Monetary and Fiscal policy
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
monetary policy
adjusting interest rates and money supply to influence AD
set by central banks
used to help govs achieve macroeconomic objectives
low + stable rate of inflation
low unemployment
reduce business cycle fluctuations
promote stable economic environment for longterm growth
control level of exports and imports
real vs nominal interest rates
nominal interest rate: headline rate presented by commercial banks, not adjusted for inflation
real interest rate: nominal interest rate - rate of inflation
calculated using CPI
monetary policy instruments
incremental adjustments to interest rate
quantitative easing, increases supply of money in economy
expansionary monetary policy
central bank wants to boost economic growth and lowers interest rates
lower interest rates = investment and consumption increases, these are components of AD
AD shifts right
economy has higher price level and greater national output

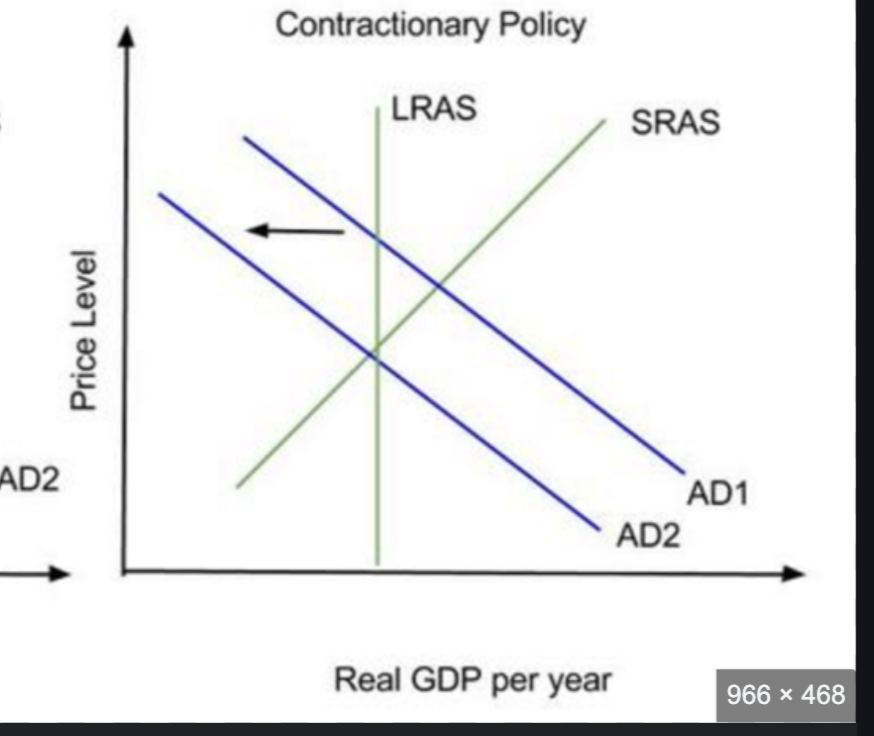
contractionary monetary policy
central bank wants to lower inflation toward its target, so increases interest rates
higher interest = decrease in investment and consumption
AD shifts left
economy has lower average price level and smaller level of national output
strengths of monetary policy
central banks can operate independently from gov
meaning they can consider the long term outlook
contractionary policy useful in reducing inflationary gap
reducing inflation increase exports
incremental and flexible, can be implemented/changed quickly by the central bank, allows for constant adjustments to macroeconomic variables
rate changes can be quickly reverse/amended
weaknesses of monetary policy
conflicting goals
e.g economic growth puts an upward pressure on inflation
expansionary policy less effective during a a recession
consumers/firms may not respond to low interest rates with consumption/investment when confidence is low
time lags between policy and desired impact
interest rate has limitations on downward adjustment
when interests rates are already close to 0, its hard to lower them further
ineffective against cost-push inflation
can reduce demand-pull inflation, but cost-push depends on costs to produce
fiscal policy
use of government spending and taxation to influence AD
sources of gov revenue
taxation
direct taxes imposed on income and profits
indirect taxes imposed on spending
paid by supplier to gov
sale of goods
gov owned firms charge for the goods they provide
sale of gov owned assets
gov expenditure
current expenditures
daily payment required to run gov and public sector
capital expenditures
investments in infrastructure and capital equipment
transfer payments
payment made by gov where no goods are exchanged
doesn’t contribute to AD
goals of fiscal policy
maintain low and stable rate of inlation
maintain low unemployment
reduce business cylce fluctuations
create stable economic environment for long term economic growth
redistribute income to ensure equity
control level of exports and imports
expansionary fiscal policy
reducing taxes/increasing gov spending with aim of increasing AD
gov wants to boost economic growth, lowers rate of income and corporation taxes
lower taxes = increase in consumption and investment
AD shifts right
economy has higher average price level and greater national output
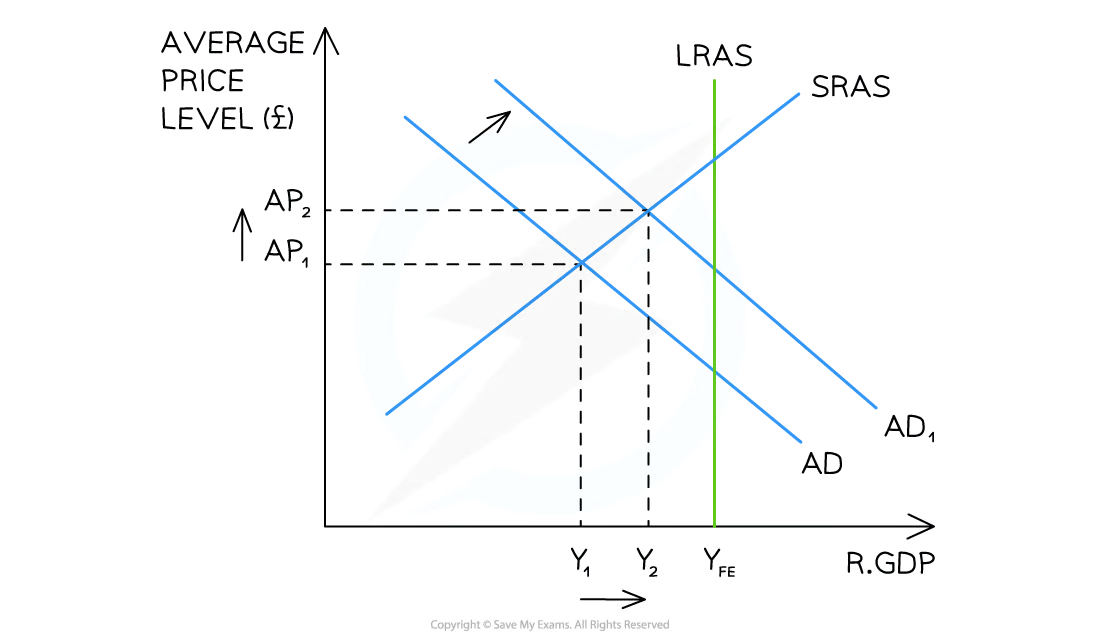
contractionary fiscal policy
increasing taxes/decreasing gov spending with aim of decreasing AD
gov wants to lower inflation, so raises rate of income tax
higher tax = less disposable income = decrease in consumption
AD shifts left
economy has lower average price level, smaller level of national output
strengths of fiscal policy
highly effective in restoring confidence in an economy during recession
spending can be targeted at specific industries
redistributes income through taxation
reduces negative externalities through taxation
weaknesses of fiscal policy
political pressures
policies may fluctuate significantly when new governments are elected
this can mean lack of follow-through for long term projects
unsustainable debt
increased gov spending creates budget deficits
time lags
takes a longer time to implement than monetary policy as it must be debated by government