Chapter 14: The Cardiovascular System: Blood vessels, flow, and pressure
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
blood pressure
the pressure that is exerted by the blood against the walls of blood vessels
systolic pressure
Blood pressure in the arteries during contraction of the ventricles.
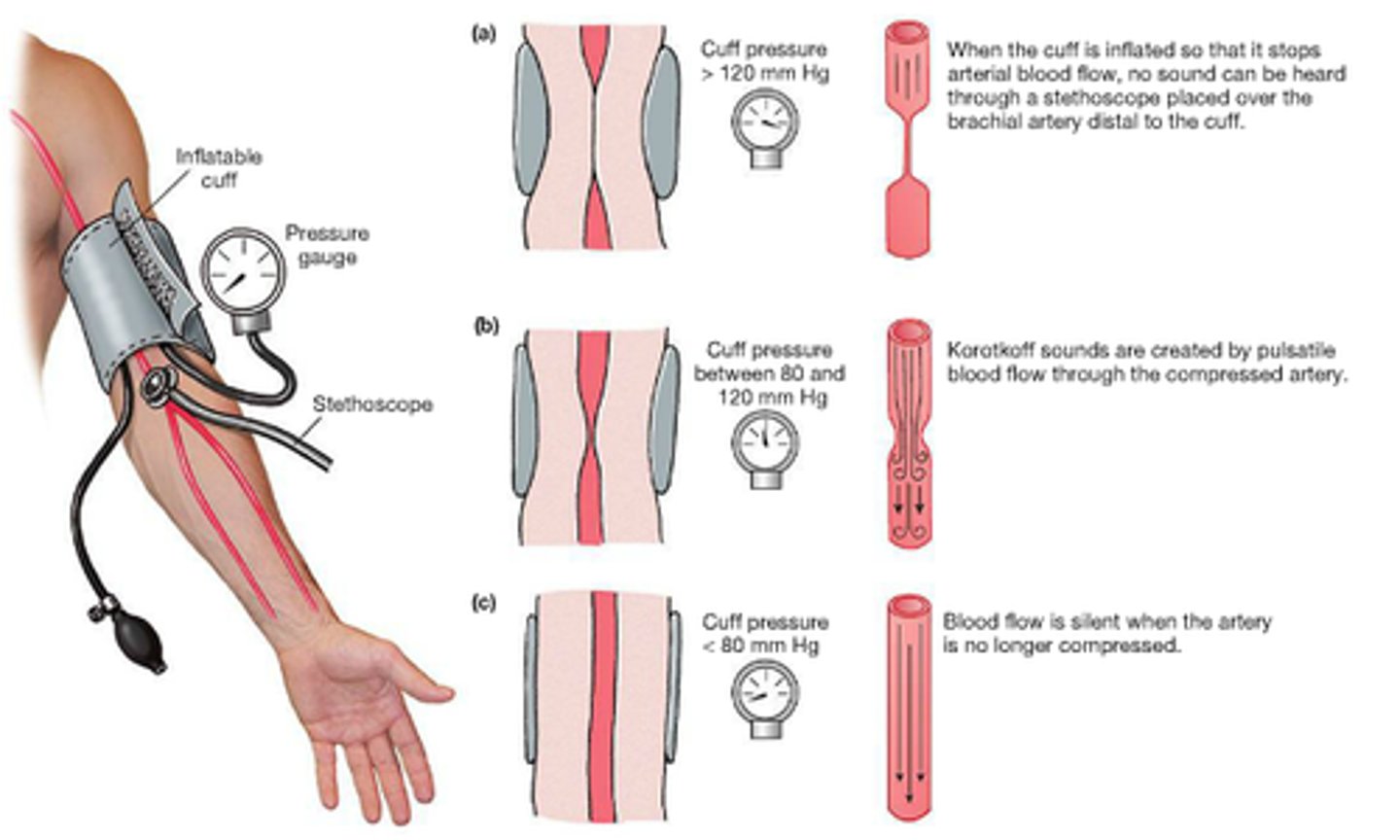
diastolic pressure
the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest
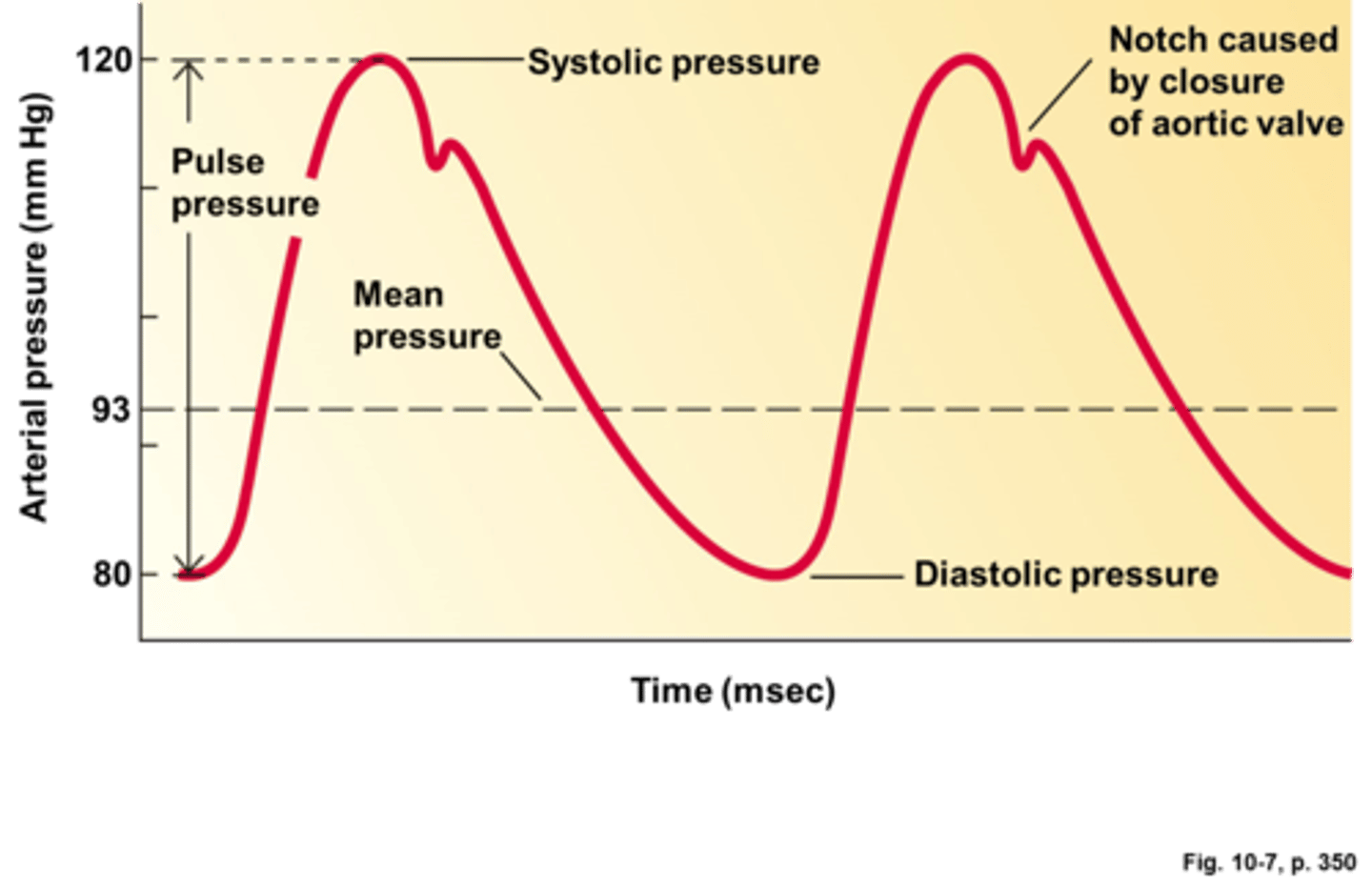
pulse pressure
the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure
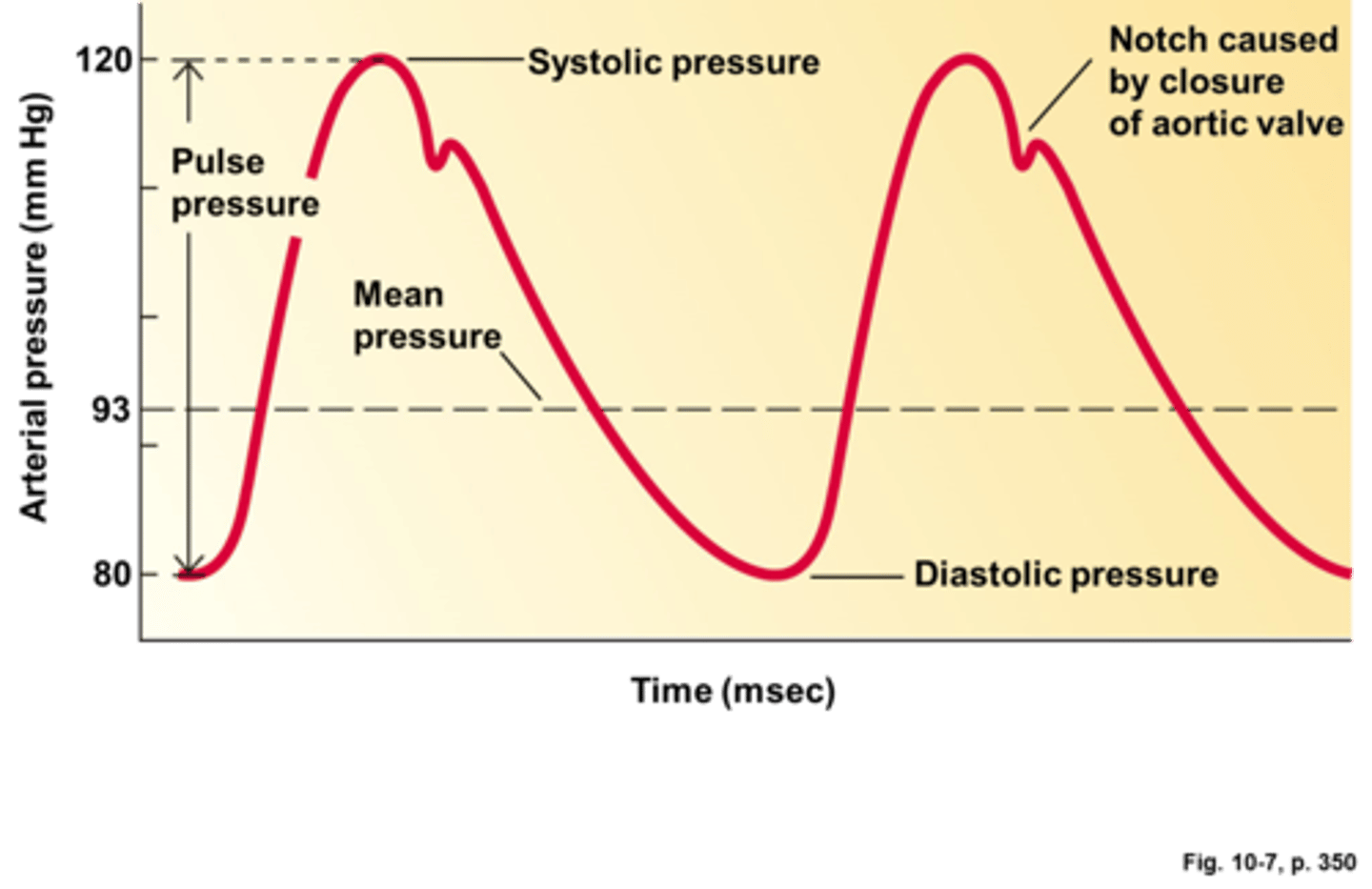
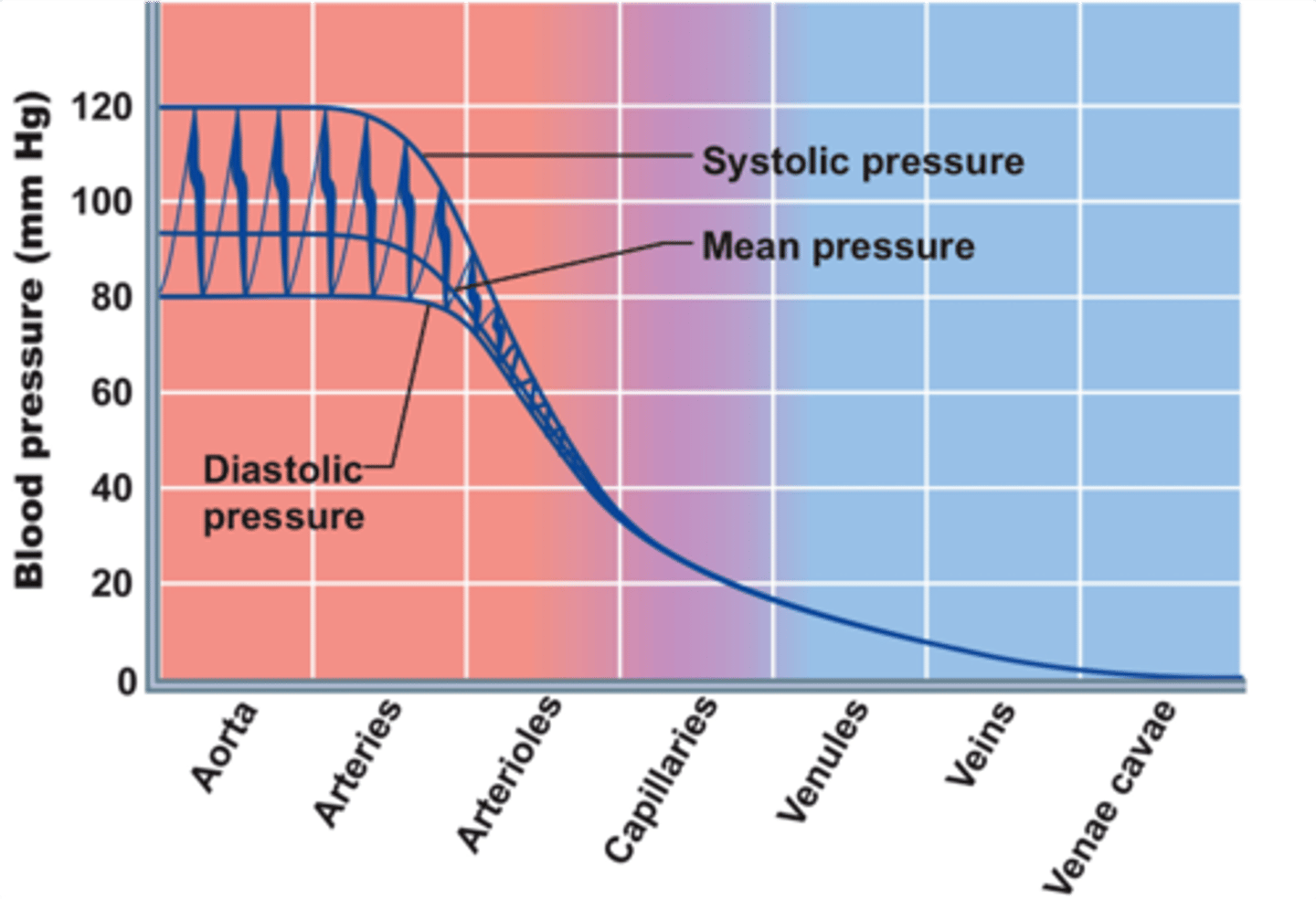
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)
pressure forcing blood into tissues, averaged over cardiac cycle
resistance
The slowing or blocking of blood flow
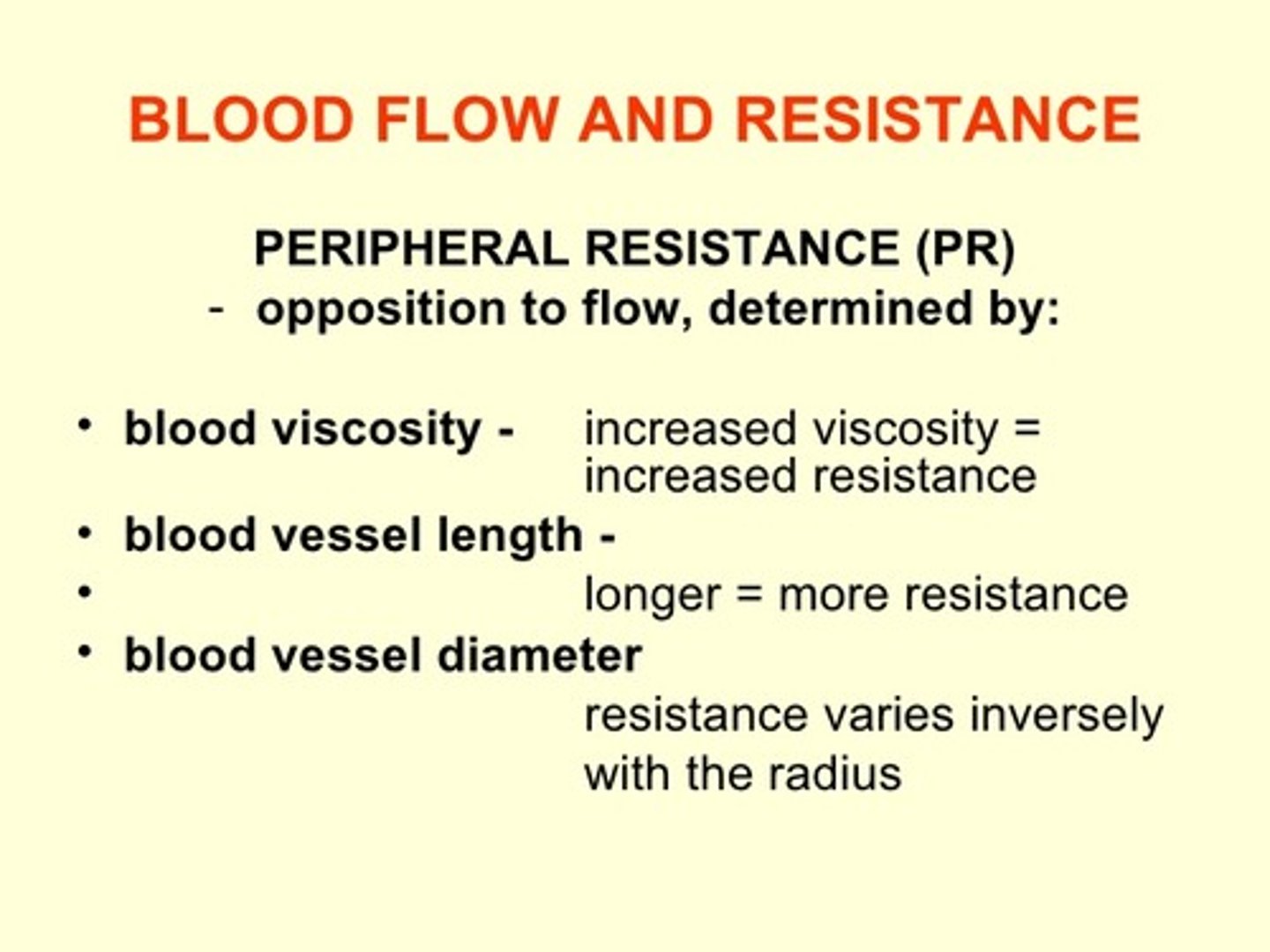
flow rule
Flow = Pressure/Resistance
blood viscosity
the thickness and stickiness of blood
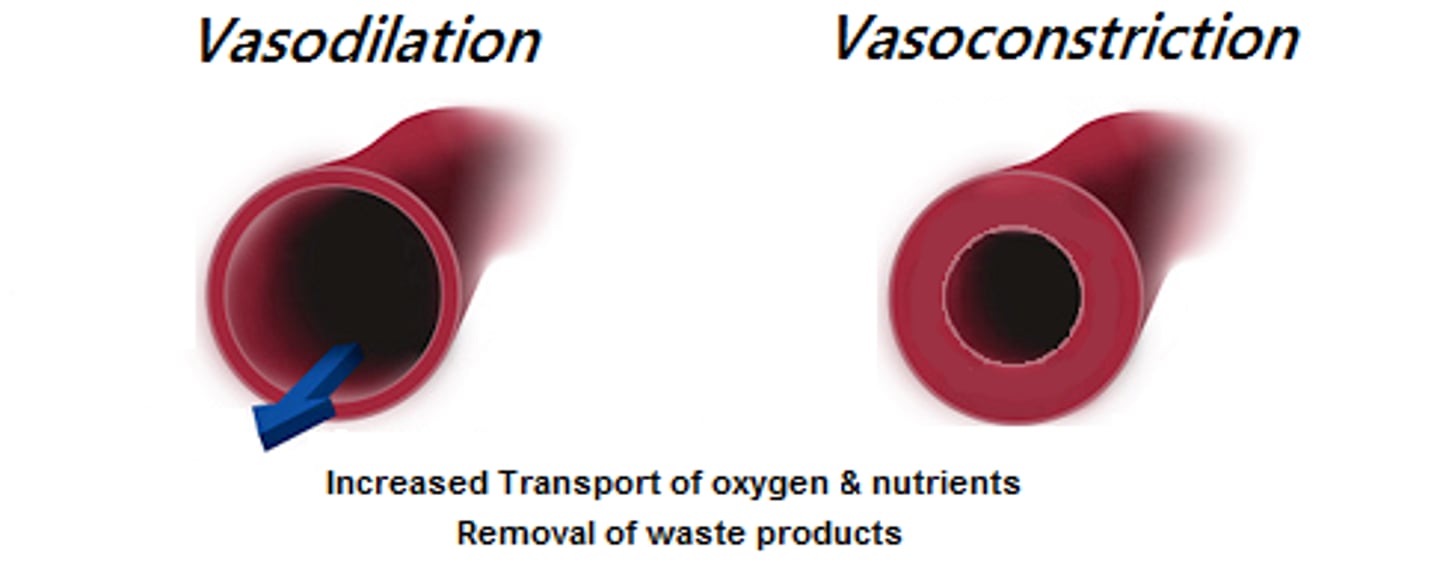
vasoconstriction
the constriction of blood vessels, which increases blood pressure.
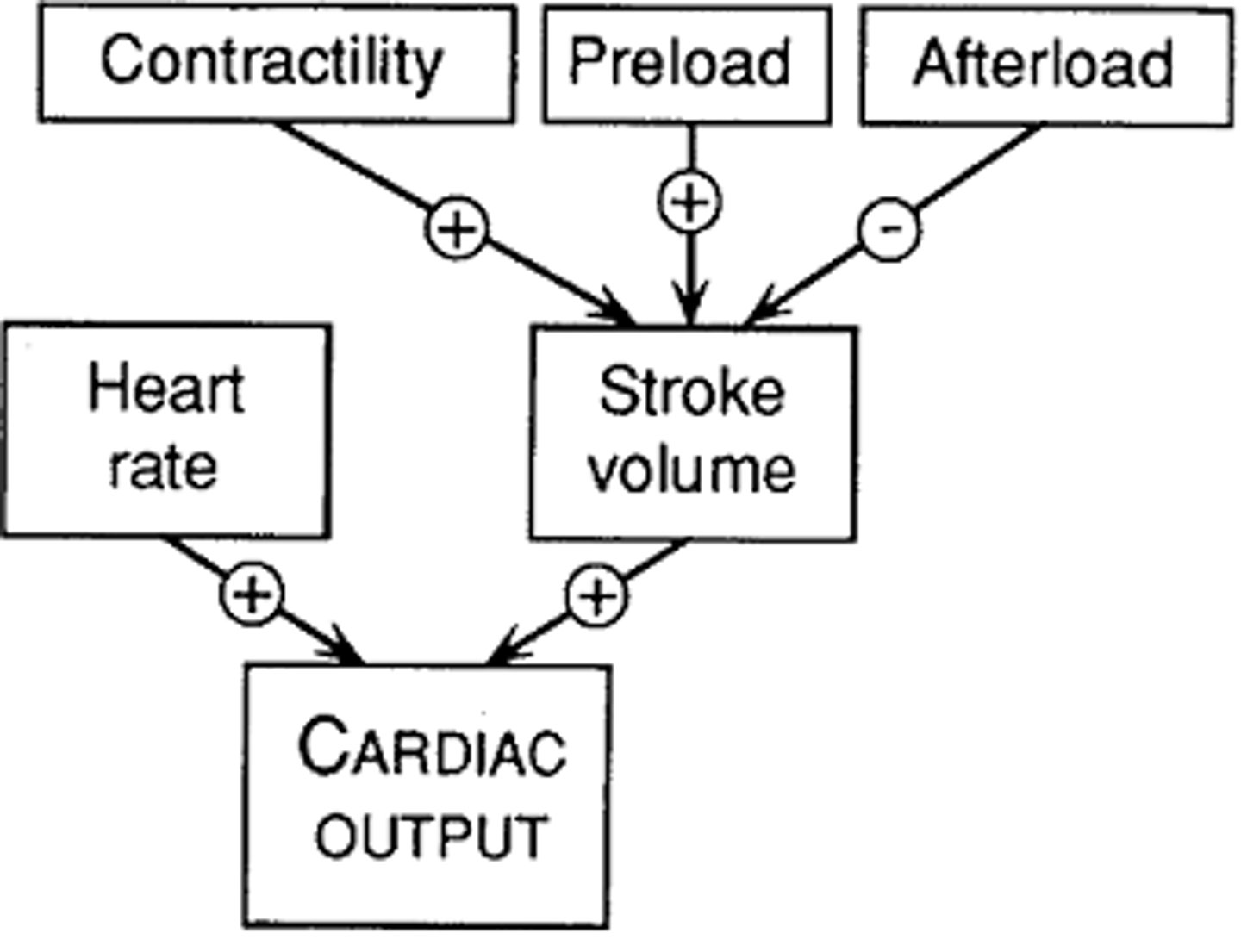
cardiac output
The volume of blood ejected from the left side of the heart in one minute.
total peripheral resistance
the resistance of the entire cardiovascular system
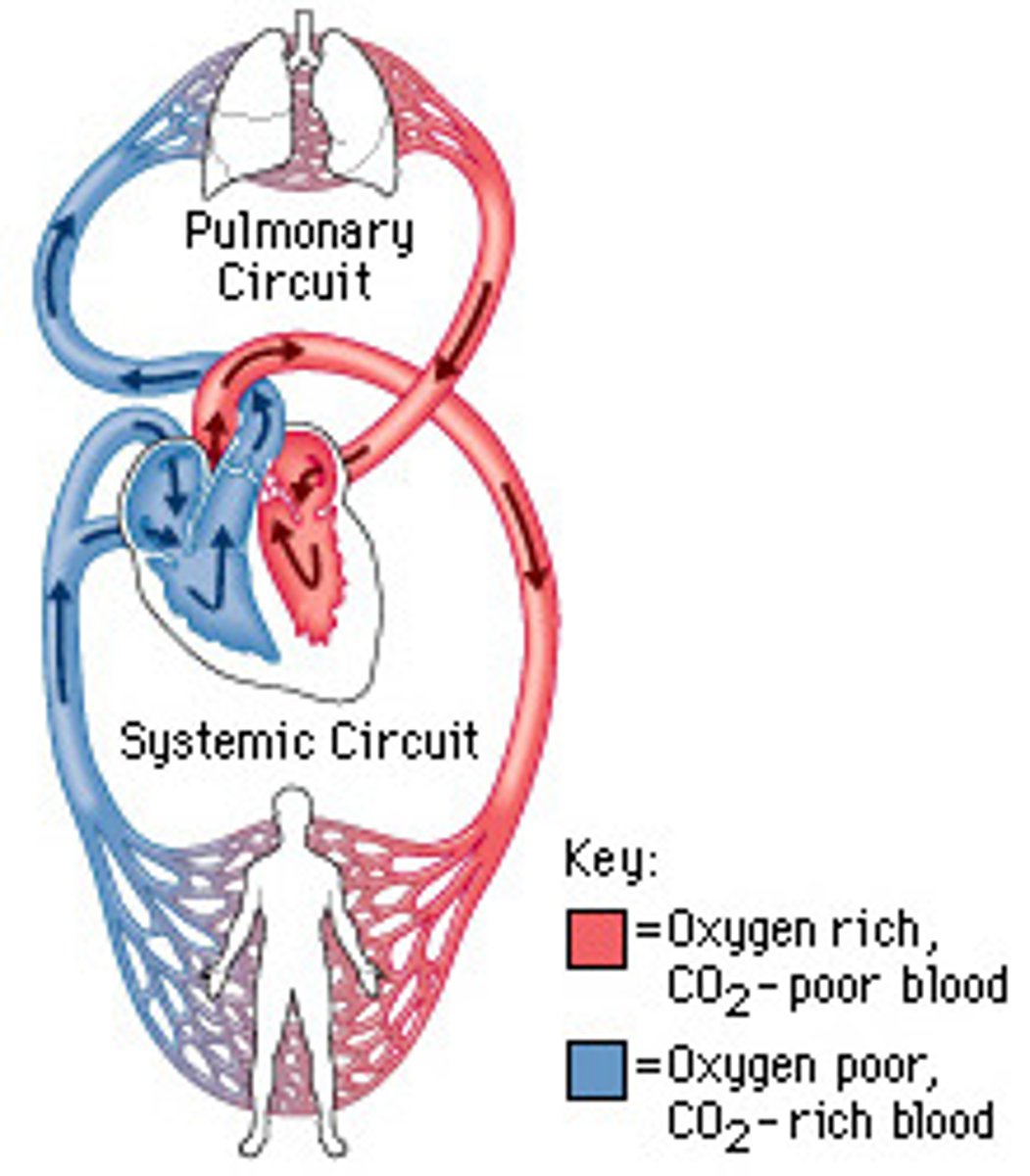
systemic circuit
Circuit of blood that carries blood between the heart and the rest of the body.
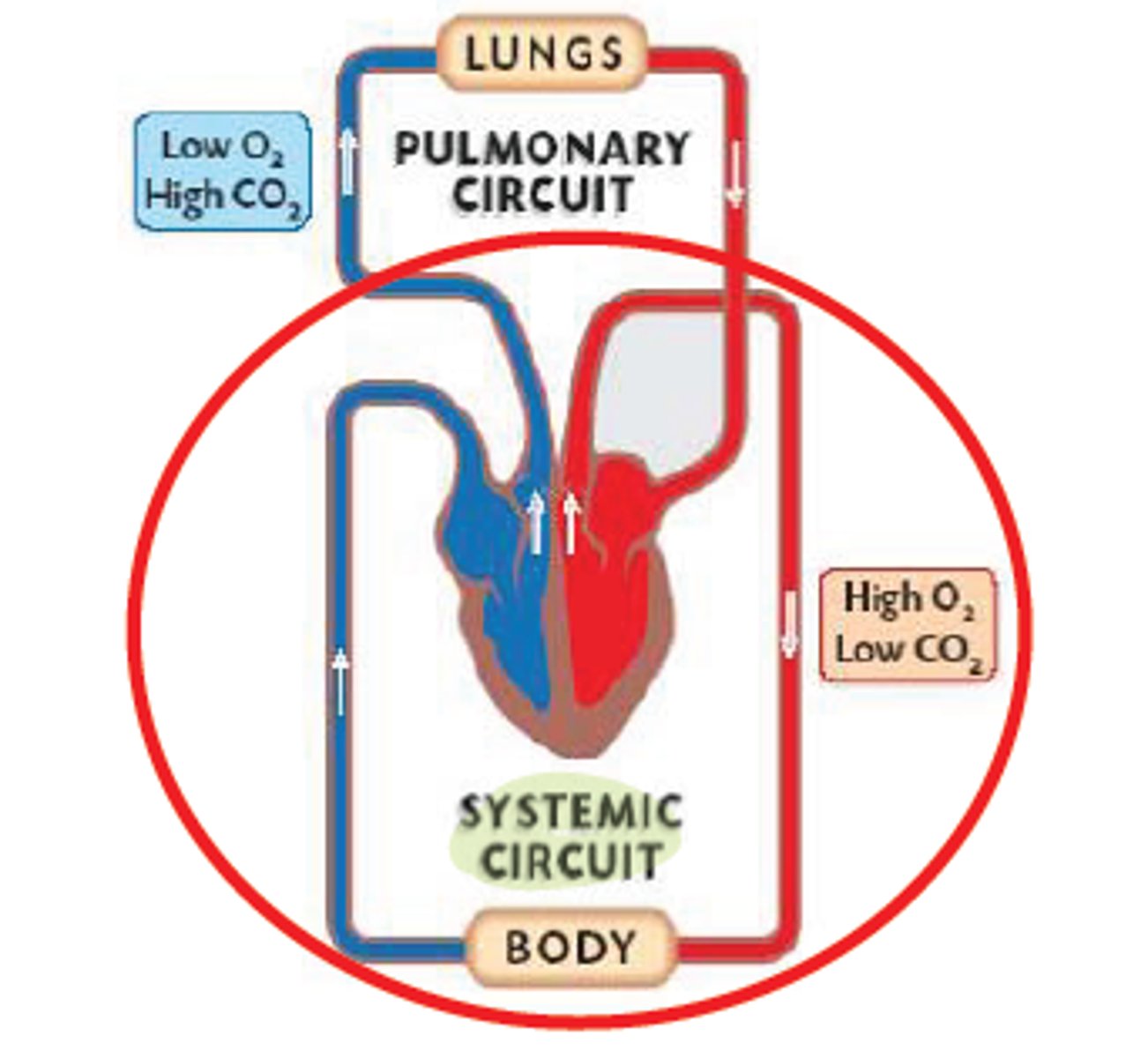
pulmonary circuit
system of blood vessels that carries blood between the heart and the lungs
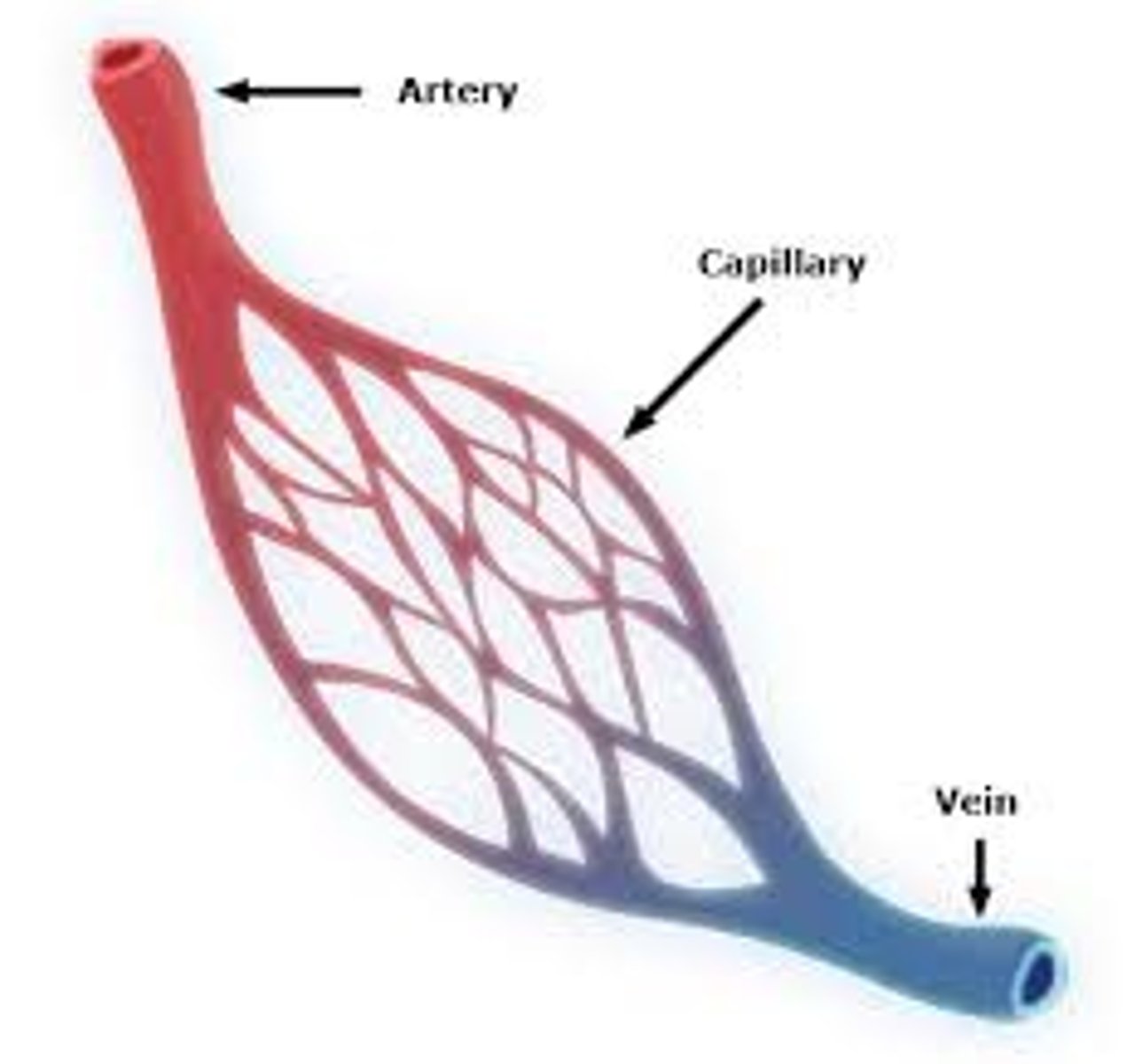
arteries
Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart
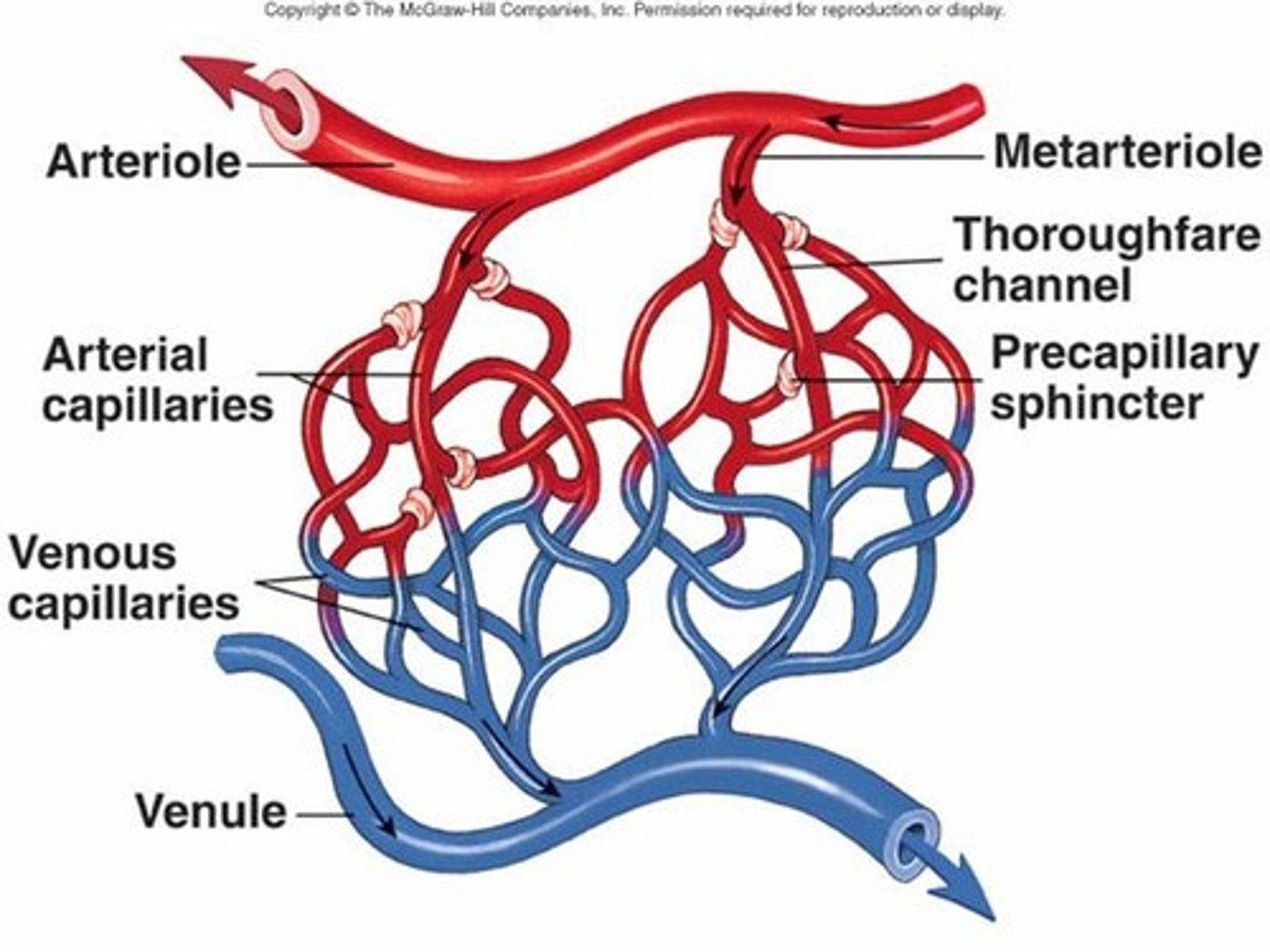
arterioles
small vessels that receive blood from the arteries
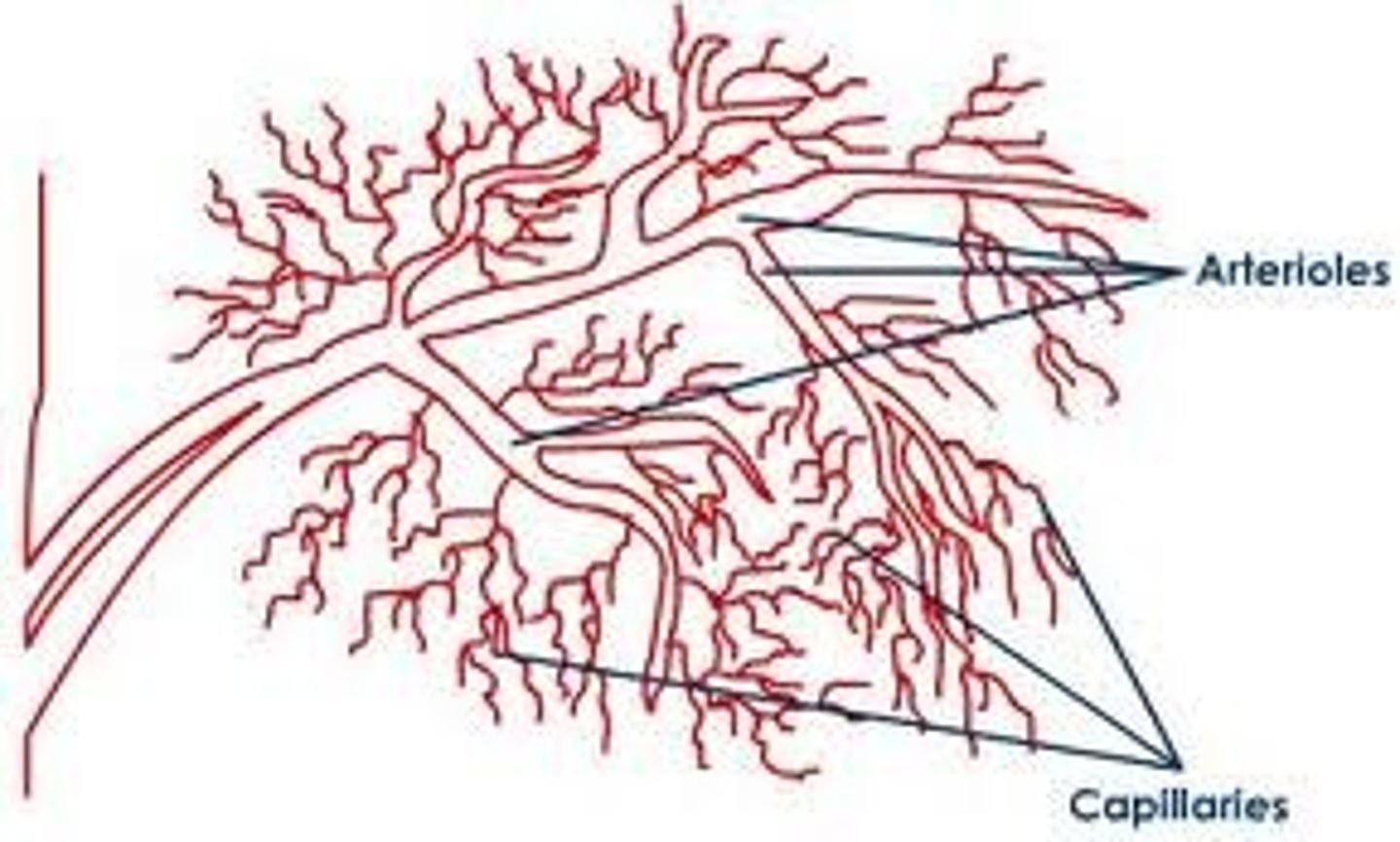
capillaries
Microscopic vessel through which exchanges take place between the blood and cells of the body
venules
small vessels that gather blood from the capillaries into the veins
veins
Blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart
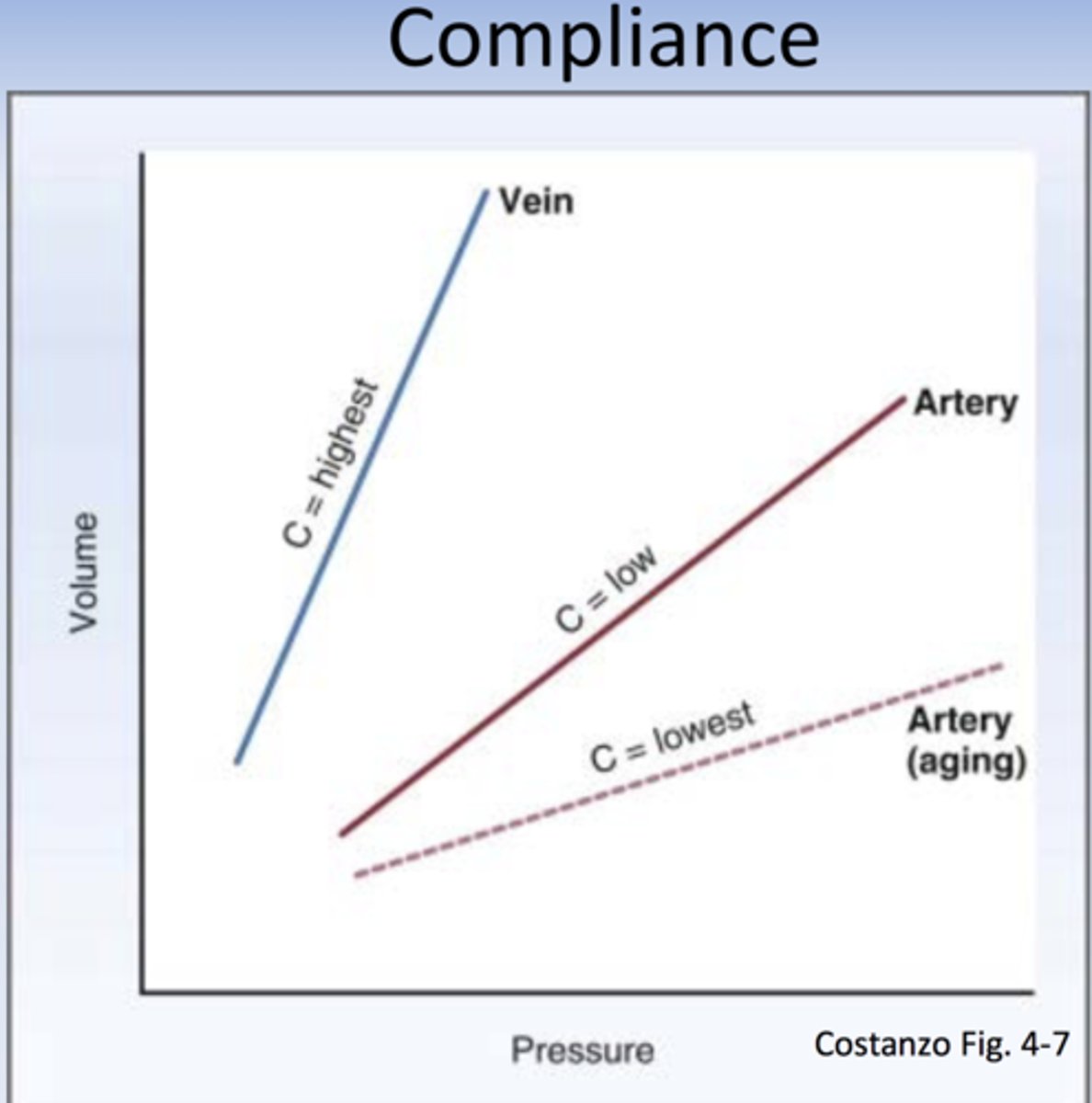
compliance
the ability of a vessel to respond to an increase in pressure by to distending or swell and increase the volume of blood it can hold, or with decreased pressure, a decrease in volume
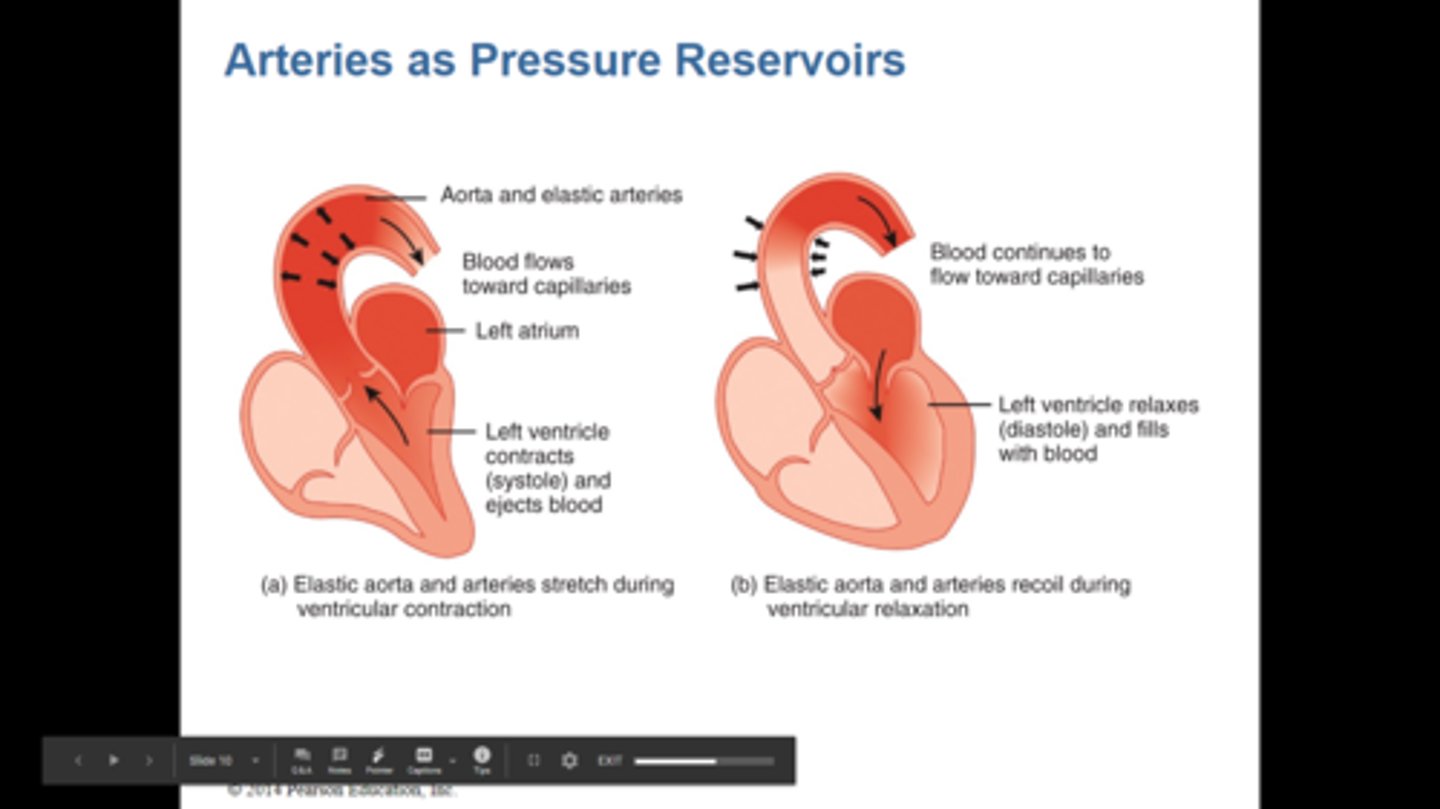
pressure reservoir
the temporary storage of potential energy by elastic arteries as their walls are stretched by the incoming surge of blood, followed by the release of kinetic energy as the vessels recoil, which moves blood through the arteries
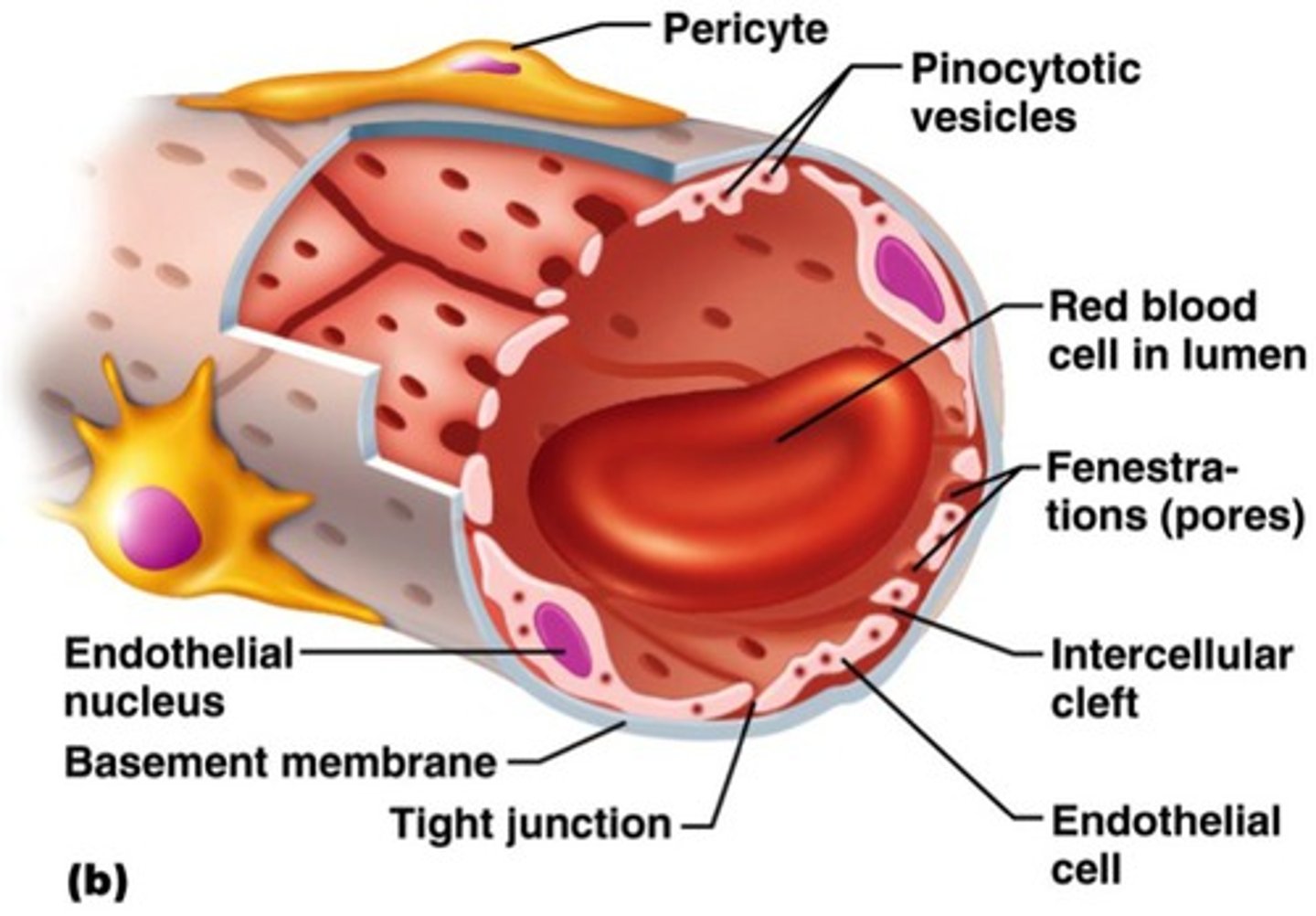
pores/fenestrations
holes in capillaries of glomerulus
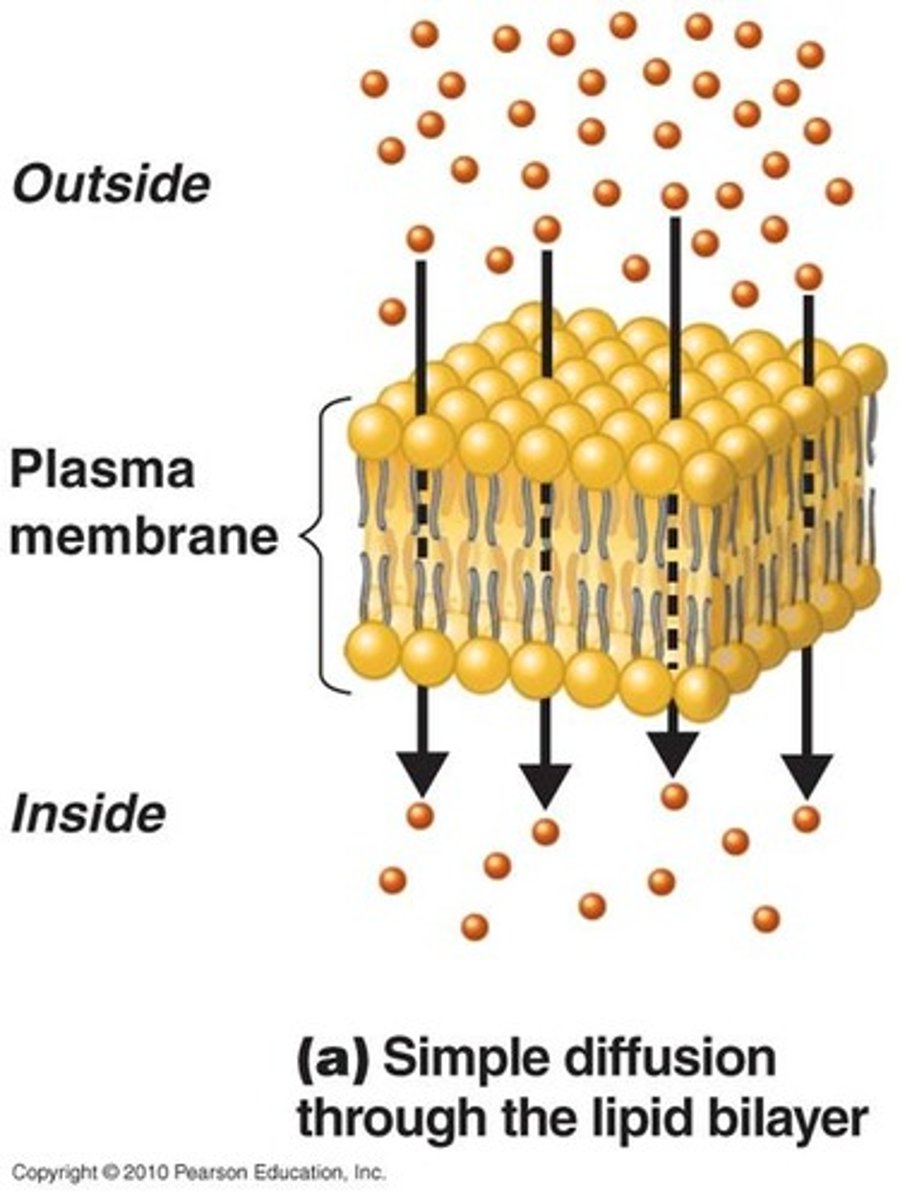
simple diffusion
movement of a solute from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
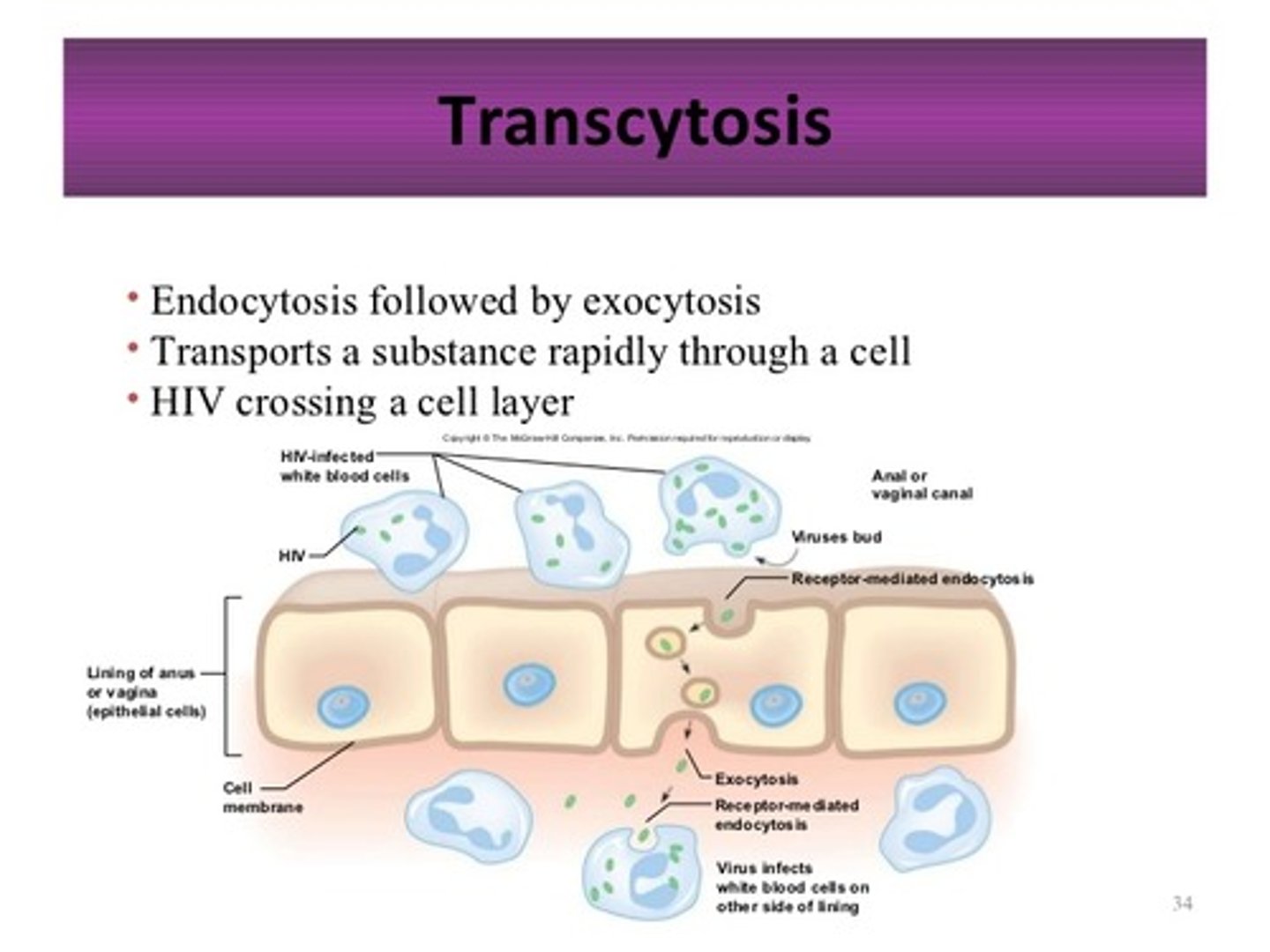
transcytosis
moving substances into, across, and then out of a cell
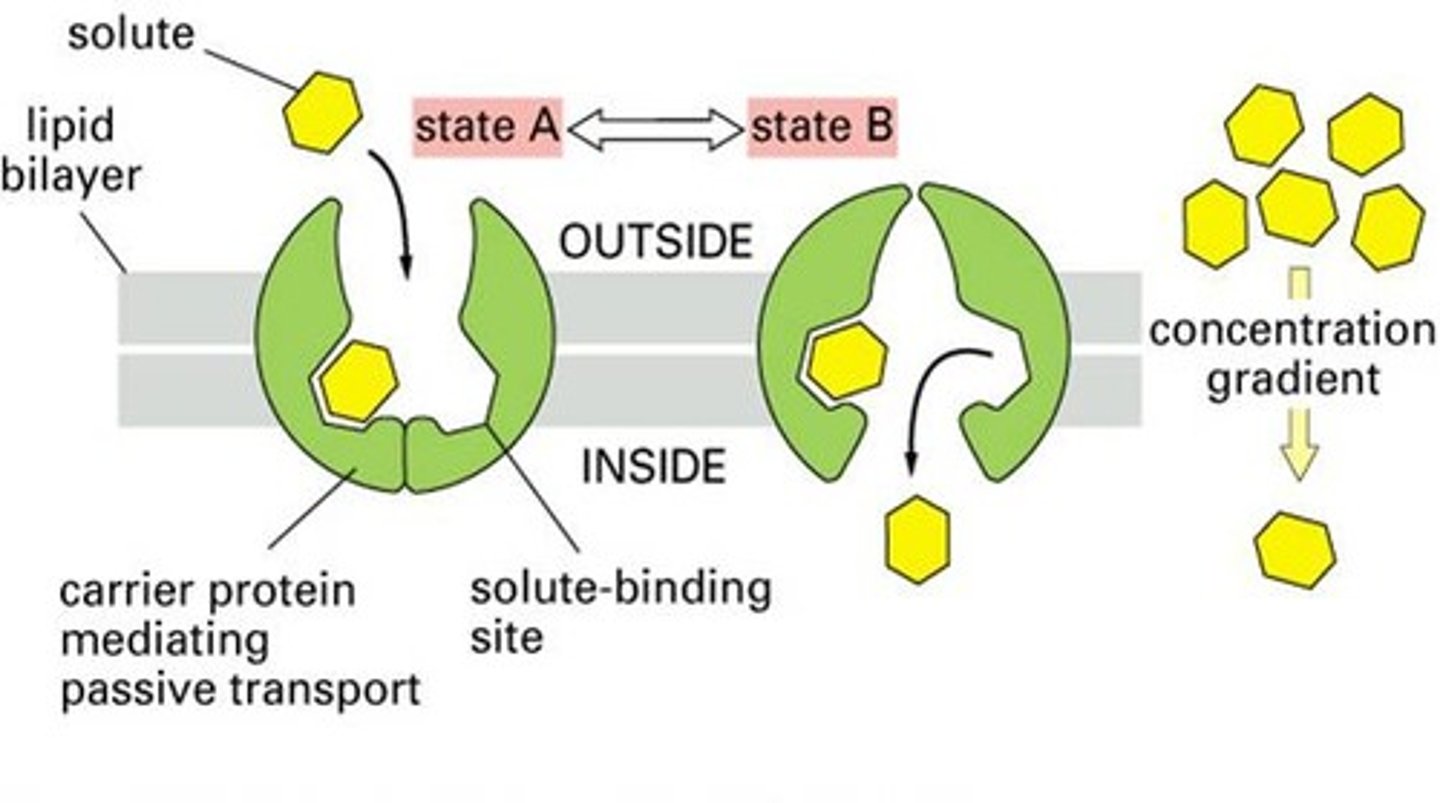
carrier mediated transport
The type of transport in which proteins bind to ions or substrates and carry them across the plasma membrane
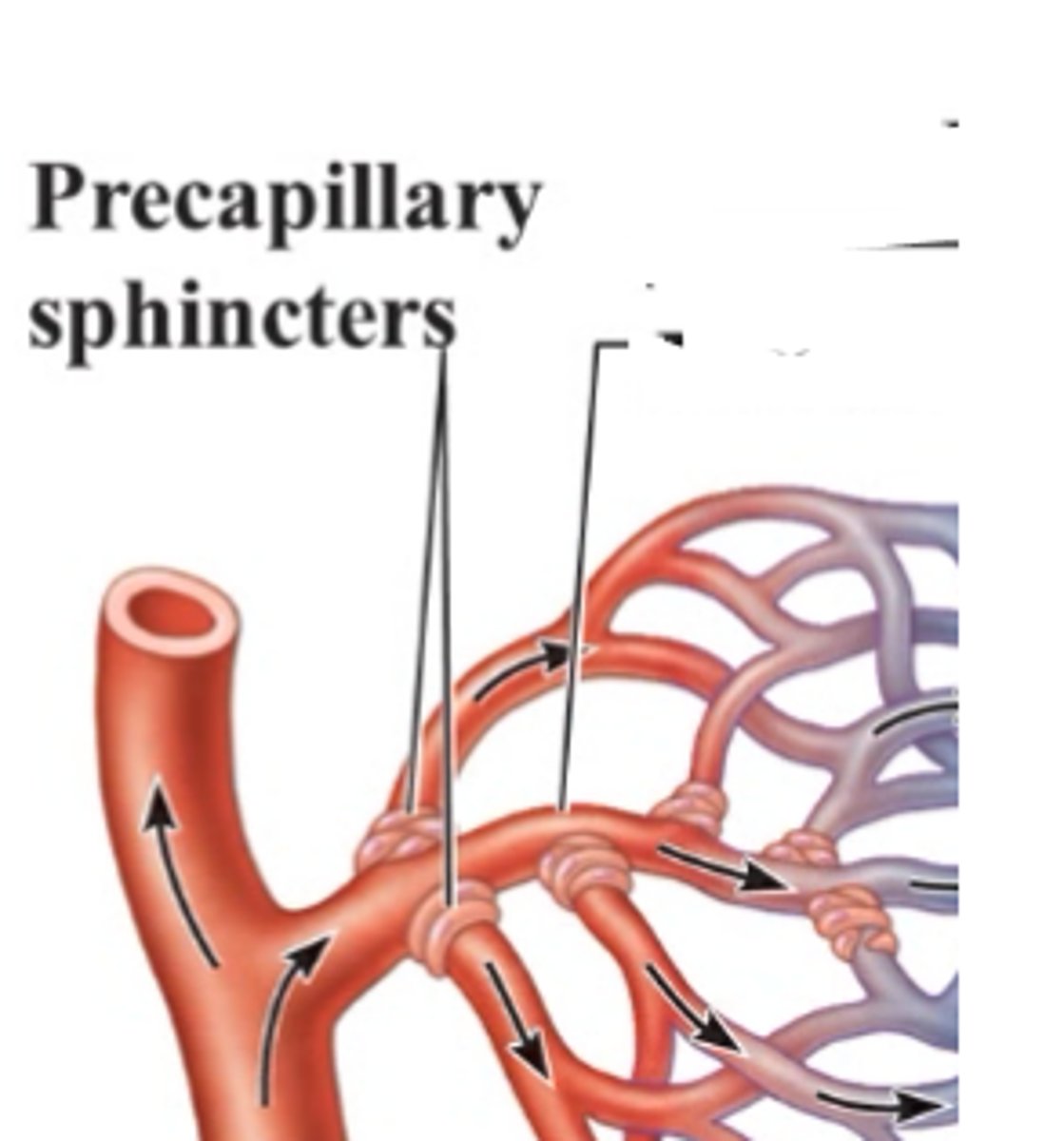
precapillary sphincters
control the blood flow into capillary beds.
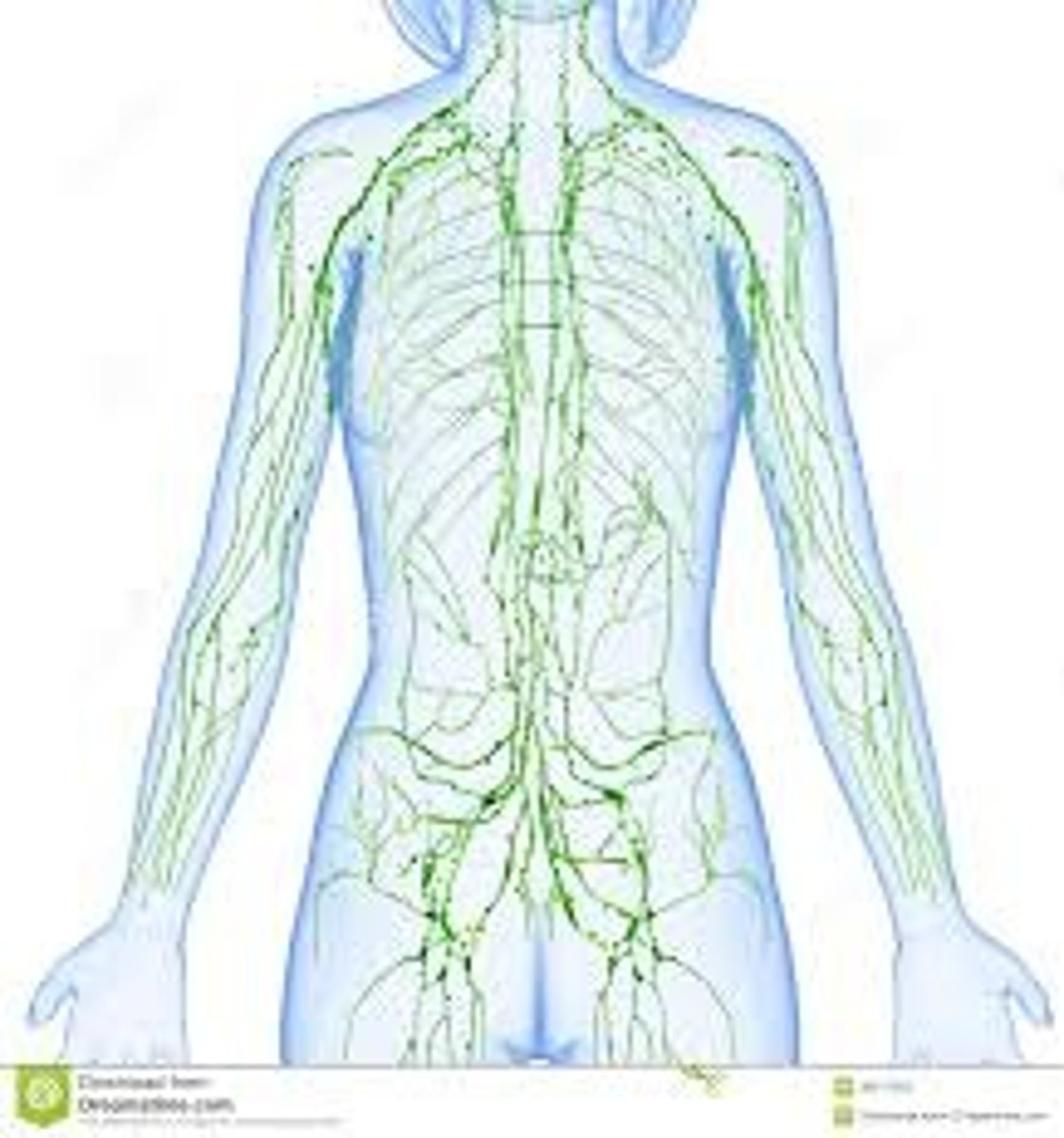
lymphatic system
the network of vessels through which lymph drains from the tissues into the blood.
osmotic pressure
the external pressure that must be applied to stop osmosis
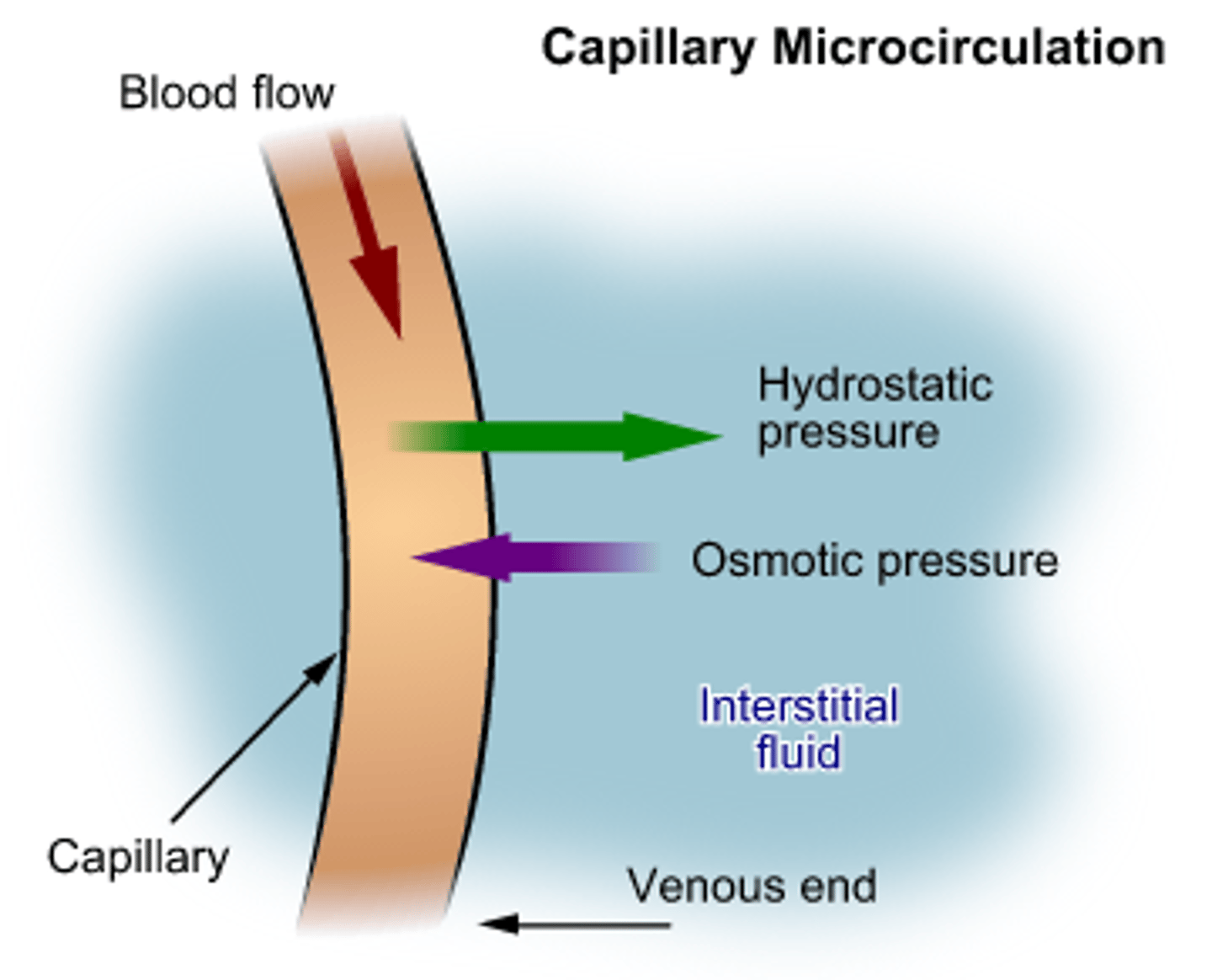
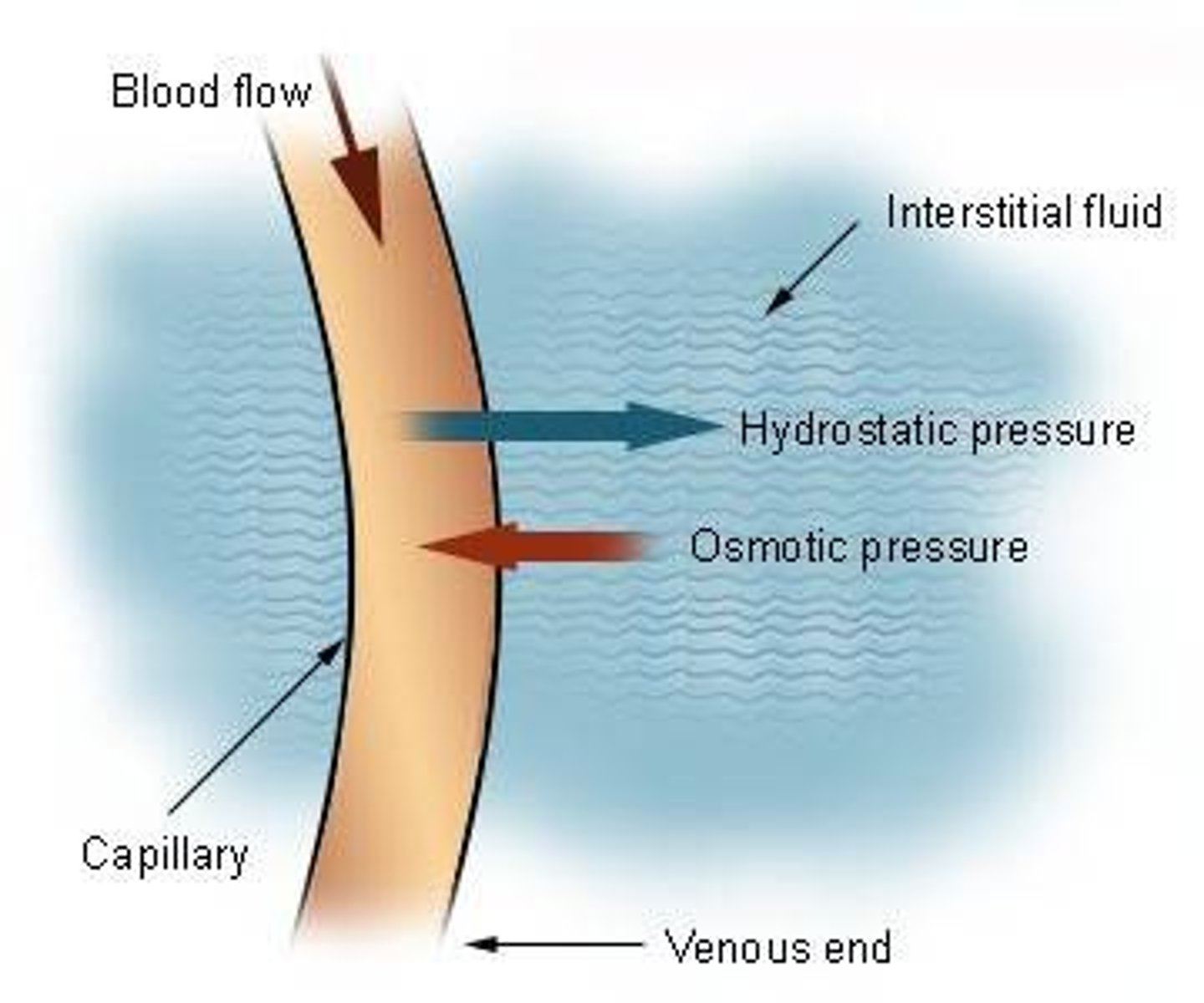
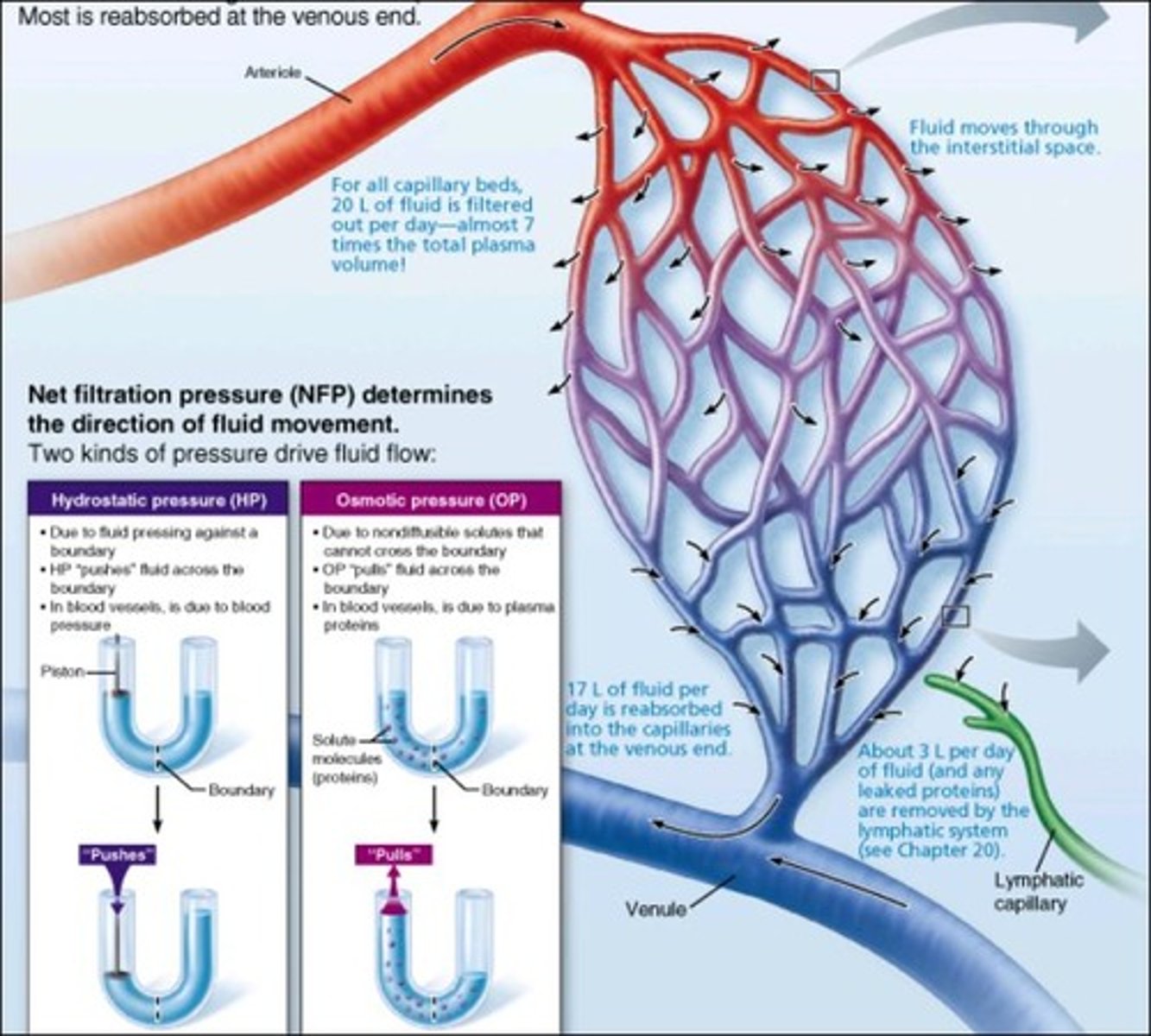
capillary hydrostatic pressure
facilitates the outward movement of water from the capillary to the interstitial space
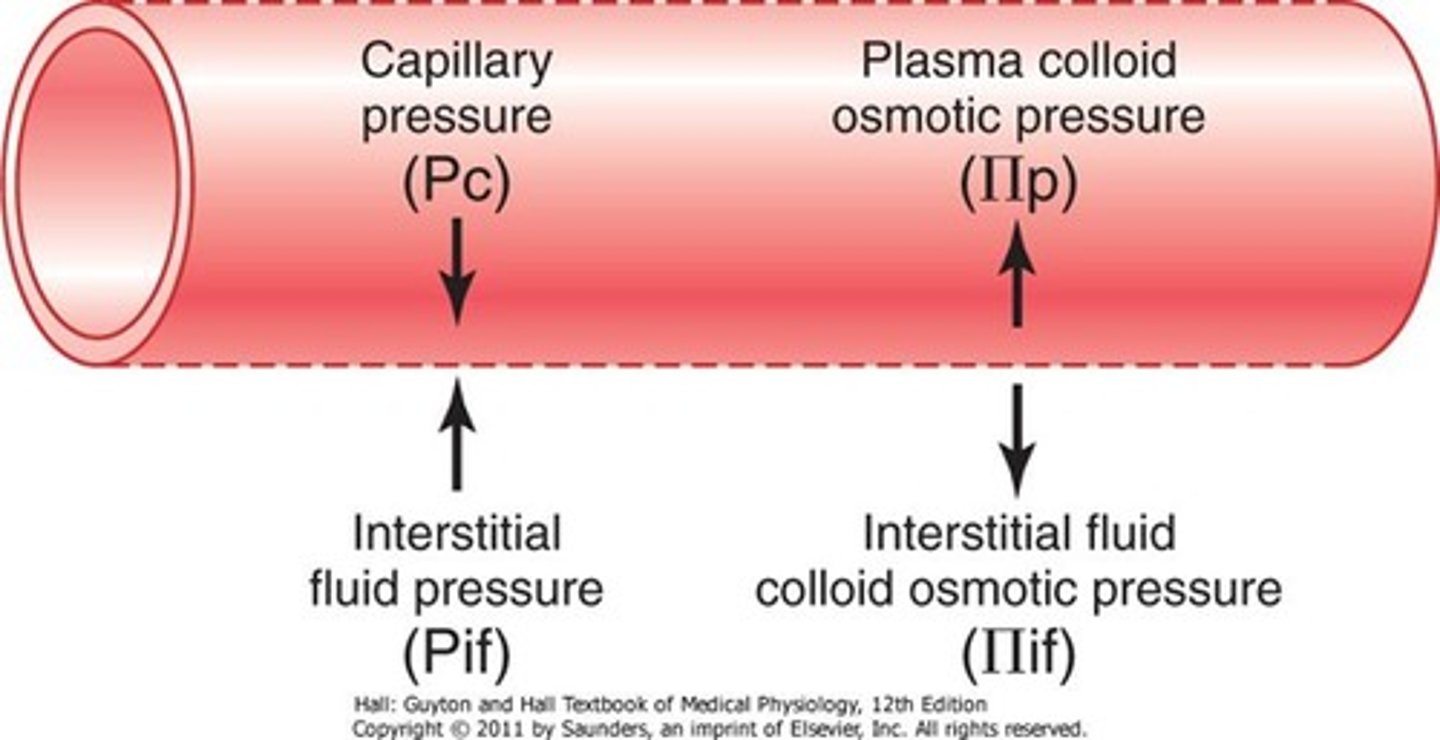
interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure
the pressure created by fluid located in the interstitial spaces which helps push fluid and solutes into capillaries
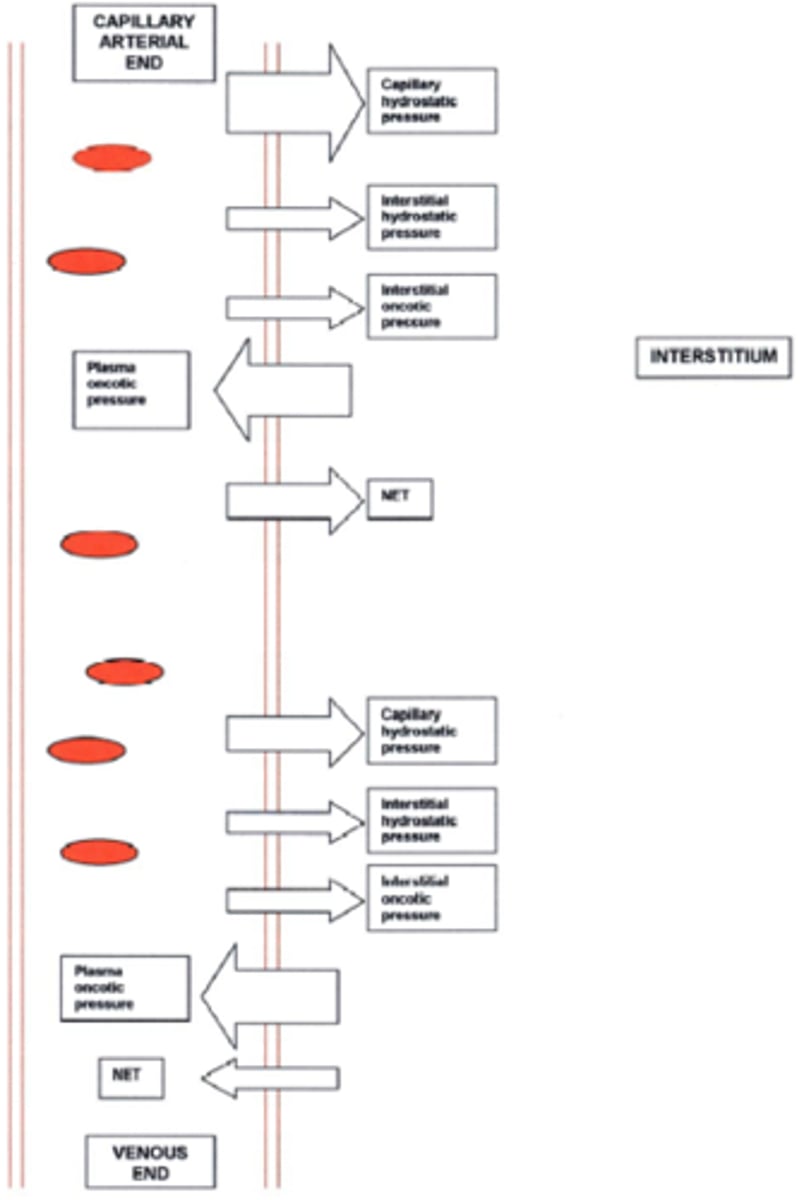
capillary osmotic pressure
pulls water into the capillary; albumin is the major contributor
interstitial fluid osmotic pressure
inward pulling force of particles in the interstitial fluid
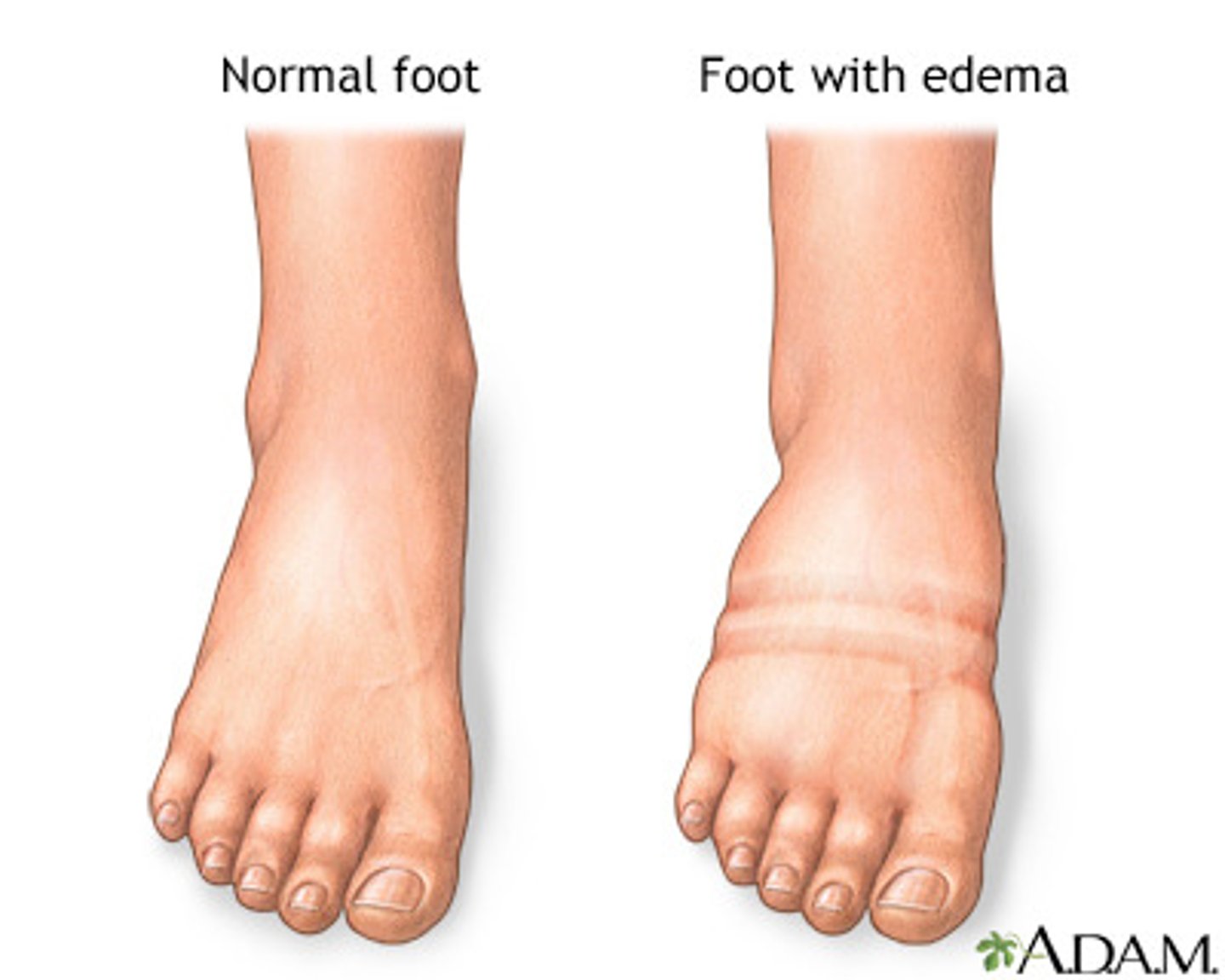
edema
puffy swelling of tissue from the accumulation of fluid
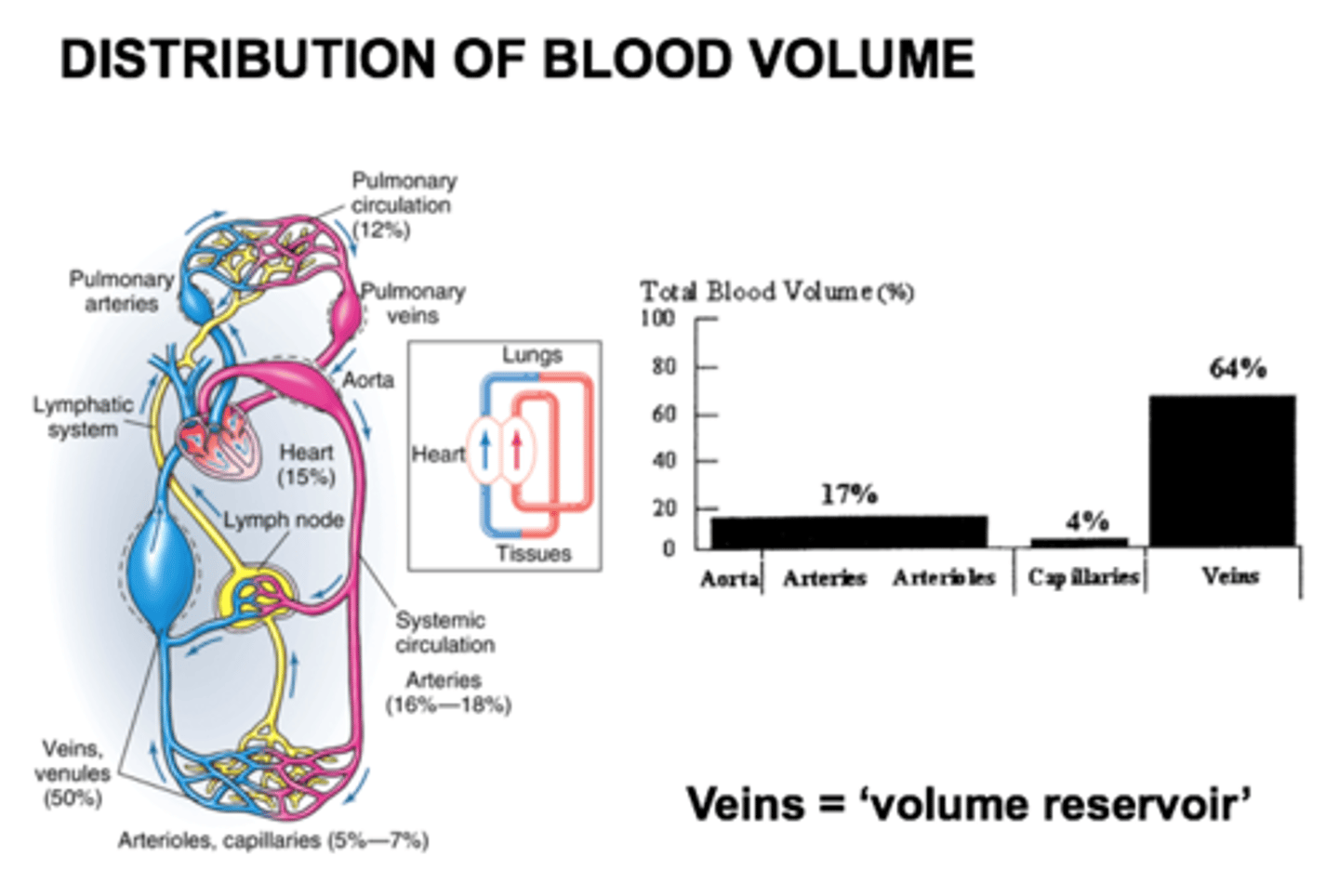
volume reservoirs
Veins serve as blood reservoirs because they are able to stretch and hold onto a larger percentage of blood volume
venous pressure
pressure in the venous system
venous return
The amount of blood returned to the heart by the veins
end-diastolic volume
volume of blood in each ventricle at end of ventricular diastole
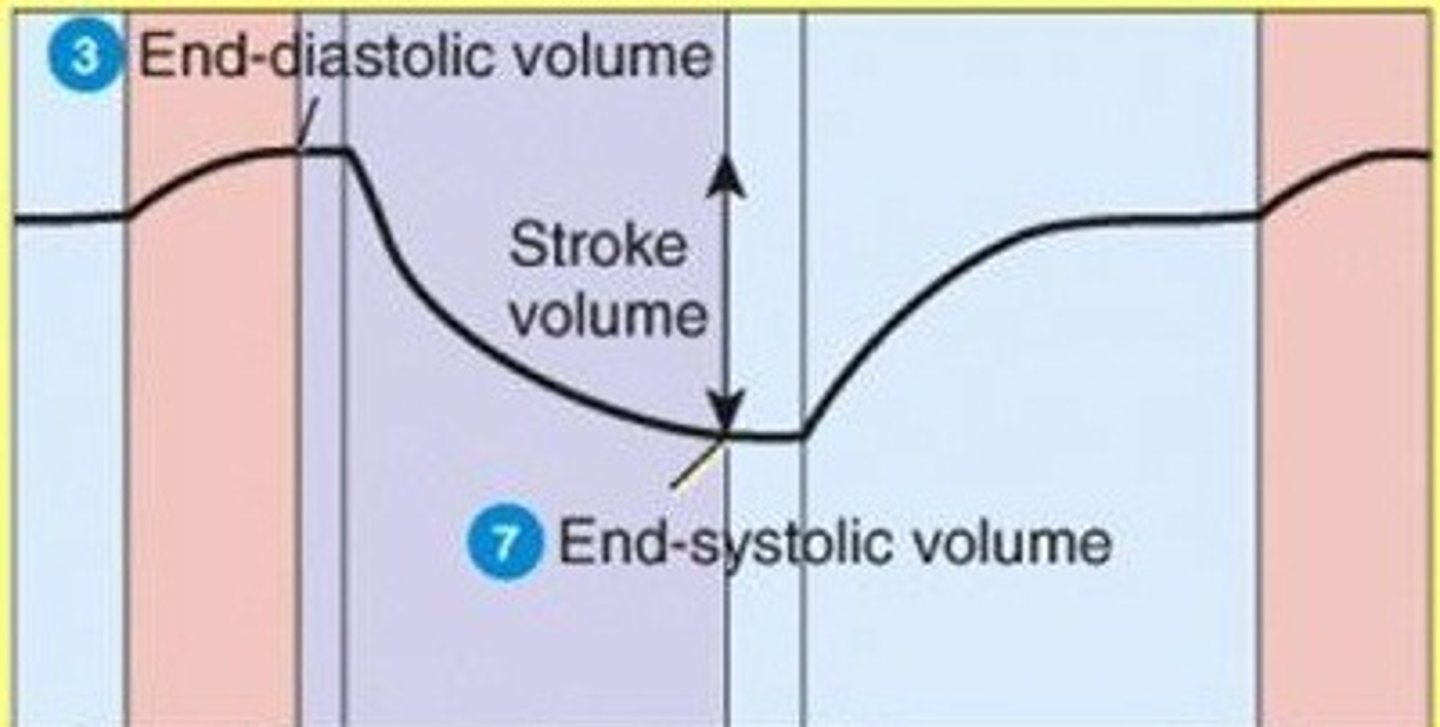
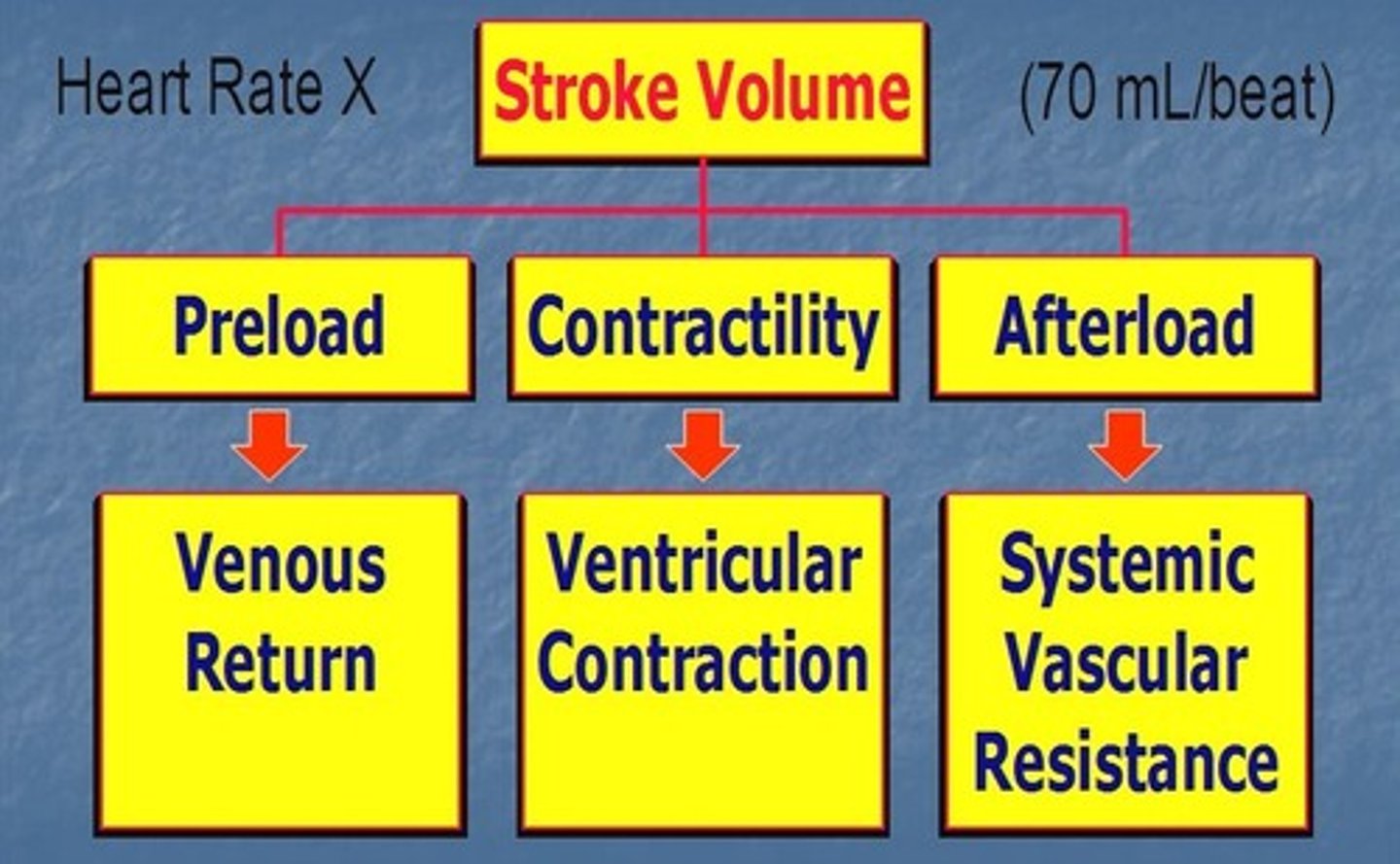
stroke volume
The amount of blood ejected from the heart in one contraction.
skeletal muscle pump
pumping effect of contracting skeletal muscles on blood flow through underlying vessels
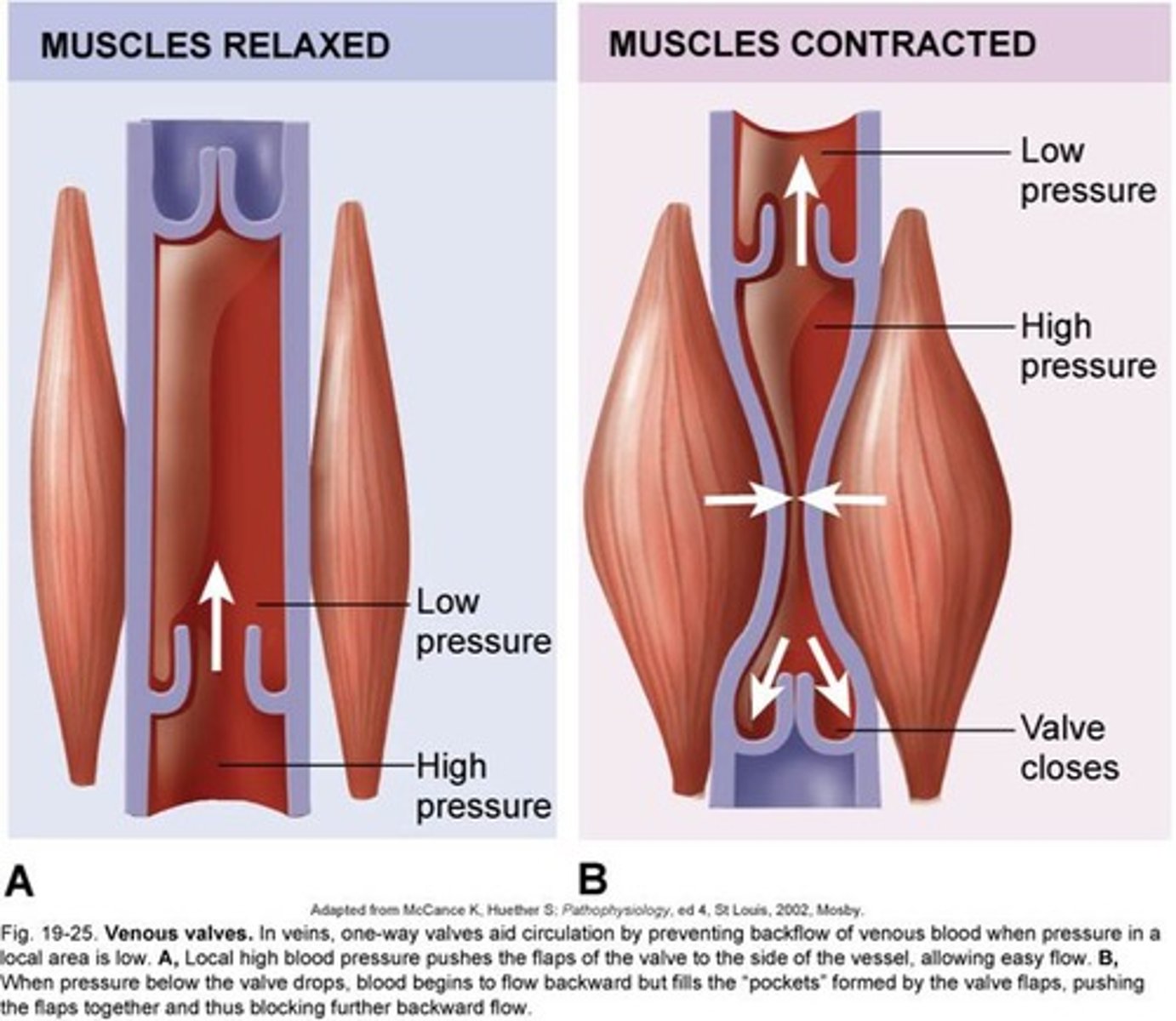
respiratory pump
Is composed of skeletal structures (bones) and soft tissues (muscles) that work together to allow proper respiratory mechanics to occur and help pump blood back to the heart during inspiration.
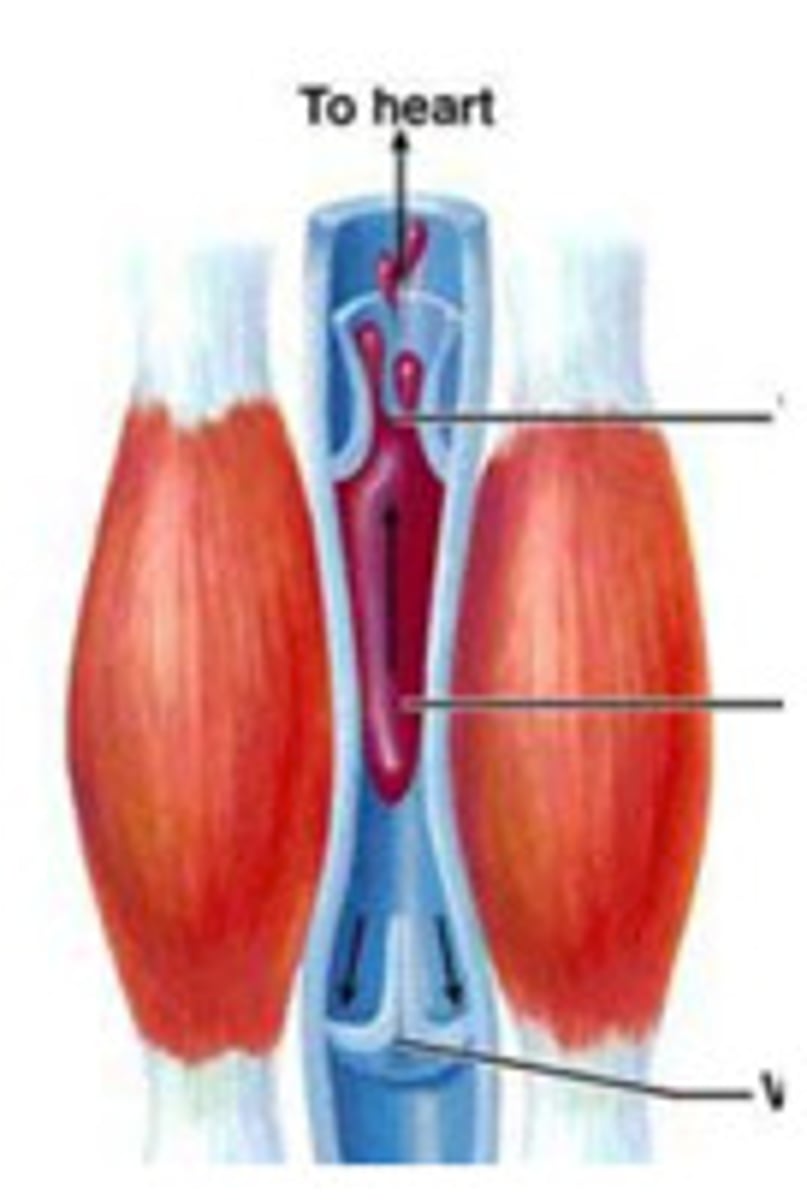
venomotor tone
The degree of muscle tone present within venous walls to promote venous return
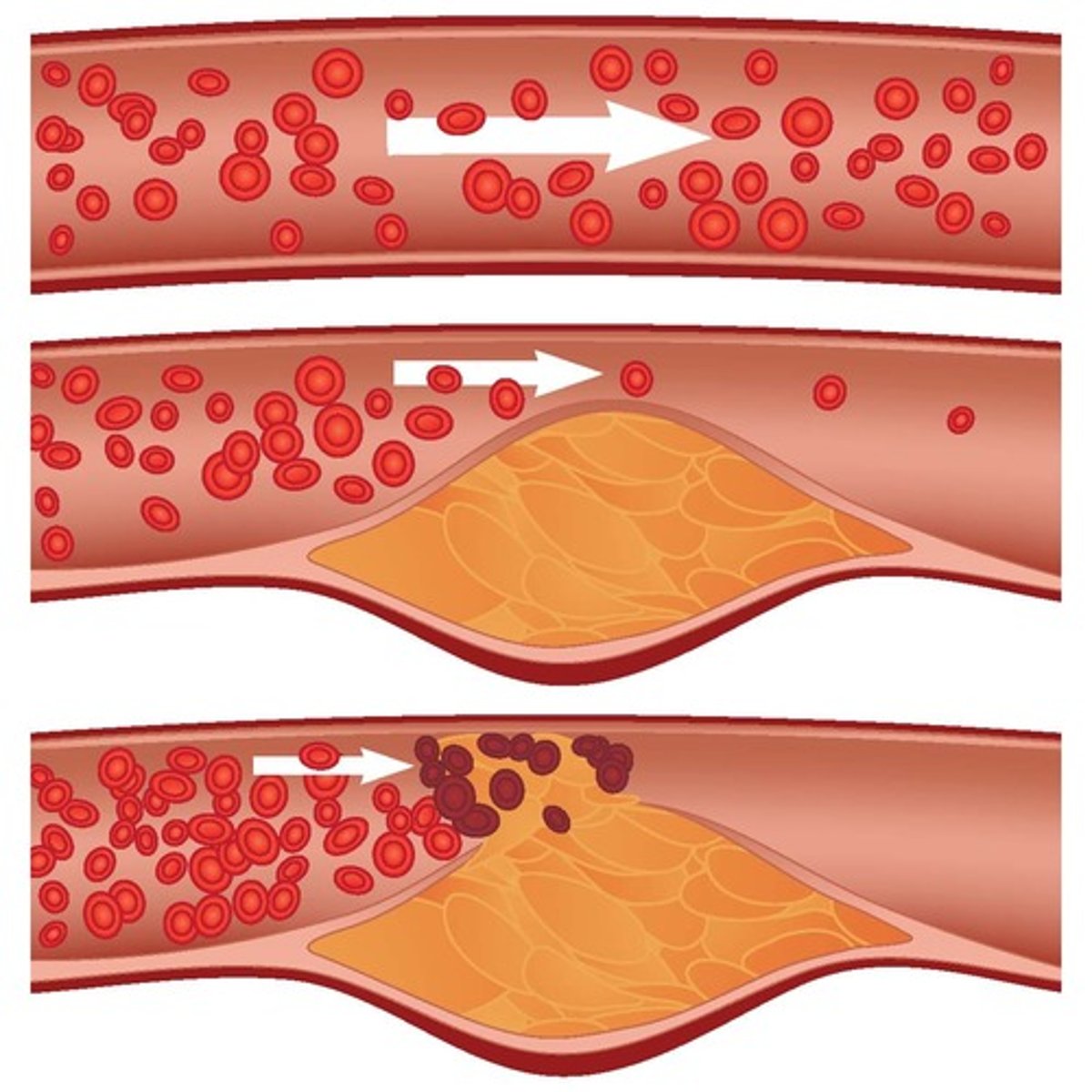
atherosclerosis
hardening of the arteries
hypotension
abnormally low blood pressure
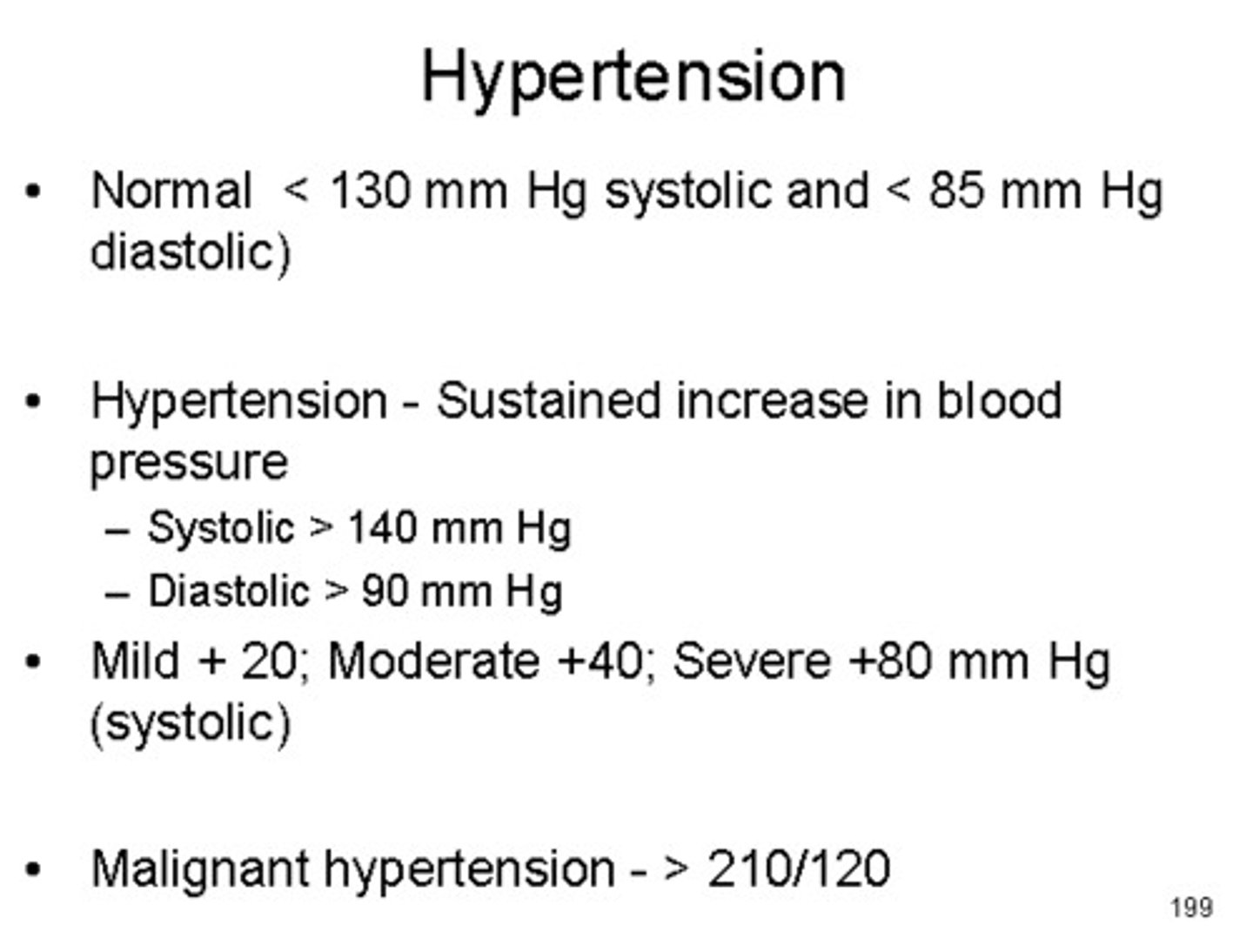
hypertension
abnormally high blood pressure
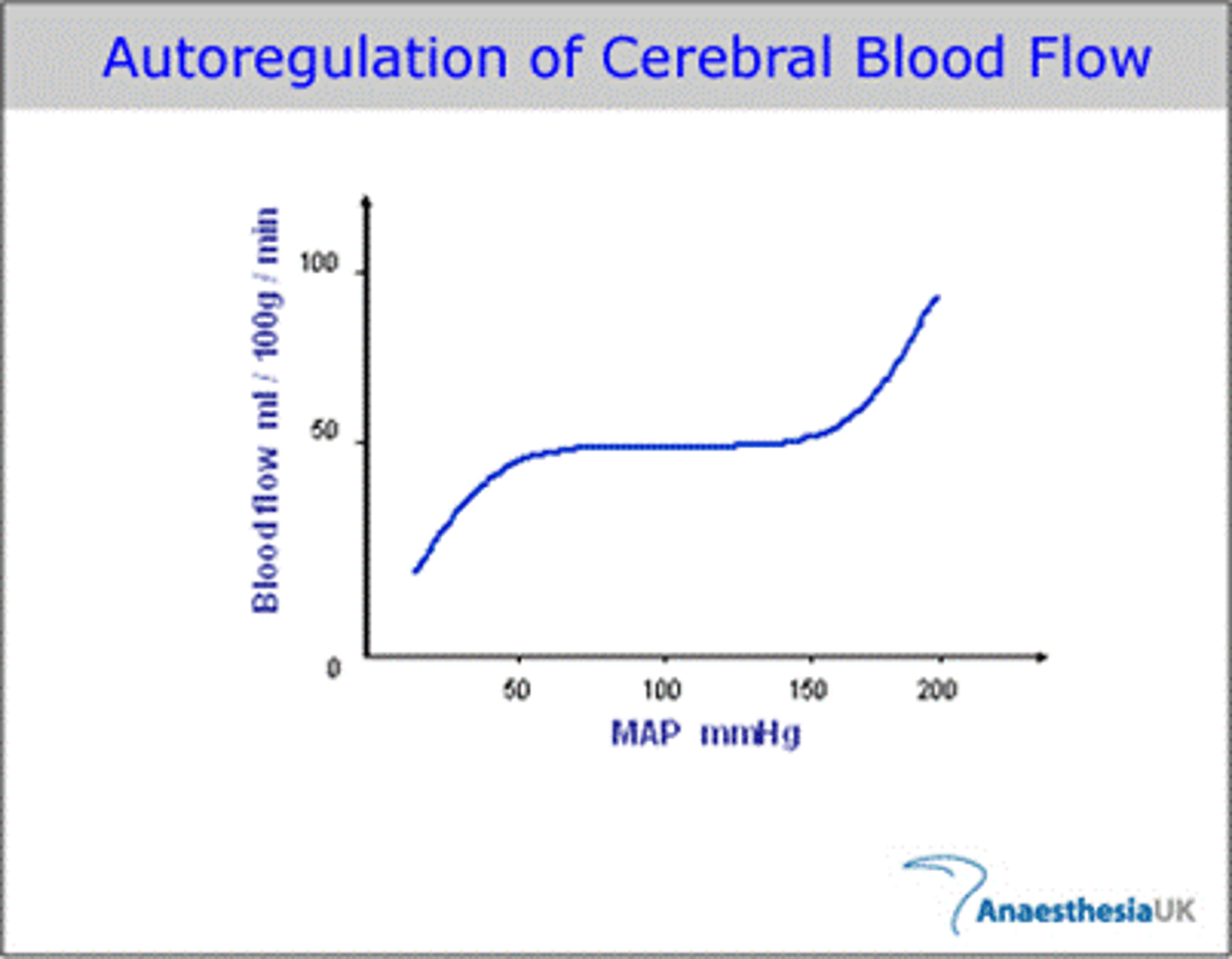
autoregulation
the ability of tissues to regulate their own blood supply
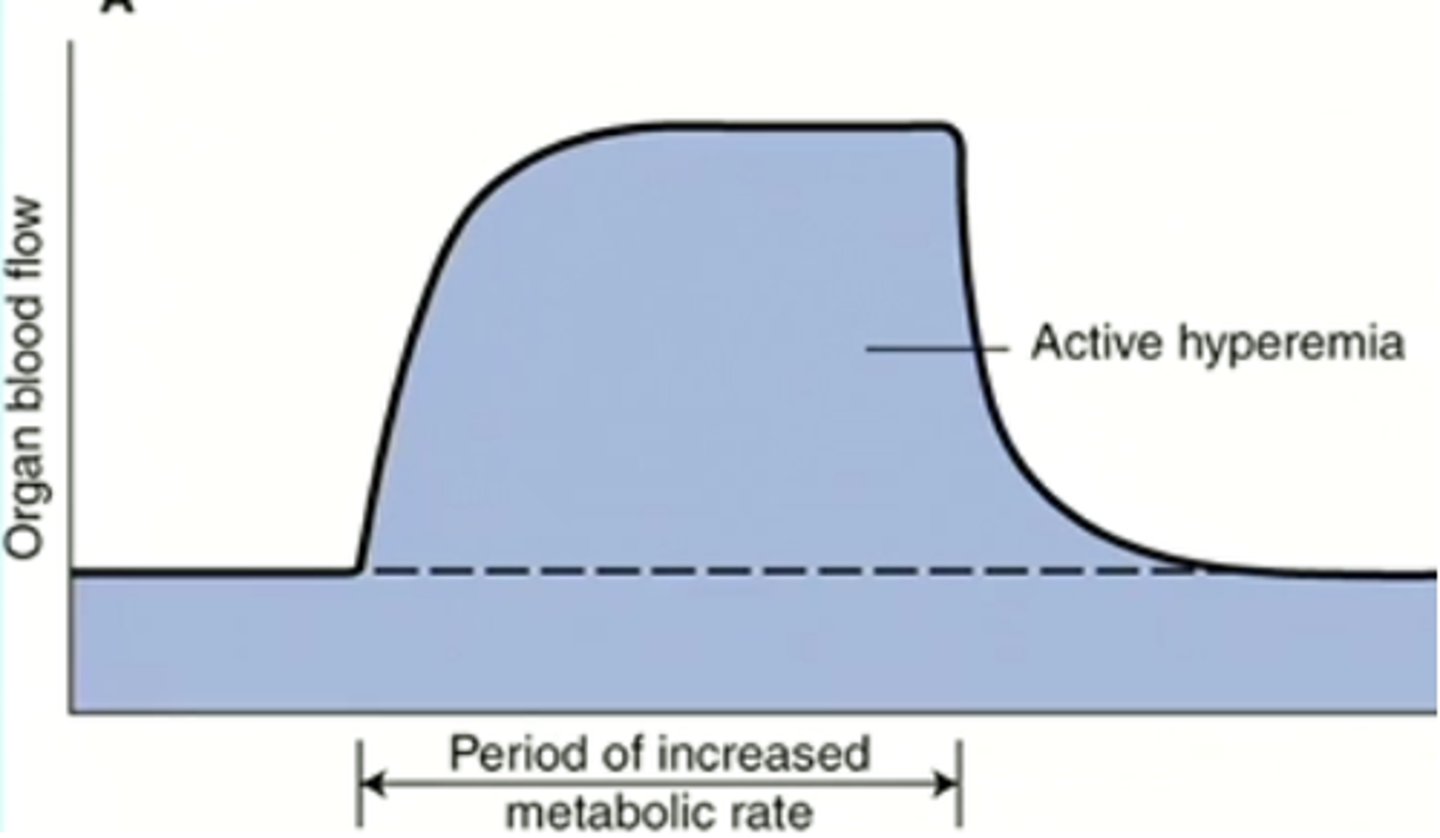
active hyperemia
increased blood flow in response to increased metabolic activity
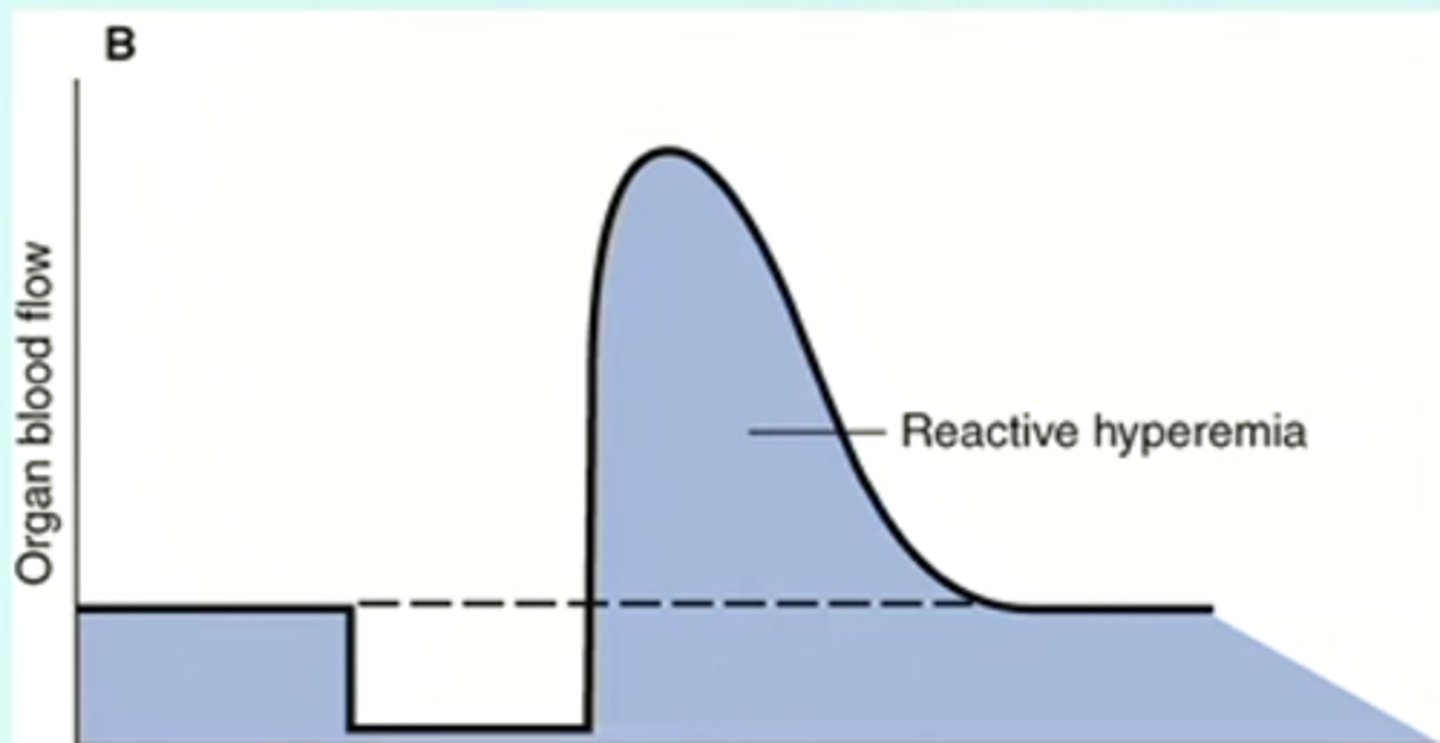
reactive hyperemia
redness of the skin resulting from dilation of the superficial capillaries
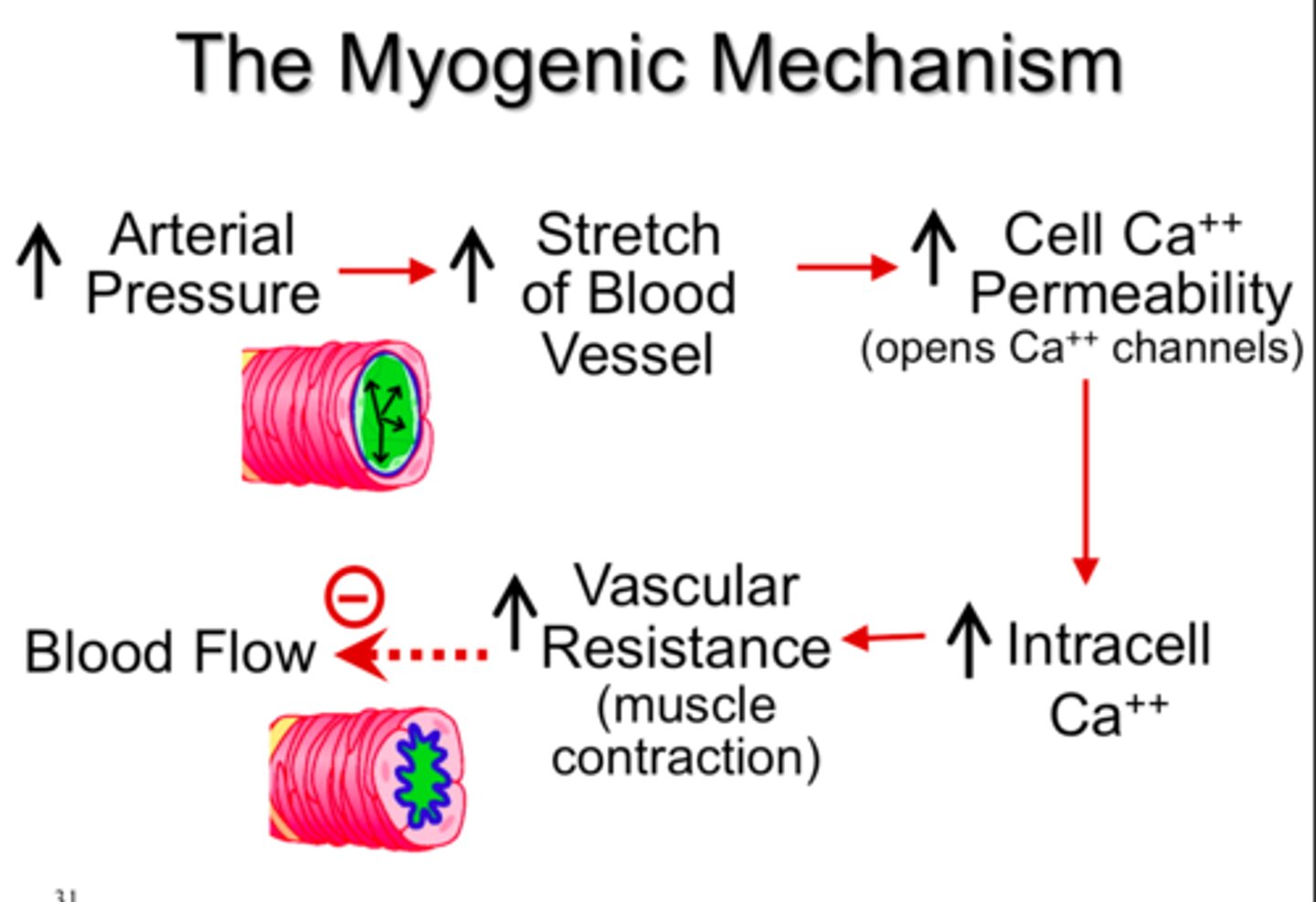
myogenic response
change in vascular resistance in response to stretch of blood vessels in the absence of external factors
vasoactive chemicals
substances that stimulate vasomotion; histamine, bradykinin
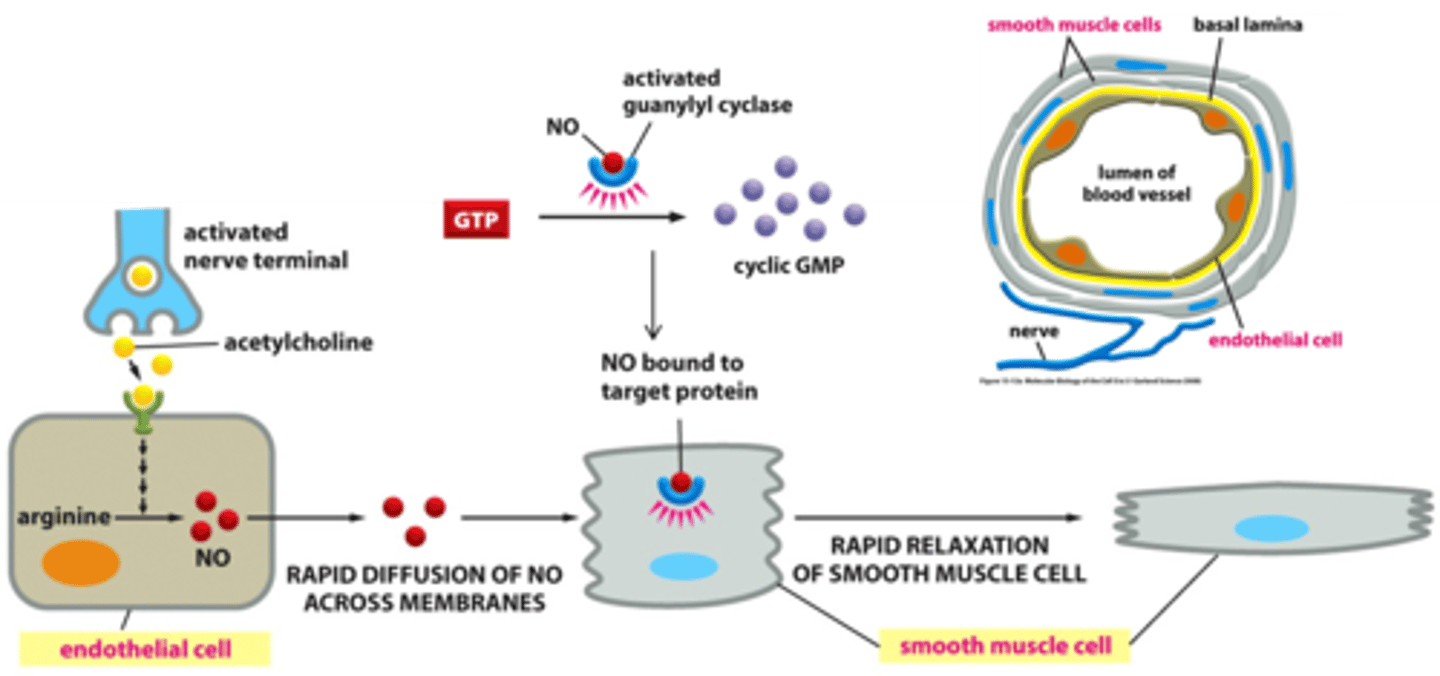
nitric oxide
a gas released by the endothelial cells to promote blood flow
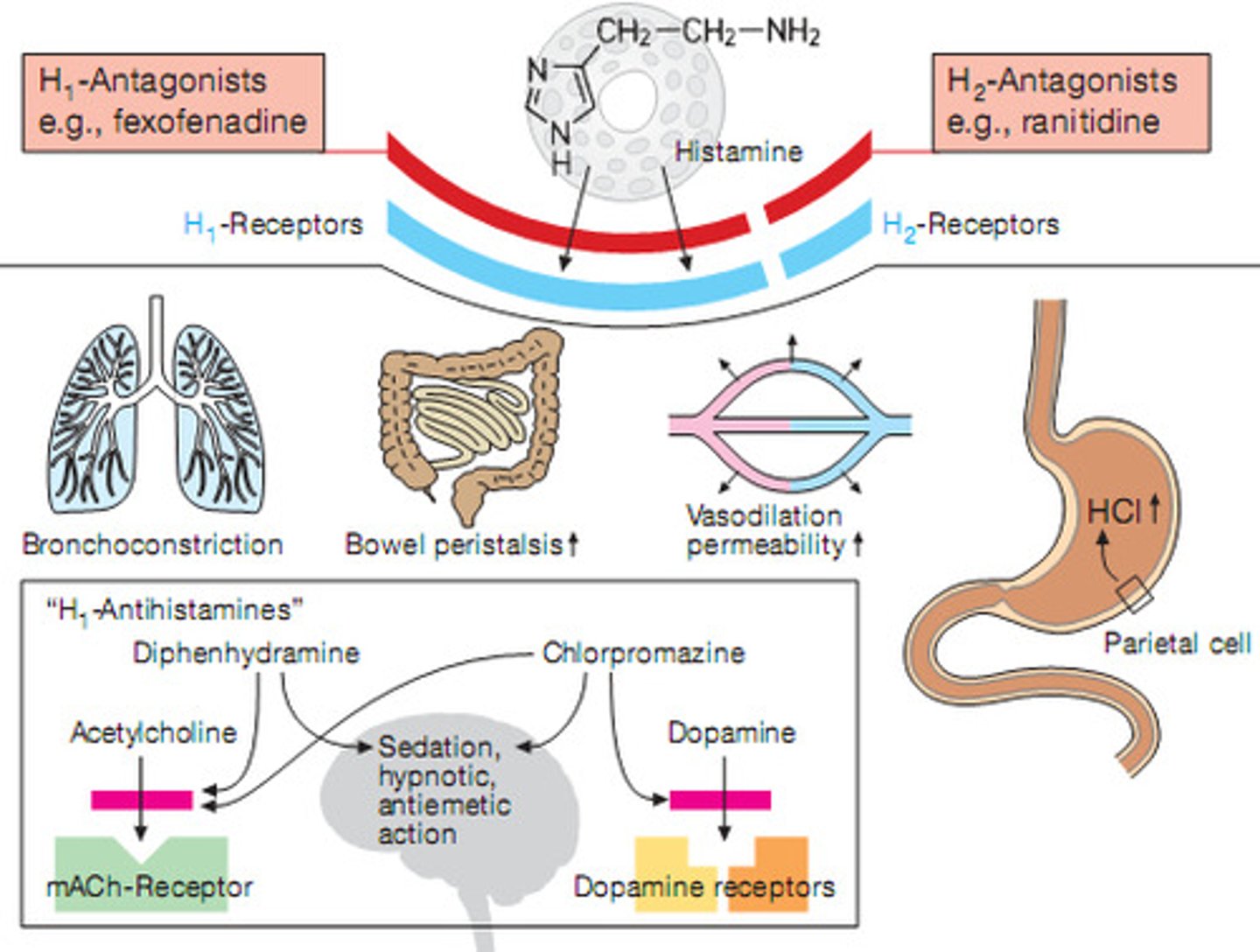
histamine
A chemical that is responsible for the symptoms of an allergy
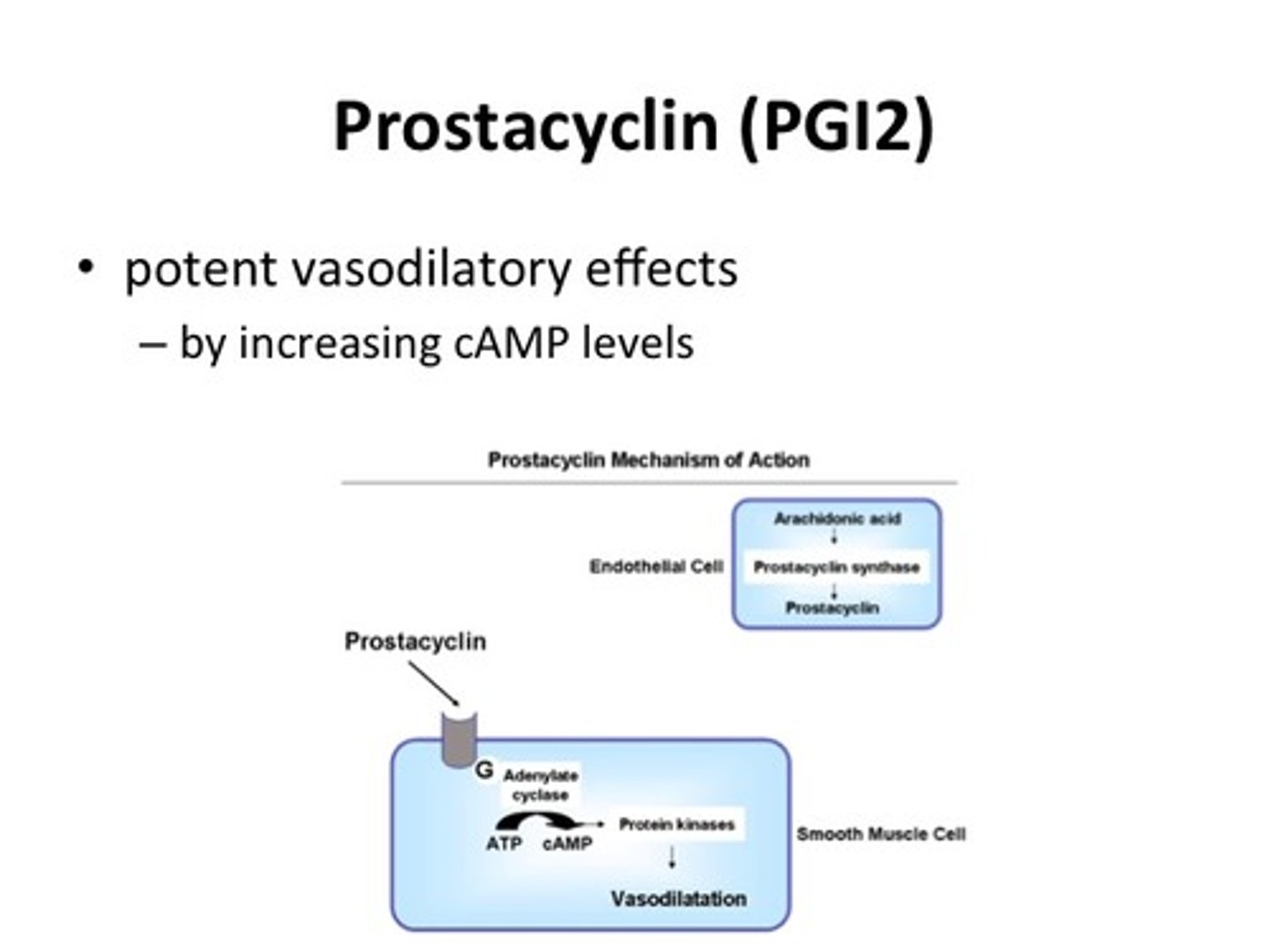
prostacyclin
inhibits blood clotting and vasoconstriction
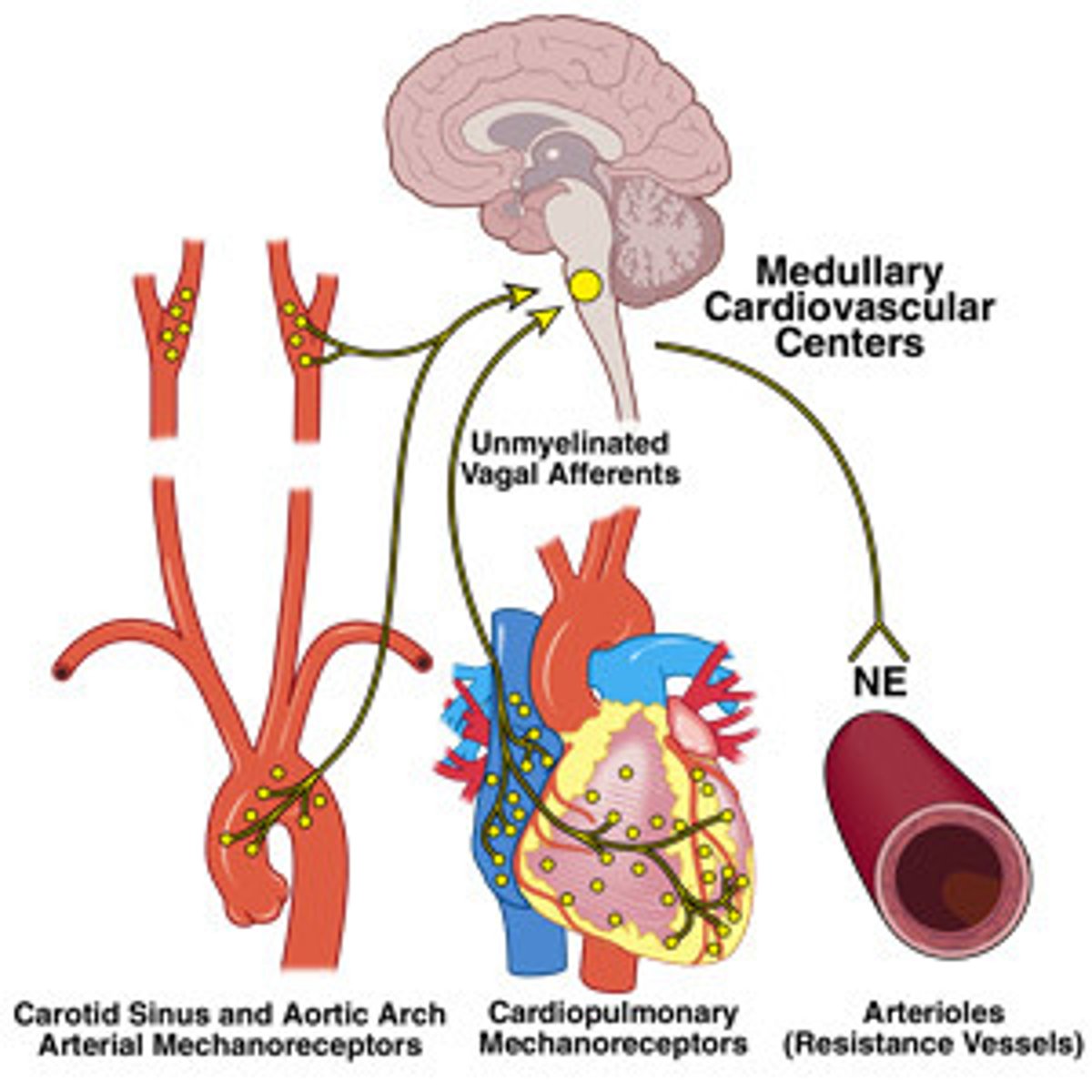
cardiovascular control center
the area of the medulla that regulates the cardiovascular system
medulla oblongata
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
baroreceptors
Cells that are sensitive to blood pressure changes.
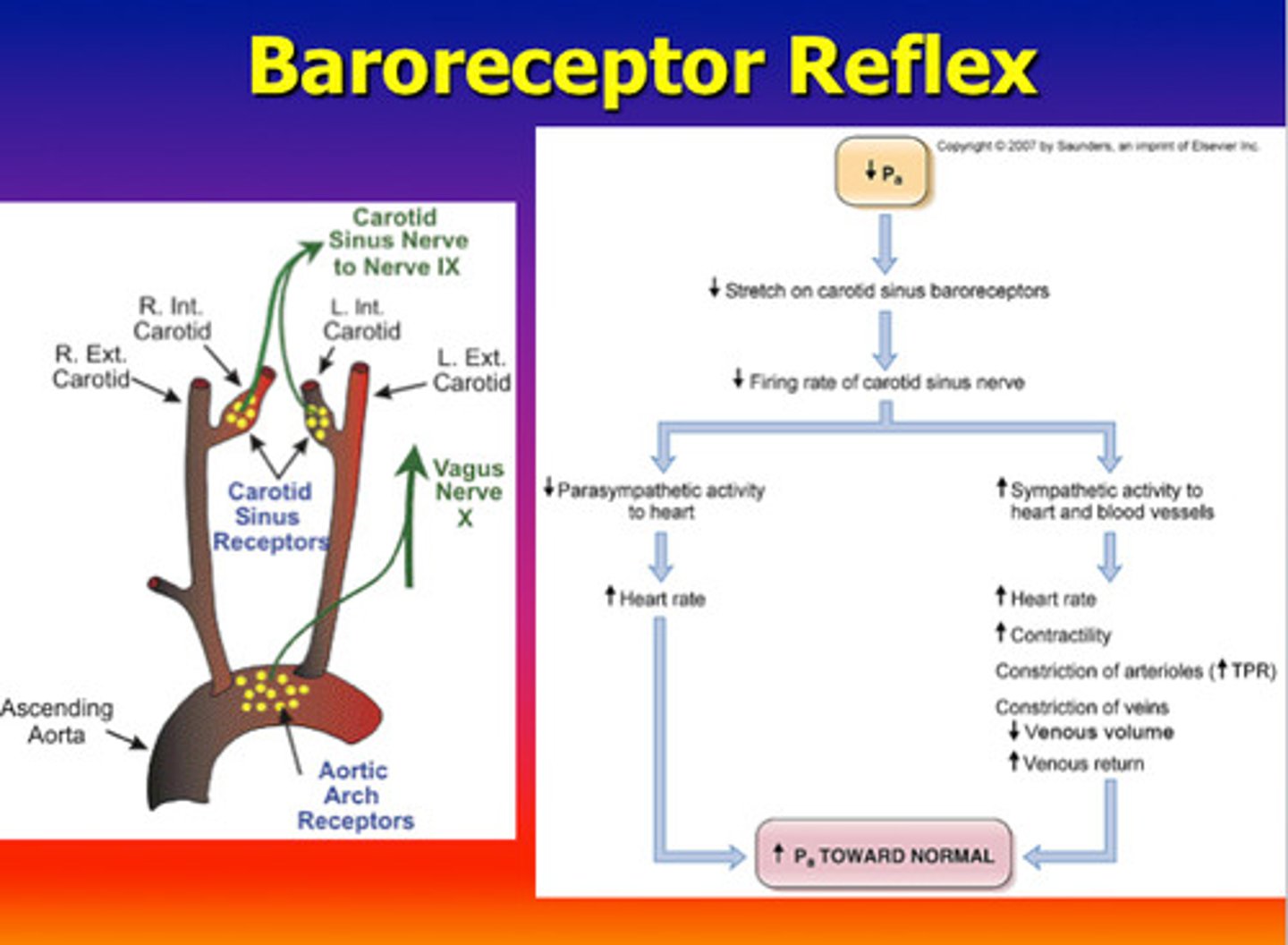
chemoreceptors
chemical sensors in the brain and blood vessels that identify changing levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide
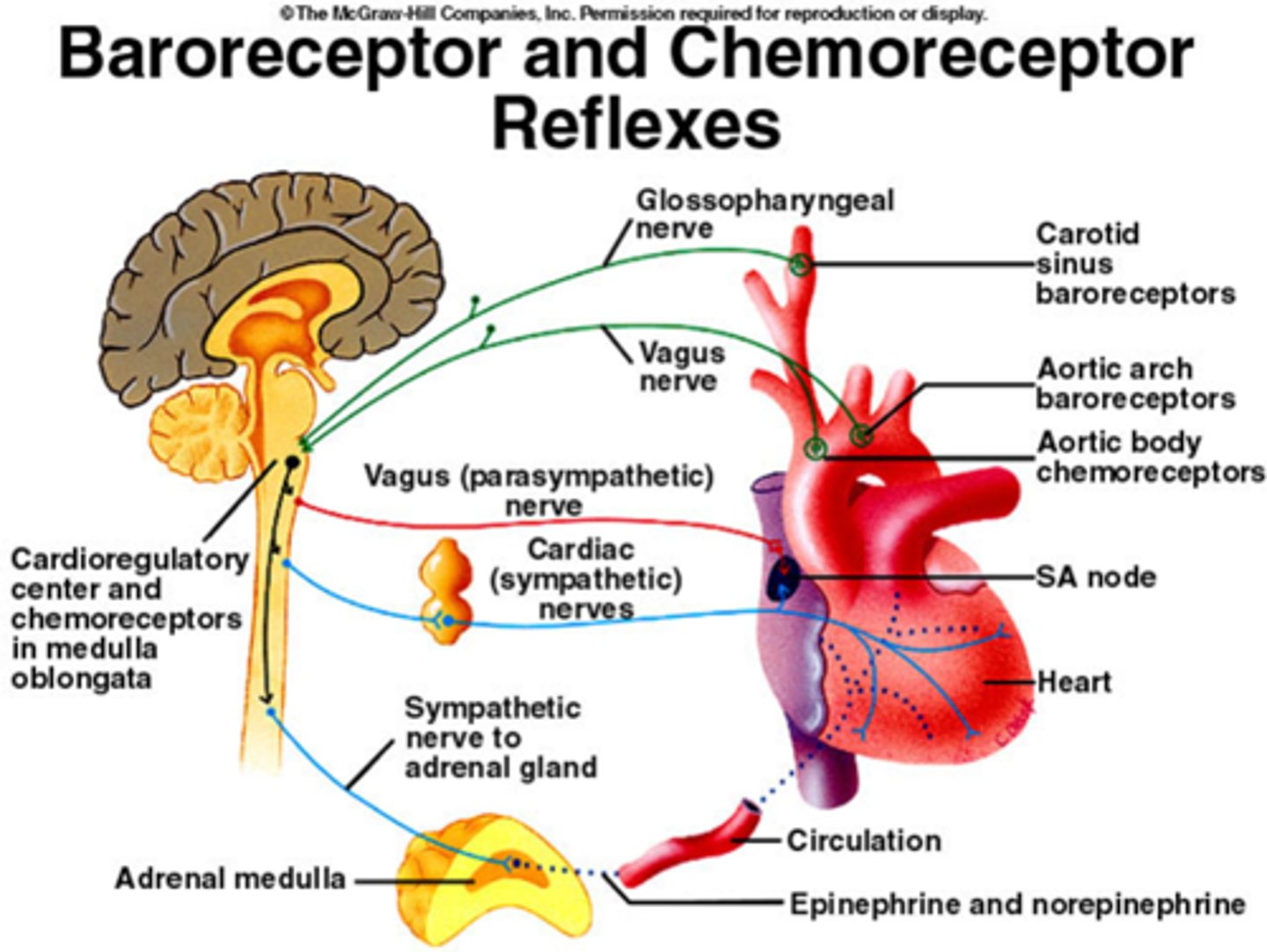
adrenal medulla
secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine
ADH
antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin)
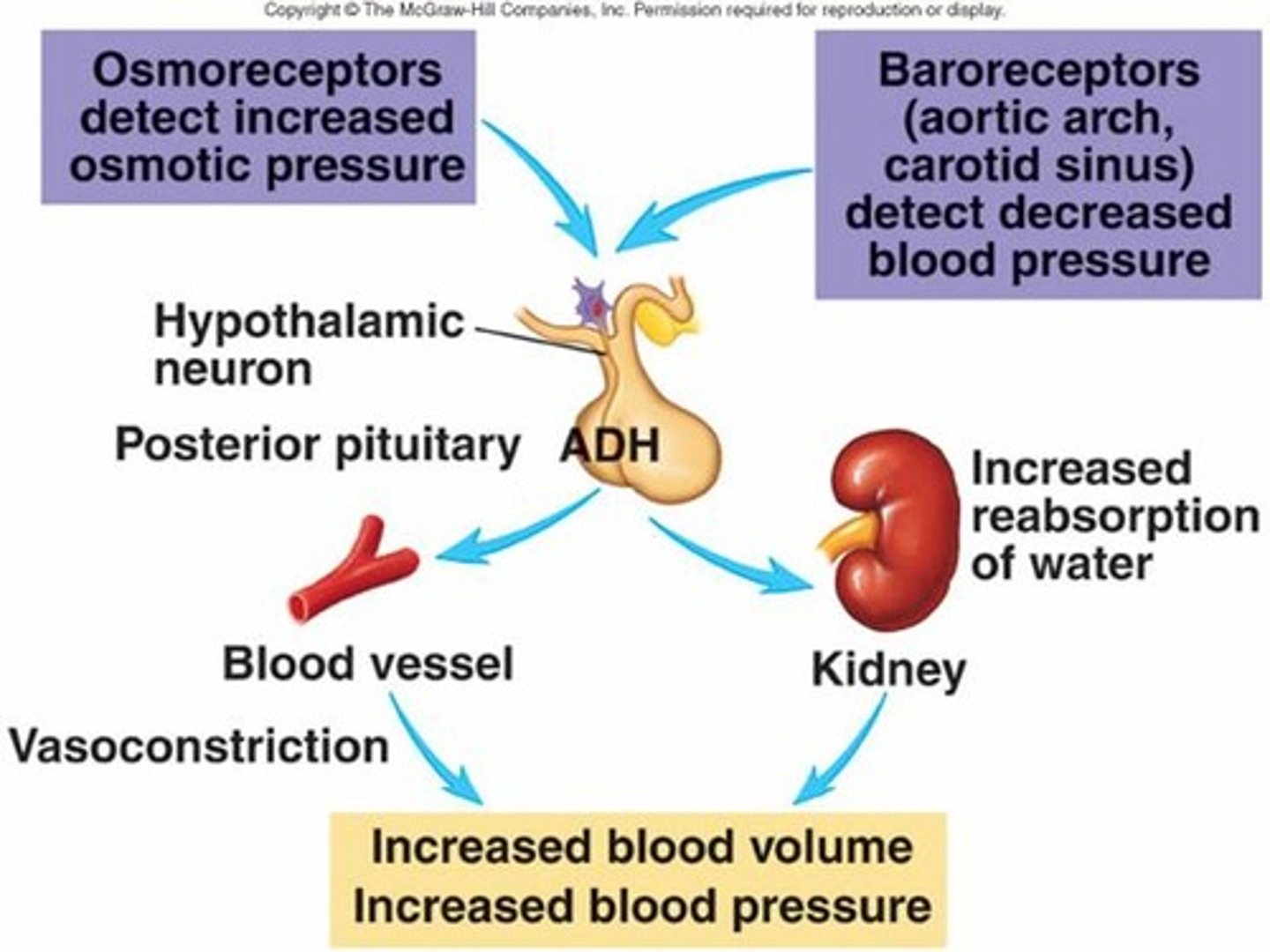
aldosterone
Hormone that stimulates the kidney to retain sodium ions and water
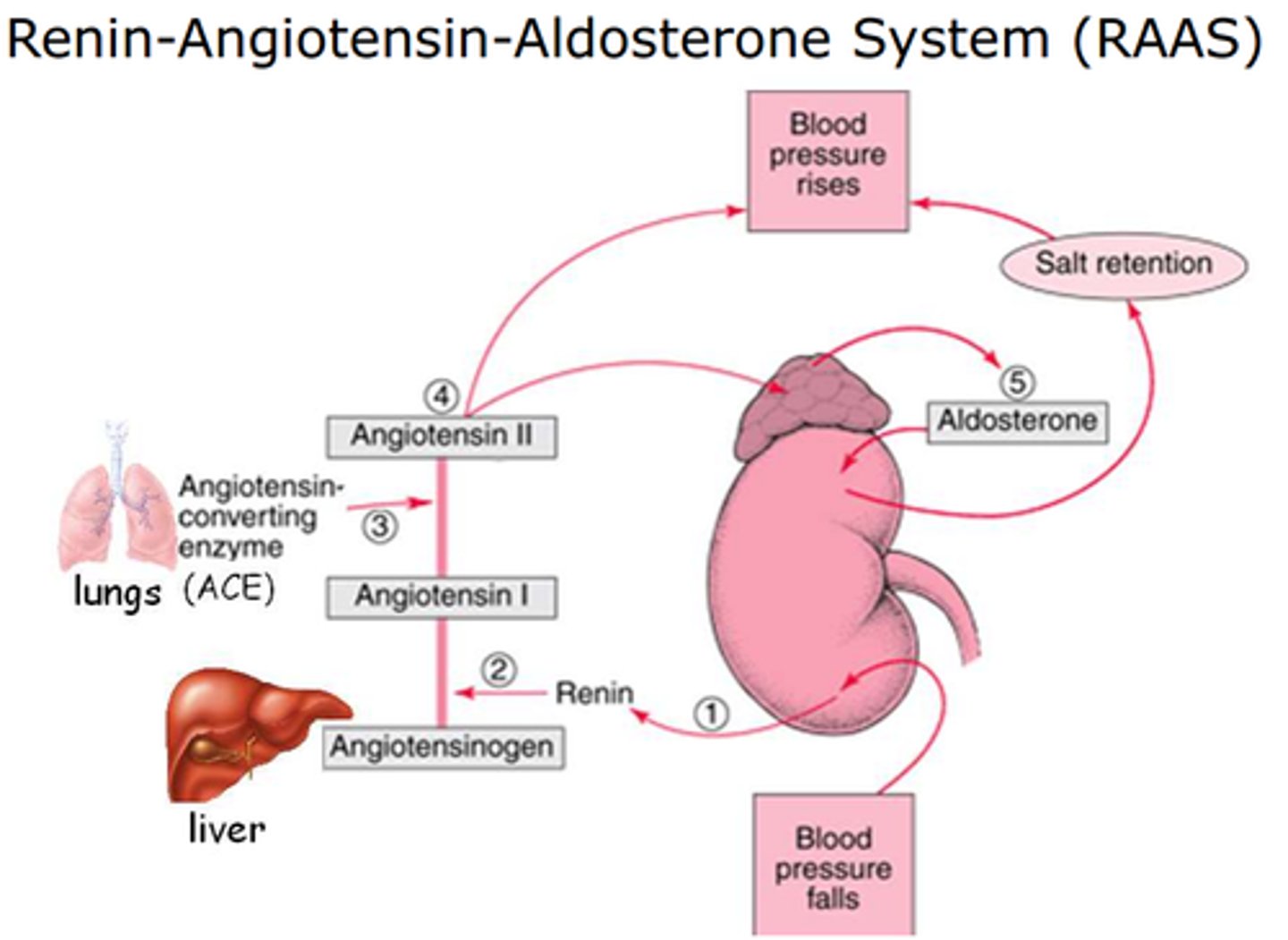
hypothalamus
brain structure that acts as a control center for recognition and analysis of hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, and body temperature