Female reproduction
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
Define Estrous
The reproductive cycle in females that are of an estrual species
How is estrous calculated?
from the period of estrus and inculcation to the subsequent period of estrus and obvulation
Define Estrus or Heat
The period of time in which a female is sexually receptive to the male for the purposes of mating
Define Anestrous Period
The one when a female is not in estrus. The non-breeding season.
Define Estrus Synchronization
Controlling the estrous cycle so that a high percentage of the females in the herd express estrus (receptivity) at the same time
Define Clone
An individual grown from a single somatic cell of its parent and genetically identical to it
Define A.I
Abbreviation for artificial insemination, a common technique used in reproductive biology that involves placing semen into the reproductive tract of the female by artificial techniques rather than natural mating
Define E.T
Abbreviation for embryo transfer, which is a procedure used to transfer embryos from a donor female to a group of recipient females
Define Haploid
Half the normal number of chromosomes found in sperm and ova (half from mom and half from dad)
Define open
Refers to non-pregnant female
Define Fertility
The capacity to initiate, sustain, and support reproduction
Define dystocia
Difficult birth, intervention required
Role of Vulva/Vagina
Female organ of copulation; birth canal for parturition
Role of Cerivx
Passageway for sperm following breeding; seals off uterus during pregnancy
Role of Uterus
Secretory organ; incubator for embryo and placenta; control of cyclicity (Leuteolysis); contraction for parturition
Role of Oviduct
Passage for ovum and sperm; site of fertilization
Role of Ovary
Produces female gamete and female sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone)
Define Leuteolysis
Destruction of the corpus luteum
Functions of the Vulva/Vagina
Passageway for urine, Receptor for penis during copulation, Expands at parturition for delivery of fetus, Not to be confused with the anus
Protective structures of the Vagina and cervix
tissue is keratinized to protect against abrasion
Secretory
Provides berries
Functions of vagina
Copulatory Organ
Fornix vagina is site of semen deposition (cow/ewe), No glands secretions come from passage of plasma components as well as cervix, It provides lubrication, pH is acidic (5.7). bacteriostatic, Stimulates gland penis of bull temperature and pressure
Birth Canal
Dilates for fetus during parturition
What is the site of semen deposition in cows/ewes?
Fornix vagina
Functions of the cervix
composed of cartilage surrounded by soft tissue, Openings are the External or Internal Os, Passageway for sperm following breeding, Secrets mucous, seals off uterus during pregnancy, Passageway of fetus, Species specific configuration (rings, spiral, or folds)
What specie(s) have a ring configuration cervix
Cattle, Goat, Sheep
What specie(s) have a Spiral configuration cervix
Pigs
What specie(s) have a folds configuration cervix
Horses
Functions of the uterus as the organ of pregnancy
incubator for fertilized ovum, nutrients to ovum, Aids in travel of sperm, Secretory organ, Has two horns or branches and a single body, Shape differs between species
Components of the cervix in a cow
Cervix is a very hard and ridgid during estrus composed of thick connective tissue, typically closed except during estrus, cow has 4-5 annular rings, contains crypts which provide surface area for sperm reservoir, Os cervix, Fornix vagina, mucus discharge during estrus
Function of crypts
cause the sperm to get lost, the strongest swimmers survive
Function of the mucus
helps sperm move through the reproductive tract and protects the baby during parturition
Components of mare cervix
longitudinal folds, Os cervix, Fornix Vagina, no obstacles in the mare after the fornix vagina (straight shot), mare is opposite of other species as cervix is soft and pliable during estrus flattens on floor of vagina. during pregnancy is tight and closed.
Components of a sow cervix
Os cervix, so cervix has many interdigitating pads
Does a sow have a fornix vagina
No
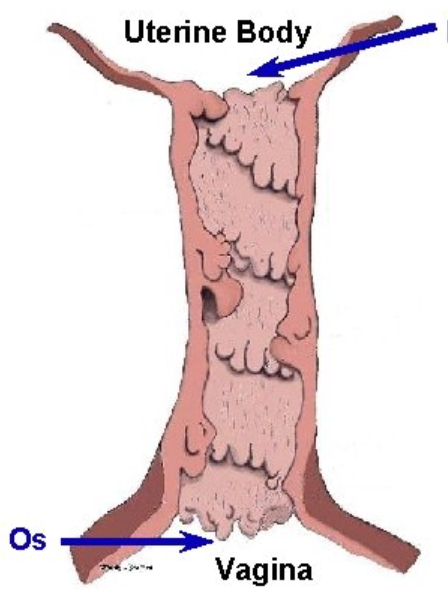
What species does this cervix belong to?
Cow
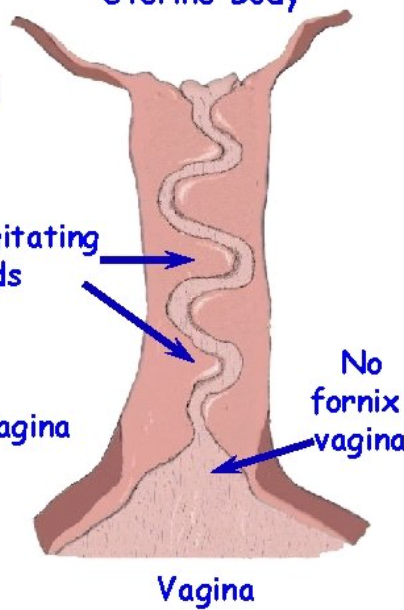
What species does this cervix belong to?
Sow
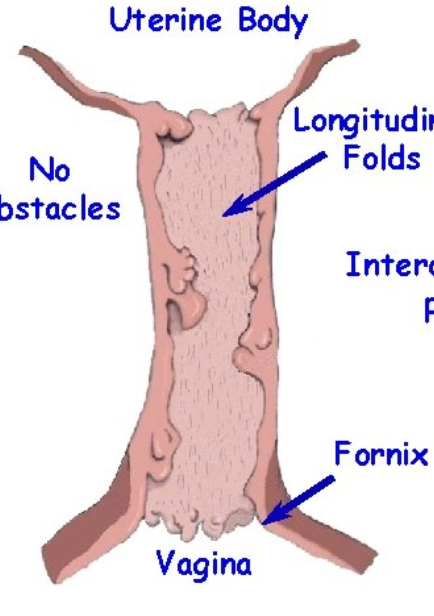
What species does this cervix belong to?
Mare
Follicular Aspiration
stick a needle in the follicle to suck out eggs & allow for a variety of genetic combinations
Why is the uterus the organ of pregnancy
incubator for fertilized ovum, nutrients to ovum, aids travel of sperm, secretory organ, has two horns or branches and a single body, shape differs between species, creates environment for fetus and placenta.
What species has two long uterine horns?
Sow
What species has short uterine horns but big uterine body
Mare
Why does the sow have long uterine horns
it’s a litter-bearing species
What type of uterus does a cow and ewe have?
Bipartite
What type of uterus does a pig have?
Bicornuate
What type of uterus does a mare have?
Modified bipartite
functions of the uterus
transport sperm, muscle contractions, sperm motility, absorption and phagocytosis, partially prepares sperm for fertilization, provides environment for embryo, supports development of fetus, At birth expels fetus, recovers from pregnancy
How does the uterus transport sperm
estrogen stimulates myometrial contractions so that sperm moves to site of fertilization
what is the path of muscle contractions in uterus during estrus and ovulation
towards the oviduct during estrus (heat) but following ovulation are towards the cervix until progesterone increases from CL
Why are viable sperm (motile) important?
Won’t be absorbed
How does absorption and phagocytosis occur in the uterus?
occurs by uterine epithelium and leukocytes which fight infection
How does the uterus prepare sperm for fertilization?
Estrogen stimulates uterine secretions which capacitate sperm (zona pelucida)
What must take place before a sperm cell can penetrate the egg
capacitation
How does the uterus provide an environment for the embryo?
uterine secretions stimulated by estrogen and progesterone
How does the uterus support development of the fetus
quiescent myometrium - progesterone, immunological protection from rejection by the maternal immune system
How does the uterus expel fetus at birth
Strong rhythmic myometrial contractions (progesterone low)
how does the uterus recover from pregnancy
uterine involution
define uterine involution
Myometrial contractions and enzymatic activity shrink the uterus back to its normal size
If a female is not pregnant, what does the uterine endometrium release?
Prostaglandin (PGF2a) to cause the CL to regress
If a female is pregnant, what chemical signal does the embryo provide?
interferon tau
What species releases ECG to signal pregnancy instead of Interferon tau
Equine Chorionic Gonadotrophin
Define oviduct
tube that connects the ovary to the uterus
What are the three distinct regions in the oviduct
Infundibulum, Ampulla, Isthmus
What is the function of the infundibulum region?
Surrounds ovary
What is the function of the ampulla region?
Transports oocyte
What is the function of the isthmus region?
Transports sperm
Where is the site of fertilization
Ampulla-Isthmus Junction (AIJ)
What are the ovary’s two main regions?
Cortex and Medulla
Where is cortex found on Cows, sheep, and pigs
outer of the ovary
Where is cortex found on horses?
inner of the ovary
What does the cortex region of the ovary do?
Produces female gamete (ovum or oocyte)
released from follicle
Induces ovarian structures
produces hormones
What does the Medulla region of the ovary do?
support tissue including blood vessels and immune cells
Where is the medulla located on the ovary for cows, sheep, pigs
Inner of the ovary
Where is the medulla located on mares
outer of the ovary
What are the days in the estrous cycle of a cow is progesterone present in the system?
day 7 - day 18
What gland is used during the flehmen response
Vomeronasal gland
How many ovaries does a farm animal have?
Two
What connective tissue is in the ovary?
Tunica Albuginea
What are the functions of the ovary?
produces the female gamete (the ovum)
Procures female sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone)
What is the largest single cell in the body?
The ovum
Define the follicle
Blister-like Structure on the ovary that contains ovum and hormone-rich fluid
What is the estrogen-rich fluid in the graffian follicle called?
Liquor Folliculi
What is the embryo to corpus luteum ratio
1:1 ratio (for every embryo there is a corpus luteum)
On day 0 of a cow’s estrus cycle, which structure would we find on the ovary?
Graafian Follicle
Define a Graafian follicle
Mature follicle
Define Atretic follicle
deteriorated follicle
Define cystic follicle
Continuous corpus luteum or Graafian or atretic structure
what is the zona pellicuida?
eggshell
Define corpus luteum
“Yellow body” forms after ovulation
Produces progesterone, which is important for maintaining pregnancy
Solid tissue which is composed of luteal cells that originate from granulosa and theca cells of the Graafian follicle
What does progesterone do
inhibits estrus and parturition, blocks myometrial contractions, stimulates endometrial secretion of nutrients, stimulates the production of a luteolytic agent to kill the CL if no embryo is present (prostaglandin PGF2a)
Why is progesterone important
want the uterus to be still, not give premature birth
What can progesterone be used as
synchronization tool and birth control
Ovarian shape of the mare ovary
Single ovulation from the interior cortex is funneled to the oviduct via a specialized structure called the ovulation fossa
What is the only species with an ovulation fossa?
Mare (horse)
Ovarian shape of the sow ovary
Multiple ovulations form the cortex located on the exterior or surface of the ovary
What is a UFO
unfertilized ovum
What are the stages of the structures on the ovary
Primordial/Primary/secondary/tertiary follicle → graafian follicle → (Ovulation) → corpus hemorrhagicum (CH) → Corpus luteum (CL) → Corpus Albicans (CA)
Summary of what goes on in the ovary
Follicles develop on the ovary and undergo stages of maturation until one becomes a Graafian follicle, follicles not selected for ovulation become atritic and regress, and following ovulation the follicles will transition through CH, CL, and CA structures
Define ovulation
when the oocyte is released from the follicle
function of granulosa cells
produce estrogen and testosterone
Function of thecca internal cells
produce testosterone
What stimulates LH receptors
Stimulated by hormones FSH and LH