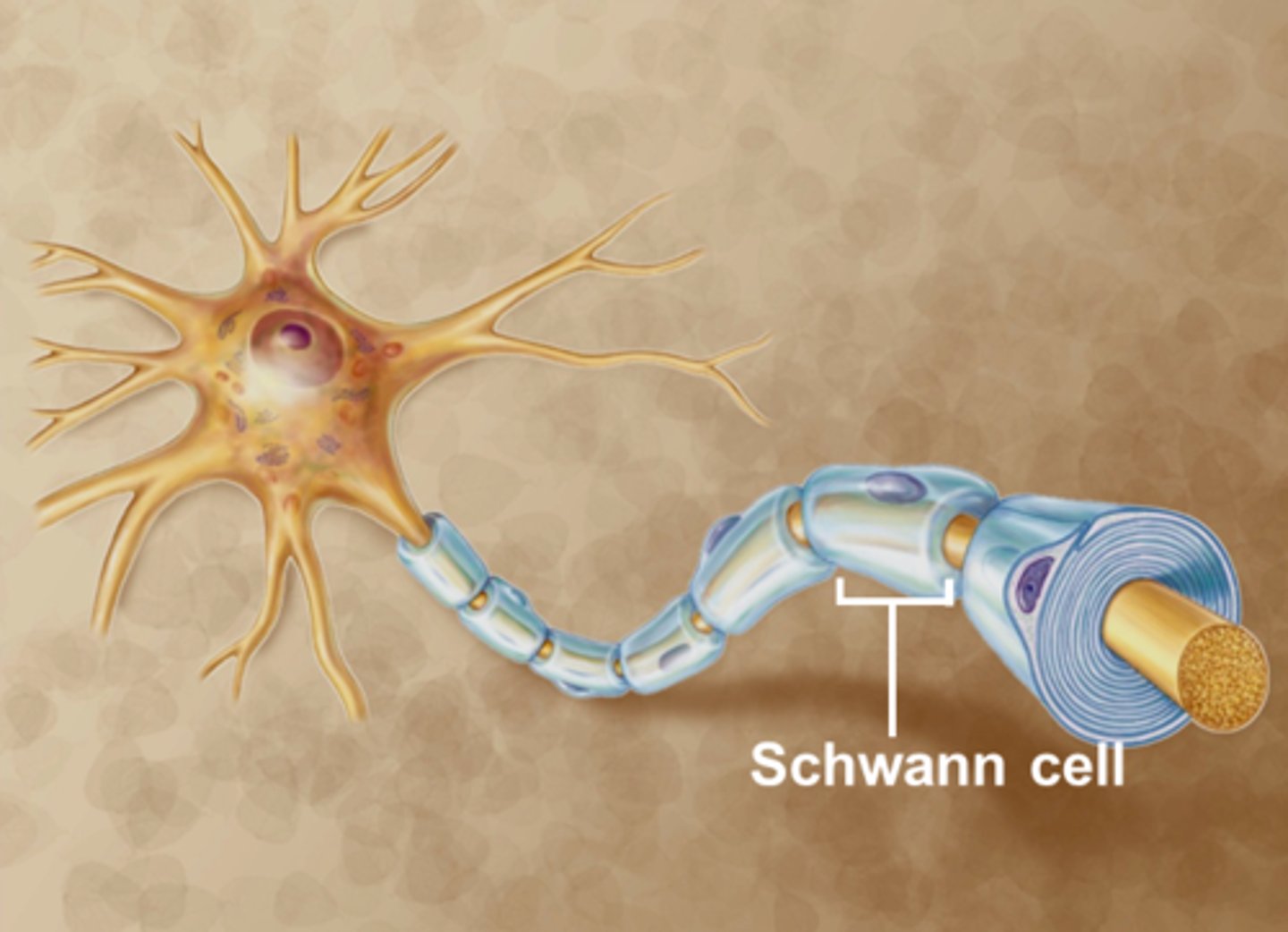
Produce myelin in PNS.
Schwann cells
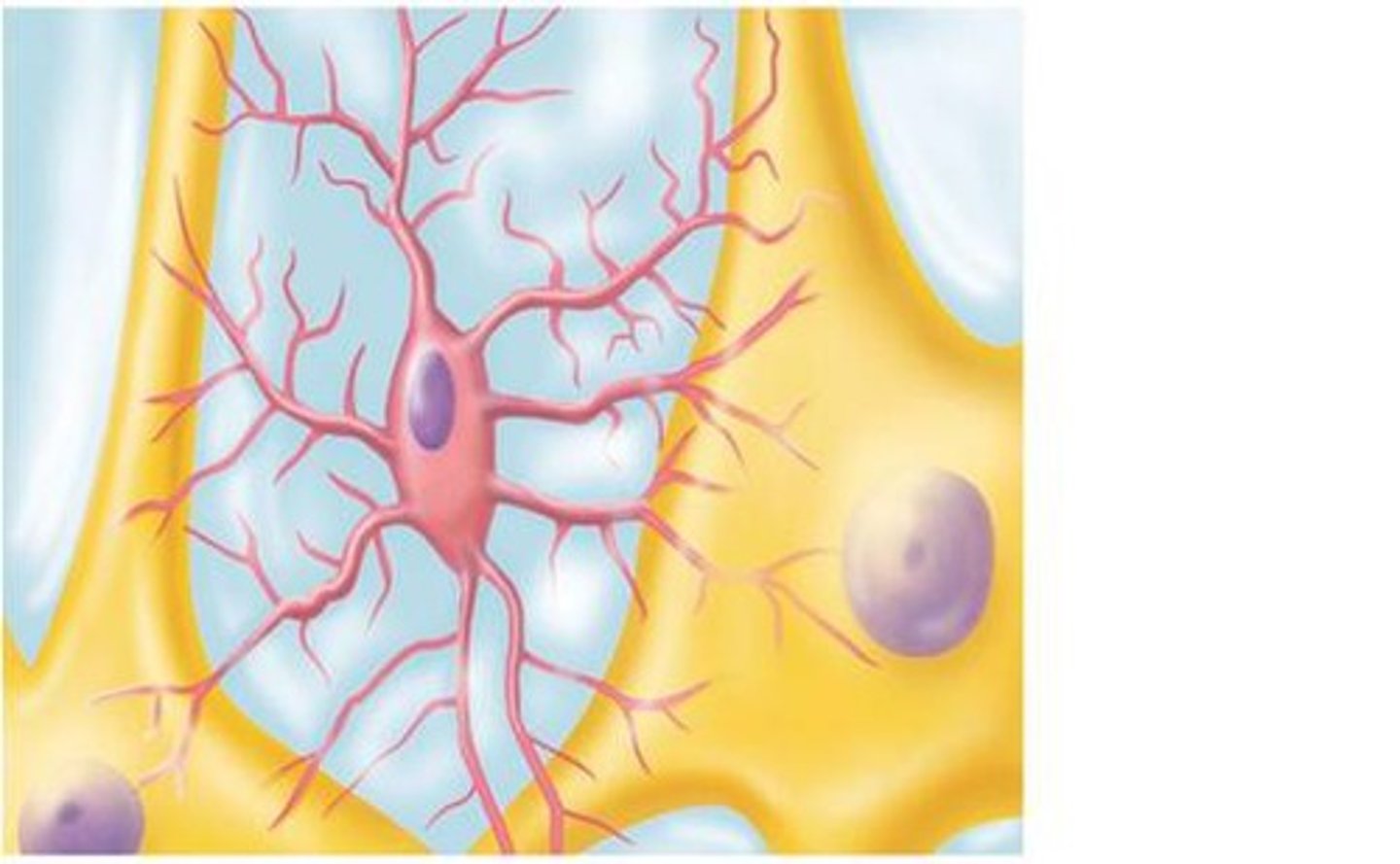
CNS phagocytes.
Microglia
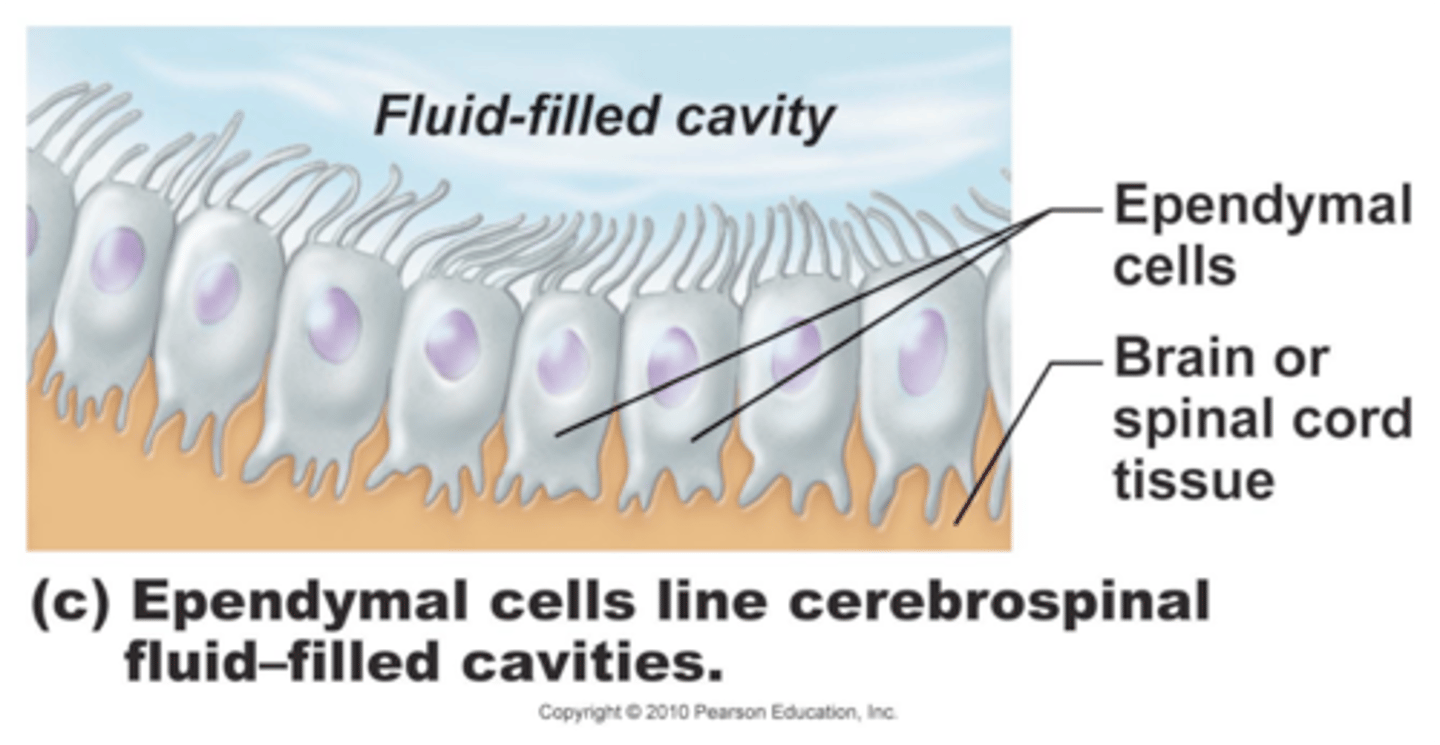
Circulate CSF with cilia.
Ependymal cells
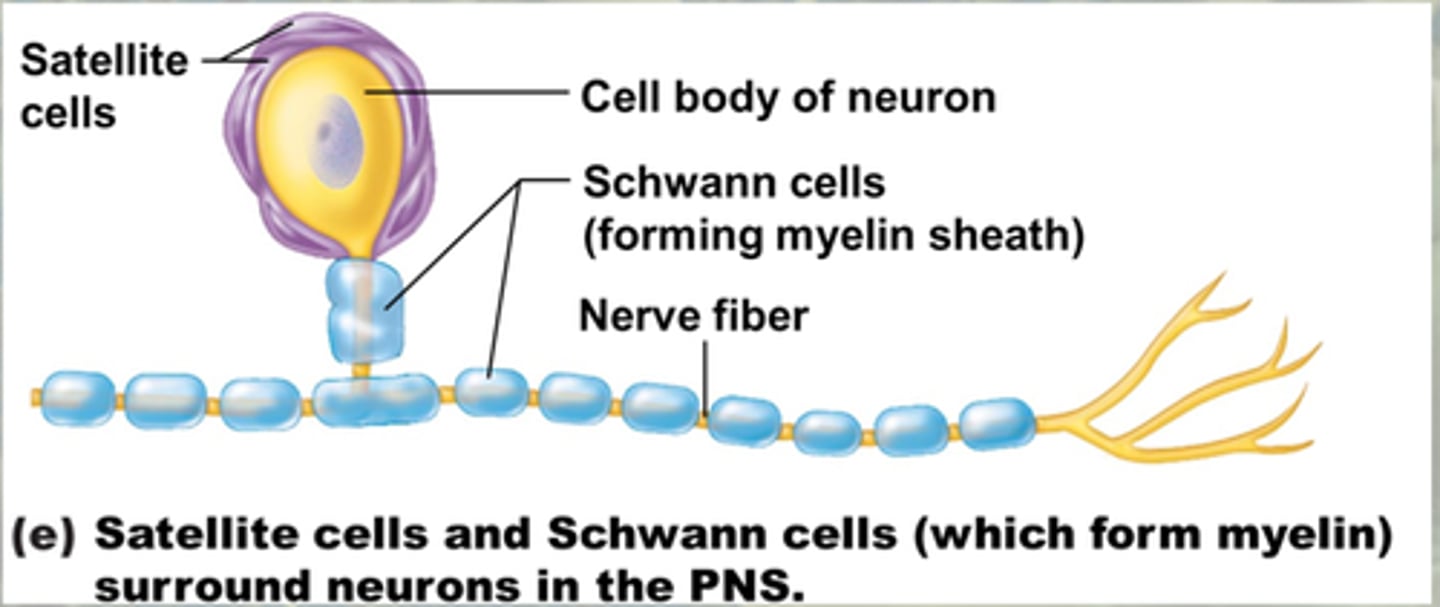
Support cells in PNS.
Satellite cells
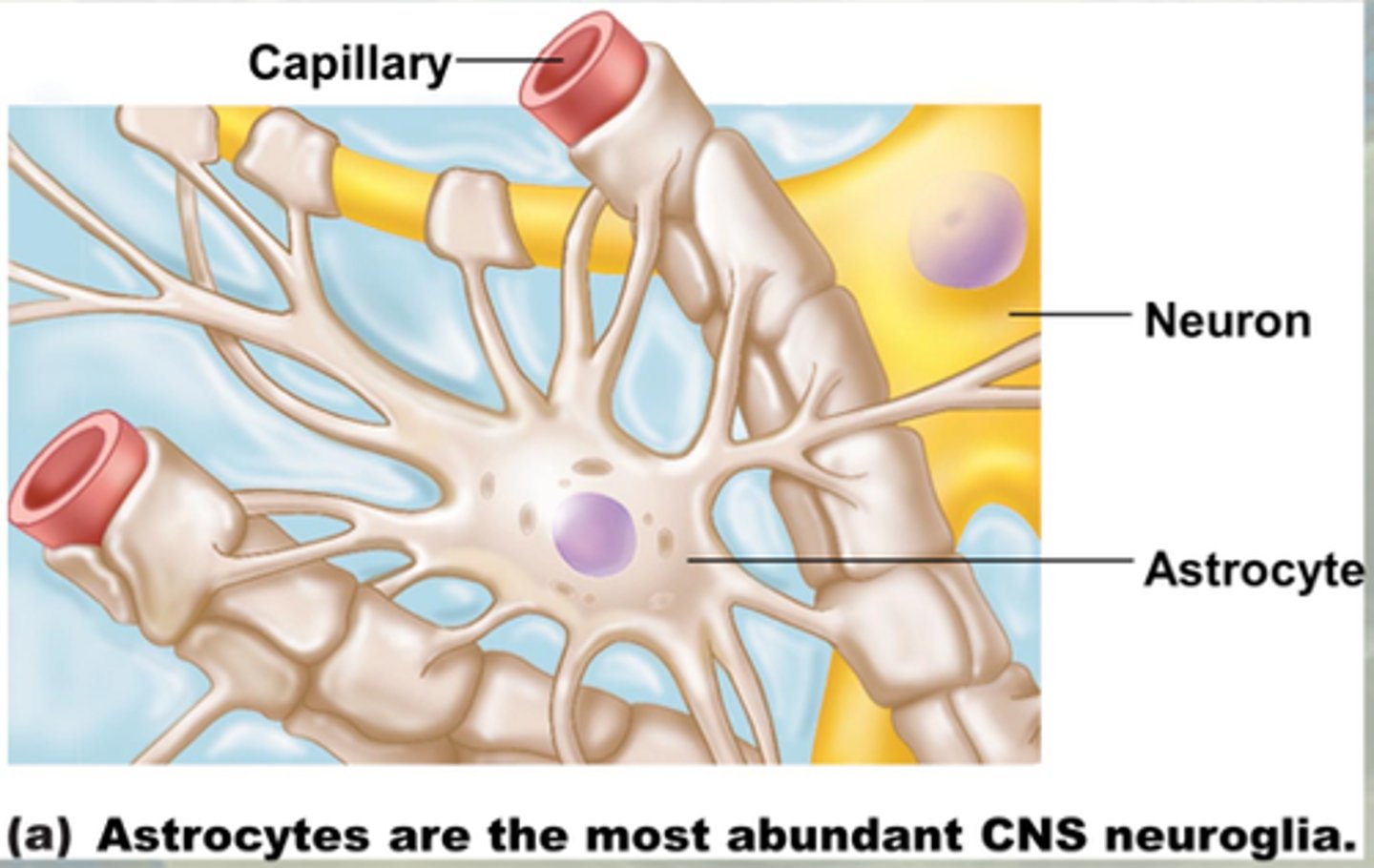
Physically support CNS neurons; maintain nutrient and mineral balance.
Astrocytes
Utilizes preganglionic/postganglionic axons, various neurotransmitters, and differing receptors to act on the effector organs (targets).
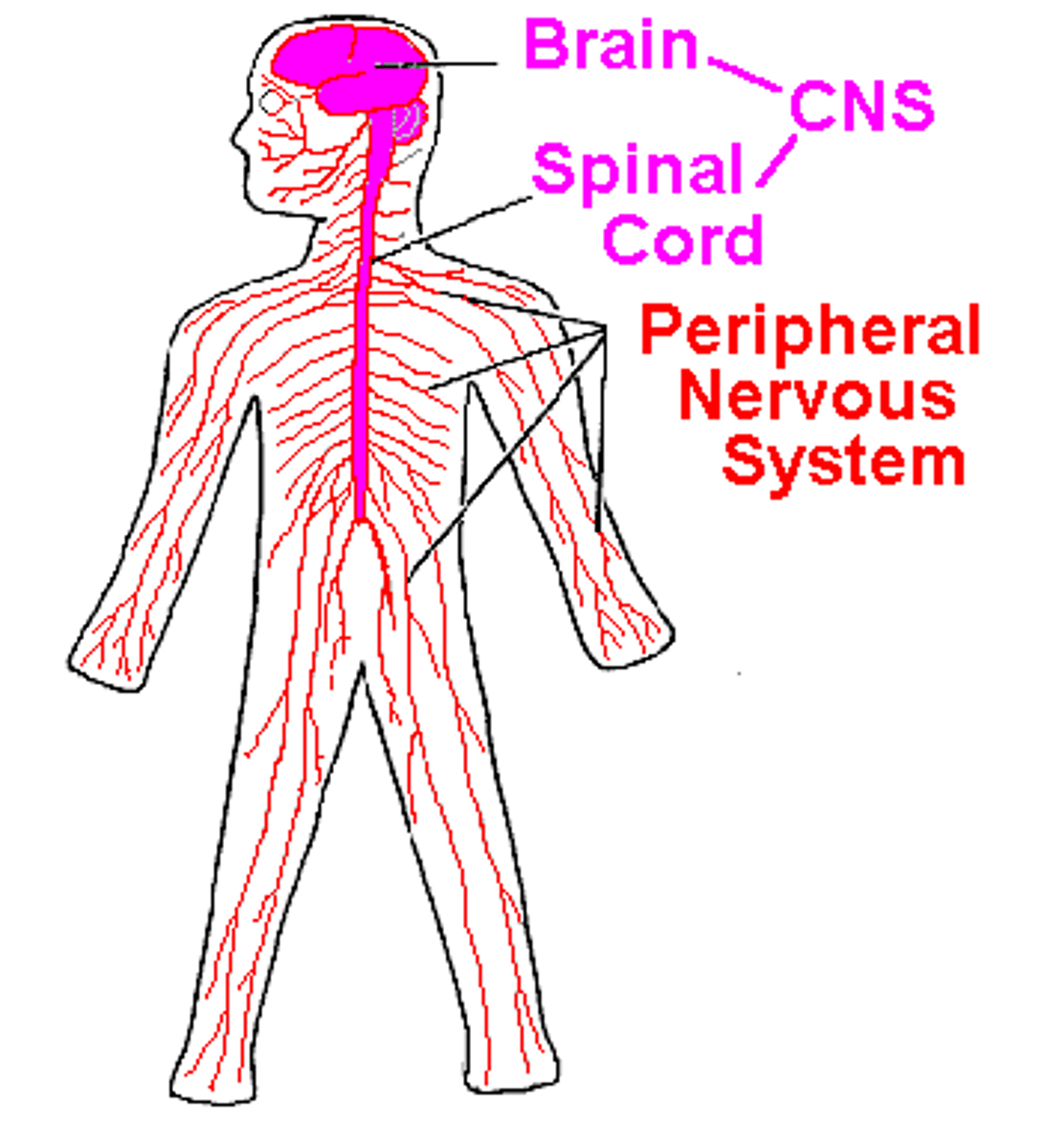
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
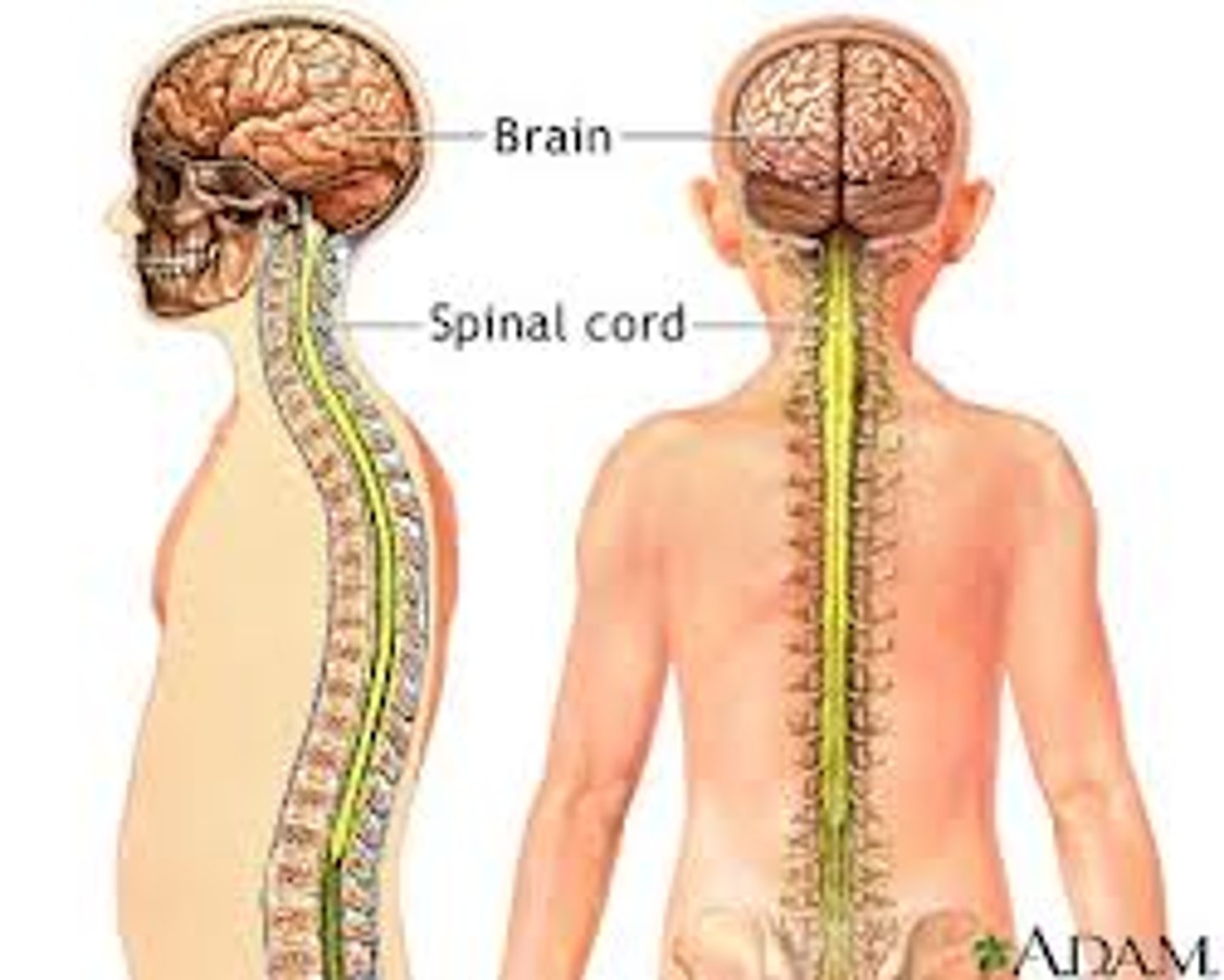
Contains the brain, spinal cord, and interneurons.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
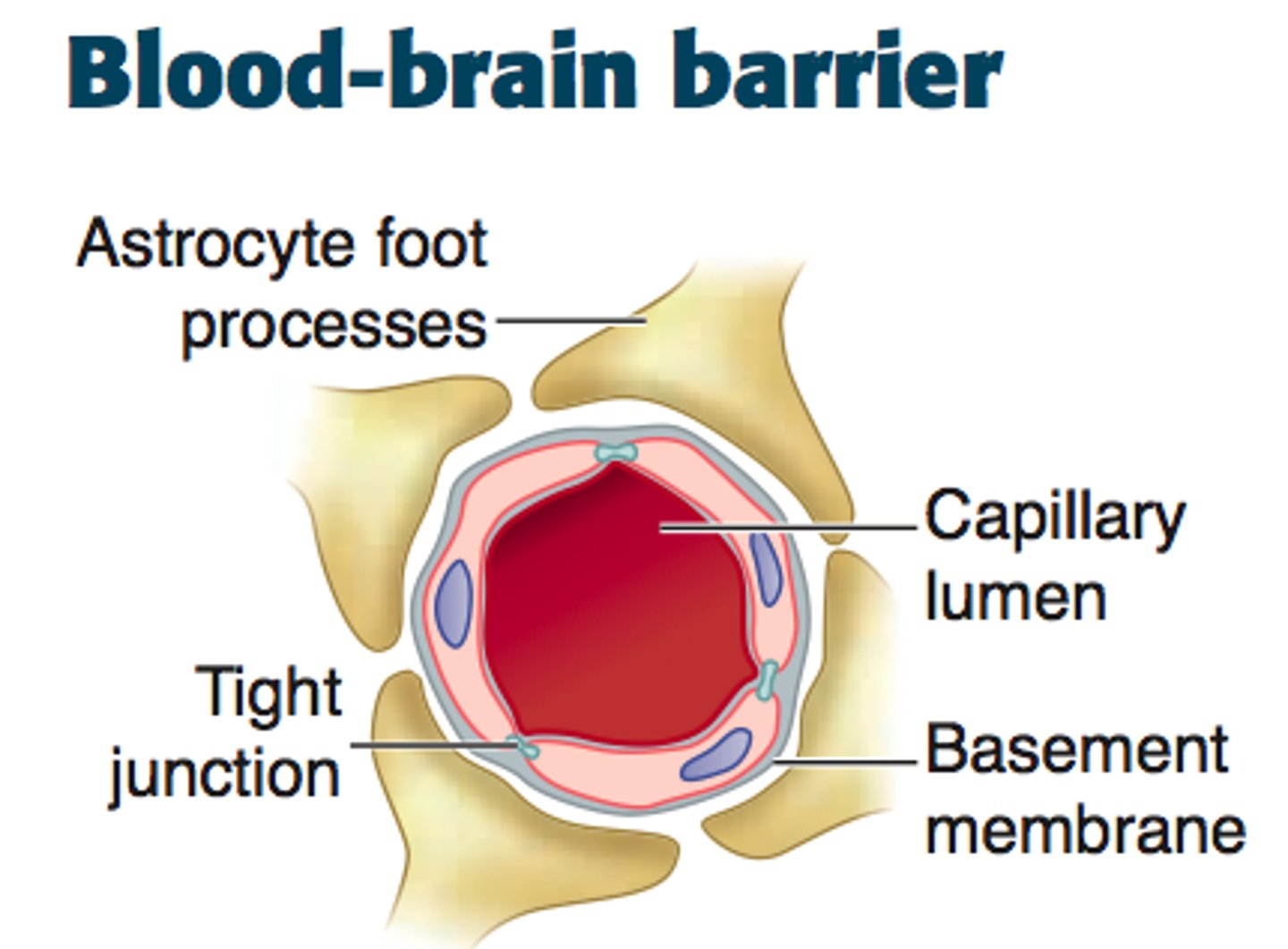
A blockade of cells that prevents or slows the passage of drugs, ions, and pathogens into the CNS; permeable to O2, CO2, glucose, and small non-polar molecules.
Blood-brain barrier
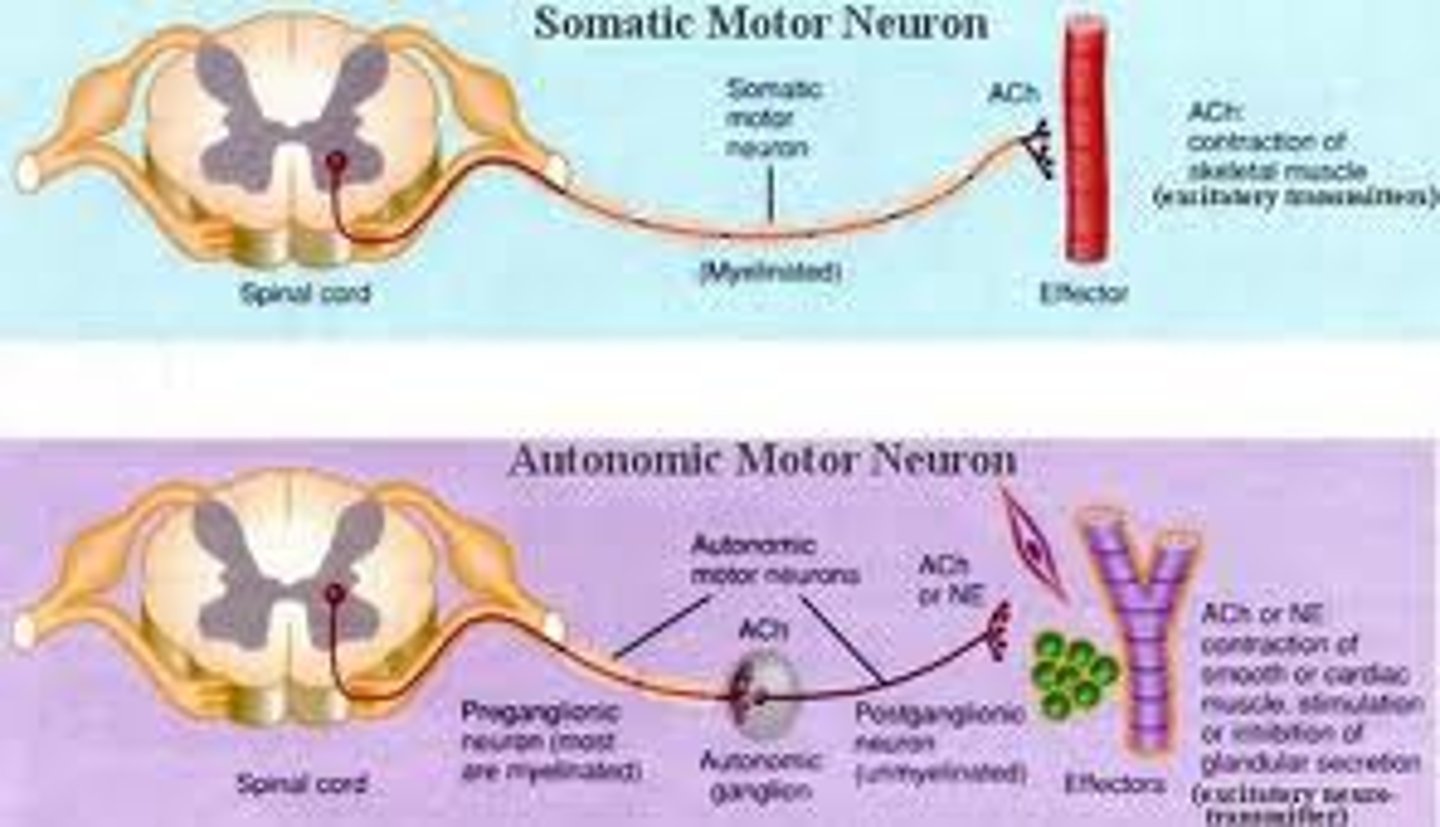
Innervates skeletal muscle; voluntary or involuntary movements; uses ACh at neuromuscular junctions.
Somatic Nervous System
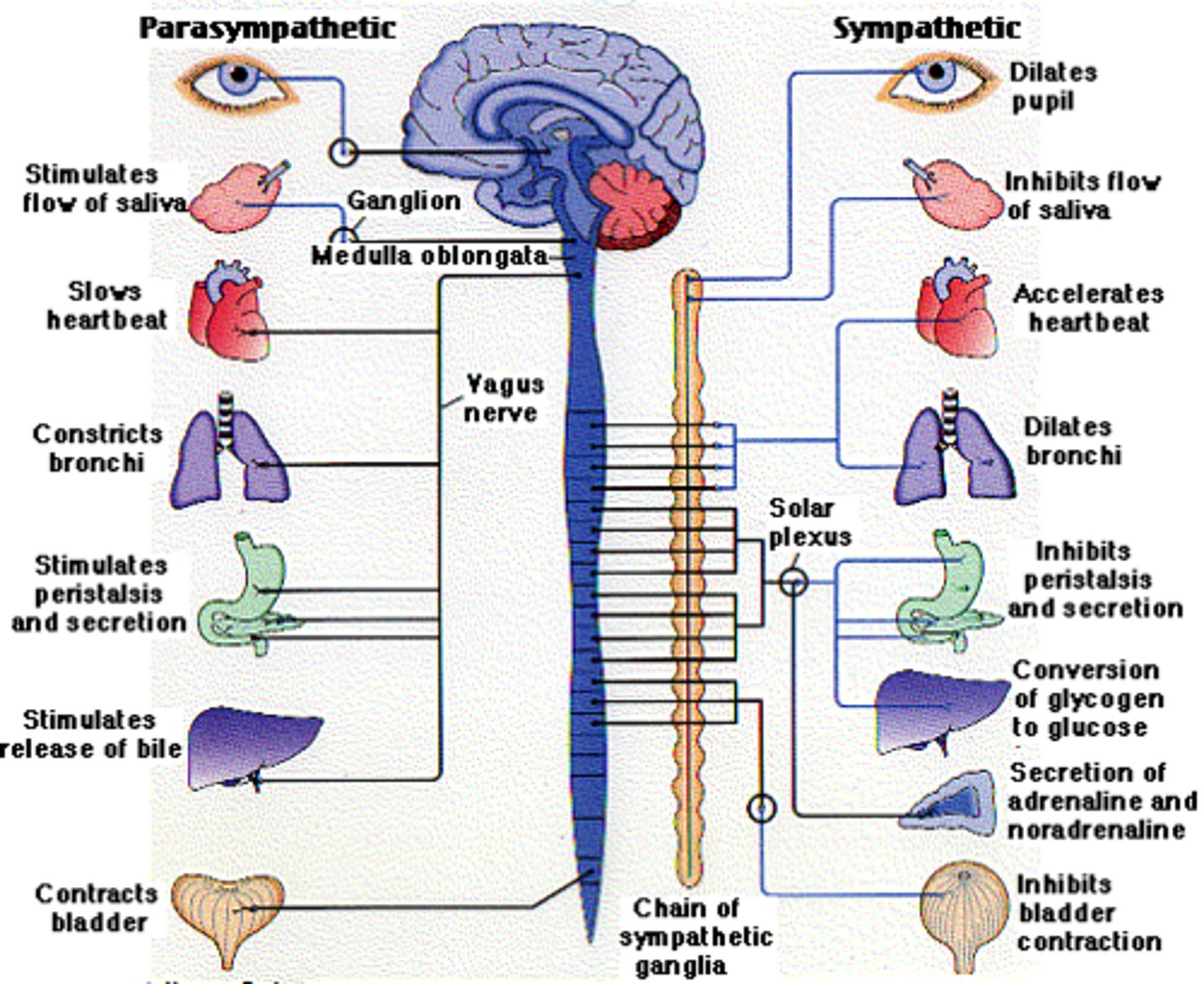
Regulates involuntary bodily functions.
Autonomic Nervous System
Involved in fight or flight response; increases blood pressure & heart rate, ejaculation, generation of energy; inhibits digestion, urination, and salivary secretion.
Sympathetic Branch
Rest and digest
• Lowered heart rate
• Increased digestion, relaxation,
and sexual arousal
Parasympathetic branch
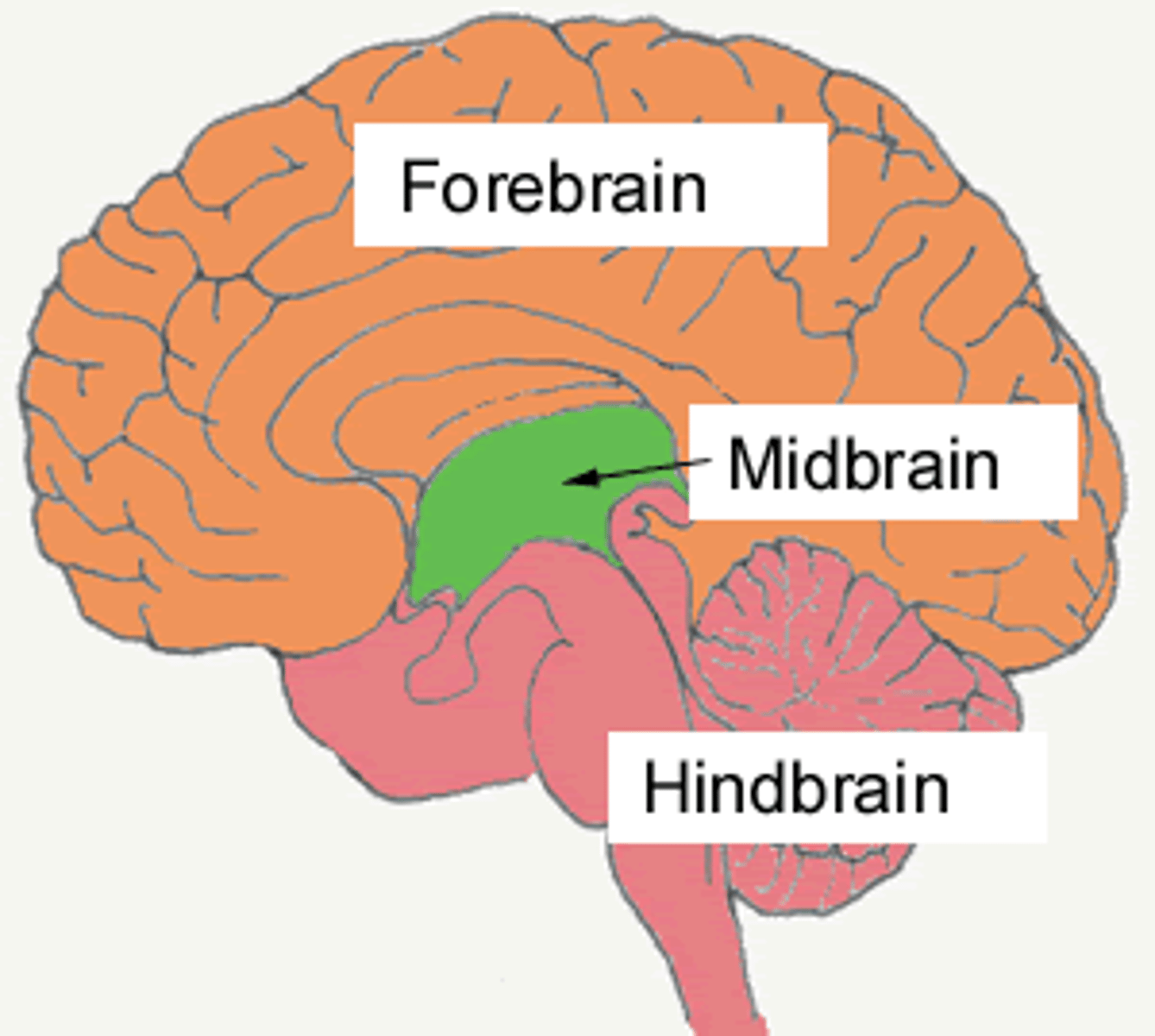
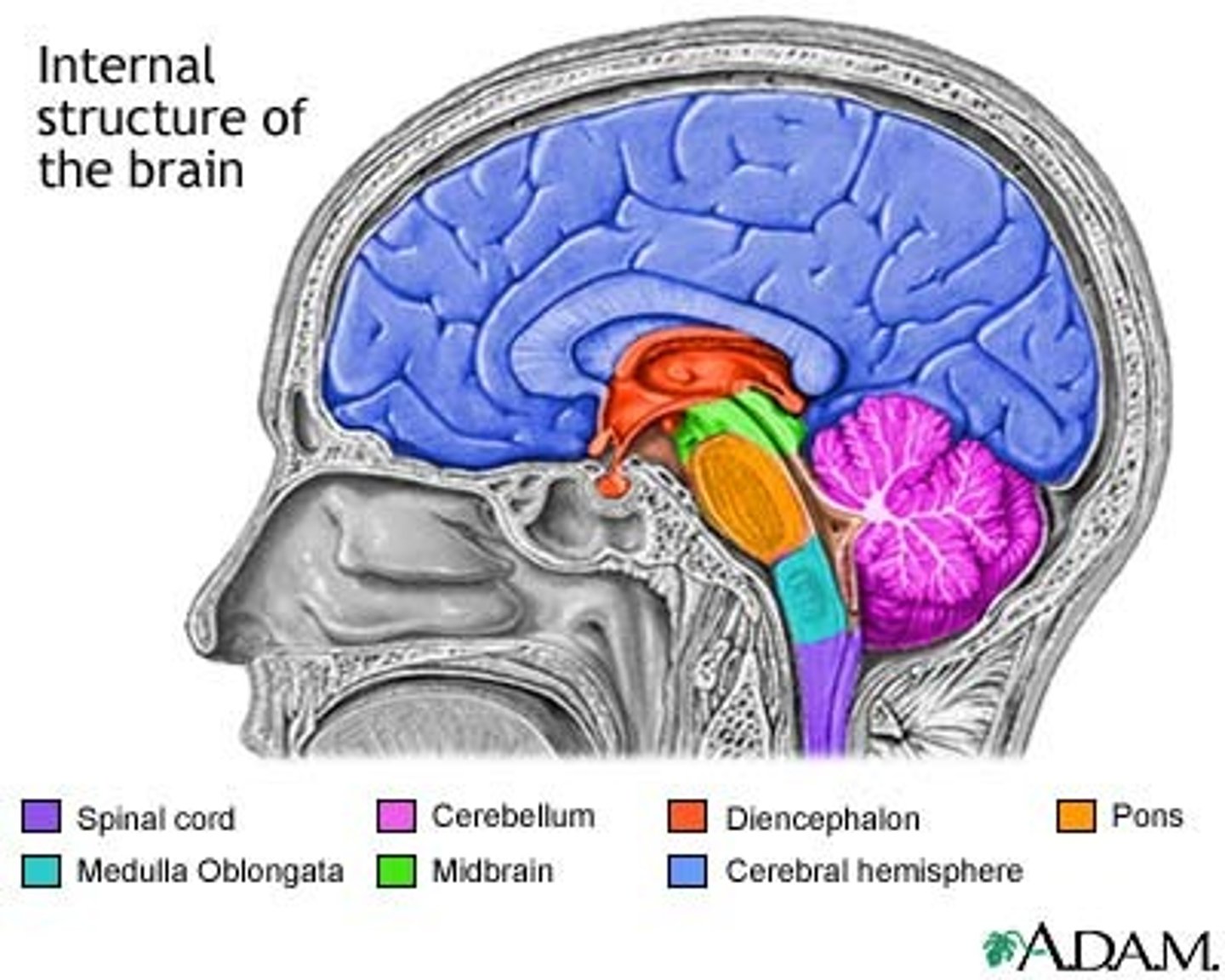
Largest part of the brain.
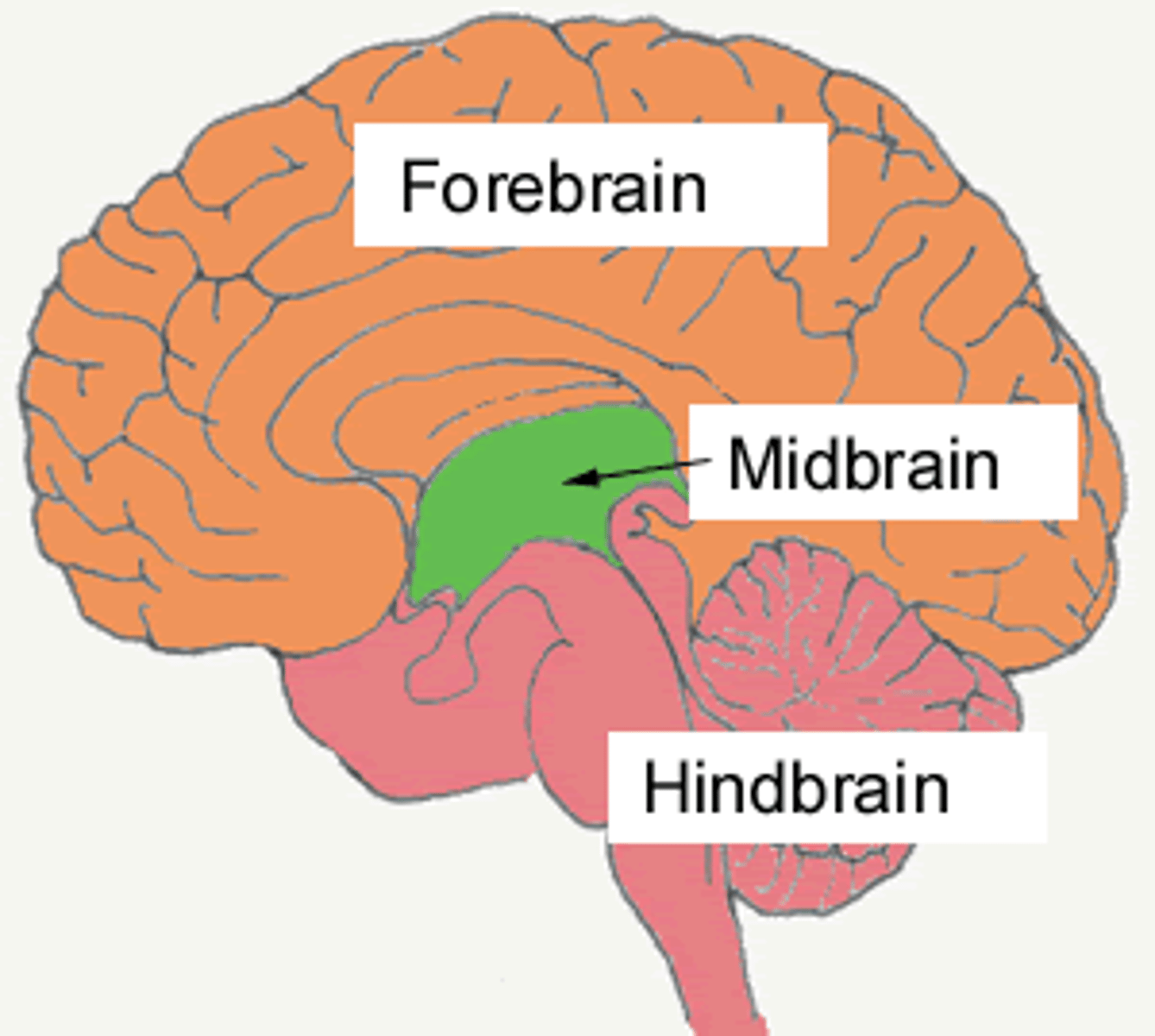
Forebrain
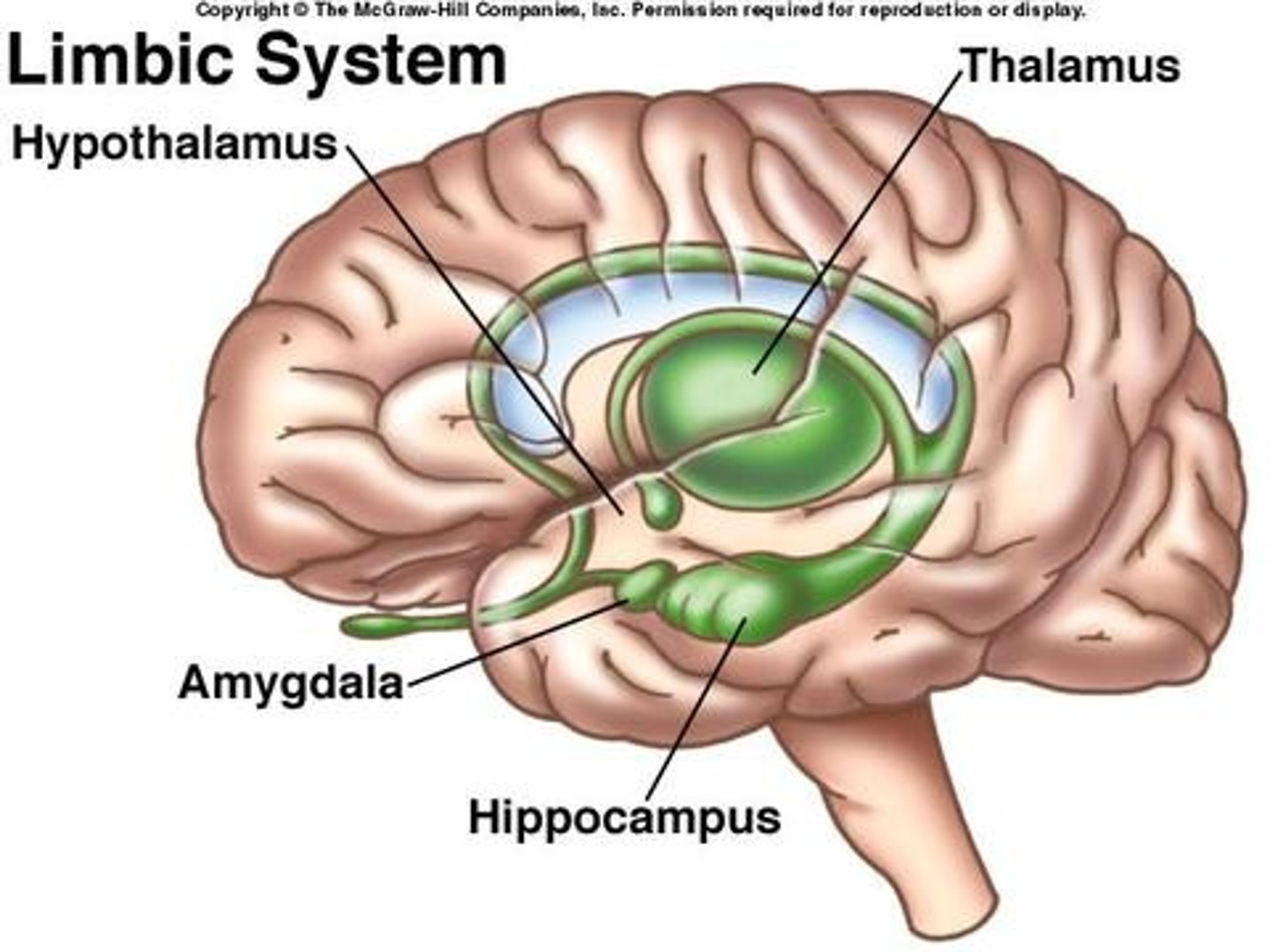
Includes hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus; responsible for behavioral and emotional responses.
Limbic system
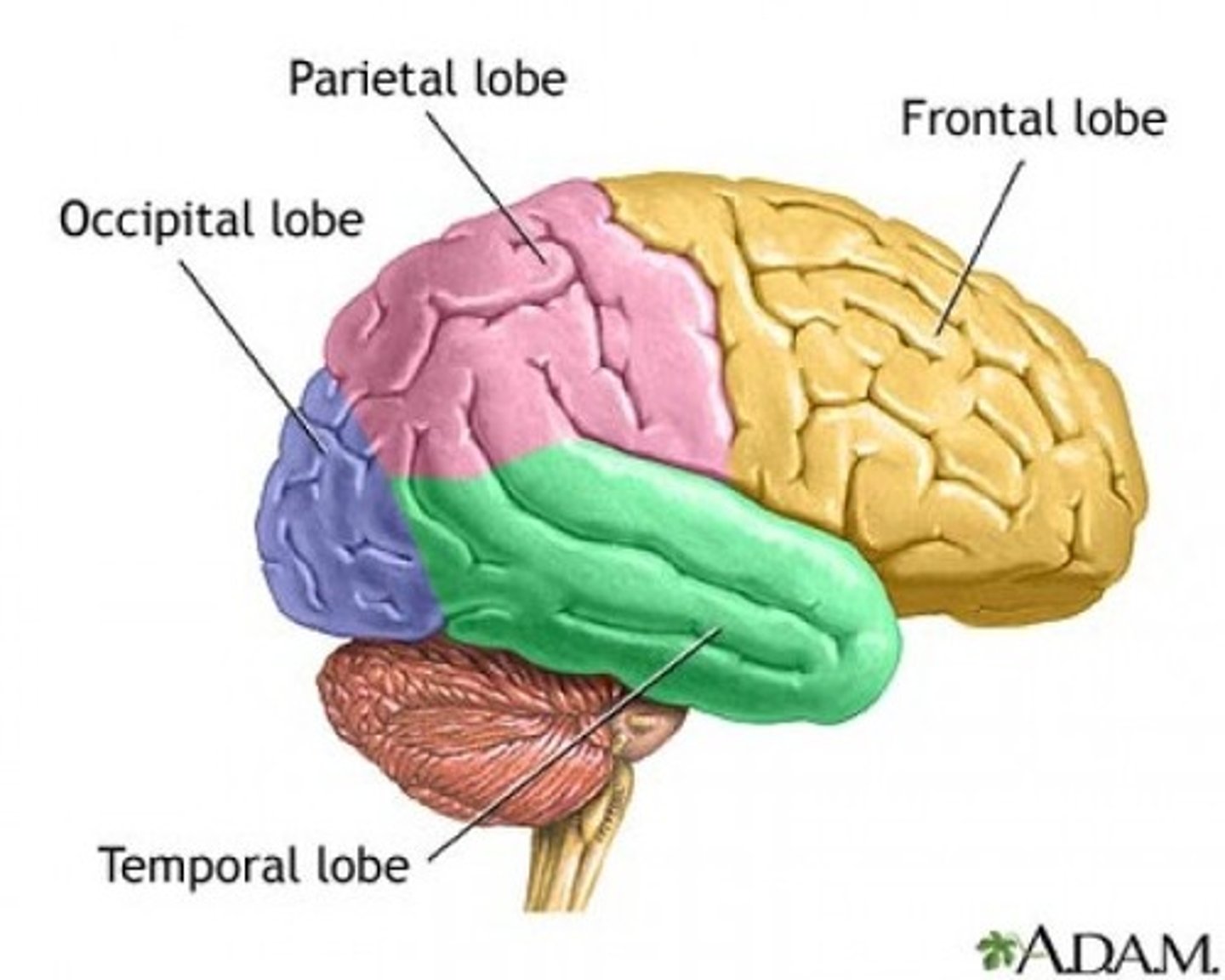
Contains cerebral cortex; divided by lobes (telencephalon subdivision).
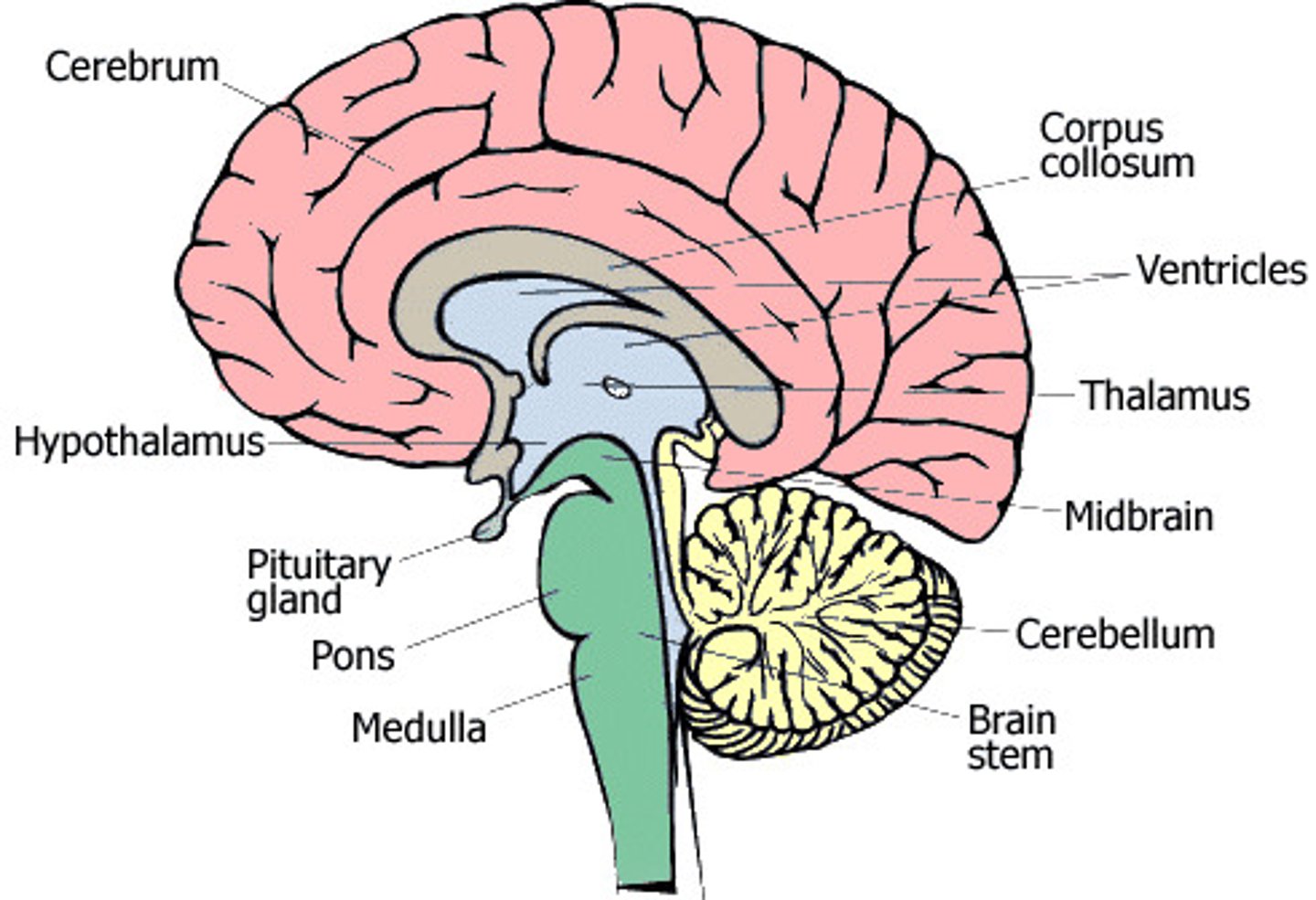
Cerebrum
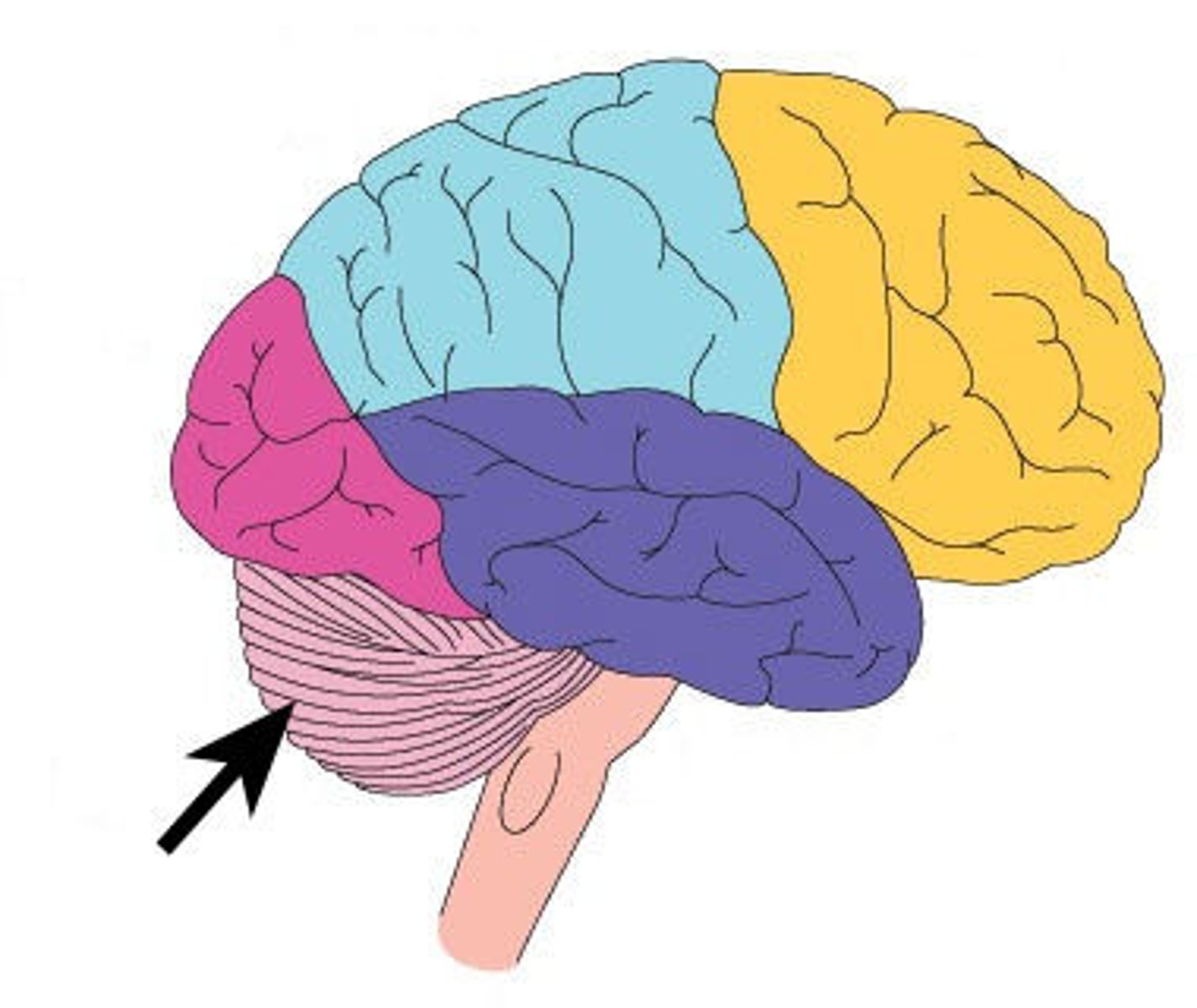
Balance and coordination
Cerebellum
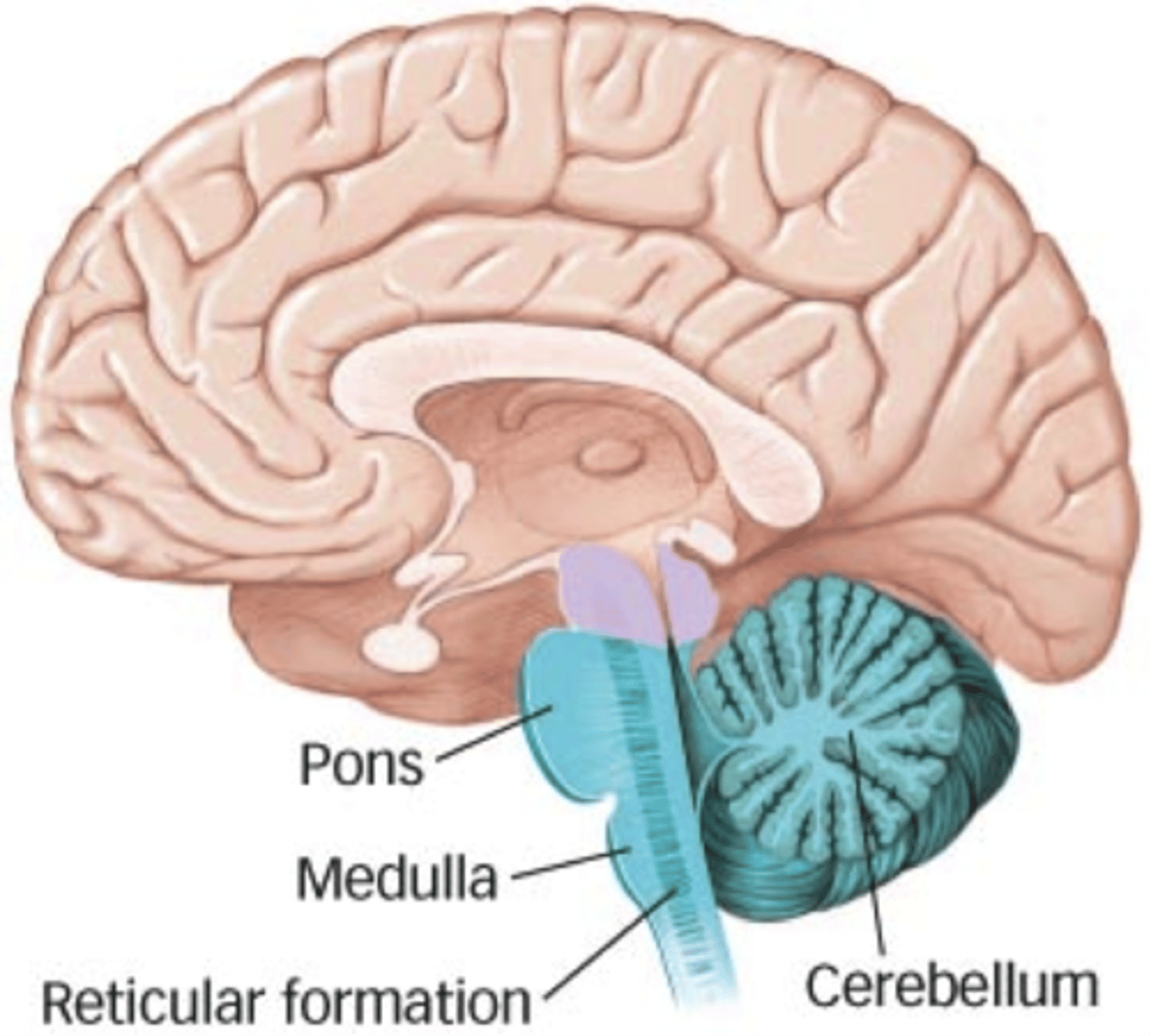
the posterior part of the brain, consists of the medulla, the pons, and the cerebellum
Hindbrain

Connects cerebrum to spinal cord.
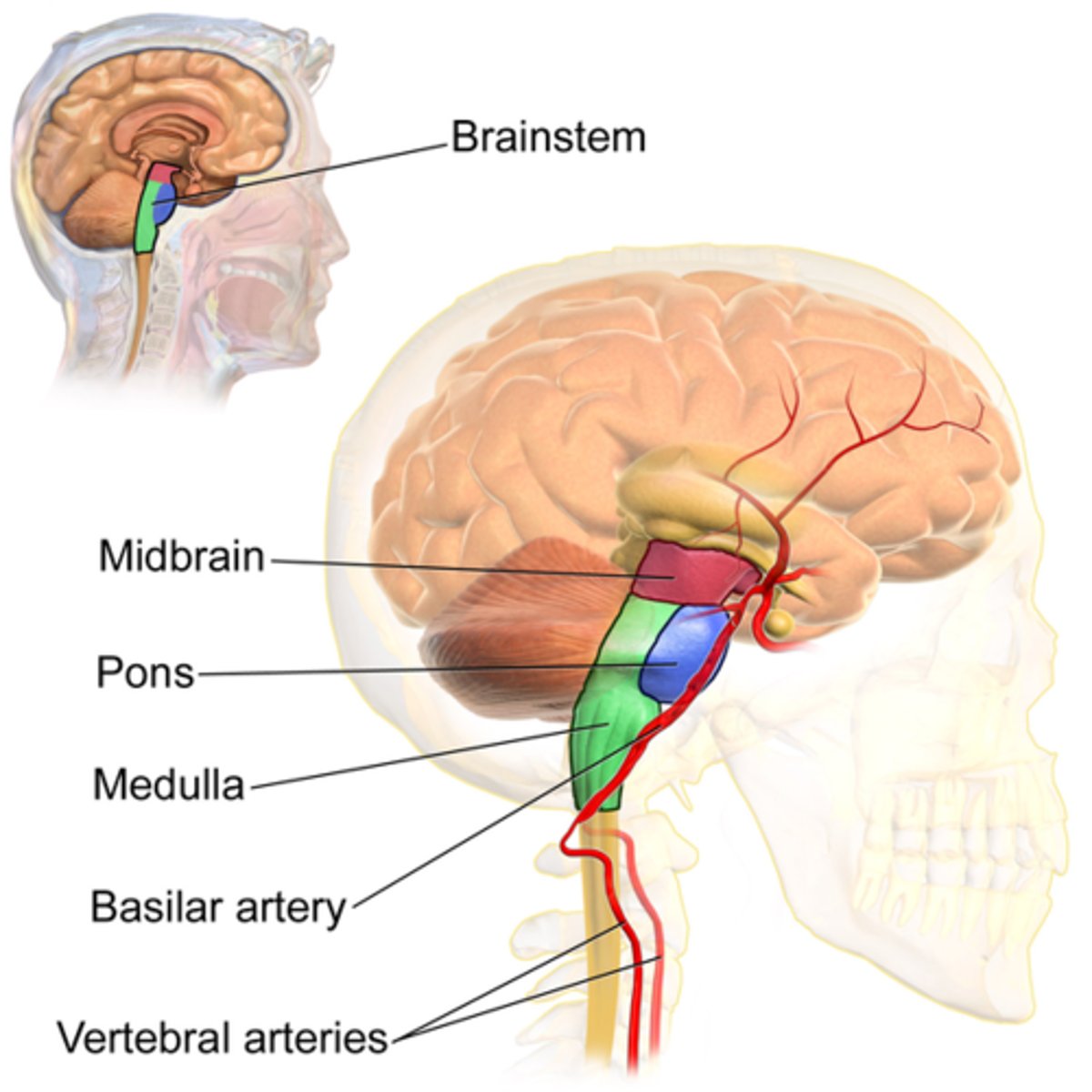
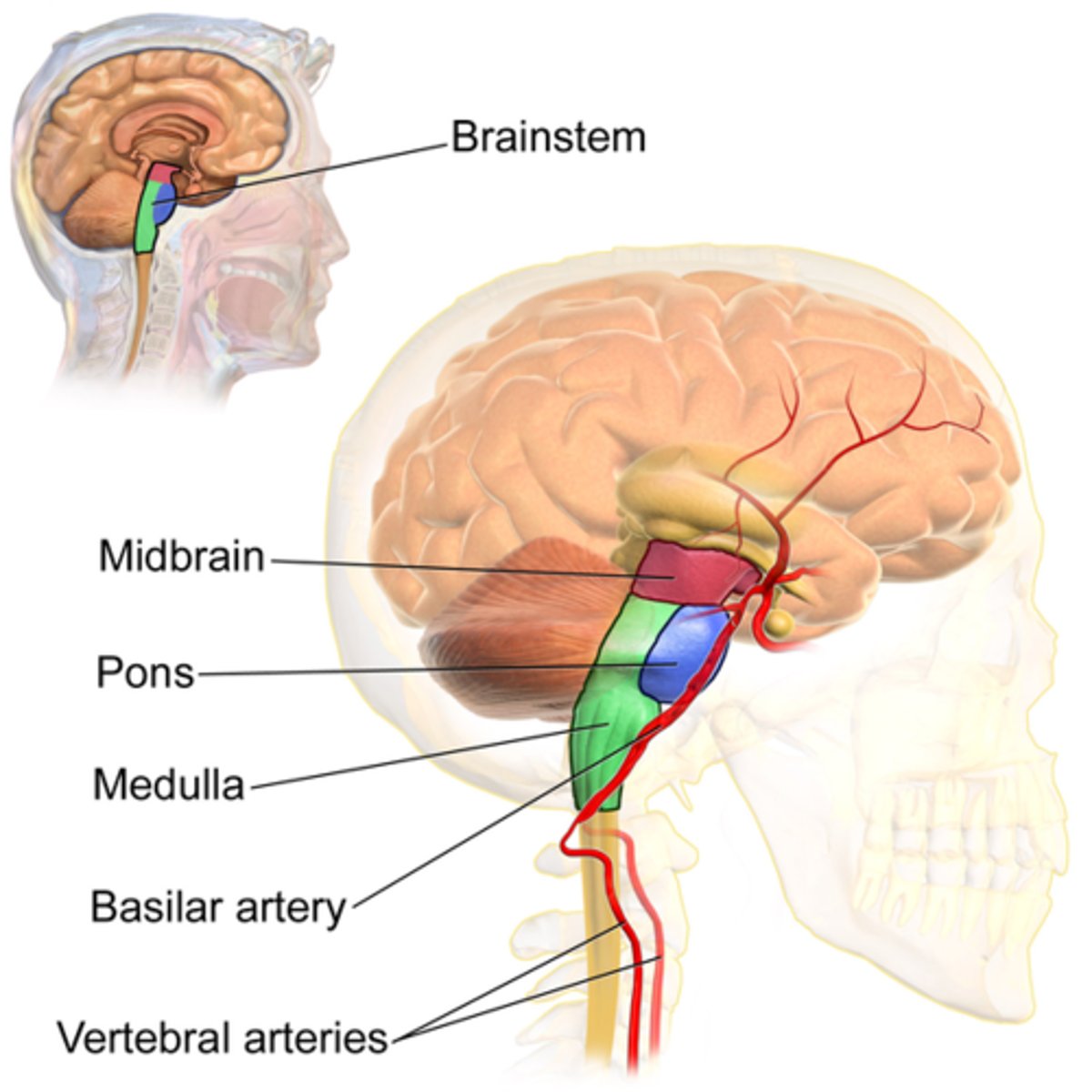
Brainstem
Relay center between cortex and cerebellum.
Pons
Controls breathing, heart rates, and gastrointestinal activity.
Medulla oblongata
Relay center for visual/ auditory impulses
- motor control
Midbrain
smell
Olfactory bulb (forbrain)
Relay center between spinal cord and cerebral cortex
Thalamus
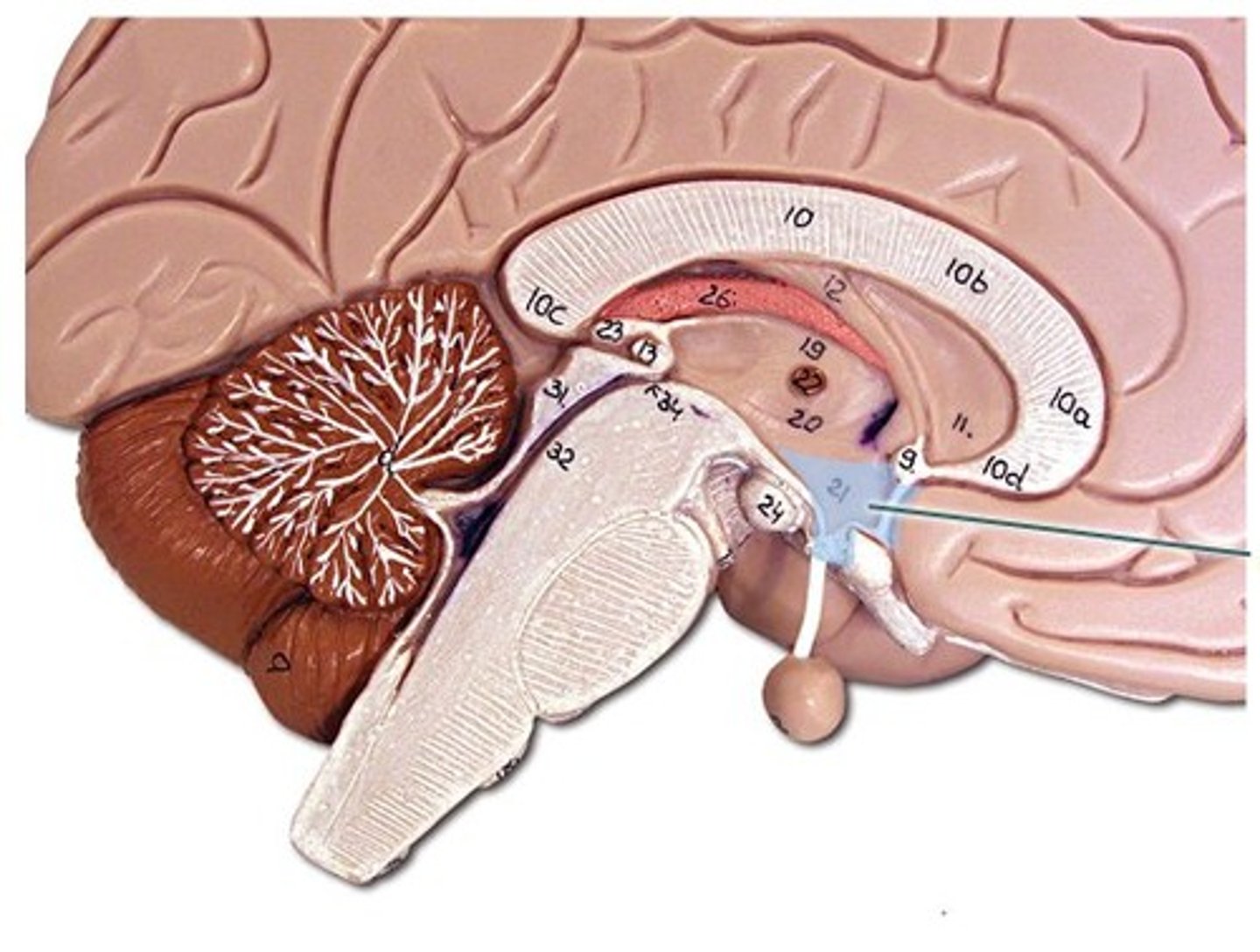
visceral functions ex. sleep, hunger, temperature regulation
Hypothalamus
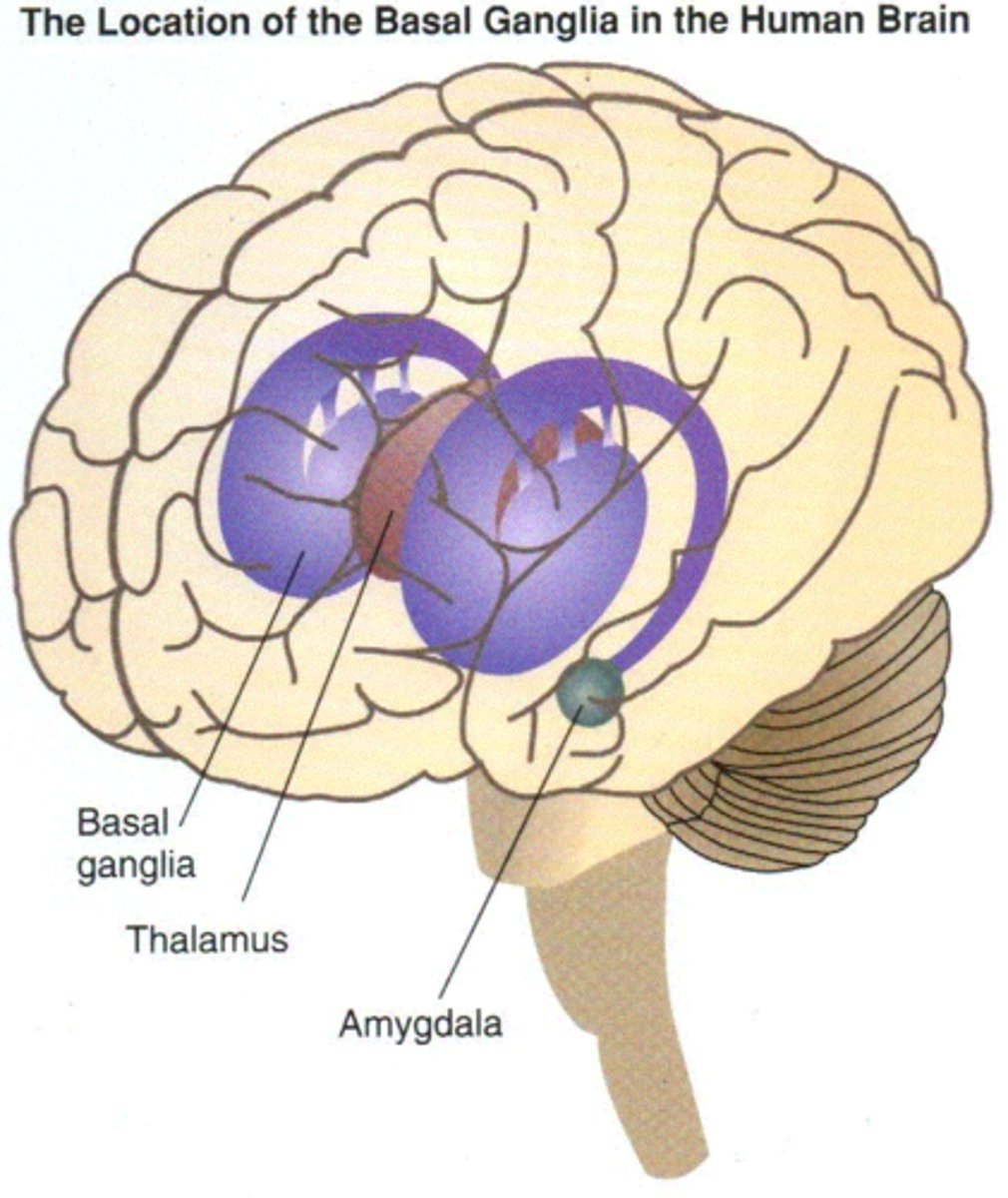
planning/learning movement sequences
basal ganglia
Division that contains the thalamus, hypothalamus, and pineal gland
Diencephalon

Cerebrum contains cerebral cortex; divided by lobes (telencephalon subdivision) (4)
i. Frontal: Conscious thought (attention)
ii. Parietal: Sensory; somatosensation, proprioception
iii. Temporal: Sound processing/interpretation
iv. Occipital: Visual input
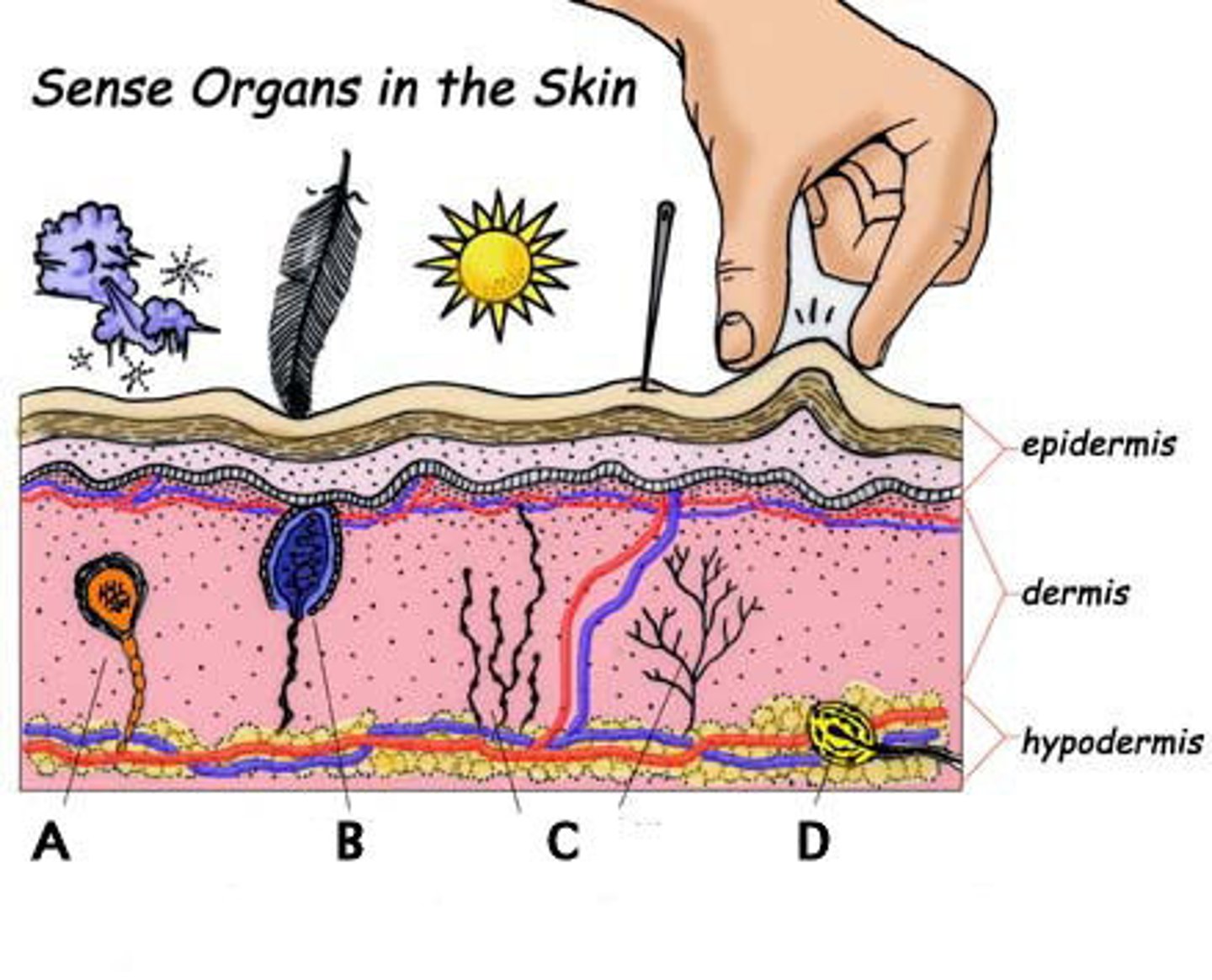
Sensory receptors that respond to touch.
Mechanoreceptors
Sensory receptors that respond to temperature.
Thermoreceptors
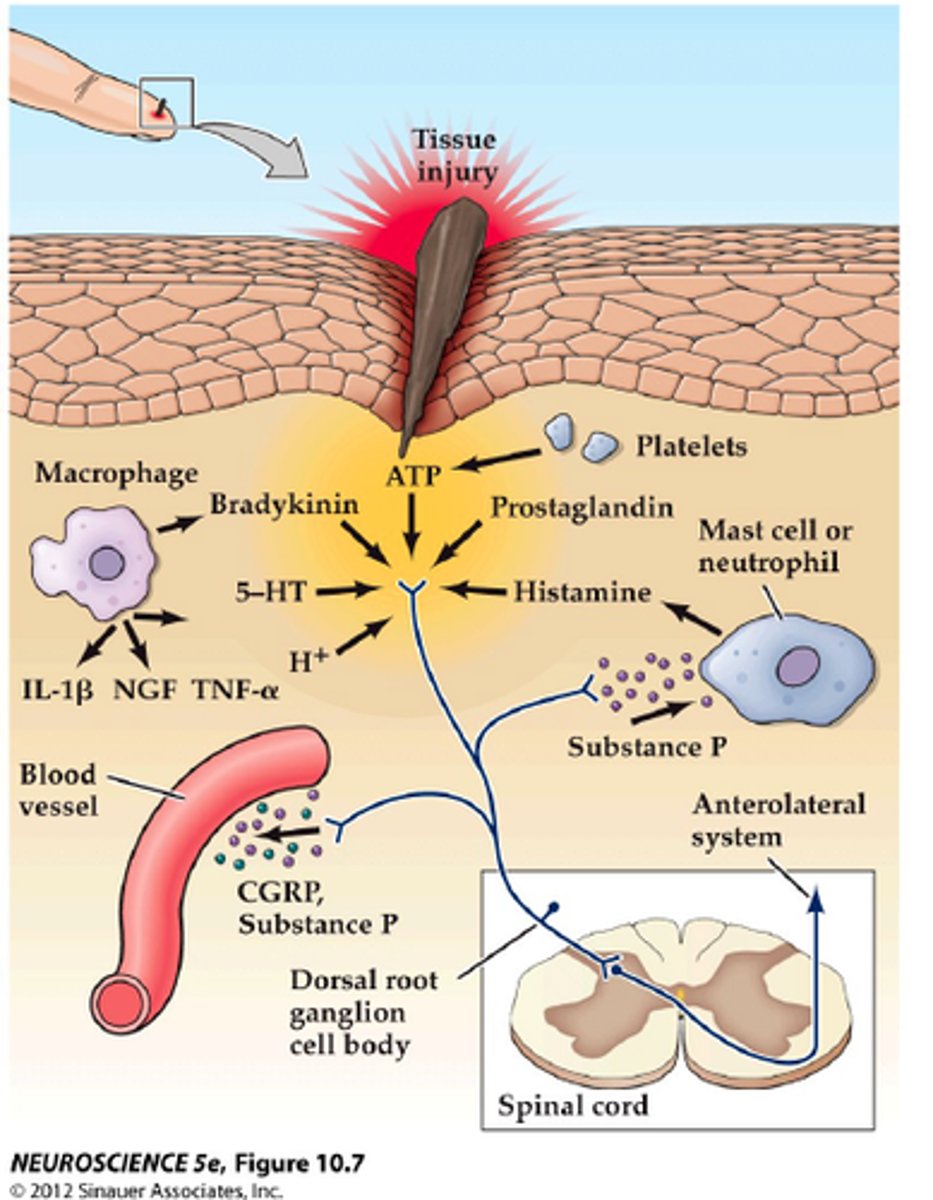
Sensory receptors that respond to pain.
Nociceptors
Sensory receptors that respond to light.
Electromagnetic Receptors
Binds to ACh receptors on post-synaptic membrane for nerve transmission.
Acetylcholine (ACh)

Most common CNS neurotransmitter in vertebrates; excitatory.
Glutamate
Found in brain; inhibitory neurotransmitter.
GABA
Found in CNS outside brain; inhibitory neurotransmitter.
Glycine
Acts in sympathetic nervous system; causes bronchodilation and vasodilation to lungs and skeletal muscles.
Epinephrine (E)
Acts in sympathetic nervous system; causes vasoconstriction to the digestive system and kidneys.
Norepinephrine (NE)