Alkyne reactions
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Elimination : 1) xsNaH2 / 2) H2O
elimination reaction (1 of 2 ways to form alkyne), markovnikov and anti markovnikov

hydrohalogenation: xs HX (two equivalents)
added to most substituted carbon
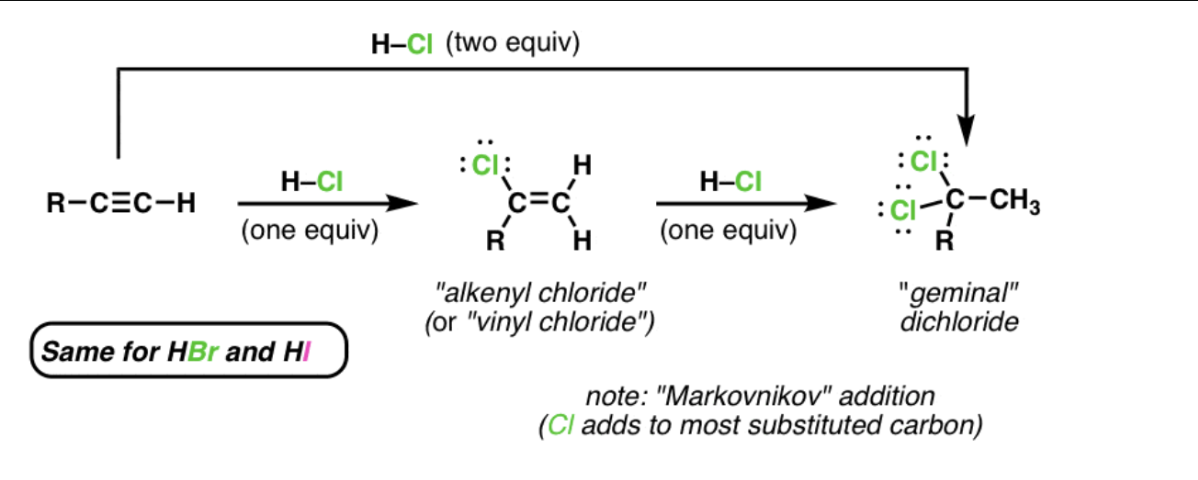
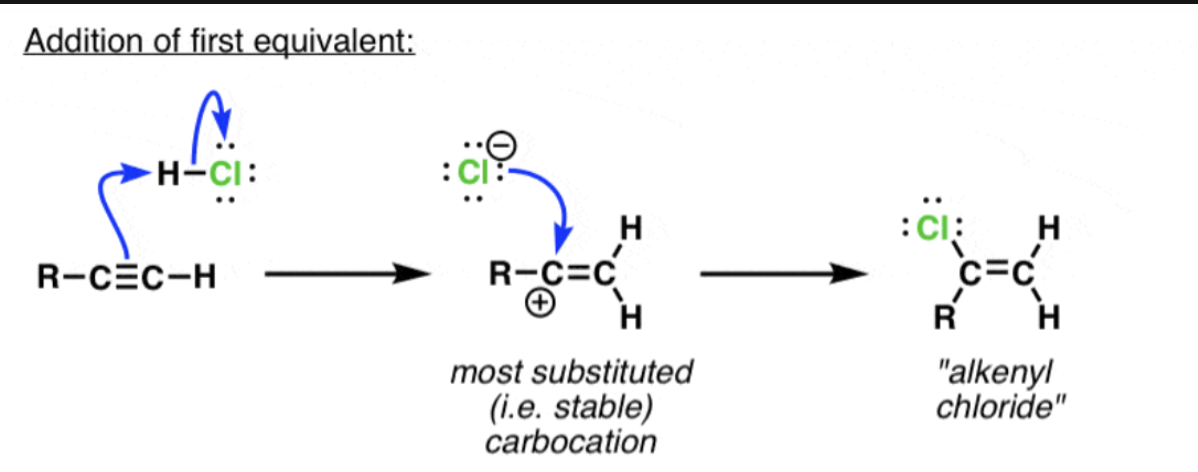
hydrohalogenation: Hx (one equivalent)
attacked by the π bond of the alkene to give a carbocation on the most substituted carbon, giving “Markovnikov” regioselectivity (See Post: Markovnikov’s Rule) followed by
attack of halide ion on the carbocation.
acid catalyzed hydration: HgSO4, H2SO4, H2O
forms enol and ketone, equillibrium favors ketone
OH forms on more substituted carbon (Mark.)

hydroboration oxidation: 1) R2BH / 2) H2O2, NaOH, H2O
OH forms on the least substituted carbon (anti Mark.)

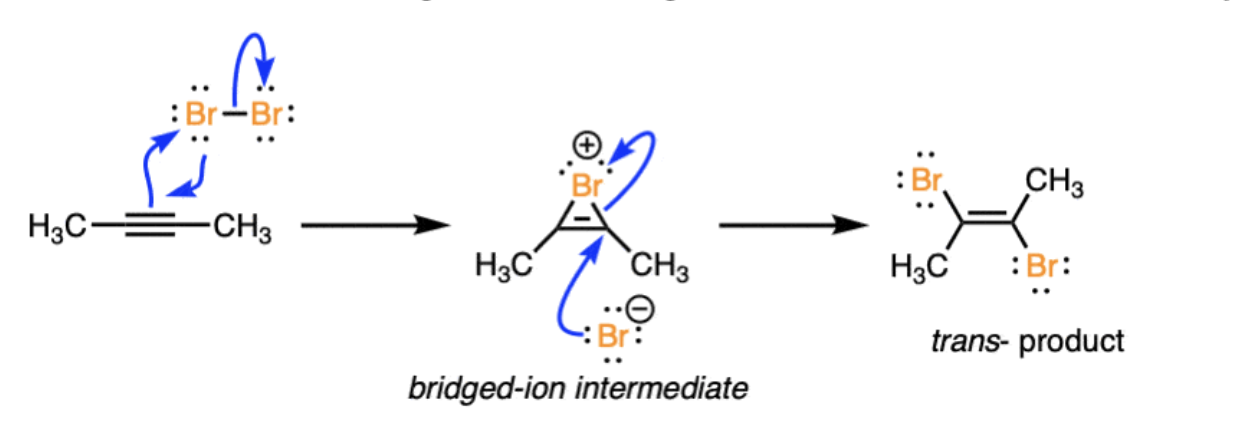
Halogenation: X2 (ex Br2)
bridged intermediate forms trans dihaloalkenes
halogenation: xs X2 (two equiv.)
tetrahalogenated alkene is formed

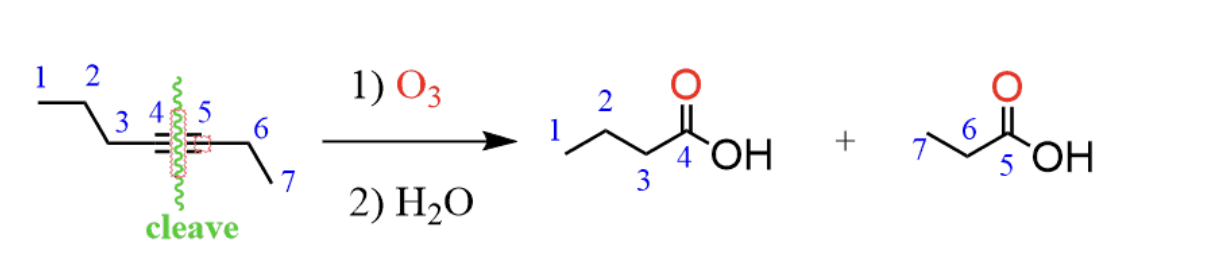
ozonolysis: 1) O3 2) H2O
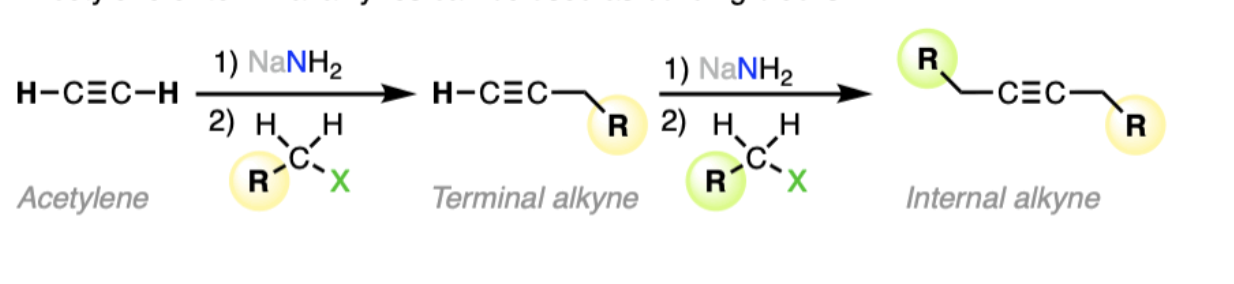
alkylation: 1) NaNH2 2) RX
(2nd way to form alkyne)
performs an SN2 reaction with a primary or methyl halide, yielding a longer internal alkyne
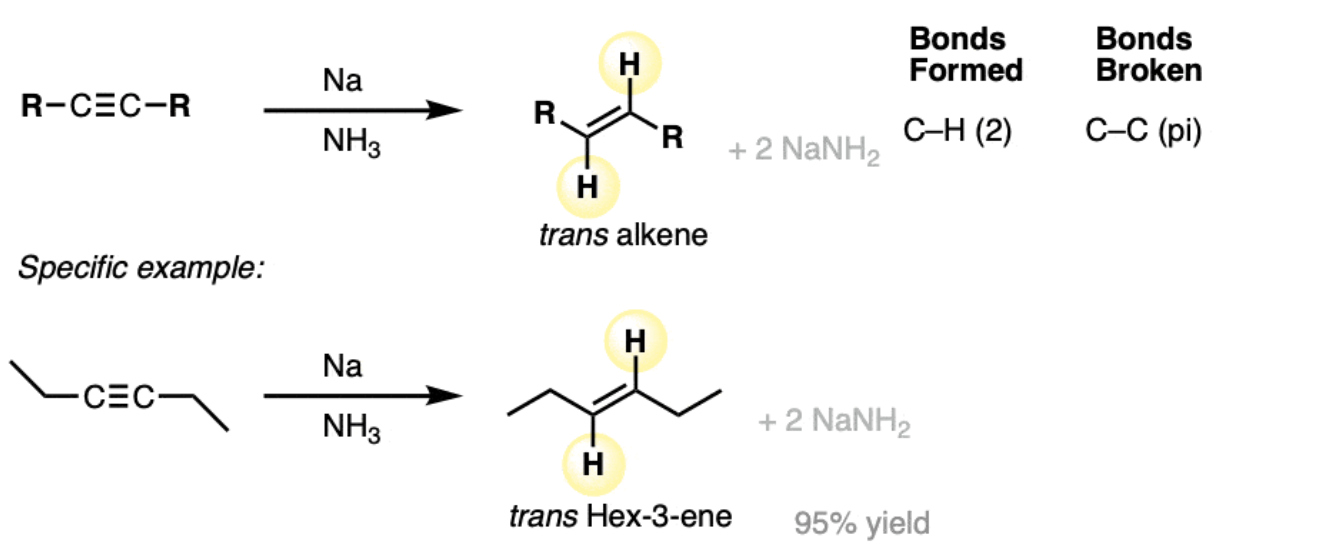
dissolving metal reduction: Na / NH3 (L)
forms trans
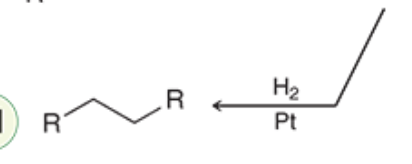
hydrogenation: H2/ pt
turns into alkane
hydrogenation with poisoned catalyst
syn addition