APES Vocab (Packet review)
1/102
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
Commensalism
a symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits while the other is neither helped nor harmed.
Mutualism
a symbiotic relationship where both species benefit.
Interspecific / Intraspecific competition
Competition between different species / competition within the same species.
Resource Partitioning
the process by which species divide resources to reduce competition.
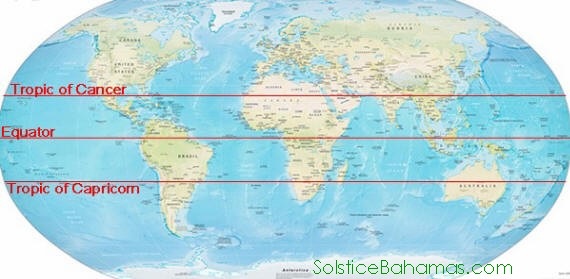
Where are the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn located?
They are located at 23.5 degrees north and south of the equator, respectively.
10% Rule
only 10% of energy consumed will move to the next trophic level. All other energy is converted to (mainly) heat.
Estuary/Wetland
A coastal area where freshwater from rivers meets and mixes with saltwater from the ocean, serving as a rich habitat for diverse species.
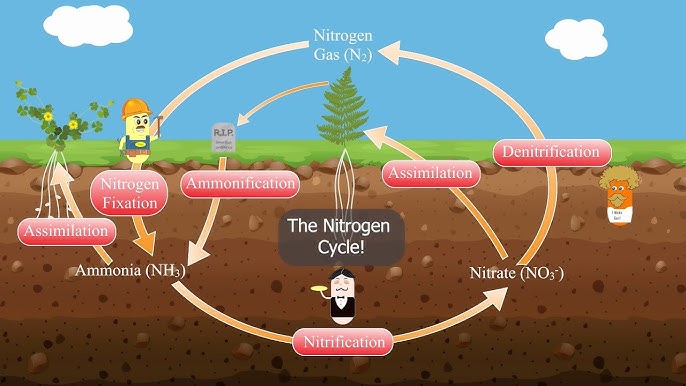
Nitrogen Cycle (Biogeochemical cycle)
The process by which nitrogen is converted between its various chemical forms in the environment, including fixation, nitrification, and denitrification.
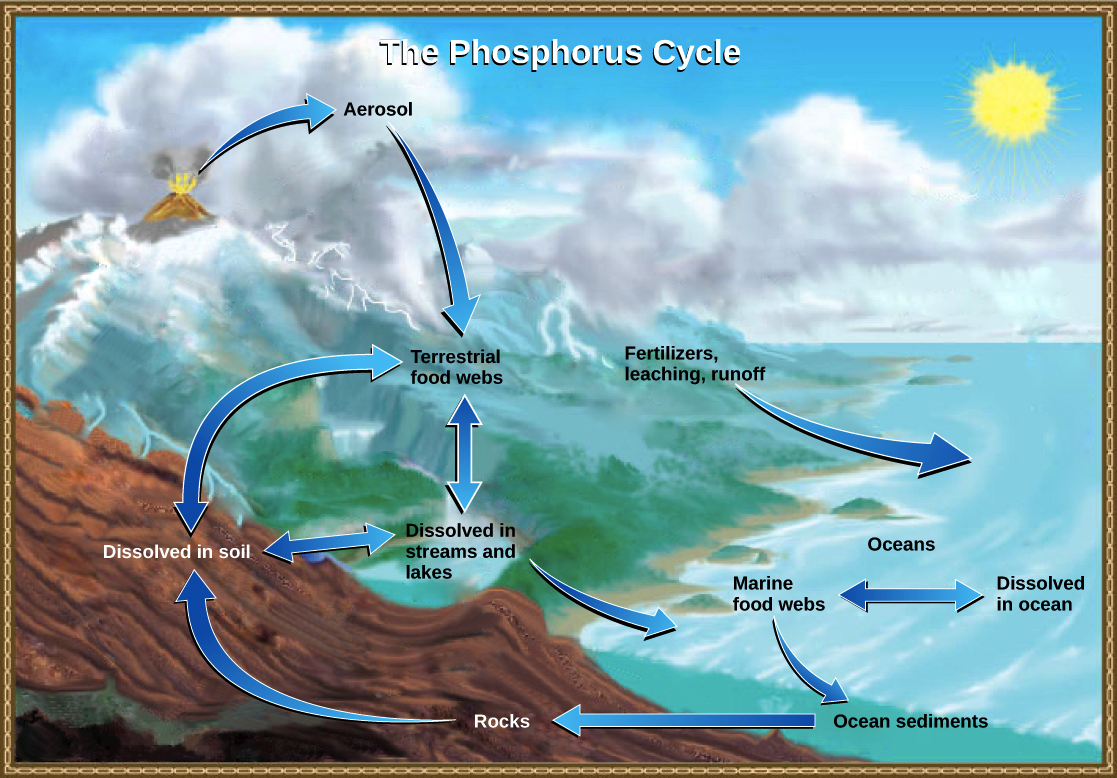
Phosphorus Cycle (Biogeochemical Cycle)
The biogeochemical cycle that describes the movement of phosphorus through the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere, essential for DNA, RNA, and ATP.
Nitrification
The biological process in which ammonia is converted into nitrate ions (NO3-) by bacteria, making nitrogen accessible to plants.
Denitrification
The process by which nitrogen oxides are converted back into nitrogen gas, completing the nitrogen cycle.
Assimilation
The process by which plants and animals absorb ammonium and nitrate from the soil to incorporate nitrogen into their biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids.
Nitrogen Fixation
The process of converting atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into ammonia (NH3) by bacteria, making it available for use by plants.
Ammonification
The process by which organic nitrogen is converted into ammonia by decomposers, making nitrogen available in the soil.
First Law of Thermodynamics
The principle that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.
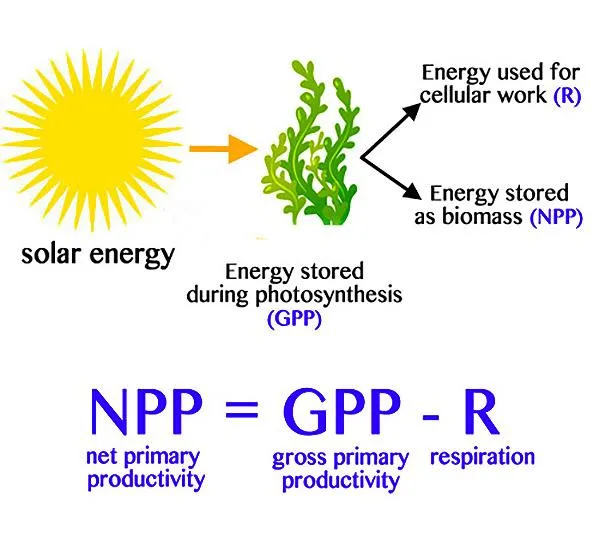
NPP Equation
NPP = GPP-R
Terrestrial sink (carbon reservoirs)
Natural environments, such as forests and soils, that absorb and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
A sustainable approach to managing pests that combines biological, cultural, physical, and chemical tools in a way that minimizes economic, health, and environmental risks.
Endemic Species
Species that are native to and found only in a specific geographic area.
Species Richness
The number of different species represented in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
Species Abundance
The total number of individuals of each species within a specific area. It reflects the population density of species in an ecosystem.
Ecosystem Service: Provisioning
The benefits provided by ecosystems that include the production of food, water, and other essential resources for human use.
Ecosystem Service: Regulating
The benefits provided by ecosystems that help maintain environmental balance, such as climate regulation, flood control, and water purification.
Ecosystem Service: Cultural
The non-material benefits people obtain from ecosystems, including recreation, aesthetic enjoyment, and cultural identity.
Ecosystem Service: Supporting
The benefits provided by ecosystems that maintain the conditions for life on Earth, including nutrient cycling, soil formation, and habitat provision.
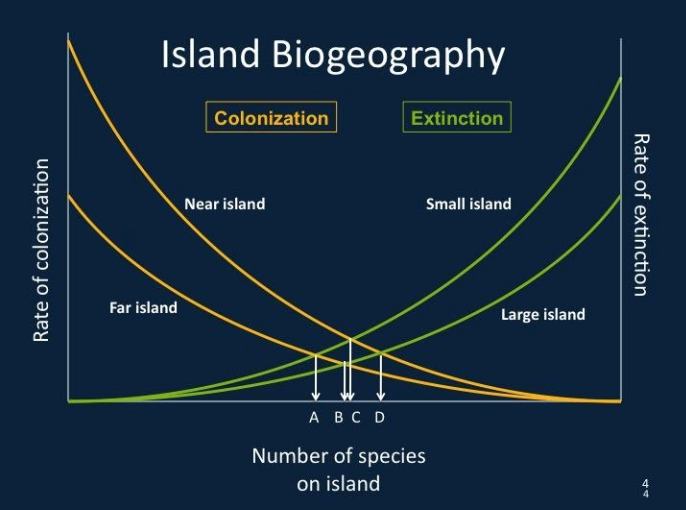
Island Biogeography Theory
A theory that explains the number and diversity of species on islands based on their size, distance from the mainland, and ecological factors. It emphasizes the effects of isolation and habitat size on species richness.
Range of Tolerance
The range of environmental conditions within which a species can survive and reproduce. Beyond this range, organisms may experience stress and reduced fitness.
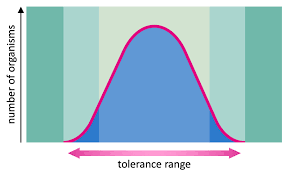
Zone of Intolerance (Ecological Tolerance)
The environmental conditions beyond the range of tolerance where a species cannot survive or reproduce, leading to population decline or extinction.
Zone of Physiological Stress (Ecological Tolerance)
The range of environmental conditions that are less than optimal for a species, causing stress but not immediately fatal. Organisms may survive but with reduced reproductive success and fitness.
Zone of optimum (Ecological Tolerance)
The range of environmental conditions that are most favorable for a species to thrive, showing the highest fitness and reproductive success.
Ecosystem Resistance
The ability of an ecosystem to withstand disturbances without changing its structure or function. Ecosystem resistance measures how much a system can tolerate changes while maintaining stability.
Ecosystem Resilience
The ability of an ecosystem to recover after a disturbance, maintaining its essential functions and processes.
Climax community
A stable, mature ecological community that has reached a final stage of ecological succession, characterized by a balance of species and environmental conditions.
Primary Succession
The gradual process of change and replacement in a community of organisms over time, starting from bare rock or soil.
Secondary Succession
The process of recovery and regeneration in an ecosystem following a disturbance where soil and organisms already exist, leading to the reestablishment of a biological community.
Rule of 70 equation
A method used to estimate the doubling time of a population by dividing 70 by the growth rate percentage.
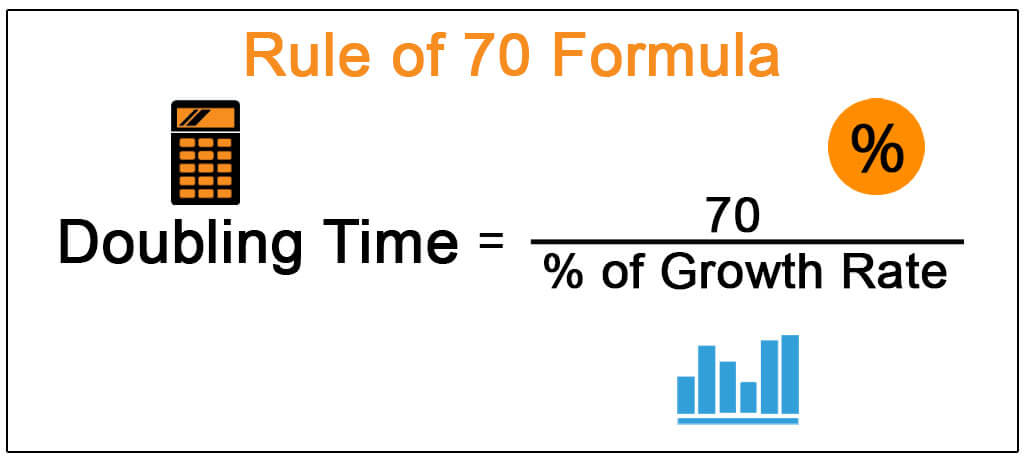
Population Growth equation
A formula used to estimate the doubling time of a population, calculated by dividing 70 by the annual percentage growth rate.
Population momentum
The tendency of a population to continue to grow even after birth rates decline, due to a higher proportion of individuals in their reproductive years.
r-selected species
characterized by high reproductive rates, short lifespans, and minimal parental care, producing numerous offspring with a low probability of survival.
K-selected species
prioritize the quality of their offspring, investing significant time and resources in raising each one.
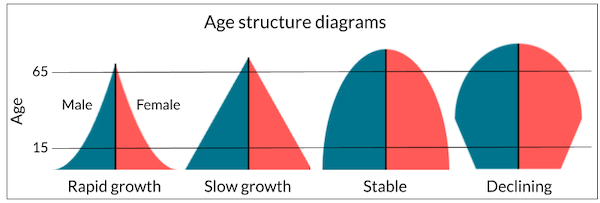
Age-Structure Diagrams
a graphical representation of a population's distribution by age and sex
Demographic Transition
a theory describing the historical shift in birth and death rates within a population,
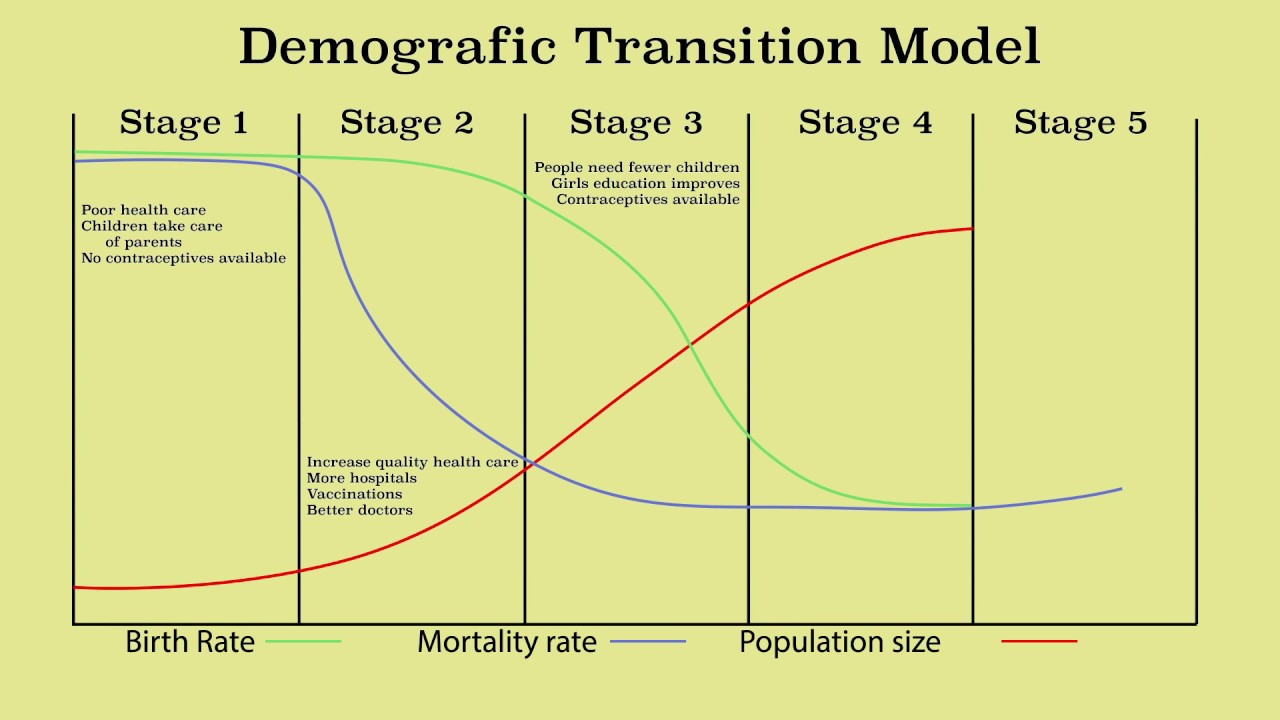
Replacement Level Fertility
the average number of children each woman needs to have to maintain a stable population size without immigration.
Infant Mortality Rate
number of infant deaths (deaths under one year of age) per 1,000 live births
Urban Sprawl
The spreading of urban developments on undeveloped land near a city, often leading to increased traffic and environmental concerns.
Mid-oceanic ridge
an underwater mountain range formed by tectonic plates pulling apart at divergent boundaries
Island Arcs / Trenches
Island arcs and trenches are formed through subduction at convergent plate boundaries, where an oceanic plate subducts beneath a continental or another oceanic plate, creating volcanic islands and deep ocean trenches.
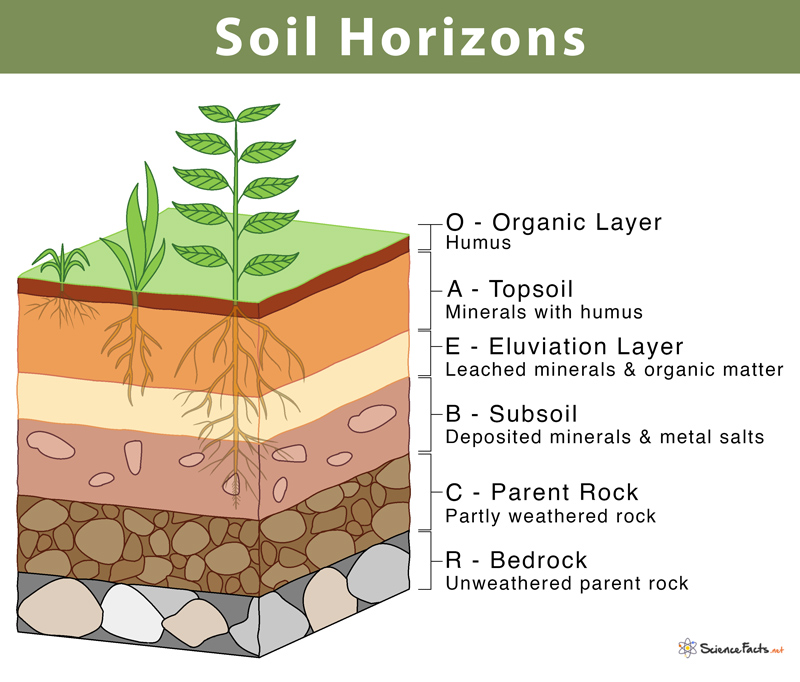
Soil Horizons
The soil horizons consist of distinct layers: Horizon O is organic matter, like decomposing leaves; Horizon A is topsoil rich in nutrients; Horizon B is subsoil where minerals accumulate; Horizon C consists of weathered rock; and Horizon R is bedrock.
Watersheds
A watershed is an area of land that drains rainwater and snowmelt into a common waterbody, such as a river, lake, or ocean
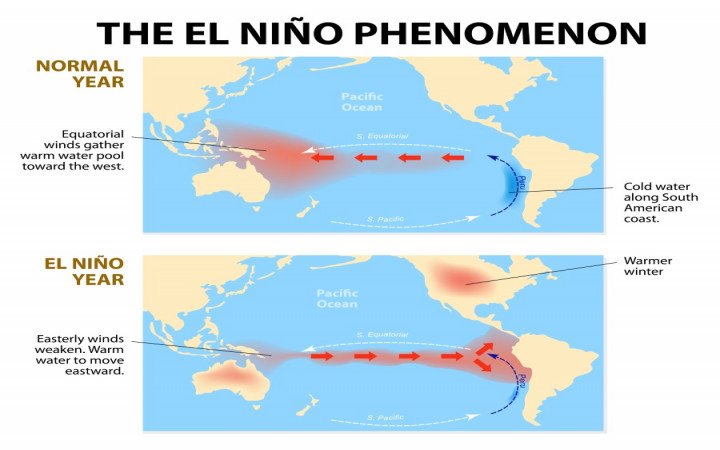
ENSO
he El Niño-Southern Oscillation, a climate pattern that describes periodic variations in ocean temperatures and atmospheric conditions in the Pacific Ocean.
El Nino
a climate phenomenon characterized by the unusual warming of ocean surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean. It significantly impacts global weather patterns, causing changes such as increased rainfall in some areas and drought in others.
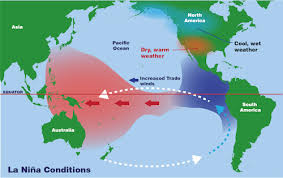
La Nina
a climate pattern, the cool phase of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO), that can influence global weather patterns
Chemical vs Physical tests
Physical tests examine a substance's macroscopic properties like color, density, or melting point, without changing its chemical composition. Chemical tests, on the other hand, investigate a substance's chemical structure, elemental composition, or reactivity, often involving chemical reactions that alter the substance's composition
Clearcutting
a forestry practice that involves uniformly cutting down most or all trees in a given area
Green Revolution
a period of significant advancements in agricultural technology and practices, primarily focused on increasing crop yields to address global food security concerns
Furrow Irrigation
a surface irrigation method where water is directed into shallow, parallel channels (furrows) that run between rows of crops

Salinization
the process of accumulating salts in soil or water, reducing its fertility and potentially harming plant life
Impervious
not allowing fluid to pass through.
Pesticide Treadmill
a cycle where pests develop resistance to pesticides, forcing farmers to use increasingly stronger and more toxic chemicals to control them, ultimately leading to further resistance

IPM methods - examples
soil treatment;
selection of suitable plants;
crop rotation;
interplanting or strip cropping;
choice of planting dates;
weed control;
use of trap plants.
Subsurface Mining
extracting materials from beneath the Earth's surface

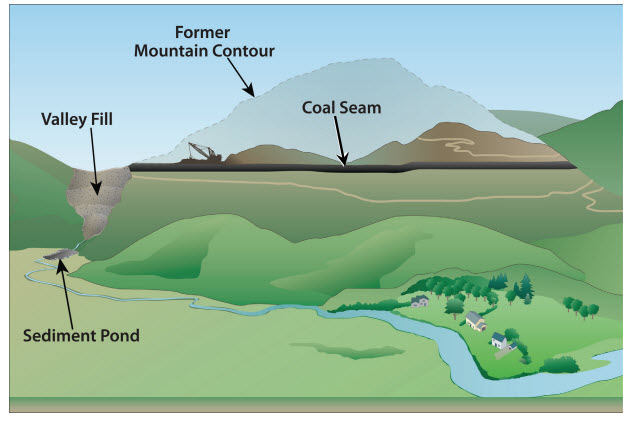
Mountaintop removal
Ecological Footprint
a measure of how much biologically productive land and water area a population needs to produce the resources it consumes and to absorb the waste it generates
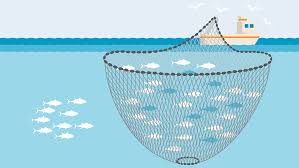
Purse Seine
a type of fishing net used to encircle and capture large schools of fish, particularly in the open ocean
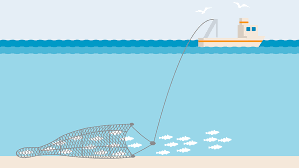
Drift Net

Bottom Trawling
a fishing method where heavy nets are dragged along the ocean floor to catch fish.
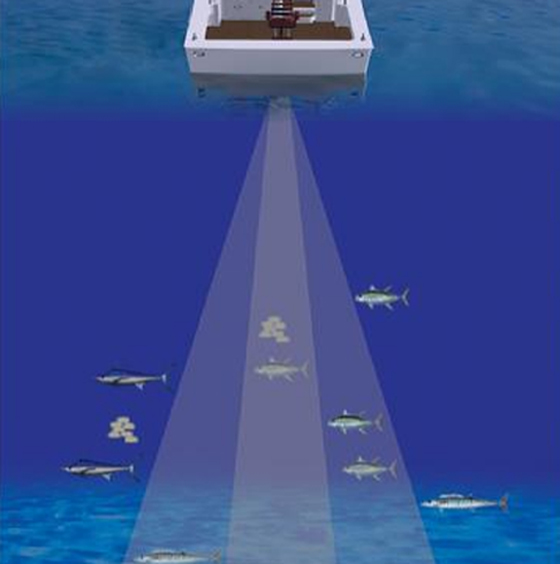
Sonar (fishing technique)
Exxon Valdez
The Exxon Valdez oil spill in 1989 occurred when the oil tanker ran aground on Bligh Reef in Alaska's Prince William Sound, releasing an estimated 11 million gallons of crude oil.
Montreal Protocol
regulates the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances (ODS) like CFCs
US Endangered Species Act
protect and recover threatened and endangered species and their habitats
OPEC
Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries
Deepwater Horizon
occurred in the Gulf of Mexico in 2010, was the largest accidental marine oil spill in history. The Deepwater Horizon drilling rig exploded on April 20, 2010, leading to a massive oil leak from the Macondo well. The incident resulted in the deaths of 11 workers and the sinking of the rig. The spill released an estimated 3.19 million barrels of oil into the ocean over 87 days
ANWR
Arctic National Wildlife Refuge
CAFE
Corporate Average Fuel Economy standard, which is a regulation in the United States designed to improve the average fuel economy of vehicles sold in the US
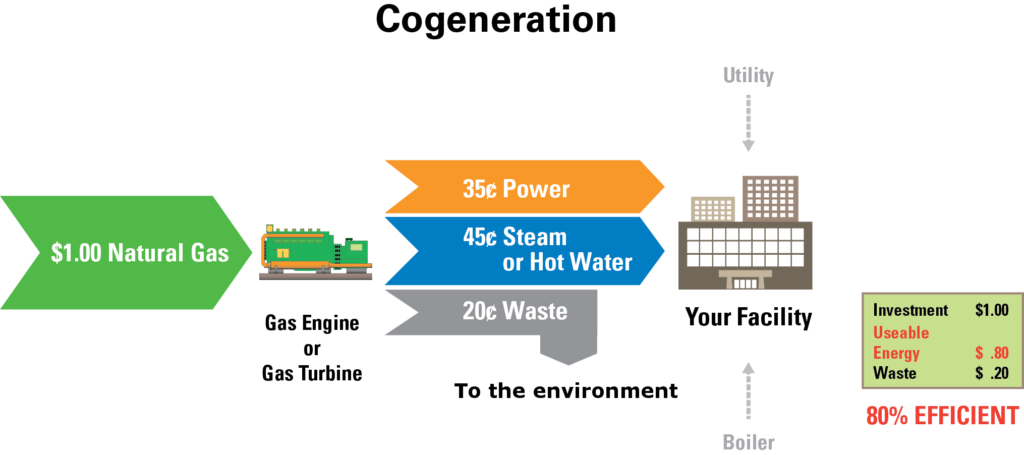
cogeneration
The concurrent production of electricity or mechanical power and useful thermal energy (heating and/or cooling) from a single source of energy
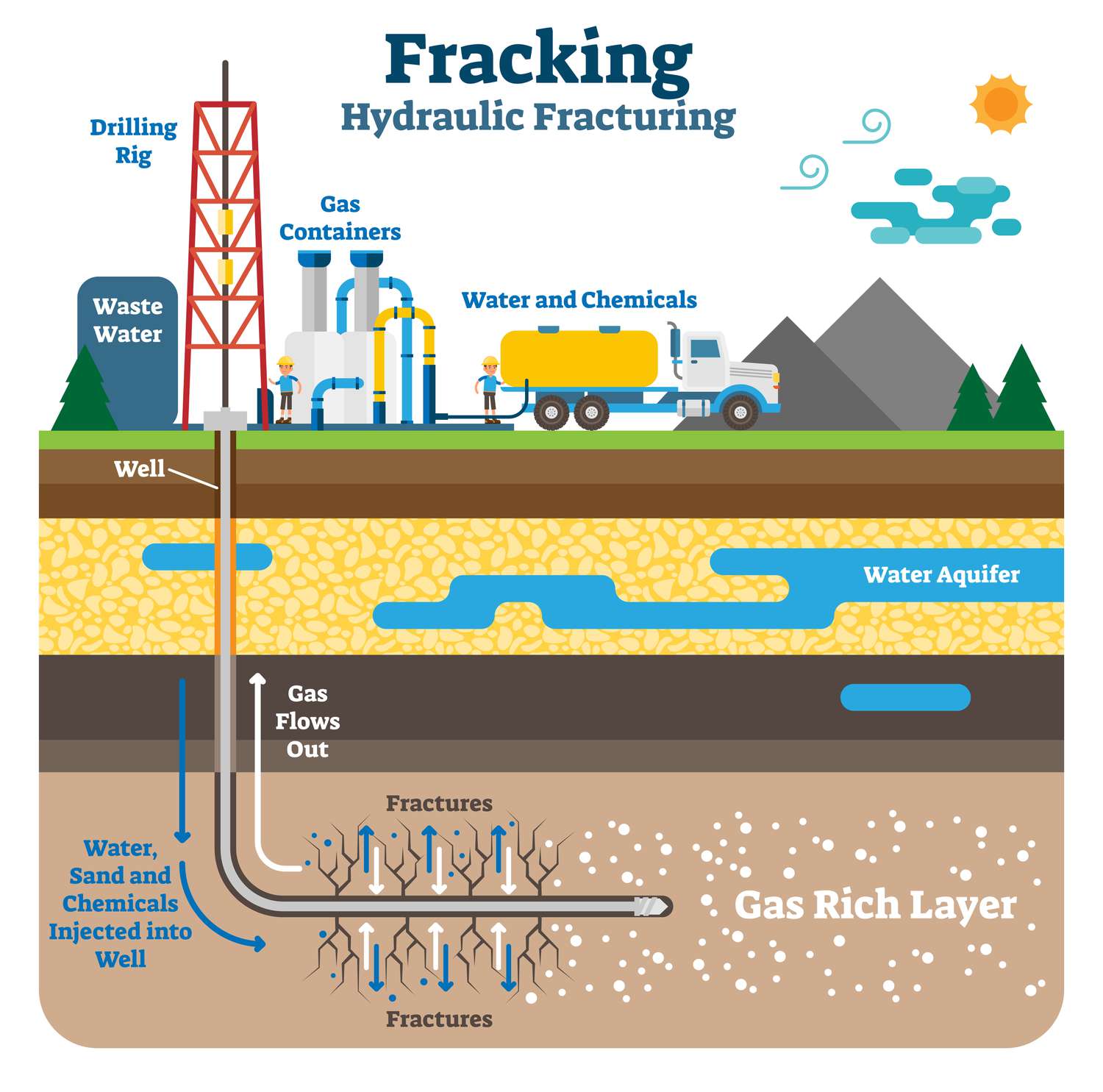
Fracking
a technique used to extract oil and natural gas from deep within the Earth's shale formations. It involves drilling a well, then pumping a high-pressure mixture of water, sand, and chemicals into the well to fracture the rock and release trapped oil and gas.
Hydroelectric power
a renewable energy source that harnesses the power of moving water to generate electricity
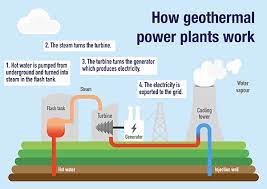
Geothermal Energy
heat from the Earth, a renewable resource used for heating, cooling, and electricity generation. It's harnessed through various methods, including geothermal power plants and heat pumps
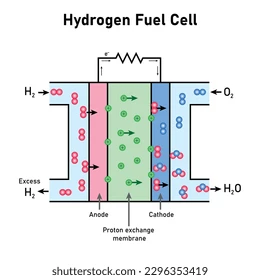
Hydrogen Fuel Cell
A fuel cell uses the chemical energy of hydrogen or other fuels to cleanly and efficiently produce electricity.
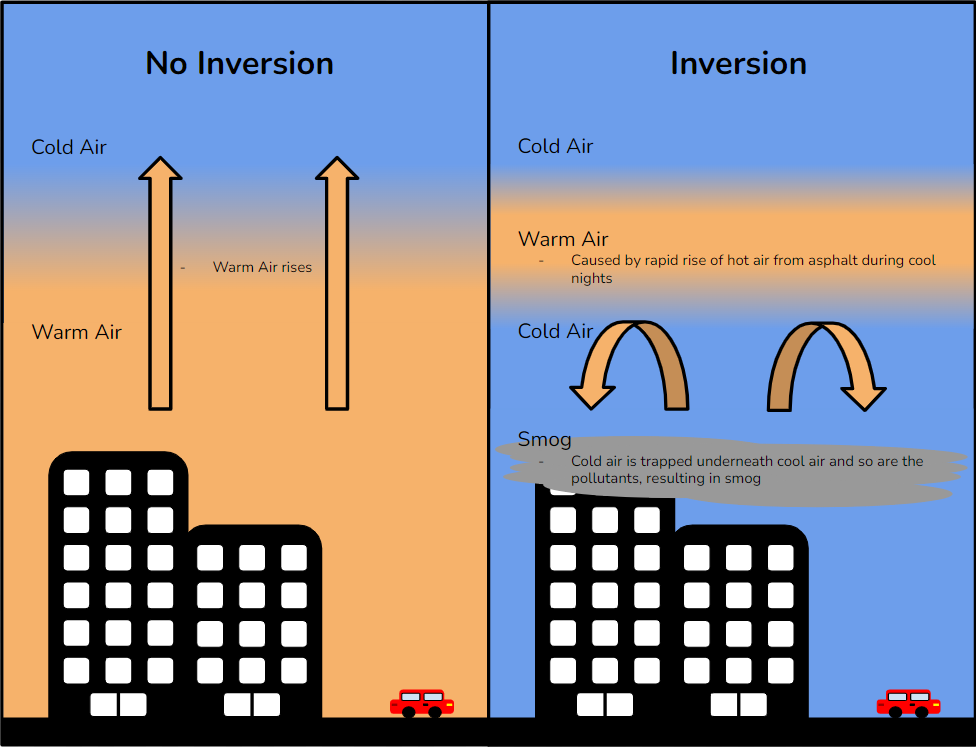
Thermal Inversion
a layer of warm air sits above a layer of cooler air, inverting the normal atmospheric temperature gradient. This inversion can trap air pollution near the ground, leading to poorer air quality
Formaldehyde
a colorless, flammable gas with a strong, pungent odor. It is a chemical compound that is used in various industrial processes and consumer products. It is a common component of adhesives, glues, and resins used in building materials like pressed wood products (particleboard, plywood, fiberboard)
Sick Building Syndrome
is a condition where occupants of a building experience health issues linked to time spent indoors, often due to poor air quality and inadequate ventilation.
Baghouse filter
an air pollution control technology designed to capture particulate matter from exhaust gases.
Electrostatic Precipitator
is a device that uses electric charge to remove particles from a gas stream. It charges particles and collects them on oppositely charged plates, reducing air pollution.
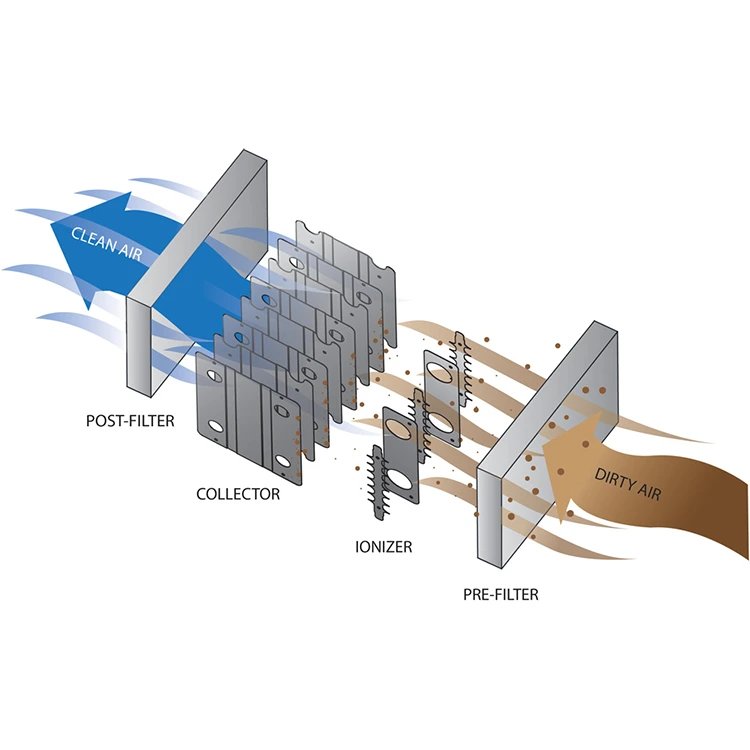
Catalytic Converter
an emissions control device in vehicles' exhaust systems that converts harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide, unburned hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful substances
Chemical Equation for the formation of Carbonic Acid from the reaction of water with carbon dioxide
H 2 O + C O 2 ⇌ H 2 C O 3
Limestone (neutralizing acid rain)
Limestone, primarily composed of calcium carbonate, reacts with acids in rainwater, effectively raising the pH and neutralizing acidity. This chemical reaction helps to mitigate the harmful effects of acid deposition on ecosystems and structures.
Ocean Dead zone
areas of low oxygen in the water that cannot support most marine life.These zones are primarily caused by excessive nutrient pollution, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus, from human activities like agriculture and wastewater runoff.
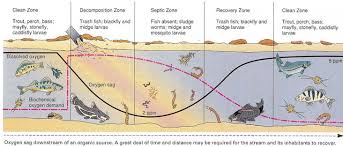
Oxygen SAG curve
The oxygen sag curve illustrates how dissolved oxygen levels in a river decrease as a result of pollution, particularly the discharge of organic waste, and then gradually recover downstream
Methylmercury
a highly toxic organic form of mercury that can accumulate in aquatic food webs and be ingested by humans, primarily through fish consumption
Eutrophication
the process where a water body, like a lake or river, becomes overly enriched with nutrients, primarily phosphorus and nitrogen. This excess nutrient loading leads to excessive growth of algae and aquatic plants, followed by the decomposition of these organisms, which depletes dissolved oxygen in the water
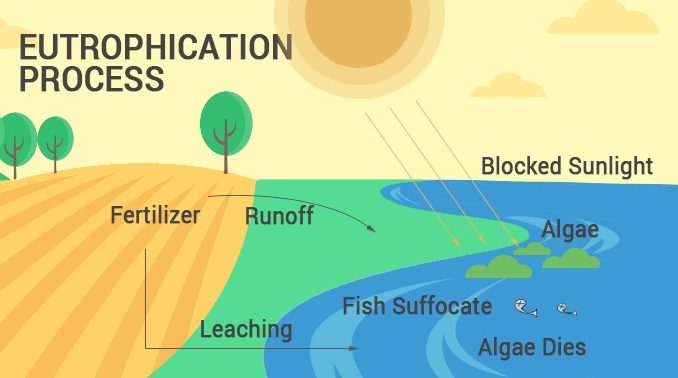
Cultural Eutrophication
the enrichment of water bodies with nutrients, primarily from human activities, that leads to an increase in plant and algae growth
Hypoxia
a condition where the body or a specific tissue doesn't receive enough oxygen
Persistent Organic Pollutants
synthetic, carbon-based chemicals that persist in the environment for long periods, travel long distances, and accumulate in living organisms, leading to negative health and environmental effects
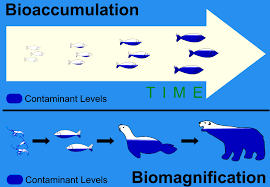
Bioaccumulation
the gradual accumulation of substances, like pollutants or pesticides, within an organism's tissues, particularly when the rate of intake exceeds the rate of excretion or metabolism
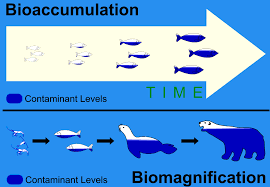
Biomagnification
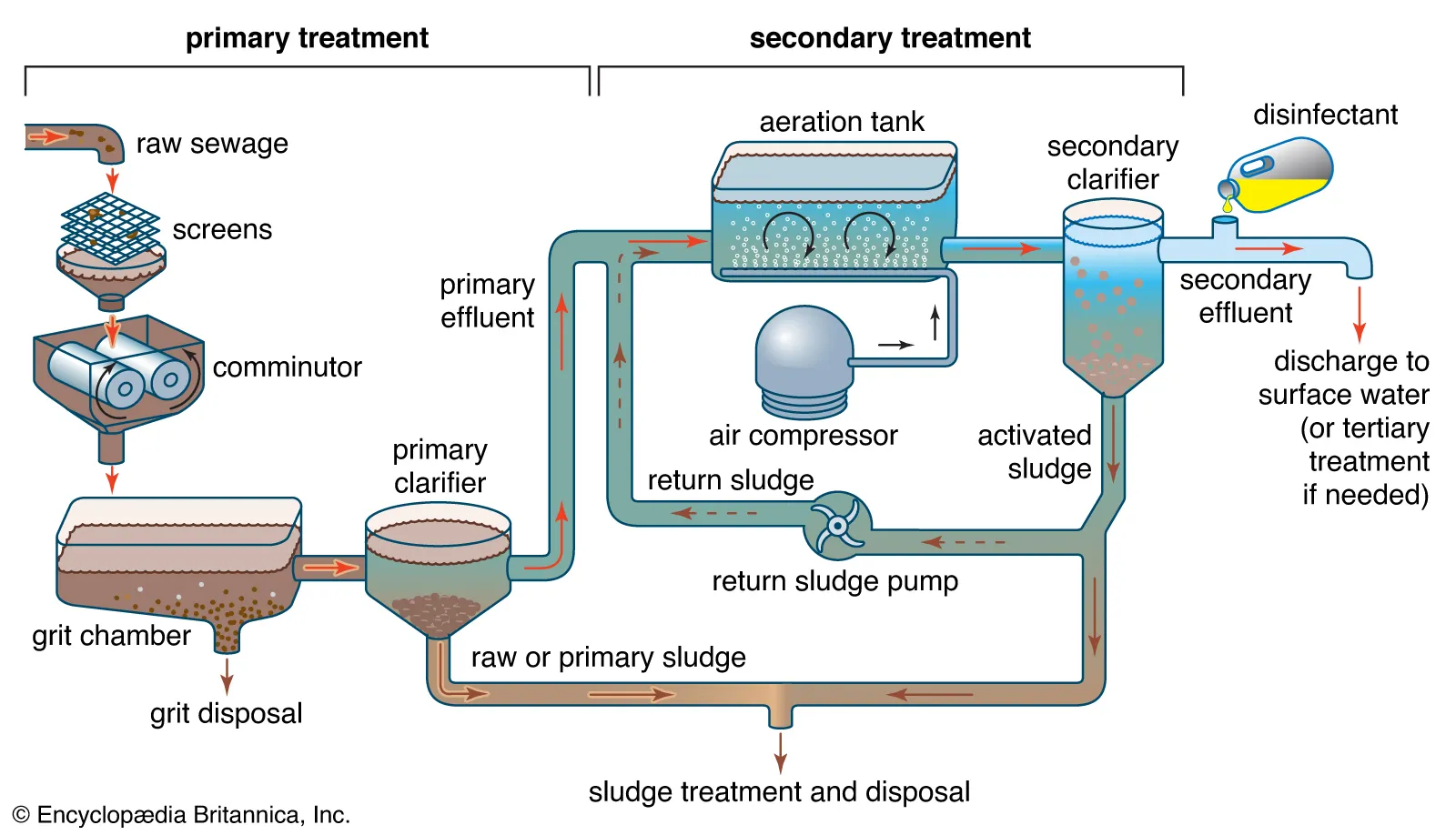
Sewage treatment process
primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment. Primary treatment removes large solids and debris, while secondary treatment uses bacteria to break down organic matter. Tertiary treatment provides additional purification before the treated water is discharged or reused
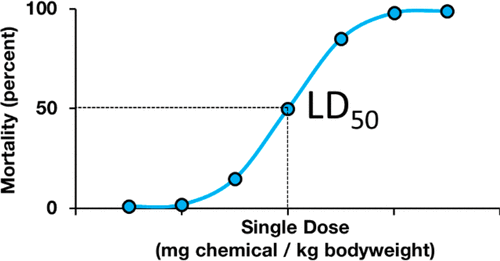
LD50
a measure of the toxicity of a substance, specifically the amount of a substance that, when administered, will cause death in 50% of a test population within a given time period
Dose Response Curve
The dose–response relationship, or exposure–response relationship, describes the magnitude of the response of an organism, as a function of exposure to a stimulus or stressor after a certain exposure time.

Mesothelioma
a rare cancer that develops from the mesothelium, the thin tissue lining internal organs like the lungs, abdomen, and heart. It's almost exclusively caused by exposure to asbestos.