LIFE SCIENCES - HUMAN RESPONSE TO THE ENVIRONMENT
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Receptor
A structure that receives a stimulus and converts it into an impulse
Effector
Gland or organ that brings about a response to stimuli received by the body
Stimulus
Detectable change in the internal or external environment
Impulse
Electrical signal created by receptor organs in response to stimuli
Autonomic nervous system
Controls our involuntary bodily functions; divided into the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system
Peripheral nervous system
consists of nerves that extend outside the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord)
Co-ordinating system
consist of receptors and effectors which respond to stimuli and allow for changes to take place to maintain internal conditions
nervous system
endocrine system
Cranium
part of the skull that contains and protects the brain
Meninges
protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord
Cerebrospinal fluid
fluid around the brain and spinal cord to aid in protection
Grey matter
part of the brain and spinal cord consisting of cell bodies and dendrites
White matter
part of the brain and spinal cord consisting of myelinated axons
Neuron
specialized nerve cells which transmits nerve impulses
Dendrites
fibers that transmit impulses to a cell body in a neuron
Nerve
bundle of neurons
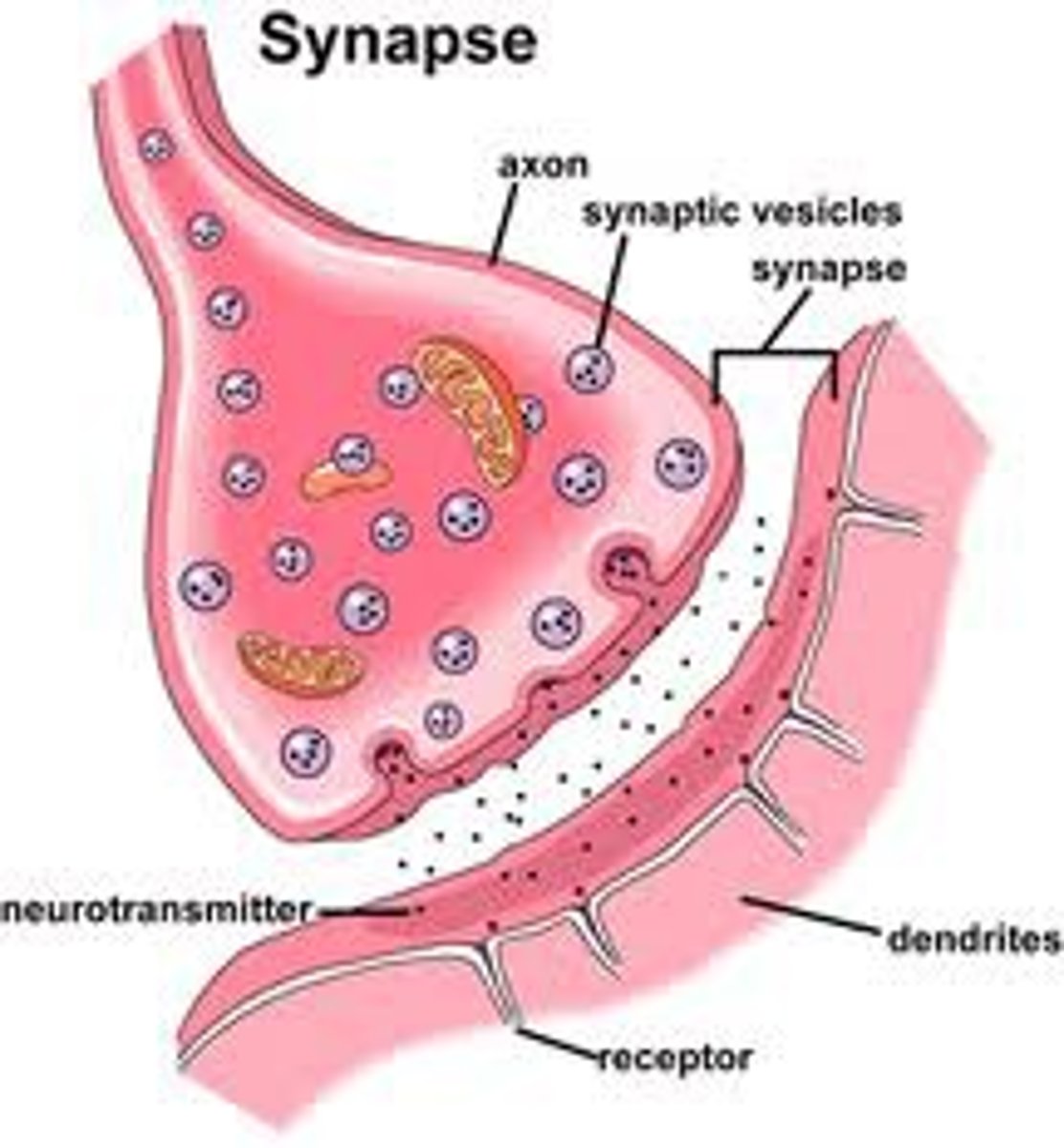
Synapse
the gap between the axon of one neuron and dendrite of another
Neurotransmitter
chemicals which transfer impulses across the synapse
Homeostasis
the tendency of living organisms to maintain their internal environment constant within narrow limits irrespective of changes in the external environments
Alzheimer's disease
disease caused by nerve defects, usually in older people (over 60 as young as 40) and is characterized by memory loss and confusion
Multiple sclerosis
disease caused by the body's immune system attacking the myelin sheath covering neurons which prevents them from functioning properly and is characterized by loss of speech and vision, difficulty walking, pain, fatigue and memory loss (ages 20 and 40)
Division of human nervous system
central nervous system (brain and spinal cord)
peripheral nervous system (autonomic and somatic)
Internal changes
body temperature
sugar levels
CO2 and O2 levels
water levels
External changes
pain
environment temperature
danger
The brain
Made up of delicate nervous tissue which cannot repair itself.
Controls all functioning of human body.
Protection of the brain
Inside bony cranium
Surrounded by three membranes (meninges)
Cushioned by fluid (cerebrospinal fluid)
Structure of the brain
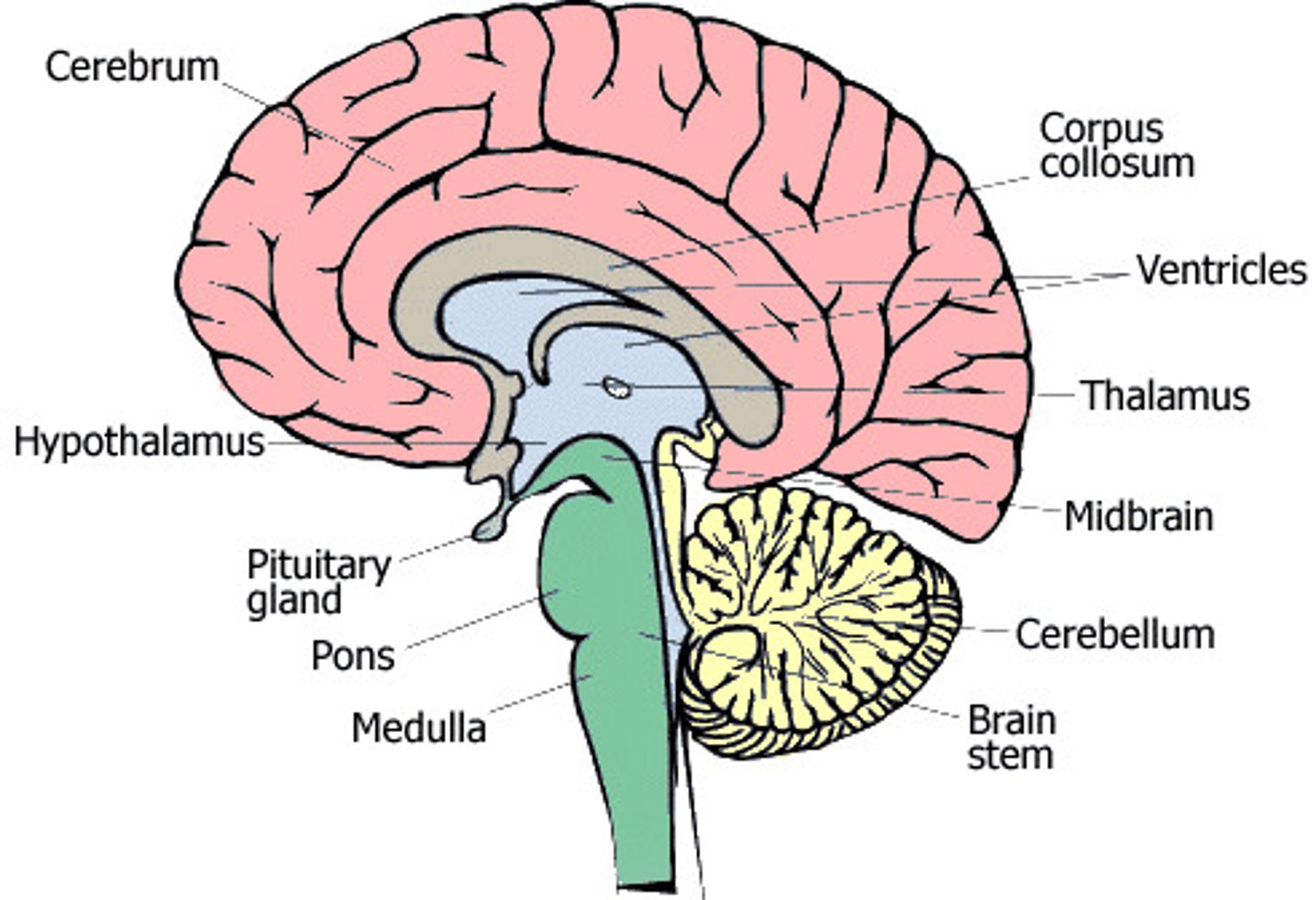
Cerebrum structure
largest part of the brain
divided into 2 hemispheres which are connected by corpus callosum
Cerebrum function
controls voluntary actions
receives and interprets sensations from sense organs
higher though processes(memory, intelligence, reasoning)
allow communication between 2 halves of brain
Cerebellum structure
second largest
located inside and below cerebrum
Cerebellum function
co-ordinates skeletal muscles to bring about balance while moving
maintains balance and posture
maintains muscle tone
Medulla oblongata structure
lower part of brain
continues down into body as the spinal cord
Medulla oblongata function
controls breathing, peristalsis, heartbeat, swallowing
transmits impulses from spinal cord to brain
controls less important reflexes: blinking, coughing, sneezing, salivating
Hypothalamus structure
small section of brain just above pituitary gland
Hypothalamus function
control centre for things such as hunger, thirst, sleep, body temperature and emotions
The internal structure of the spinal cord
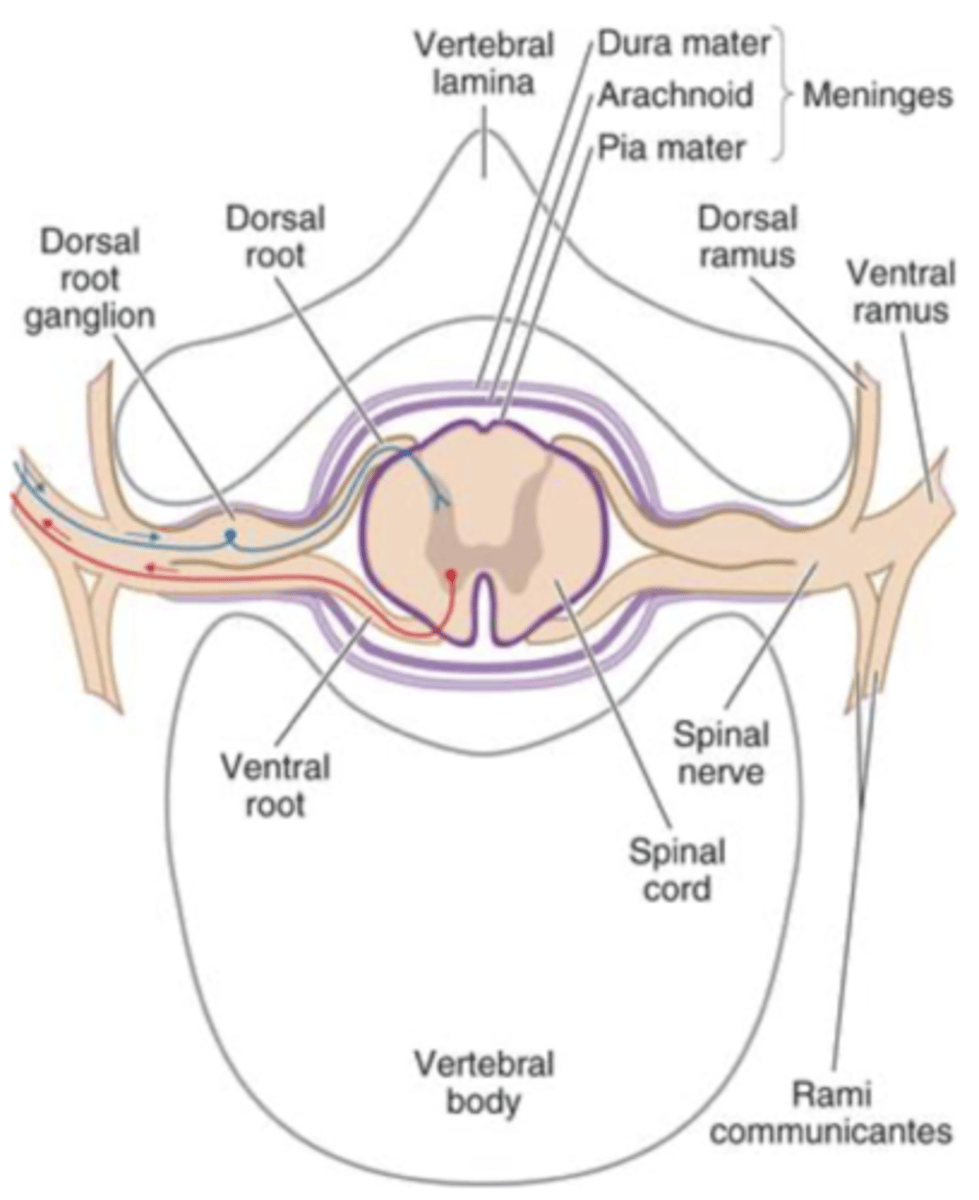
The spinal cord
Made up of delicate nerve tissue which cannot repair itself
Spinal cord protected by
33 vertebrae (bone) with discs of cartilage between them to act as shock absorbers
three membranes (meninges)
cerebrospinal fluid
Spinal nerves
31 pairs of nerves arising from the spinal cord
Dorsal root (enters)
Ventral root (leaves)
Spinal cord functions
transmits impulses from receptors to the brain and from the brain to effectors
contains reflex centres that function automatically to protect the body
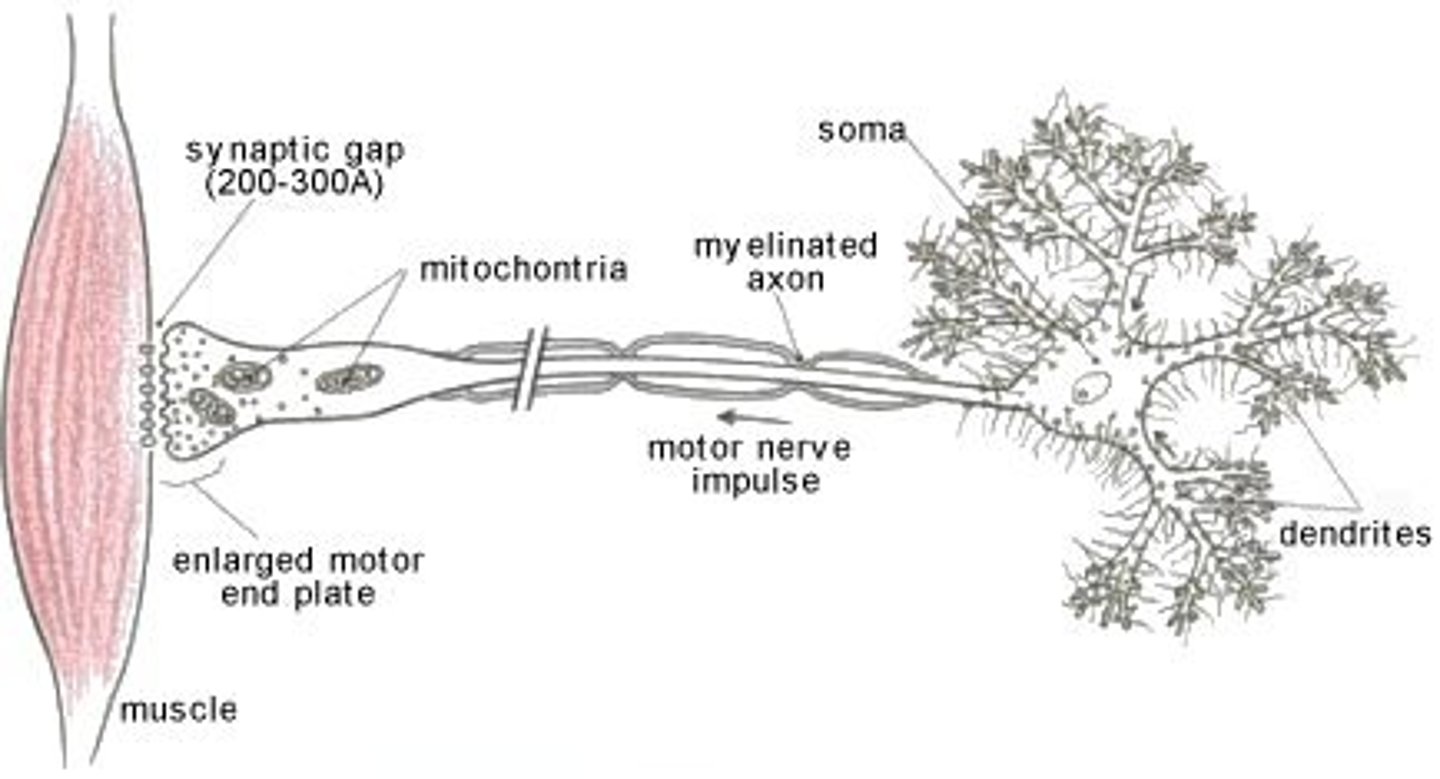
4 structures of neurons
*dendrites - transmitting impulses towards the cell body
*cell body (with nucleus) - controlling cell metabolism
*axon - transmitting impulses away from the cell body
*myelin sheath - insulating axon and speeding up transmission of impulses, enclosed by neurilemma (repair)
Structure of a motor neuron
1. dendrites
2. cell body
3. axon
4. myelin sheath
5. terminal end of axon
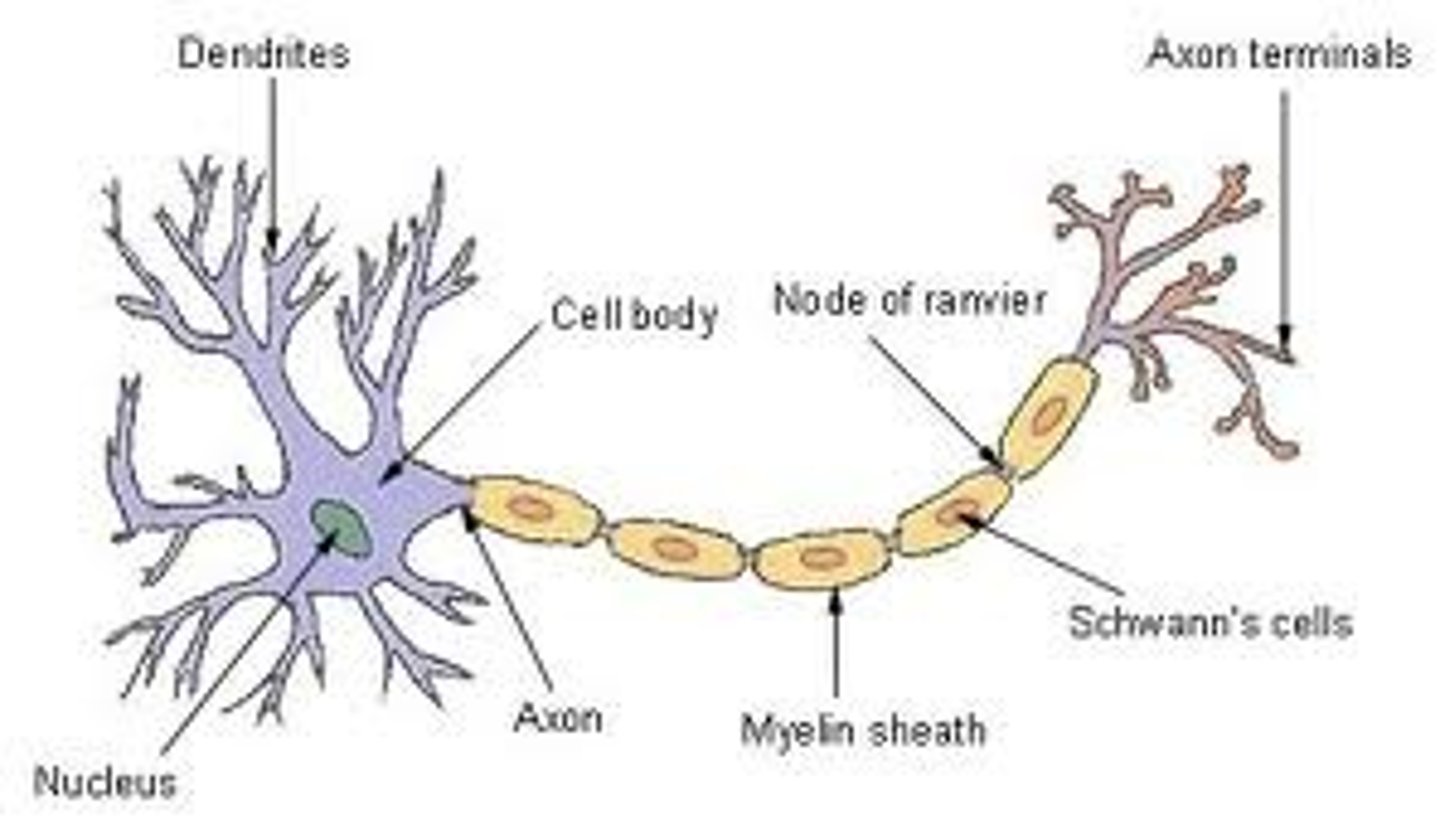
3 types of neurons
sensory neurons, motor neurons, interneurons
Sensory neurons
transmits impulses from receptors to the central nervous system
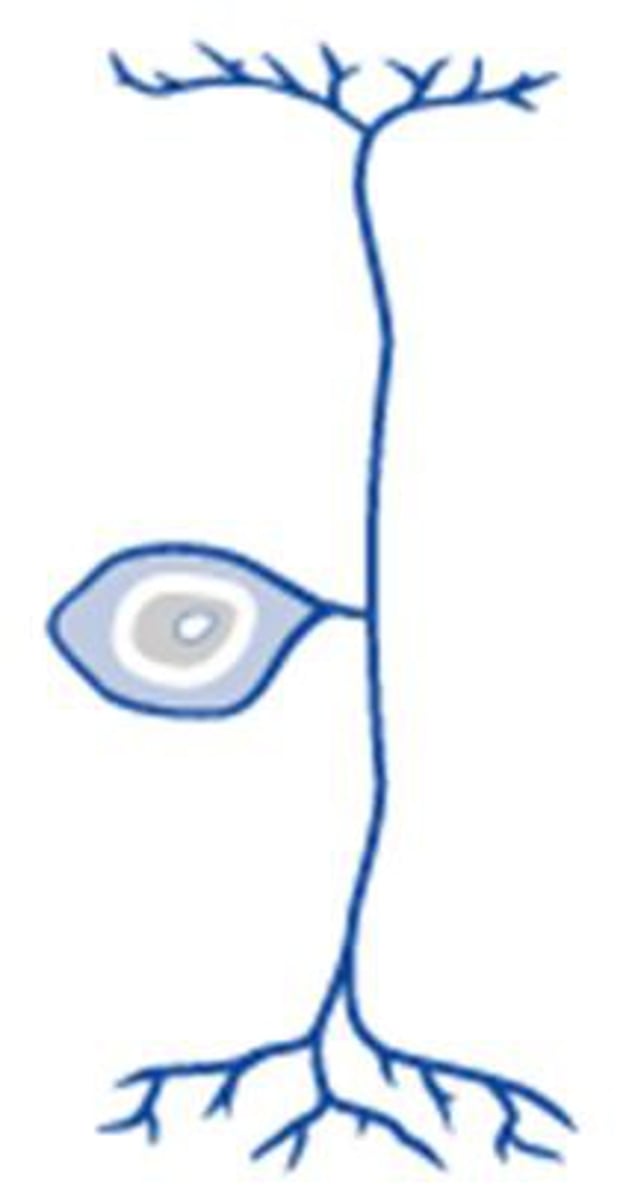
Interneuron
connects a sensory neuron to a motor neuron in the central nervous system
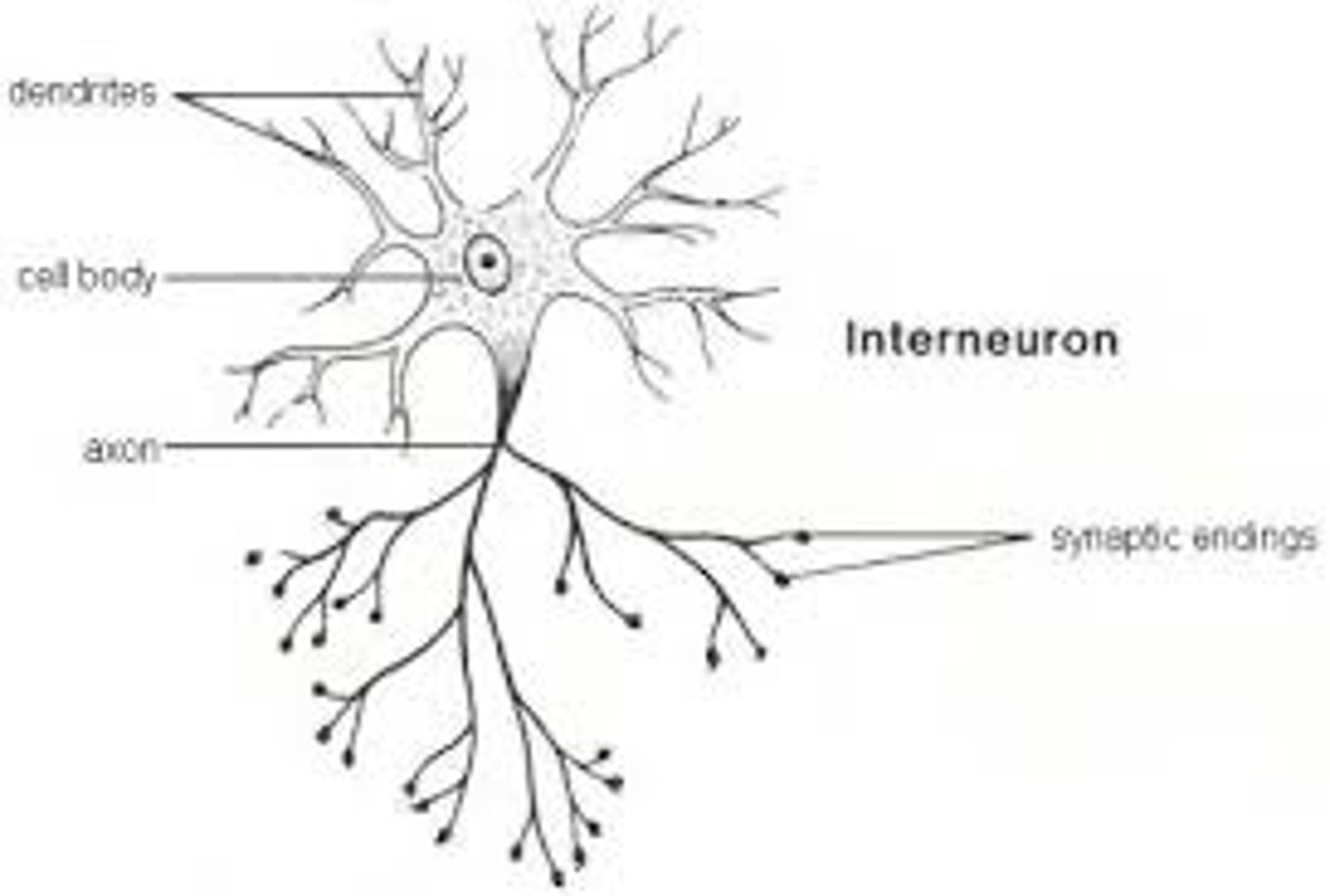
Motor neuron
transmits impulses from the central nervous system to the effectors (muscles and glands) in the body
Significance of a synapse
*ensures impulse moves in one direction only
*prevents continuous stimulation of neurons
*ensures impulses are transmitted from the sensory neuron to the motor neuron
Reflex action
quick, automatic response to a stimulus
(knee-jerk, sneezing, quickly removing body part from danger)
Reflex arc
pathway along which an impulse is transmitted to bring about a response to a stimulus during a reflex action
Receptor => sensory neuron => spinal cord =>connector neuron => motor neuron => Effector
Significance of reflex action
allows for quick response, without thinking, to protect the body from damage and danger
Reflex action of a person touching a hot pot:
1. Stimulus detected by receptors and converted into a nerve impulse.
2. The nerve impulse is transmitted along the sensory neuron through the dorsal root to the spinal cord.
3. The impulse is transmitted from the sensory neuron to an interneuron in the spinal cord.
4. The impulse is transmitted from the interneuron to a motor neuron in the spinal cord.
5. The impulse exits the spinal cord through the ventral root and is transmitted along the axon to the effector organs (muscle in arm contracts).
6. The hand pulls away from the stimulus quickly.
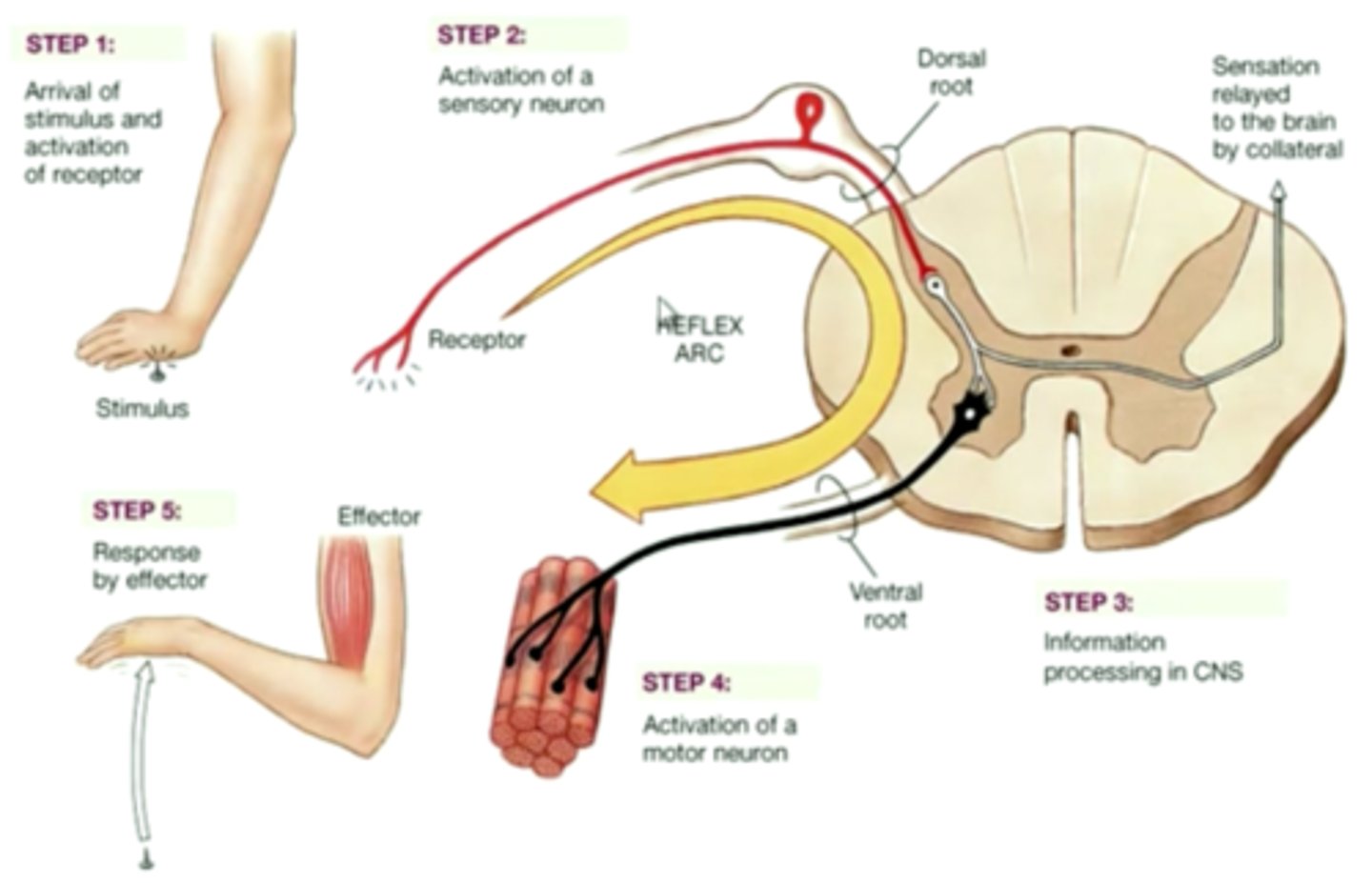
Does reflex action include the brain?
No, impulses reach the brain after the reflex arc is complete and pain will be felt.
Peripheral Nervous System can be divided:
Somatic - voluntary muscles
Automatic - involuntary muscles
Peripheral Nervous System functions:
transmits impulses from receptors to central nervous system via sensory neurons
transmits impulses from the central nervous system to effectors via the motor neuron
Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
External environment
Automatic Nervous System (ANS)
Internal environment (homeostasis)
*sympathetic nervous system
*parasympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
responsible for fight or flight function in emergency situations
Parasympathetic nervous system
restores body to a normal state after an emergency situation
Effects of sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems
sympathetic:
*increases heart rate
*increases blood pressure
*constricts blood vessels in the skin (vasoconstriction)
*widens bronchioles
*decreases peristalsis
*stimulates sweat secretion
*stimulates secretion of adrenaline
*dilates pupils
parasympathetic:
*decreases heart rate
*decreases blood pressure
*dilates blood vessels in skin (vasodilation)
*narrows bronchioles
*increases peristalsis
*no effect on sweat secretion
*no effect on adrenaline secretion
*constricts pupil
Brain injuries
Affect movement, memory and speech
long-term mental health issues
Spinal cord injuries
paralysis and the inability to move or feel below the point of injury
grommets
tiny hollow plastic button used to drain fluid from the ear via the tympanic membrane
functions of the ear
hearing and balance
Organ of Corti
converts stimulus of sound to impulse
function of eustachian tube
equalize pressure on either side of the ear drum
function of the auditory nerve
carries impulses from the cochlea to the brain
function of tympanic membrane
transmits sound from the air to the ossicles inside the middle ear and then to the cochlea via vibrations
function of ossicles
to transmit and amplify vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear
function of pinna
traps sound waves and directs them to the auditory canal
function of auditory canal
carries sound waves to the ear drum
prevents drying out of the ear by secreting wax
myopia
nearsightedness - needs concave lens
pupillary reflex
The automatic process by which the iris contracts and relaxes to control the size of the pupil, in response to the relative brightness of light entering the eye
accomodation of lens
lenses change shape to focus on objects near or far
Hypermetropia
farsightedness - needs convex lenses
astigmatism
a condition in which the eye does not focus properly because of uneven curvatures of the cornea
Cataracts
clouding of the lens
conjuctiva
the mucous membrane that covers the front of the eye and lines the inside of the eyelids.