Price Elasticity & Market Efficiency
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Price Elasticity of Demand
Measures how responsive the quantity demanded is to a change in price.
Elastic Demand
Elasticity greater than 1, indicating high responsiveness.
Inelastic Demand
Elasticity less than 1, indicating low responsiveness.
Availability of Substitutes
More substitutes make demand more elastic.
Necessity vs. Luxury
Necessities tend to have inelastic demand; luxuries are more elastic.
Proportion of Income
Goods that take up a larger portion of income have more elastic demand.
Time Period (demand)
Demand is more elastic in the long run as consumers adjust behavior.
Total Revenue and Elastic Demand
If demand is elastic, lowering prices increases total revenue.
Total Revenue and Inelastic Demand
If demand is inelastic, raising prices increases total revenue.
Price Elasticity of Supply
Measures how responsive the quantity supplied is to a change in price.
Elastic Supply
Elasticity greater than 1, meaning producers can quickly adjust output.
Inelastic Supply
Elasticity less than 1, indicating limited responsiveness.
Determinants of Price Elasticity of Supply
Factors that influence the elasticity of supply.
Production Time (supply)
Goods that require longer production times have less elastic supply.
Availability of Resources (supply)
Easier access to resources leads to more elastic supply.
Storage Capabilities (supply)
Goods that can be stored have more elastic supply.
Flexibility of Production (supply)
Industries with adaptable production processes tend to have higher elasticity.
Application of Price Elasticity to Markets
Helps businesses set optimal pricing strategies based on consumer responsiveness.
Incidence of Taxation
When demand is inelastic, consumers bear most of the tax burden; when supply is inelastic, producers bear most of it.
Price Discrimination
Businesses use elasticity insights to charge different prices to different consumer groups based on their willingness to pay.
Market Efficiency
Occurs when goods and services are produced at the lowest possible cost.
Consumer Surplus
The difference between what consumers are willing to pay (marginal benefit) and what they actually pay.
Producer Surplus
The difference between the price producers receive and their minimum willingness to accept (marginal cost).
Total Surplus
The sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus, representing overall economic welfare.
Deadweight Loss
A reduction in total surplus caused by market inefficiencies like underproduction or overproduction.
Market Equilibrium
Maximizes total surplus by aligning supply and demand at the equilibrium price and quantity.
Price Ceiling
A legislated maximum price that sellers are allowed to charge in the market.
Price Floor
A legislated minimum price that sellers are allowed to charge in the market.
Underproduction
Occurs when fewer goods are produced than the equilibrium quantity, reducing consumer and producer surplus.
Overproduction
Happens when more goods are produced than demanded at equilibrium, leading to wasted resources.
Effects of a Price Ceiling
Benefits consumers, results in shortages as quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied, creates deadweight loss.
Effects of a Price Floor
Benefits producers, leads to surpluses as quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded, causes deadweight loss.
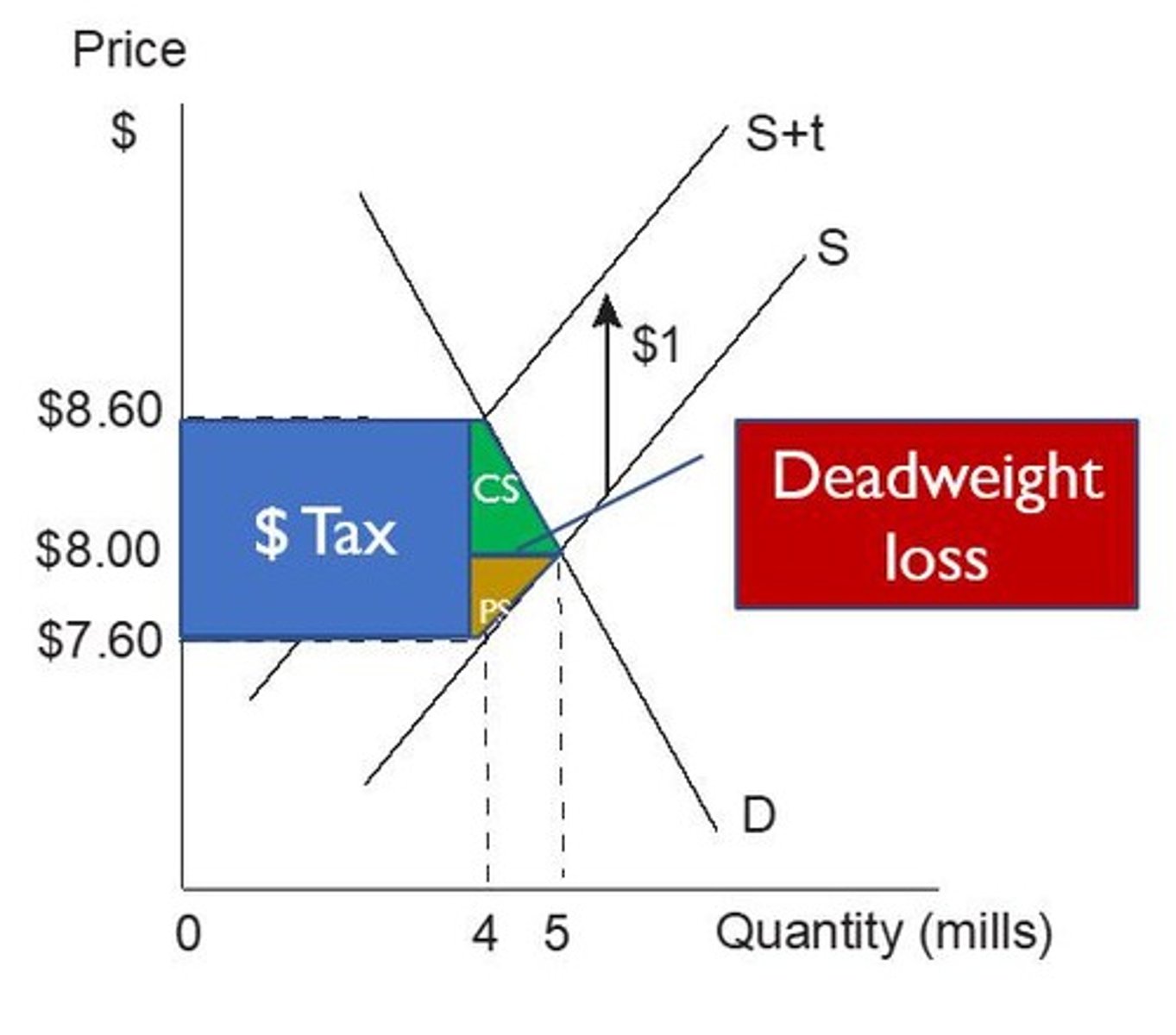
Tax
Increases costs for producers or consumers, reducing equilibrium quantity and creating deadweight loss.
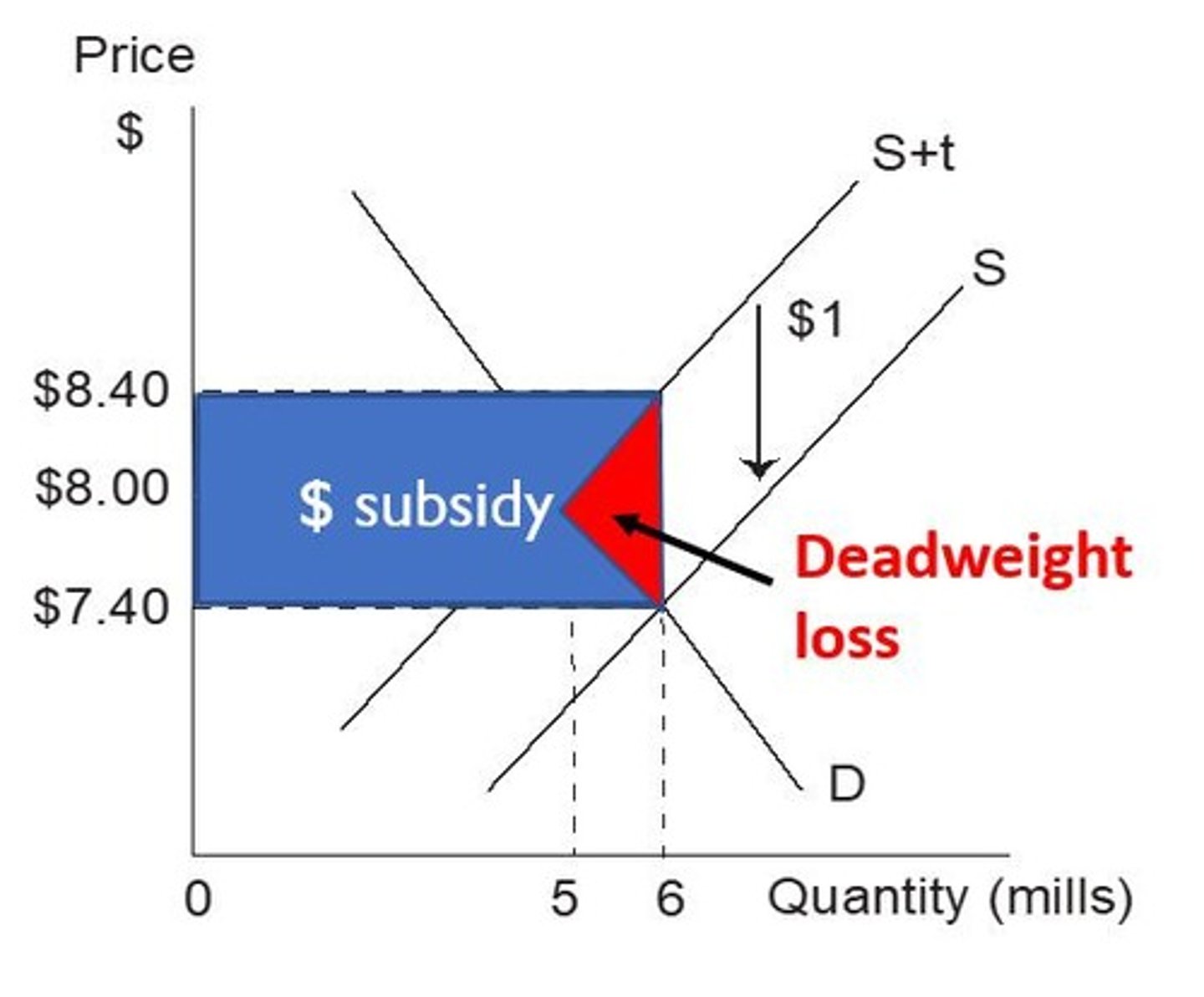
Subsidy
Lowers production costs or prices for consumers, increasing equilibrium quantity and can improve economic welfare.
Deadweight Loss from Tax
Creates deadweight loss by decreasing total surplus as fewer transactions occur.
Deadweight Loss from Subsidy
May lead to overproduction if not carefully managed.
Efficiency of Competitive Markets
Considered ideal because they achieve maximum total surplus without external intervention.
Equilibrium Price
The price at which the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded.
Equilibrium Quantity
The quantity of goods sold at the equilibrium price.