5. Salt/Water and Acid/Base Balances
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Please define the normal blood pH.
7.35-7.42
What is the normal plasma level of bicarbonate.
24 mmol/L
What is the normal plasma level of carbonic acid.
1.2 mmol/L
How do we call the respiratory compensation of metabolic acidosis?
Kussmaual breathing
Define the normal range of pH values in the urine.
4.4-6.5
What are the major effects of aldosterone?
Salt and water retention
K+/H+ secretion
What kind of ion exchange are the intercalated cells responsible for?
Reabsorb chloride from the filtrate
Secrete bicarbonate
Define the normal value for buffer base.
48 mmol/L
How do pH parameters change in metabolic alkalemia?
Standard bicarbonate: Increase
BB(Buffer Base): Increase
BE(Base Excess): Increase
How do pH parameters change in metabolic acidemia?
Standard bicarbonate: Decrease
BB(Buffer Base): Decrease
BE(Base Excess): Decrease
Which pH parameter is changed primarily in metabolic alkalosis?
HCO³- increases
Define tonicity.
Effective osmotic pressure of the plasma and extracellular fluid
Define the normal osmotic concentration of the blood.
280-300mOsm/L
The accumulation of which substances can cause hypertonicity?
1.Na+
2.Glucose
The accumulation of which substances can cause hyperosmolarity without hypertonicity?
Urea
Methanol
Ethanol
What is the main trigger of ADH secretion?
High extracellular Na+ concentration
What is the primary site of ADH?
In the renal collecting ducts
Define exsiccosis.
Loss of salt and water
List some examples for natriuretic factors.
ANP(Atrial Natriuretic Peptide)
BNP(Brain Natriuretic Peptide)
Renal kinins
Renomedullary lipids
Prostaglandins
What are the effects of angiotensin 2?
Vasoconstriction
Stimulation of aldosterone secretion
Stimulation of thirst
What is the direct stimulus for activation of RAAS?
Decreased stretch(decreased tension in the vascular wall) of renal afferent arteriole (decreased intraluminal pressure and/or perfusion)
Define non-specific factors that activate ADH.
Severe hypovolemia
Surgery
Stress
Fear
Pain
Define the anion gap.
Anion gap= Serum[Na+]- (Serum[Cl-] +Serum[HCO3-])
11mmol/L= 140mmol/L-(105mmol/L+24 mmol/L)
How can we calculate the plasma osmotic concentration?
Applying the formula: (2× Na+ +Carbamide+ Glucose)
Define the osmotic gap.
Difference between measured and calculated plasma osmolarity
Define the plasma level of potassium.
3.5-5.5 mmol/L
Define the normal plasma level of sodium.
135-145 mmol/L
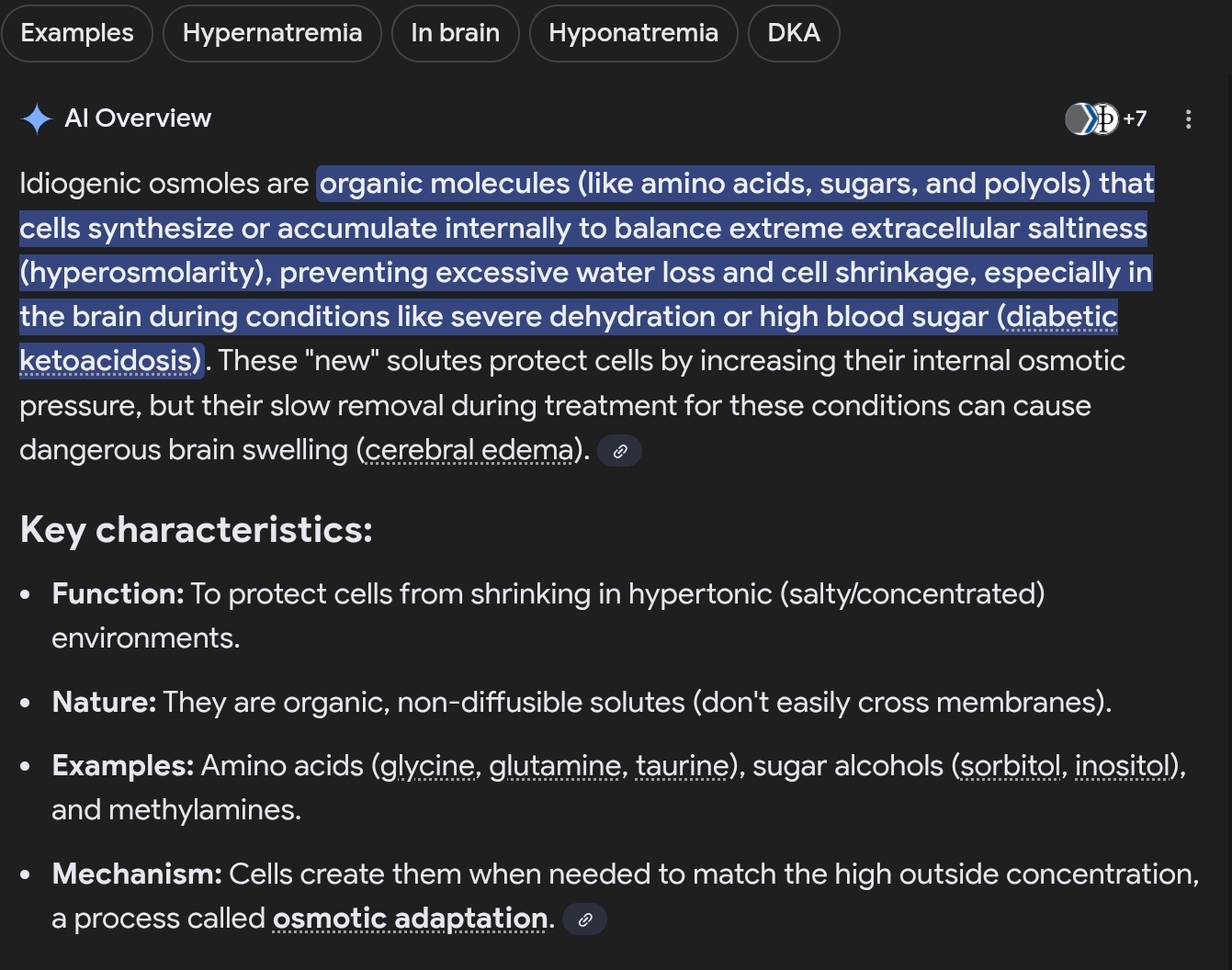
How do brain cells protect themselves from slowly developing hypertonicity?
By producing osmotically active IC substances, idiogenic osmoles.
Define the 4 mechanisms of oedema formation.
Decreased oncotic pressure
Increased hydrostatic pressure
Increased capillary permeability
Disorder of the lymphatic system