2- quantum phenomena
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
the photoelectric effect
light above a certain frequency is incident ona metal surface cuaisng electrons to be emitted from the surface
key points about the photoelectric effect (5)
photoelectrons are only emitted is the frequecny is above the threshold frequency
the maximum kinetuc energy of the electrons does not increase when light intensity is increased
light intensity increasing increases the number of photoelectrons emitted
increased frequency increases the kinetic energy of the photolectrons
there is a one to one interaction between photons and electrons
Photon energy equation
E= hf
where
E= photon energy
h= plancks constant
f= photon energy
threshold frequency equation
where-
the f is the threshold frequency in hz required for electrons to be emitted
the o is the work function in joules (minimum photon energy)
h is planck’s constant
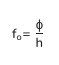
maximum photoelectron kinetic energy derivation
Emax = h f - Φ
where h is plancks constant , f is frequency and Φ is the work function
OR
½ mv2max = hf -Φ
where m is mass v is velocity h is planck’s constant and f is frequency, and Φ is the work function
stopping potential definition and equation
when photoelctrons are stopped by going against a potential difference v the potential which stops the elctrons is known as the stoppping potential
the equation for this is eVs = Ekmax
where e is electron charge, vs is stopping potential and Ekmax is the maximum potential energy
atomic energy levels
elctrons orbit certain energy levels given the number n. n =1 is the ground stater and subsequent n values are excited energy states. electrons can jump between and occupy these energy states through abosrption where they go up and emission where they go down.
phton energy through emission/ absorption equation
where delta E is photon energy Ef is final energy and Ei is initial energy |
evidence for light exhibiting wave particle duality
wave properties= interference and diffraction patterns
particle properties= the photoelectric effect
de broglie wavelength equations and definition
the realtion of wavelength to the momentum of a particle through
λ = h/p
and this can be rearranged to
λ= h/ mv
where
λ is wavelength in metres
h is planck’s constant and p is momentum in kg m s-1
key observations of electron diffraction experiments
electron diffraction patterns have similar spacing to x ray diffraction patterns, faster electrons diffract less
showing that: faster electrons have shorter wavelengths and vice versa
line emission/ absorption spectra
when excited gases are passed through a prism wavelngths are seperated in to a spectrum, with each line corresponding to a wavelngth. each element has a unique line emission spectra.
when white light passes through a gas a line absorption spectra is released, which will match with the emission spectra.