Year 12 Biology Unit 4 QCAA
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
DNA helicase
An enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix during DNA replication
DNA Replication
The process in which DNA molecules are copied -- produces two identical DNA molecules (must occur before cells divide)
Leading strand
the new complementary DNA strand synthesized continuously along the template strand toward the replication fork in the mandatory 5' to 3' direction
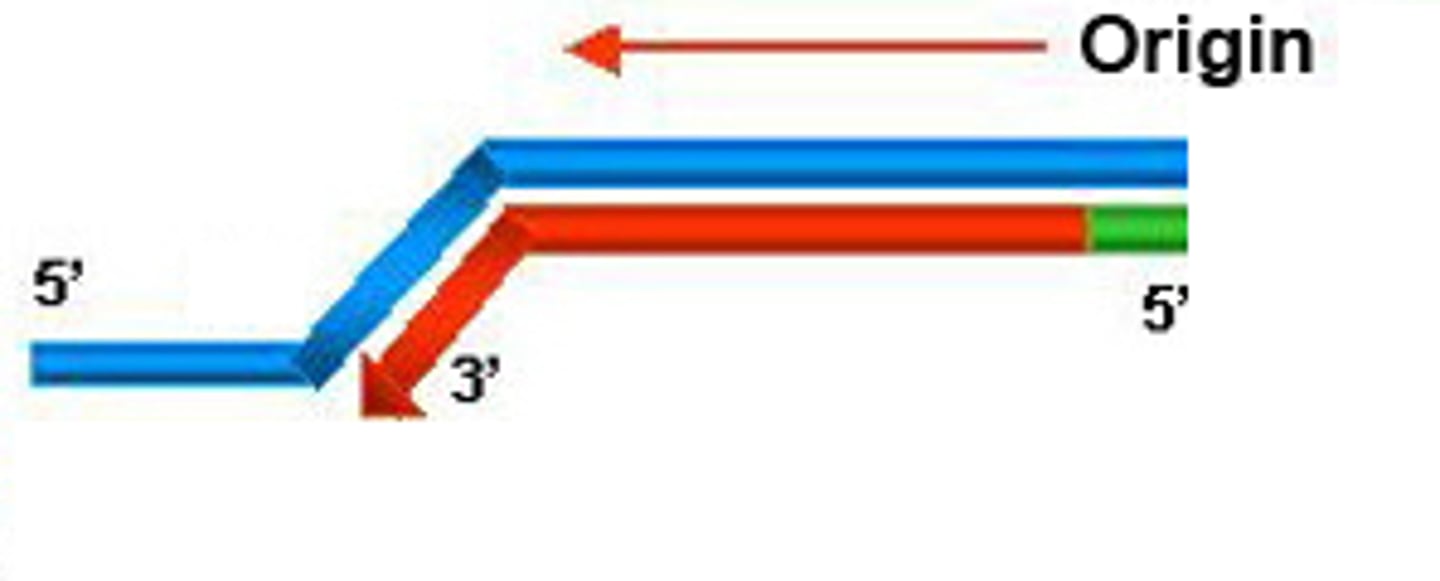
Lagging strand
The strand in replication that is copied 3' to 5' as Okazaki fragments and then joined up.
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule
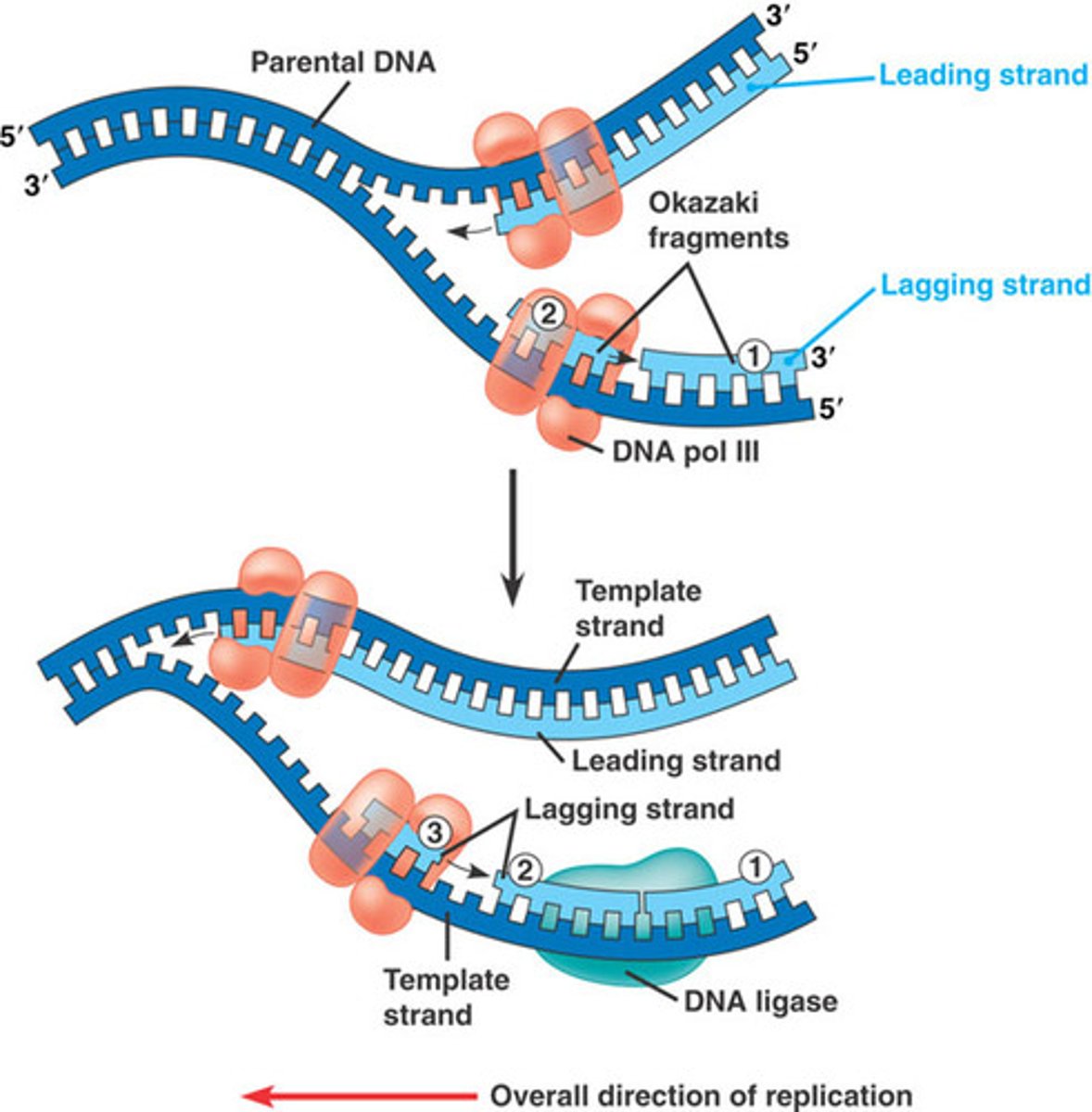
Ligase
Enzyme that joins the sugar-phosphate backbones of the Okazaki fragments, forming a signel new DNA strand

A-T and C-G
The complementary base pairs of DNA
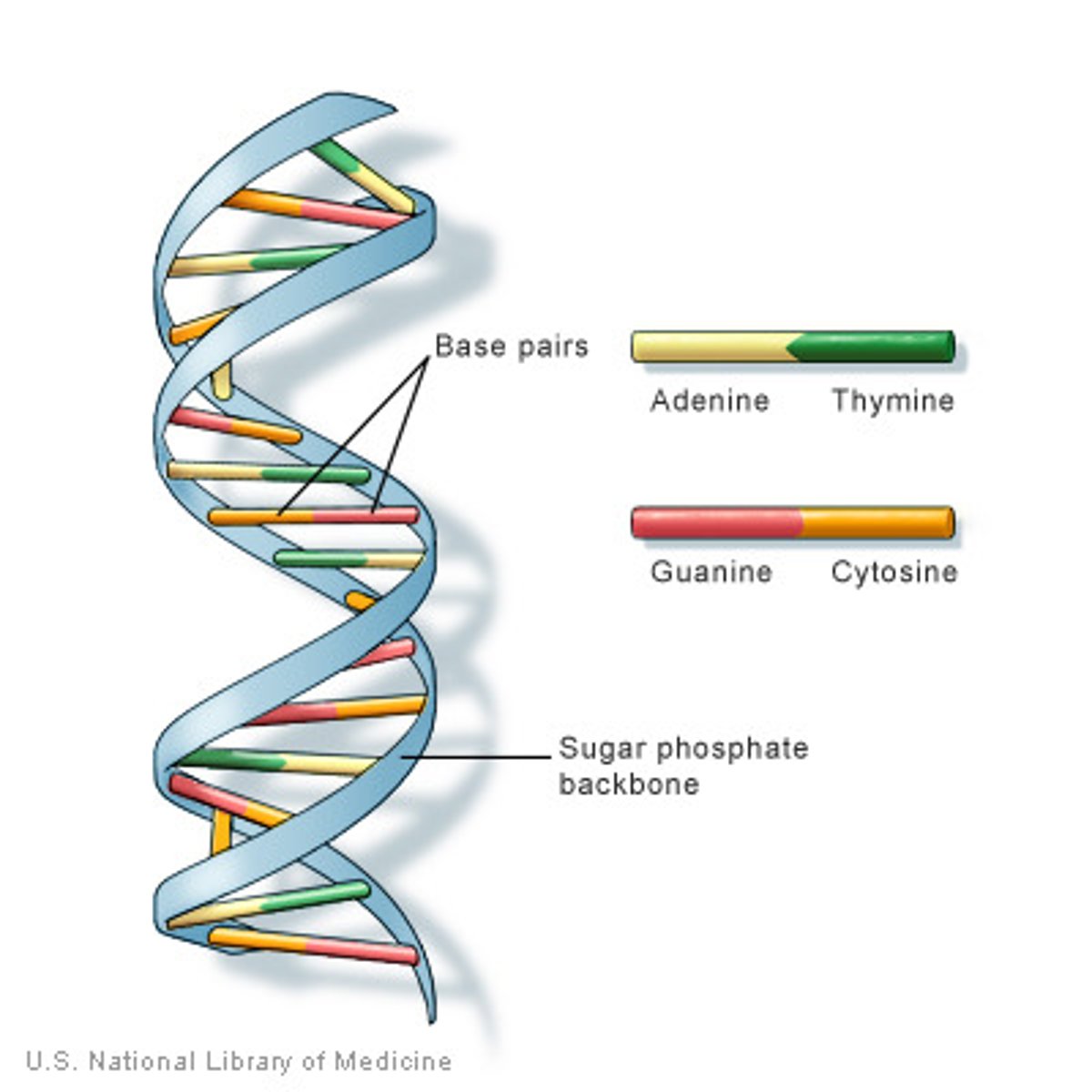
Hydrogen bond
The bond between nitrogenous bases of a DNA molecule
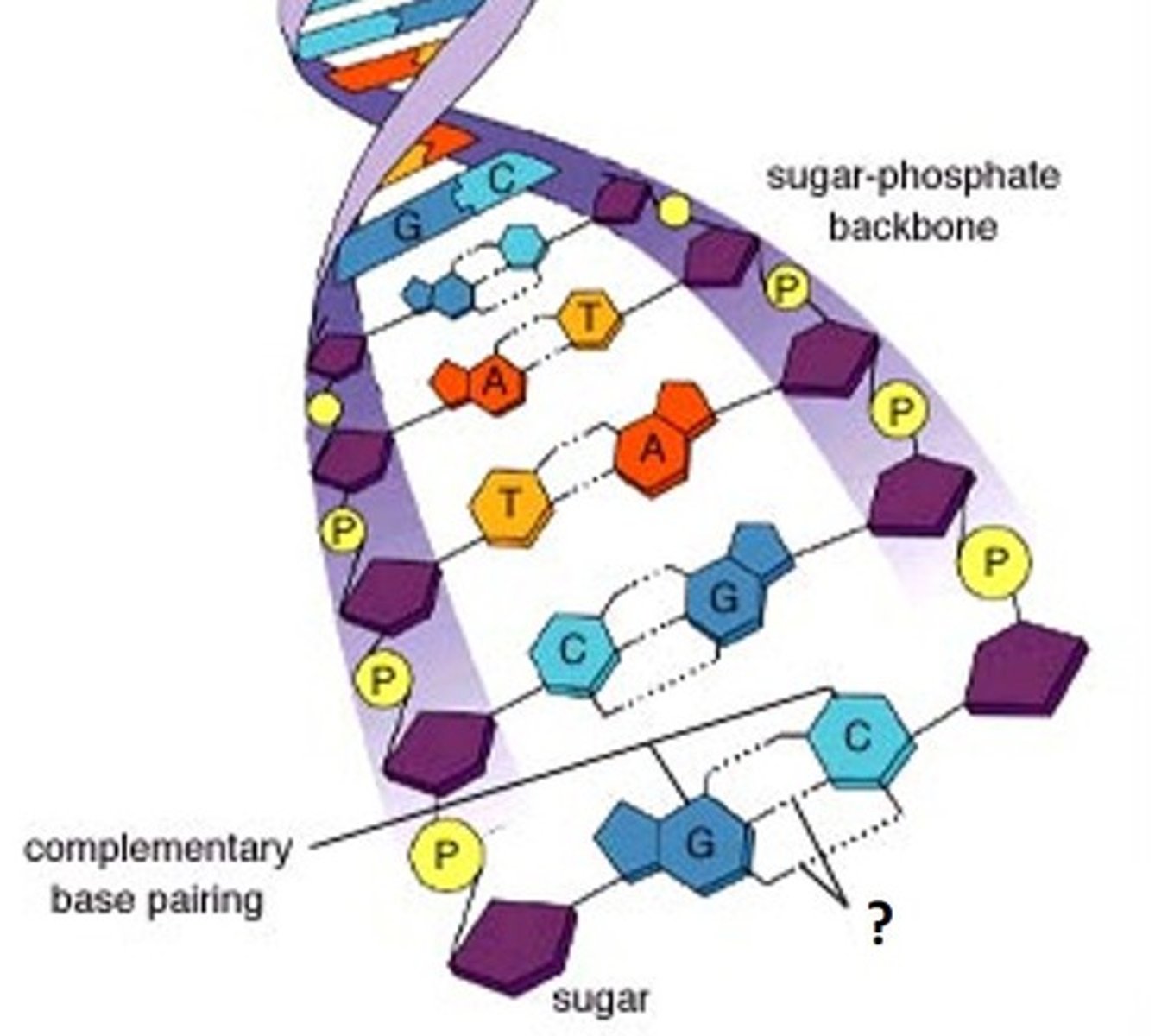
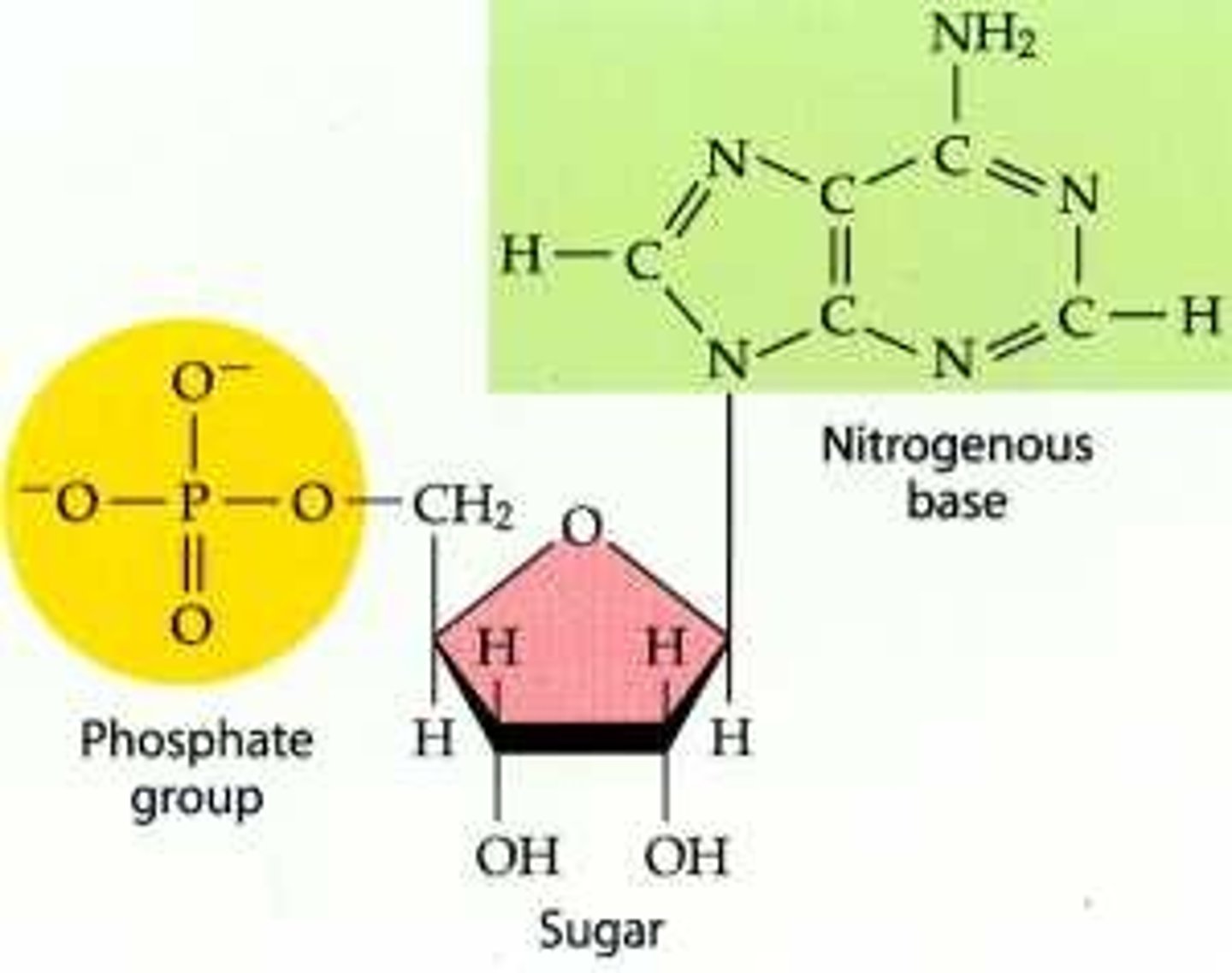
Nucleotide
The monomer of DNA - consists of phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base
Nitrogenous bases
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, and Guanine are these parts of the nucleotides of DNA; make up the "rungs of the ladder"
Phosphate and Deoxyribose sugar
Parts of the nucleotide that make up the "uprights of the ladder"
DNA
A nucleic acid that contains the genetic information of the cell; shaped as a double helix
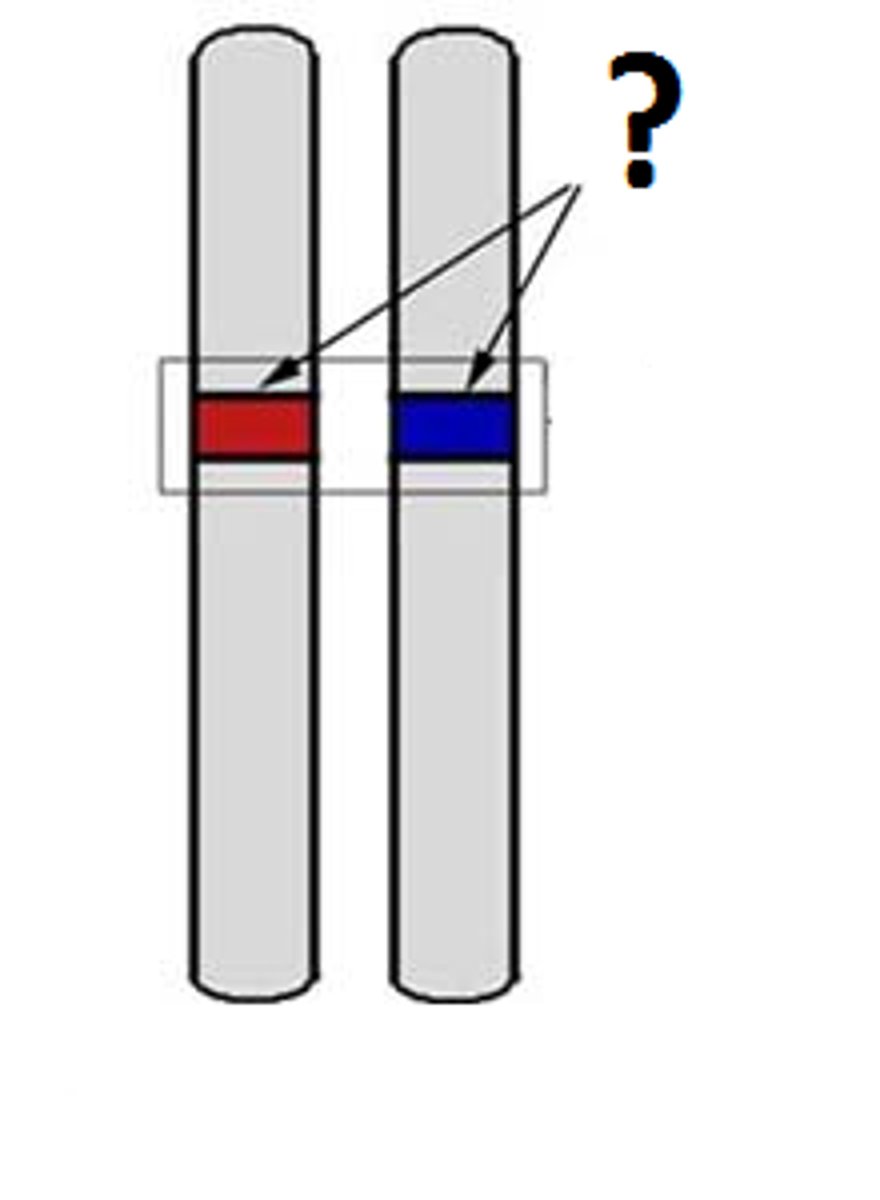
Sister chromatids
Replicated forms of a chromosome joined together by the centromere and eventually separated during mitosis or meiosis II.
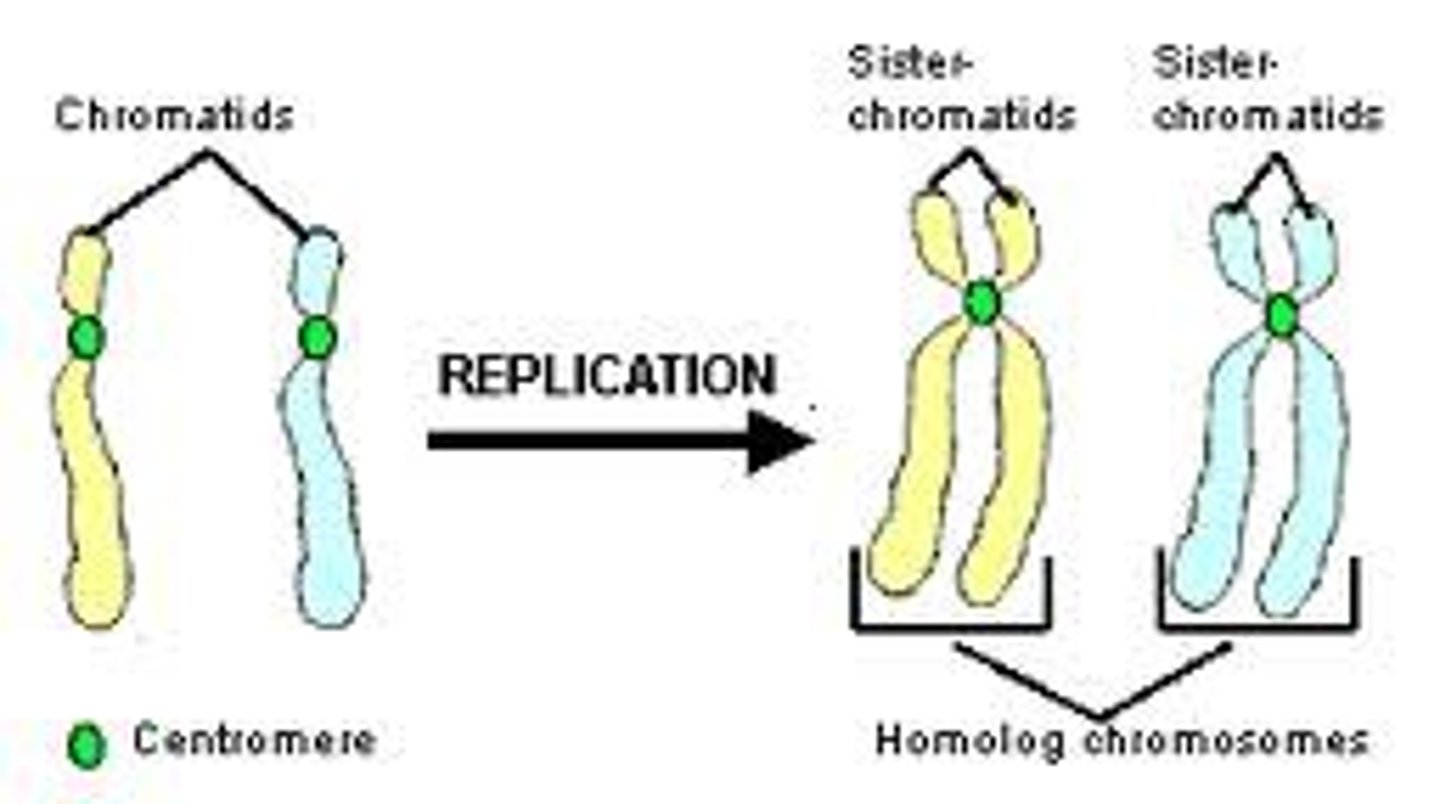
Centromere
Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached
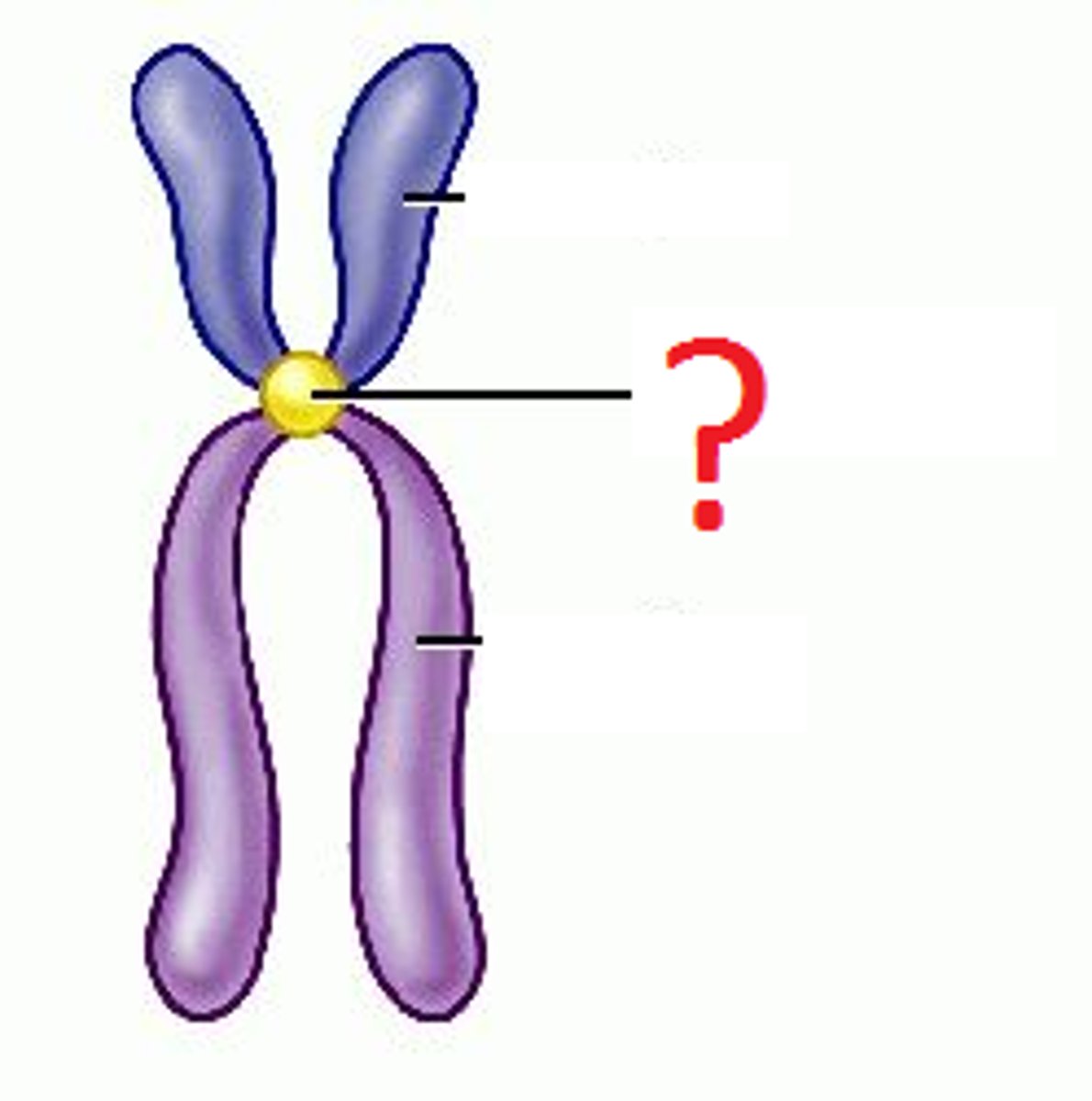
Chromosome
Tightly coiled DNA will produce this. A threadlike, gene-carrying structure found in the nucleus.
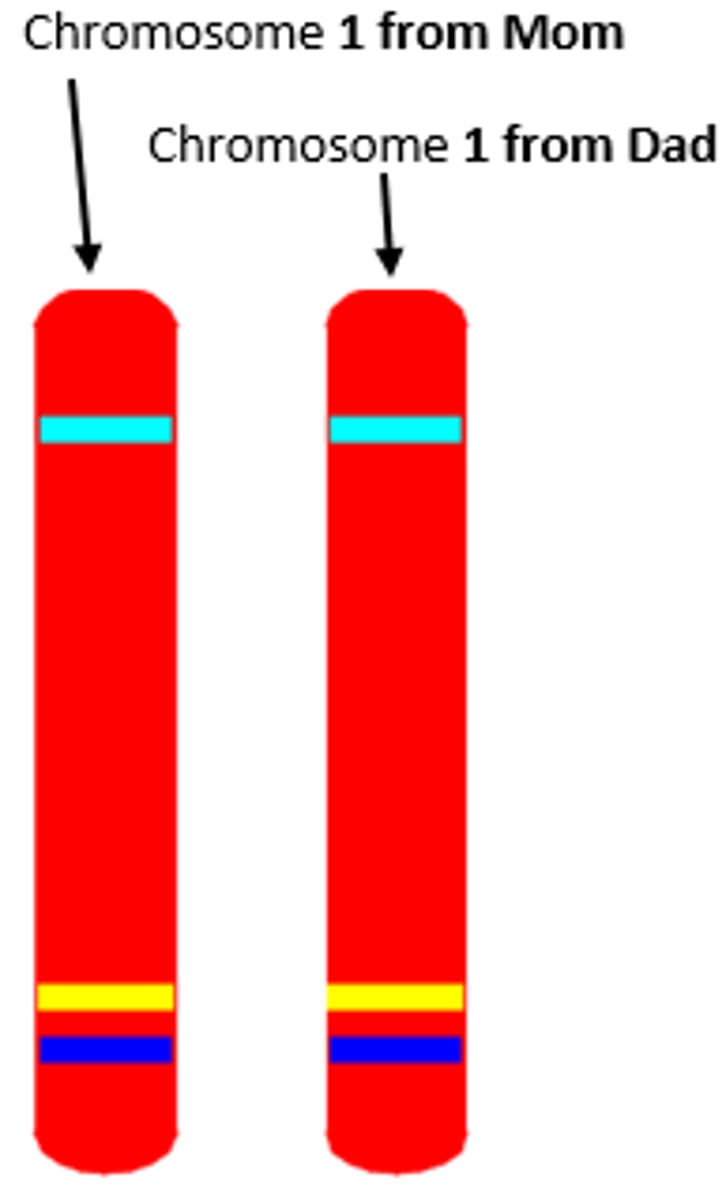
Homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes that carry genes controlling the same inherited characters
Centriole
Organelle associated with the centrosome of animal cells only -- assists in cell division
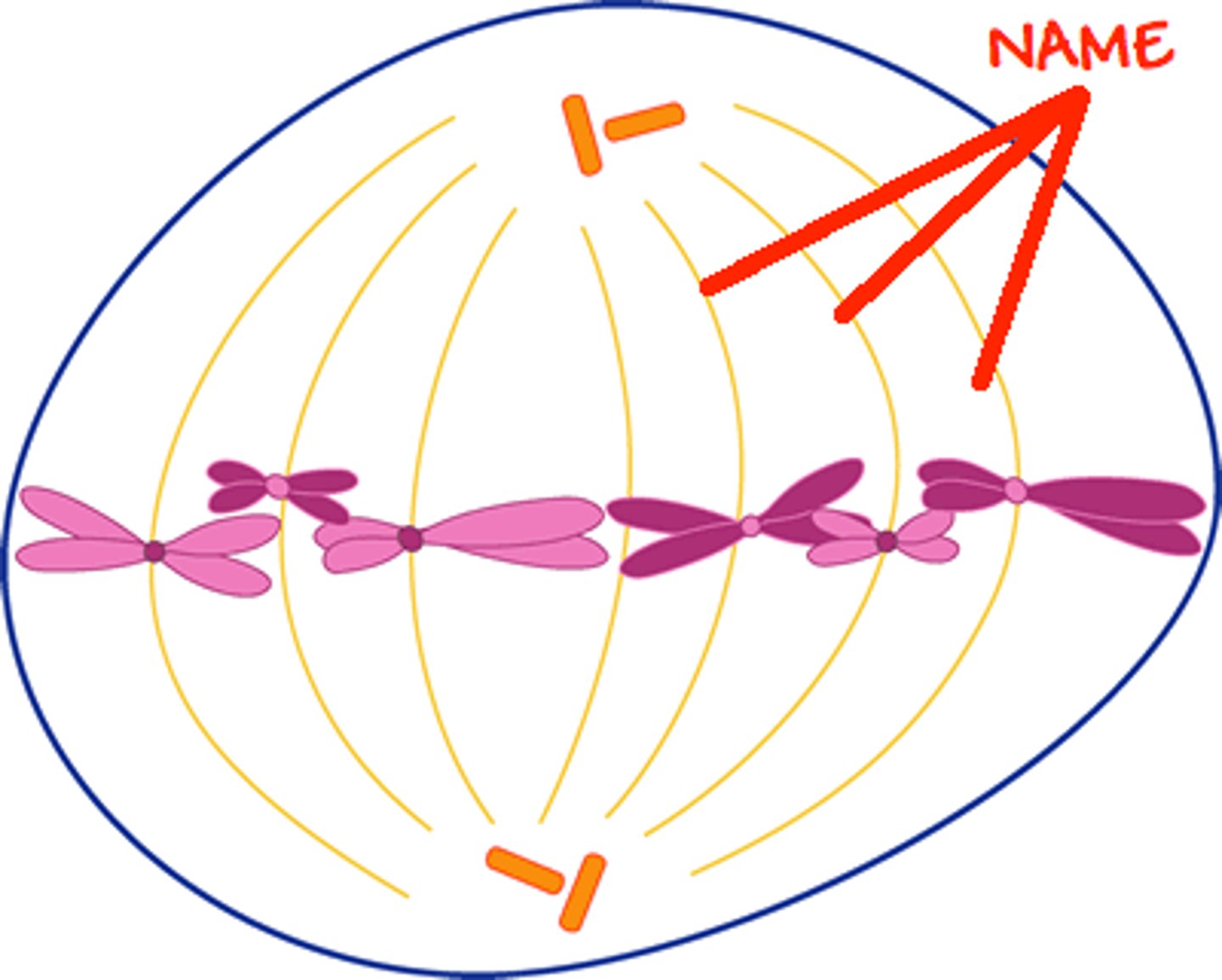
Spindle fibers
Made up of microtubules -- used to pull chromatids apart and chromosomes to opposite sides of the cell
Gene
Segment of DNA; hereditary unit with coded information
Allele
Alternate versions of a gene
Cell Cycle
The regular sequence of growth and division that cells undergo
Somatic Cell
All body cells (except reproductive cells)
Gametes
Reproductive cells (sperm and egg cells)
Interphase
~90% of cell cycle - cell grows and copies its chromosomes in preparate of cell division (consists of G1, S, and G2 phases)
S phase
Part of interphase in which the DNA replication occurs -- all of the chromosom
Mitosis
Division of chromosomes; has 4 stages (PMAT)
Prophase
The first stage of mitosis
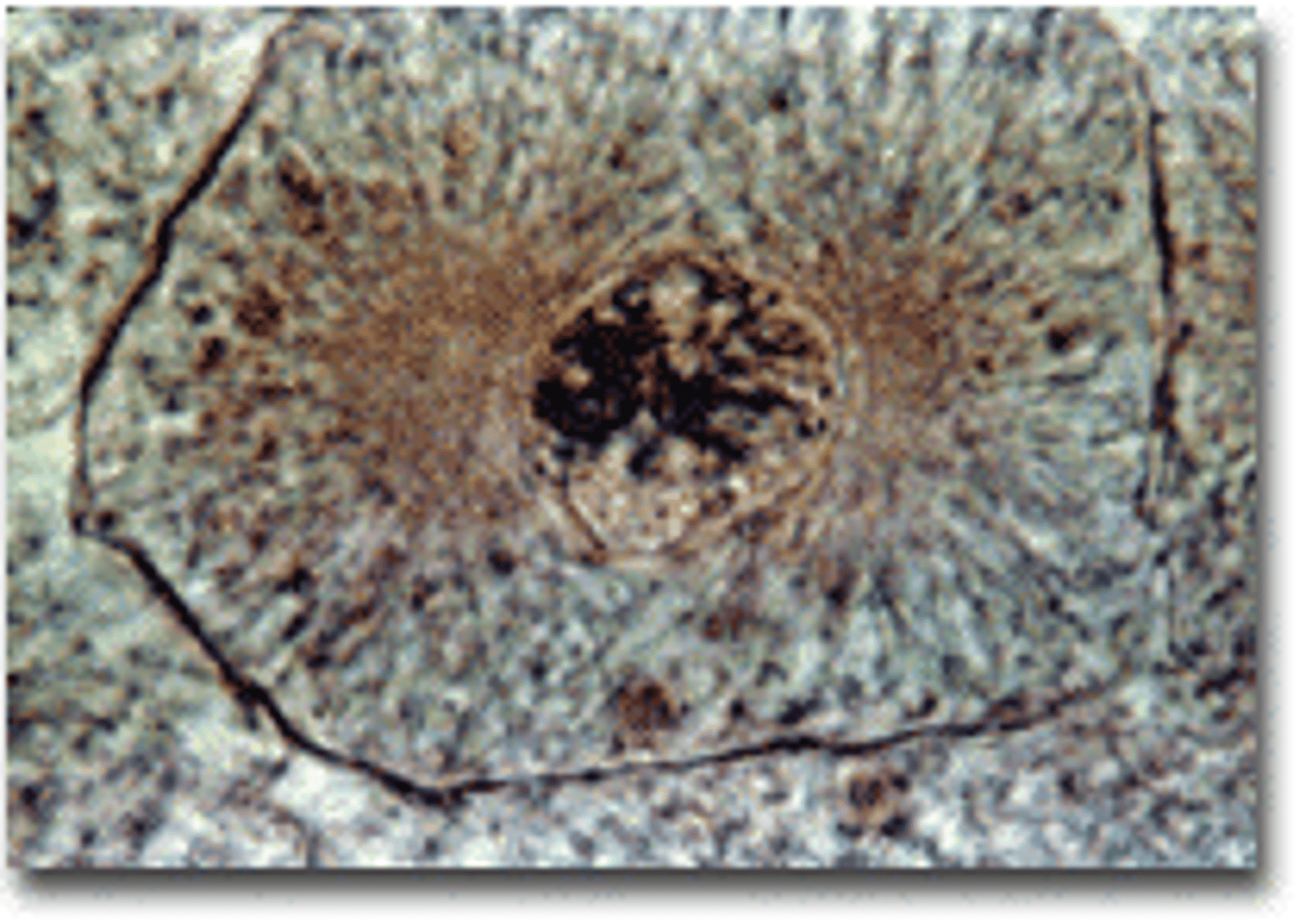
Anaphase
The third stage of mitosis: when sister chromatids are pulled apart
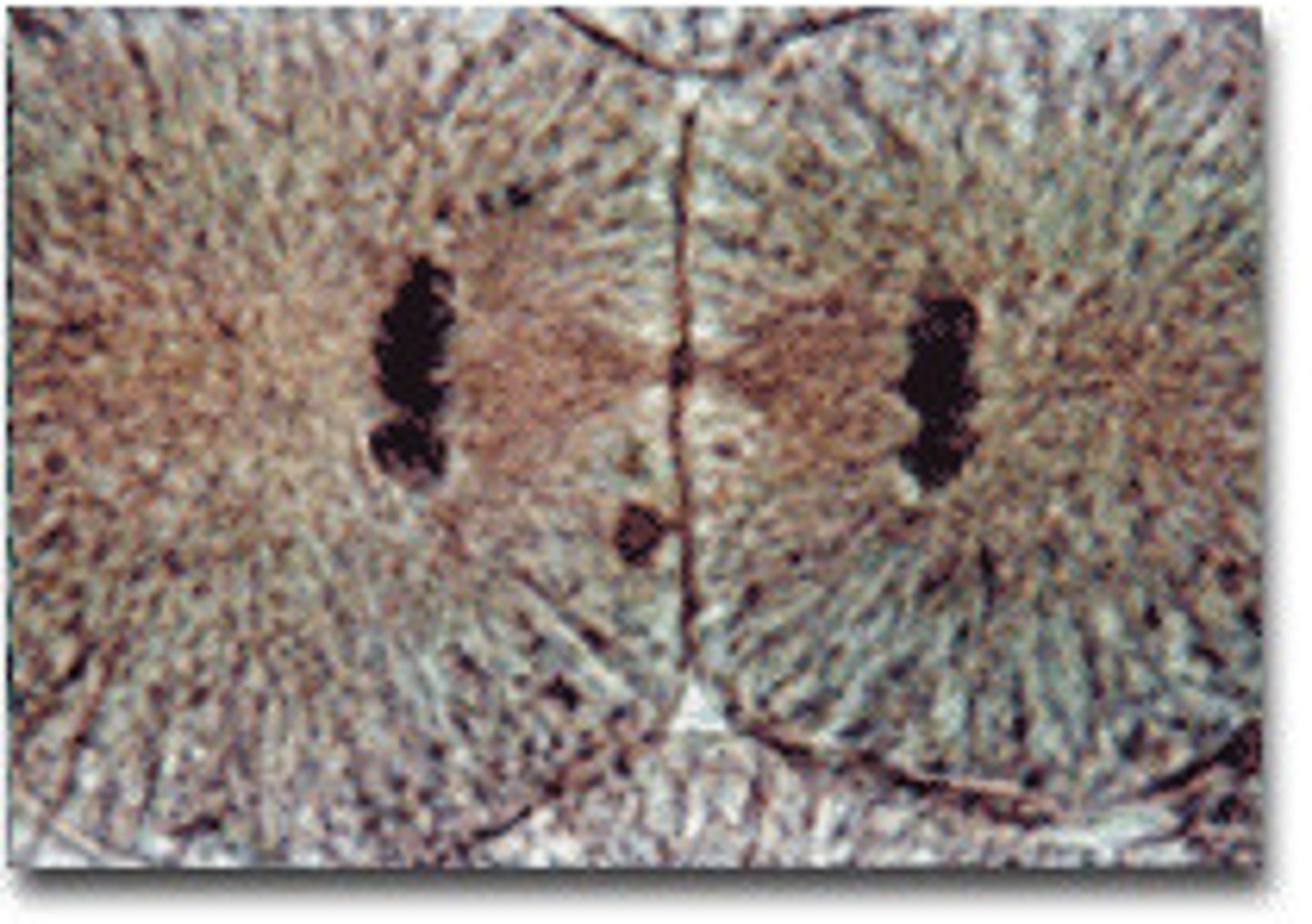
Telophase
The fourth stage of mitosis
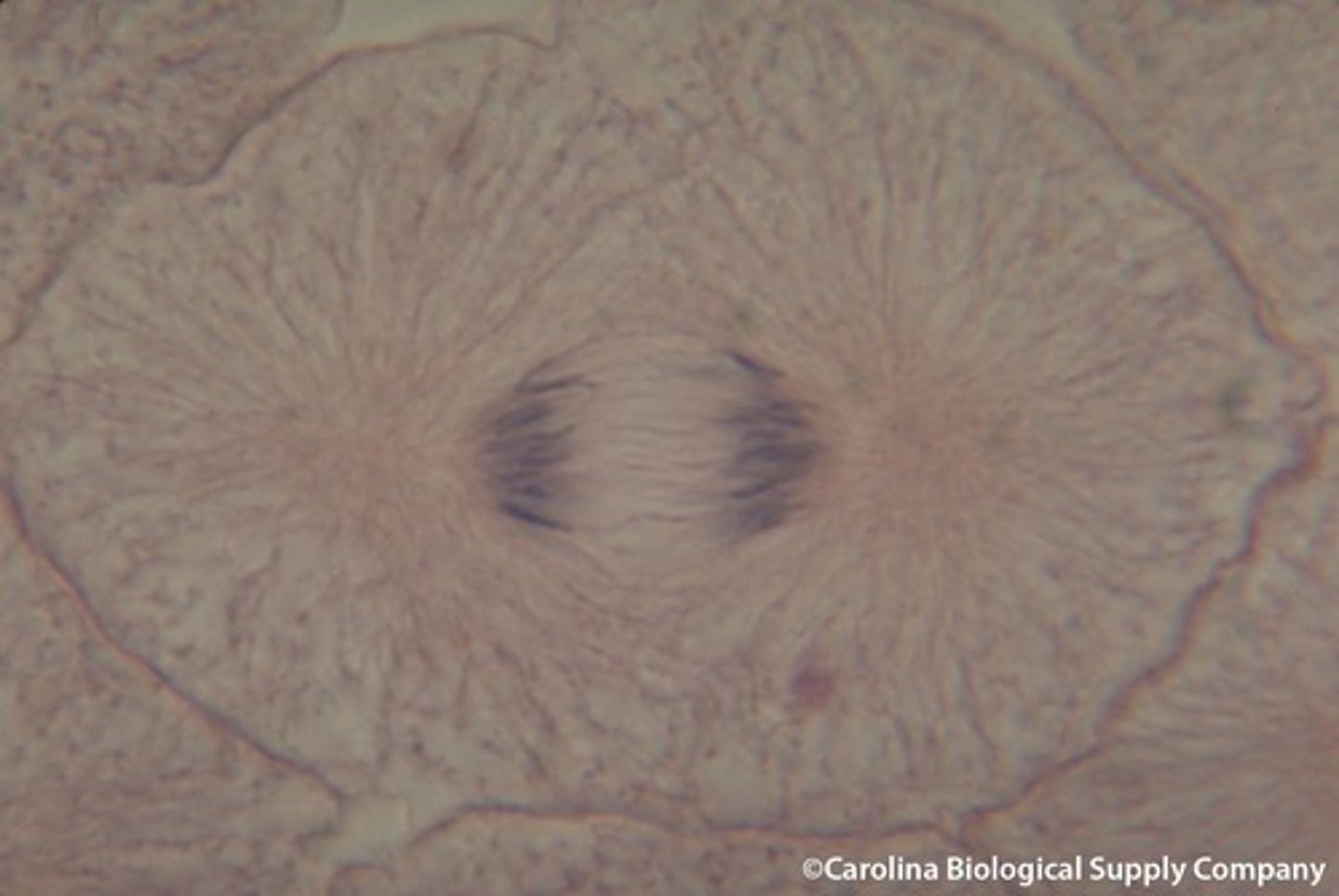
Metaphase
The second stage of mitosis: when the chromosomes are lined up in the middle
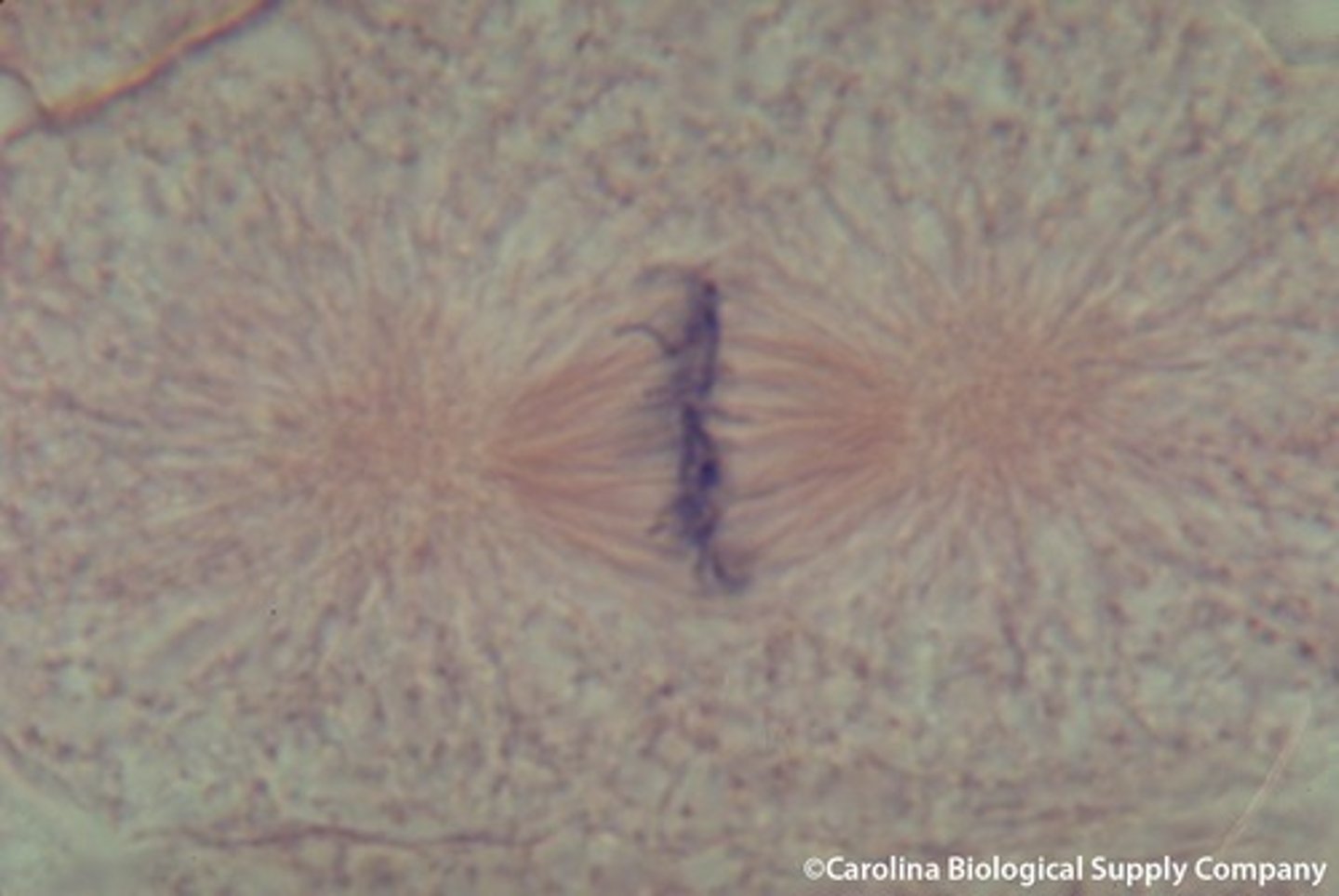
PMAT
The way to remember the steps of mitosis
Cytokinesis
At the end of M Phase --> Division of cytoplasm
Fertilization
The process of a sperm cell uniting with an egg cell
Zygote
The resultant diploid cell after a sperm cell fertilizes an egg cell
Sexual reproduction
Type of reproduction where the combination of genetic information from two separate parents produces offspring = leads to genetic diversity in a population
Autosomes
All the chromosomes in our cells other than the X and Y chromosome (the 1st through the 22nd chromosomes shown on a karyotype)
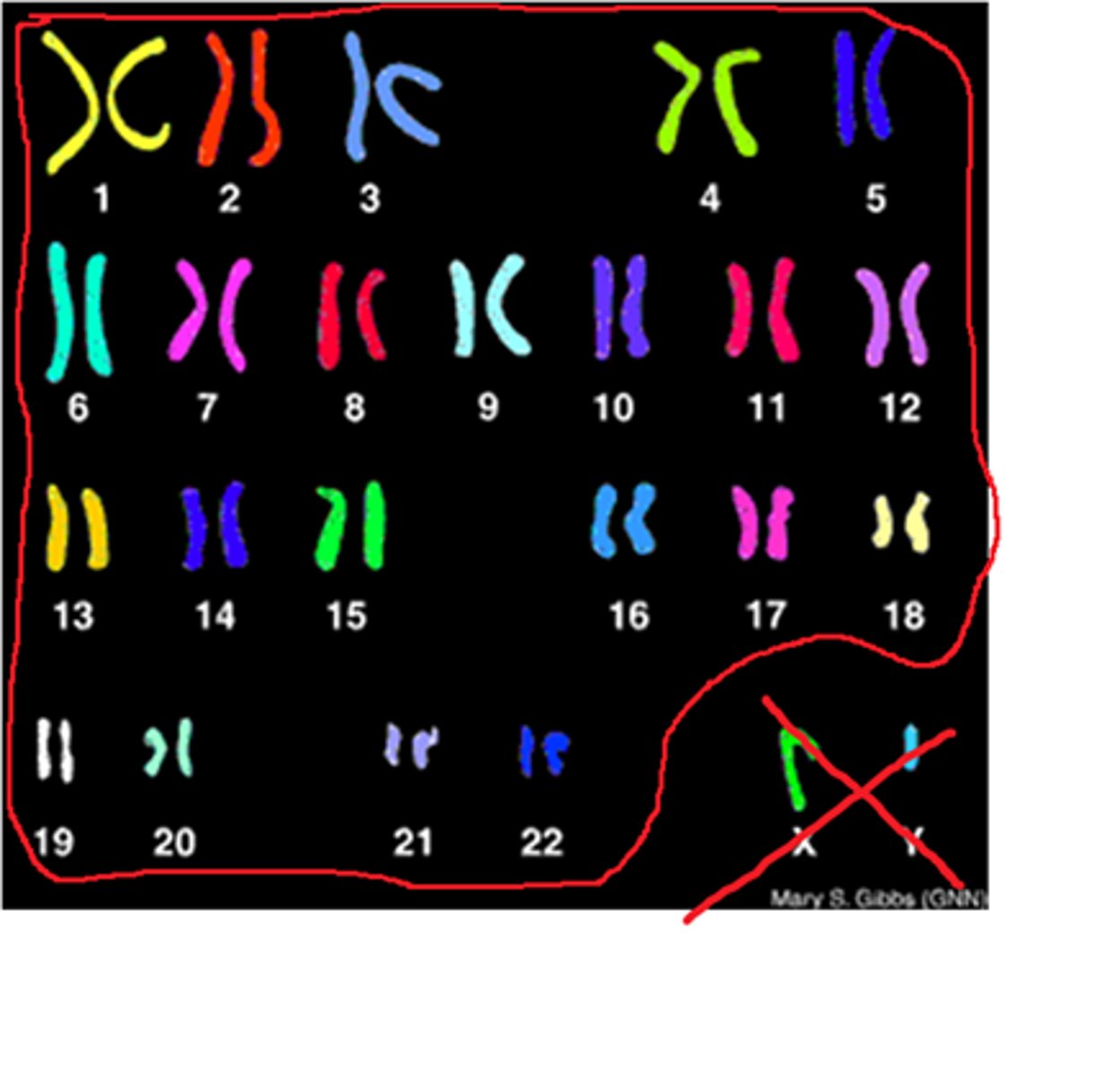
Sex chromosomes
X and Y chromosomes in human cells (the 23rd chromosomes on a karyotype)
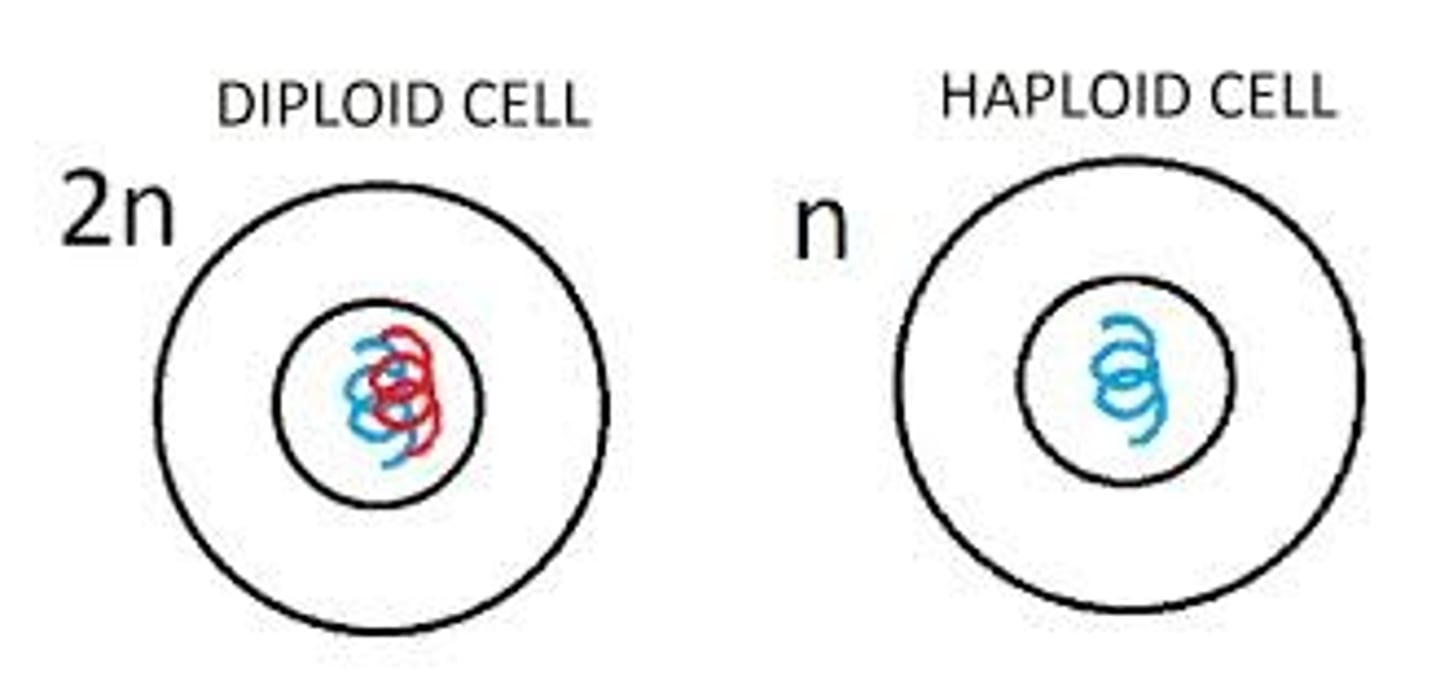
Dipolid cell
Cells that contain 2 of each chromosomes - ex: human skin cell has 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes
Haploid cell
Cells that contain only 1 of each chromosome - OR HALF the amount of chromosomes - ex: human sperm cell has 23 chromosomes
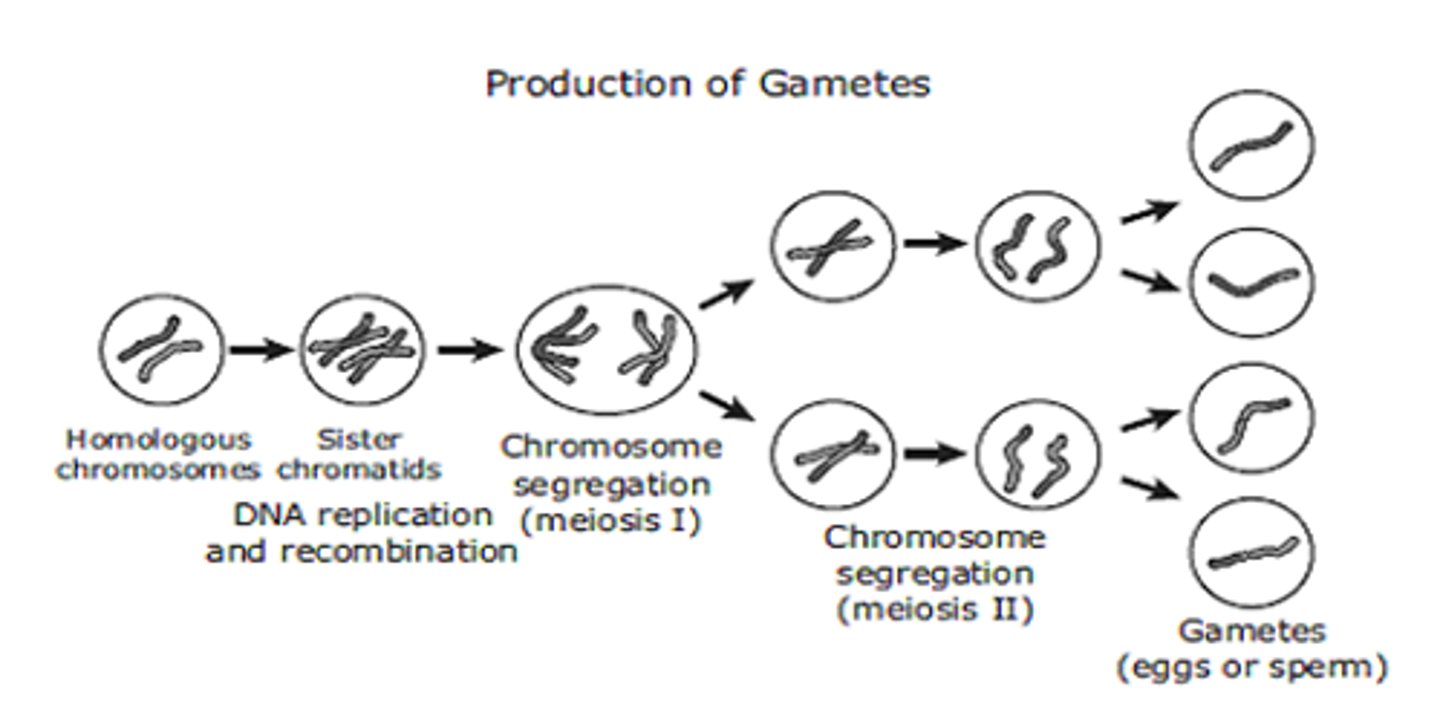
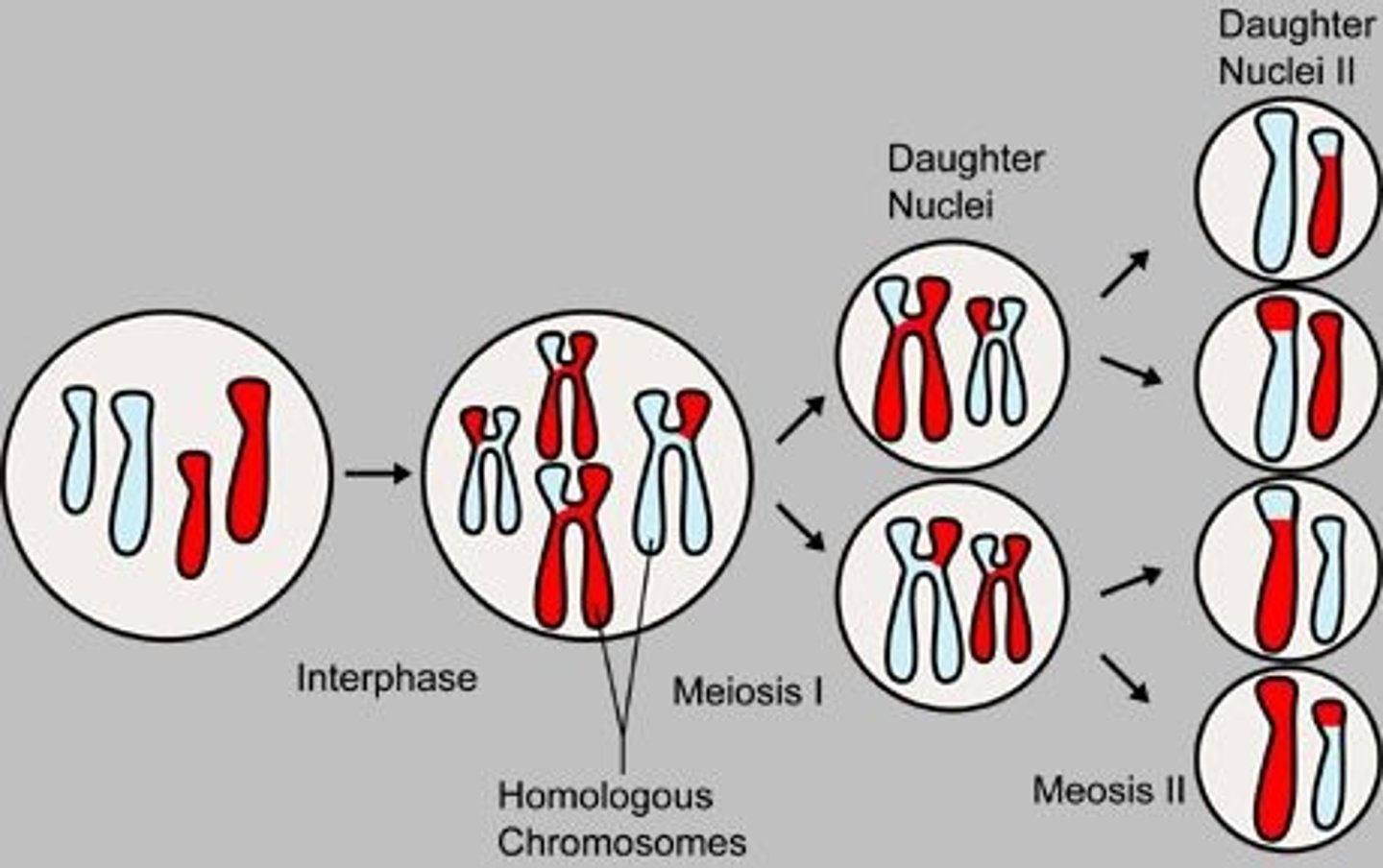
Meiosis
2 Cell divisions that produces 4 haploid daughter cells that become either sperm, if performed in the testes of a male, or egg, if performed in the ovaries of a female
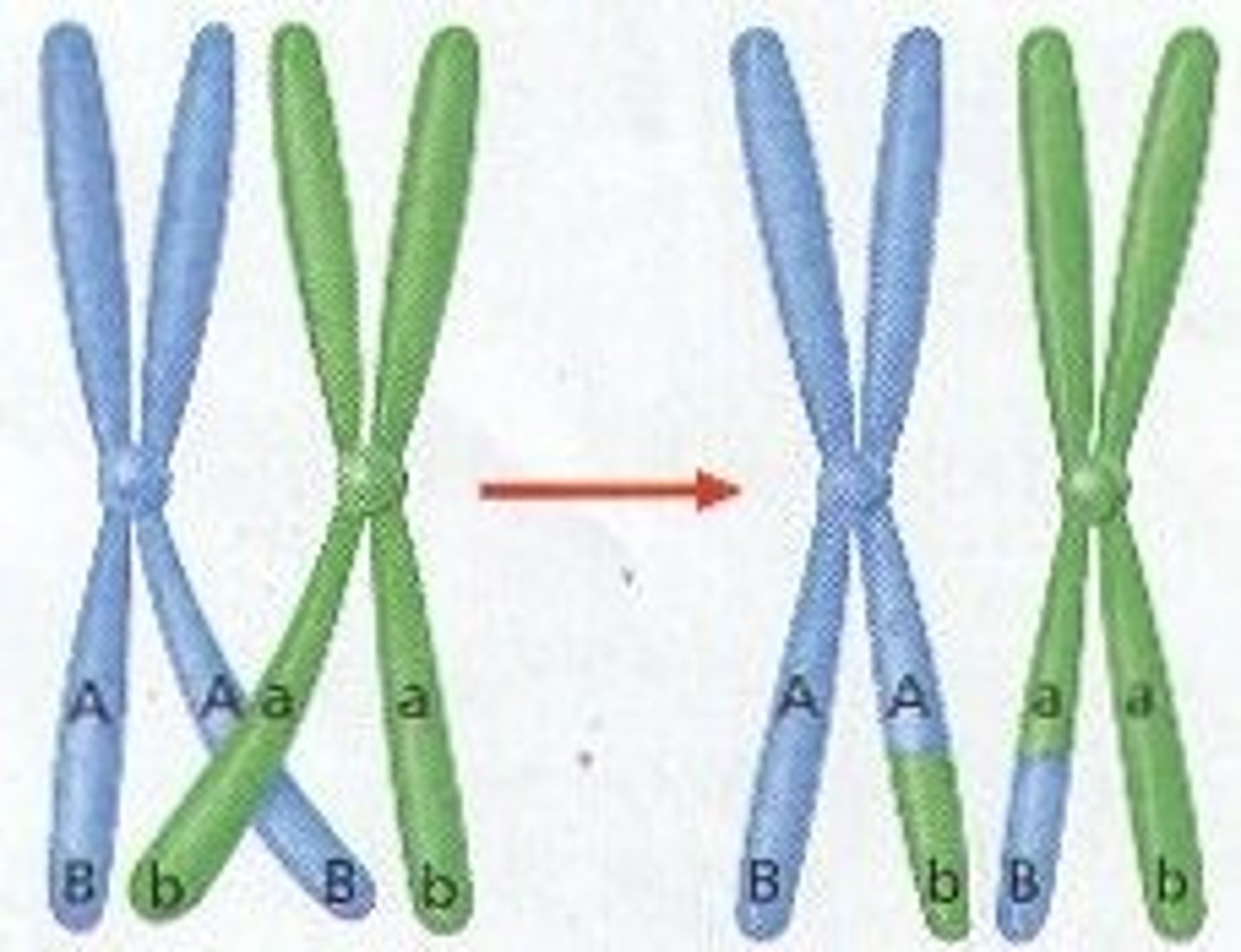
Crossing over
Event that occurs in Prophase I of Meiosis I where homologous chromosomes that are paired up exchange equal segments (genes) with each other -- leads to genetic variation in offspring
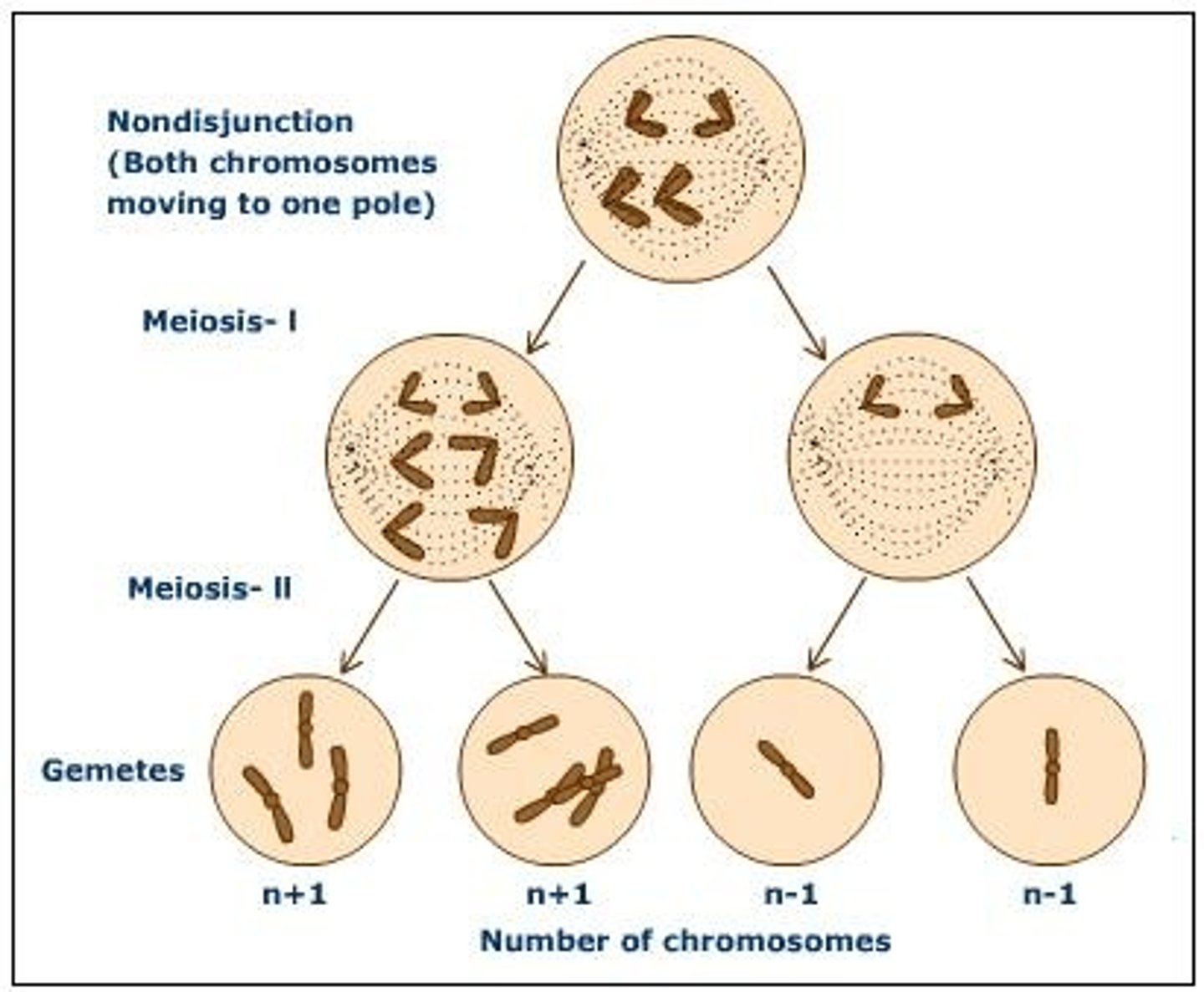
Nondisjuction
the failure of one or more pairs of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate normally during nuclear division, usually resulting in an abnormal distribution of chromosomes in the daughter nuclei.
Asexual reproduction
Type of reproduction where offspring are produced from one parent; those offspring are genetically identical to the parent
independent assortment
Independent segregation of genes during the formation of gametes
Gametogenesis
Gamete production. Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis
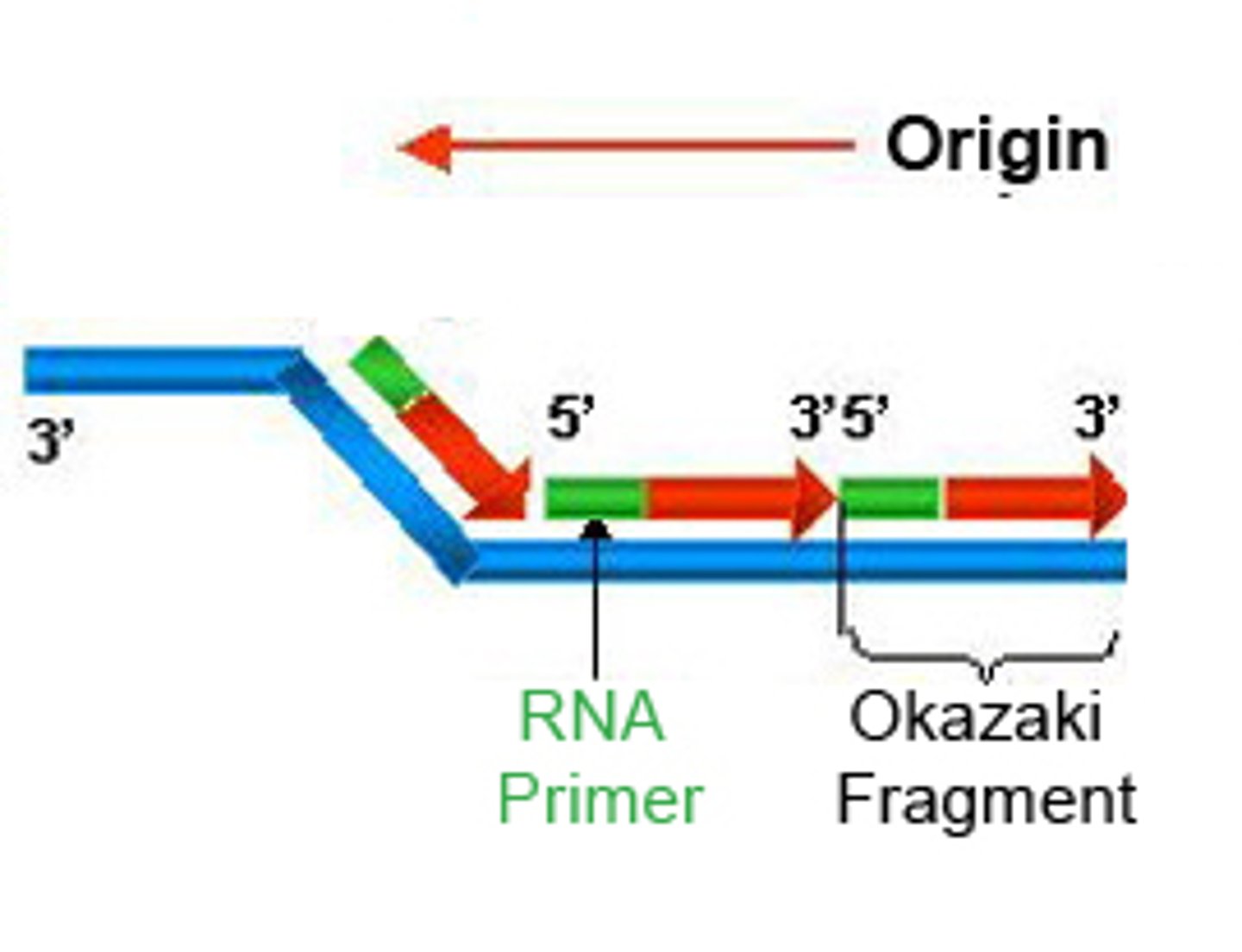
DNA primer
A small piece of single-stranded DNA. It acts a signal, binding to and marking the piece of DNA which is to be copied.
Spermatogenesis
production of sperm
Oogenesis
the production, growth, and maturation of an egg, or ovum
polar bodies
each of the small cells that bud off from an oocyte at the two meiotic divisions and do not develop into ova.
spermatozoon
sperm cell
genetic recombination
new combination of genes produced by crossing over and independent assortment
Genome
the complete set of nucleotide sequences encoded in the total DNA of an organism
structural genes
sections of DNA that carry the instructions for production of a protein
gene expression
process by which a gene produces its product and the product carries out its function
Non-coding DNA
the greater part of the DNA molecule that does not contain structural genes. Do not code for specific proteins.
regulatory gene
a non-coding segment of DNA that produces
transcription factors for gene expression
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome
DNA transcription
the formation of an RNA strand complementary to the DNA strand by RNA polymerase
Codon
three-nucleotide sequence on messenger RNA that codes for a single amino acid
Split genes
genes with intervening sequences of introns and exons
Intron
sequence of DNA that is not involved in coding for a protein
Exon
a segment of a DNA or RNA molecule containing information coding for a protein or peptide sequence.
trimming
removal of non-coding sections at the beginning and end of mRNA
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
Anticodon
group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA
polysome
A complex formed when multiple ribosomes are translating the same mRNA into proteins.
Translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
transcription factors
A regulatory protein that binds to DNA and affects transcription of specific genes.
Epigenetics
the study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
Hox genes
a sub-group of homeotic genes that control the body plan of an embryo along the head-tail axis
cell differentiation
the process by which a cell becomes specialized for a specific structure or function.
sex determination
The biological mechanism that determines whether an organism will develop as a male or female
repressor protein
a regulatory protein that binds to an operator and blocks transcription of the genes of an operon
SYR gene
sex determining region of the Y chromosome
histone modification
changes in the structure of histones that make it more or less likely that a segment of DNA will be transcribed
monozygotic twins
twins who are genetically identical
Mutation
small permanent change in the DNA of an organism
point mutation
a change in a single nucleotide in the DNA code that may result in translation of one different amino acid in a polypeptide sequence
frameshift mutation
mutation that shifts the "reading" frame of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide
Non-disjunction
the failure of one or more pairs of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate normally during nuclear division, usually resulting in an abnormal distribution of chromosomes in the daughter nuclei.
Aneuploidy
the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell
Karotype
A picture of all the chromosomes in a cell arranged in pairs
Ploidy
number of sets of chromosomes in a cell
Trisomy
3 copies of a chromosome
Mutagens
A chemical or physical agent that interacts with DNA and causes a mutation.
Homozygous
An organism that has two identical alleles for a trait
pure breeding
Individuals that are homozygous that will always produce the same offspring when crossed together
Heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for a trait
dominant trait
A genetic trait is considered dominant if it is expressed in a person who has only one copy of the gene associated with the trait.
recessive allele
An allele that is masked when a dominant allele is present
Genotype
An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations.
Phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits.
Punnett Square
A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross
monoybrid cross
genetic cross between two individuals investigating only one specific trait
dihybrid cross
Cross or mating between organisms involving two pairs of contrasting traits
frequency histogram
type of bar graph that shows frequency distributions
Codominance
A condition in which both alleles for a gene are fully expressed
incomplete dominance
A pattern of inheritance in which two alleles, inherited from the parents, are neither dominant nor recessive. The resulting offspring have a phenotype that is a blending of the parental traits.
Multiple or poly alleles
the inheritance of a characteristic governed by more than two allelic forms forms. E.g. blood groups