Lecture 2: Hematology Instruments & Blood Cell Measurements
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What three main categories does a CBC evaluate?
erythrocyte parameters
leukocyte counts
platelets
What are the erythrocyte parameters of a CBC?
hematocrit, hemoglobin, RBC count
erythrocyte indices
What are erythrocyte indices?
MCV, MCH, MCHC, and sometimes RDW
Explain the impedance method.
blood cells pass through aperture in current, creating resistance, which is then measured to determine cell volume and sizez
In the Coulter Impedance Method, change in ________ is proportional to cell ________.
resistance; volume
What information is given by platelet and RBC volume histograms such as the one shown?
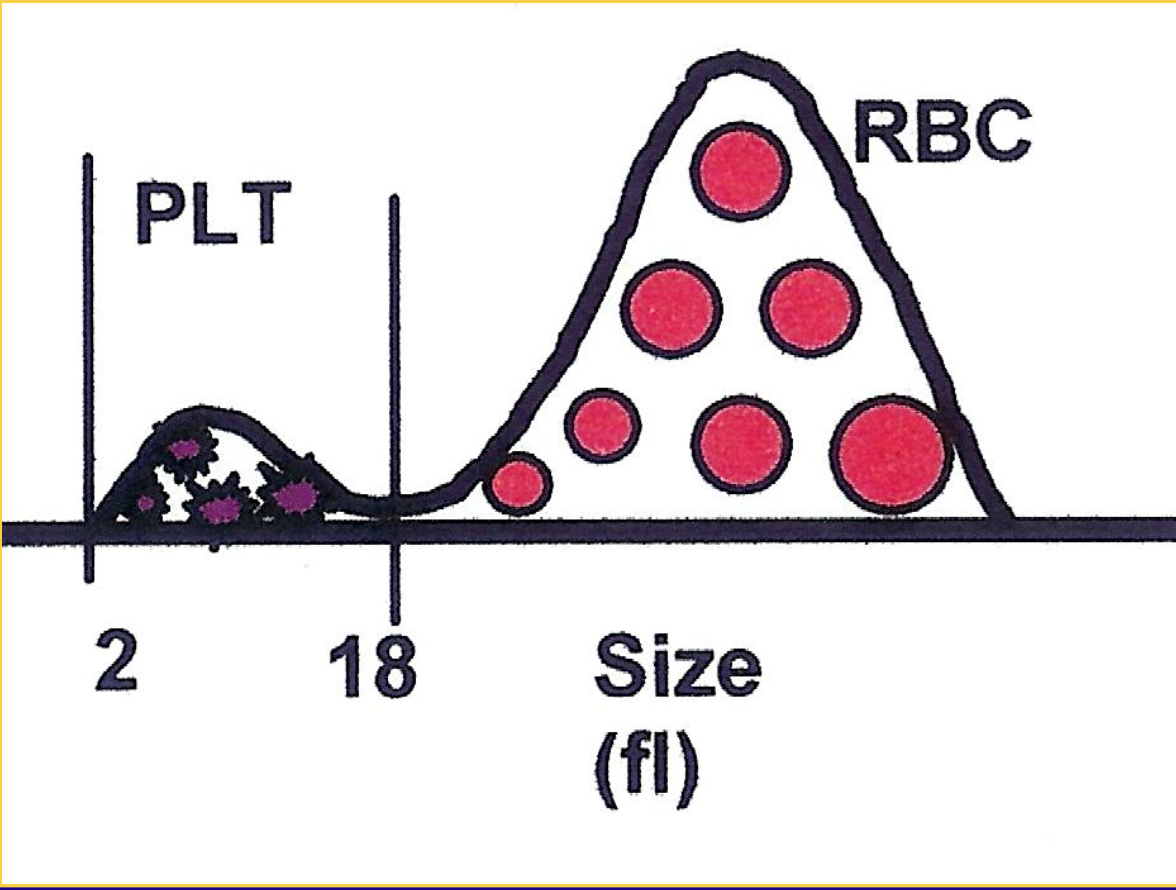
The relative number or percentage of cells at a specific size
Why do electronic cell counters have difficulty accurately counting feline platelets?
they are larger and more variable in size, making them easily misconstrued as RBCs
True or false: impedance instruments can accurately do platelet counts in cats.
false
What type of instruments have limited accuracy do to a 3-part differential based on cell size alone, but have excellent precision?
impedance instruments
What are the functions of impedance instruments?
count and size cells, providing cell volume distributions
measure Hb spectrophotometrically
HCT, RBC, Hb, MCV, MCH, MCHC, RDW
Total WBC counts (all species) and generally platelet counts
What can impedance instruments not perform?
reticulocyte counts
What cell aspects are able to be measured by laser flow cytometry?
size and complexity
What is forward scatter?
the shadow cast by a cell during laser flow cytometry when it passes through the beam and scatters the light
Where are the detectors placed during laser flow cytometry?
detectors are placed in front of the laser beam to measure forward scatter, and at angles (usually 90) to the laser beam to detect light scattered to the side
What is the forward scatter measurement a relative indicator of?
a cell’s size
What is side scatter a measure of?
a cell’s internal complexity or granularity
Neutrophils have multilobed nuclei and granules. Would they have high or low amounts of side scatter?
high
What type of instrument counts and classifies cells based on extinction of light and scattered light?
laser flow cytometry
What data can laser flow cytometry determine?
HCT, RBC, Hb, MCV, MCH, MCHC, RDW
total WBC and “5 part” differential counts
platelet counts, MPV, PDW, PCT
reticulocyte counts
What can laser flow cytometry measure that impedance instruments cannot?
reticulocyte counts
Since RBC count has little value by itself, what is it used to calculate?
Hct electronically and MCV and MCH manually
How do automated cell counters calculate the hematocrit (Hct)?
using MCV and RBC count → Hct (%) = (MCV x RBC)/10
How is hemoglobin determined?
SLS reagent lyses erythrocytes and oxidized Hb to MetHB and forms stable SLS-MetHB product that is the measured spectrophotometrically by color intensity
What can falsely increase hemoglobin values?
lipemia, heinz bodies, nuclei in non-mammals
What are the erythrocyte indices?
MCV: mean cell volume
MCH: mean cell hemoglobin
MCHC: mean cell hemoglobin concentration
RDW: red cell distribution width
What is MCV?
average volume of a single erythrocyte
What is MCH and what does it correlate with?
average amount of hemoglobin in a single erythrocyte that generally correlates directly with changes in erythrocyte size (MCV)
When are lowest MCH values reported?
severe iron deficiency anemia (low MCV and low internal hemoglobin concenration)
How is mean cell hemoglobin concentration determined?
by calculation: (Hb/Hct) x 100 = MCHC (%)
True or false: MCHC is reported as g/dL of packed erythrocytes NOT whole blood.
true
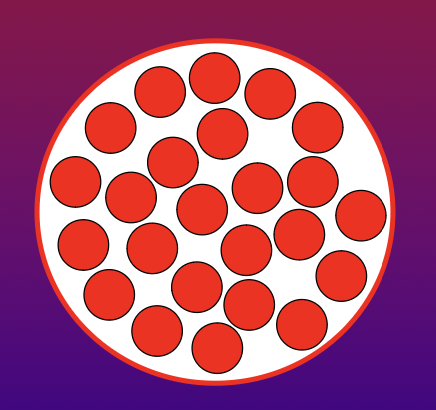
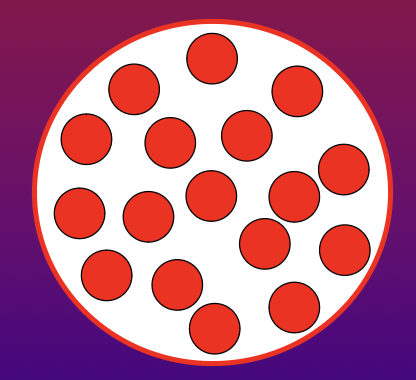
Both of these images show low MCV and low MCH. The red circles represent amount of hemoglobin. Which also depicts a low MCHC?
bottom
How is RDW calculated?
(SD of erythrocyte volumes/MCV) x 100
What is a coefficient of variation of erythrocyte volumes and an electronic measure of anisocytosis?
RDW
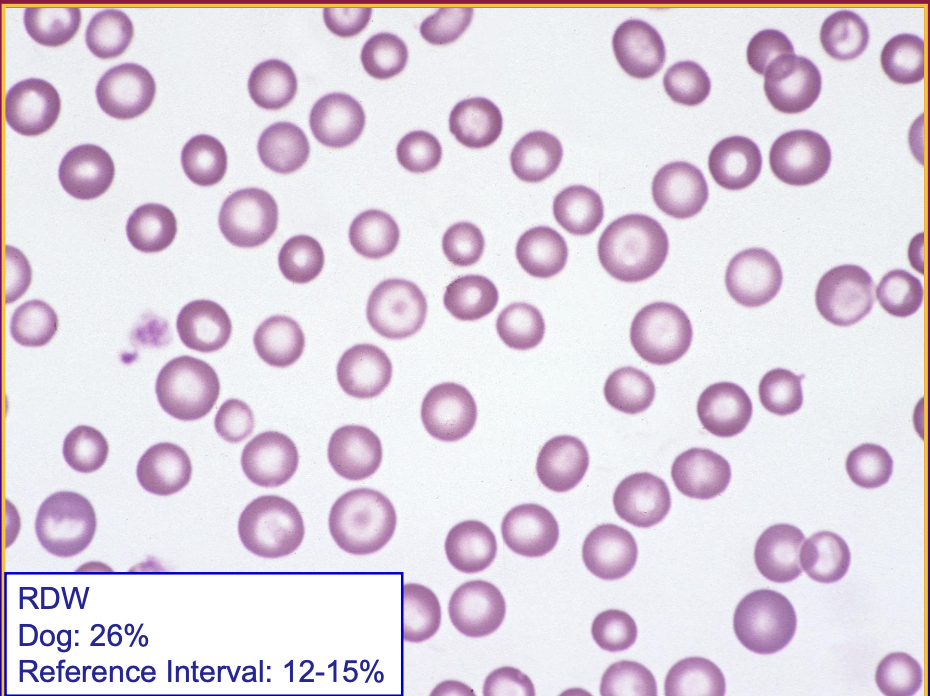
This dog shows a higher than normal red cell distribution width. What is the increased in variation in RBCs called?
anisocytosis
What can cause spuriously increased RDW?
erythrocyte agglutination
What should be done to absolute reticulocyte counts determined by flow cytometry?
validate using manual counts
Why is it important to verify which reticulocytes are counted in your instrument before running feline bloodwork
cats have two different types of reticulocytes, aggregate and punctate which two different sizes of RNA and most instruments only measure aggregate reticulocytes
What can cause spurious reticulocystosis?
Howell-Jolly bodies (micronuclei)
Large immature platelets or platelet clumps
Autofluorescence (drugs, porphyrin)
erythrocyte parasites containing RNA and DNA
nucleated erythrocytes
Heinz bodies with nonspecific fluorescence
leukocytosis
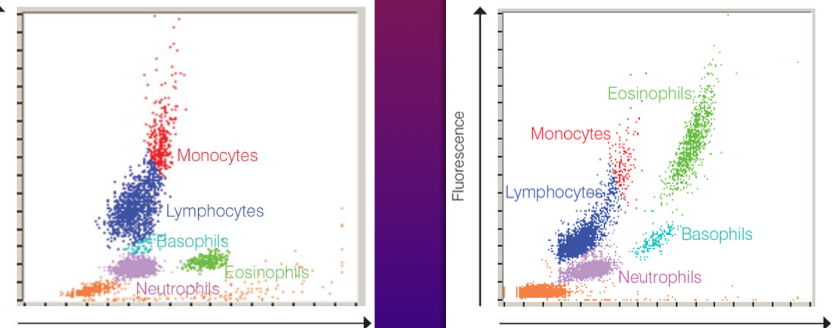
Which is a canine and which is a feline leukocyte differential count?
left is canine right is feline
What can platelet aggregates result in?
false thrombocytopenia
What diagnostic is often unreliable in cats?
automated platelet counts
What is MPV?
average volume of a single platelet
How can storage of blood at 5C affect the diagnostics?
can cause platelet aggregates and therefore spuriously increased MPV
How can nucleated erythrocytes in blood cause errors in blood cell measurements?
they can be counted as leukocytes by manual and most automated cell counters
If nucleated erythrocytes in blood skewed your blood cell measurements, how would you correct this error?
machine WBC x (100 / (100 + NRBC)) = corrected WBC
How can old blood samples cause errors in blood cell measurments?
erythrocyte swelling (increased MCV and Hct, MCHC decreased)
platelet aggregation (MPV increased and platelet count decreased)
cell lysis of all cell types = counts decrease
How does clot formation affect blood cell measurements?
all cell types decrease
How can cryoglobulins affect blood cell measurements?
may be counted as leukocytes or platelets
What sample error would cause the number of cells/uL of blood to decrease?
platelet, leukocyte, and erythrocyte aggregates
What diagnostics are impacted by erythrocyte aggregates?
MCV increases
electronic Hct decreases
MCHC increases
What diagnostics are impacted by platelet aggregates?
platelet aggregates may be coutned as leukocytes
MPV increased
What value is increased by hemolysis?
MCHC
What diagnostic values are affected by lipemia?
Hb and MCHC increased
May increase leukocyte or platelet counts
What diagnostic values can be affected by Heinz bodies?
Hb and MCHC increased
sometimes total leukoccyte counts are increased
reticulocyte counts may be increased
What are Heinz bodies?
abnormal clumps of denatured hemoglobin within red blood cells