Exercise physiology lecture 5
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What is the point of the endocrine/nervous system?
To control
Do women have more testosterone or estrogen?
testosterone
Why do things like pregnancy blockers and tren take multiple sessions to kick in?
They are lipid soluble hormones
Since vitamin D is lipid soluble what is it considered?
a hormone
What is the base for a steroid hormone?
cholesterol/lipid
Can steroid hormones diffuse into the cell? If so, why or why not?
Yes, they are lipid soluble
What are some examples of steroid hormones?
Aldosterone, cortisol, testosterone, and estrogen
What is the base for nonsteroid hormones?
amino acids
Can nonsteroid hormones enter cells? If so why or why not?
No, they are water soluble
How do steroid hormones send signals?
They bind to receptors on the outside of a cell, and that releases a second messenger to carry out the task
What type of hormones only have first messengers?
Steroid hormones
Why do steroid hormones only have first messengers?
They diffuse directly into the cell
Why do nonsteroid hormones have second messengers?
They cannot diffuse into cell, so second receptors release into the cell to complete the action
How do hormones cause change in the body?
They roam in blood till they find their proper receptors
What does negative feedback do?
Return the body to homeostais
What does positive feedback do?
Pushes the body farther from homeostasis
What hormones are released from the anterior pituitary gland?
Growth/GH, Follicle stimulating/FSH, Luteinizing/LH
What does growth hormone GH do?
Promotes growth/maintains organs, bones, etc
What stimulates the release of growth hormone?
Growth hormone releasing hormone GHRH
What stimulates the release of FSH and LH?
Gonadotropin releasing hormone GnRH
What does FSH/LH do?
Causes release of testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone
What hormone would you use as a puberty blocker?
GHRH
How does excessive GHRH inhibit puberty?
It decreases androgen production
What can occur if a women exercises too much without proper nutrient supplementation?
Amenorrhea
Why can a women experience amenorrhea if they exercise without proper nutrient supplementation?
The brain inhibits FSH because the body cannot support a baby
What hormone(s) are released from the adrenal gland? (no SNS)
Cortisol
Is cortisol a slow acting or fast acting hormone?
Slow acting
Why is cortisol a slow acting hormone? (base wise)
It is a lipid base
What does cortisol do in the body?
Suppresses immune system, promotes/catabolizes protein breakdown, promotes/catabolizes fat breakdown
Why does cortisol inhibit immune system and breakdown fat/protein?
To increase energy in the body during stressful situations
Why might you get sick at the end of a stressful semester?
Cortisol suppressing the immune system
What are the steps to stimulating the release of cortisol?
Corticotropic hormone (CrH) goes to adrenal medulla, releasing ACTH
What hormone(s) are released from the adrenal glands with SNS intervention?
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
What does epi/norepi do?
Increase HR, increases contractility, bronchodilate, vasoconstricts/increases BP, catabolize fat tissue, muscle/liver break down glycogen
What is contractility?
How hard the heart beats, more contractility allows for more blood to be pumped in the body
Is the pancreas an endocrine or exocrine organ?
Both
What hormone(s) are released from the pancreas?
Insulin and glucagon
What cells produce insulin?
Beta
What cells produce glucagon?
Alpha
If blood sugar rises what hormone increases?
Insulin
If blood sugar decreases what hormone increases?
Glucagon
What does glucagon target?
Liver
Why does glucagon target the liver?
It converts glycogen into sugar through glycogenolysis and releases the sugar
Is the endocrine system interconnected? Why or why not?
No, all glands are isolated but can influence each other
What releases hormones to the anterior pituitary?
Hypothalamus
When is testosterone highest?
The morning
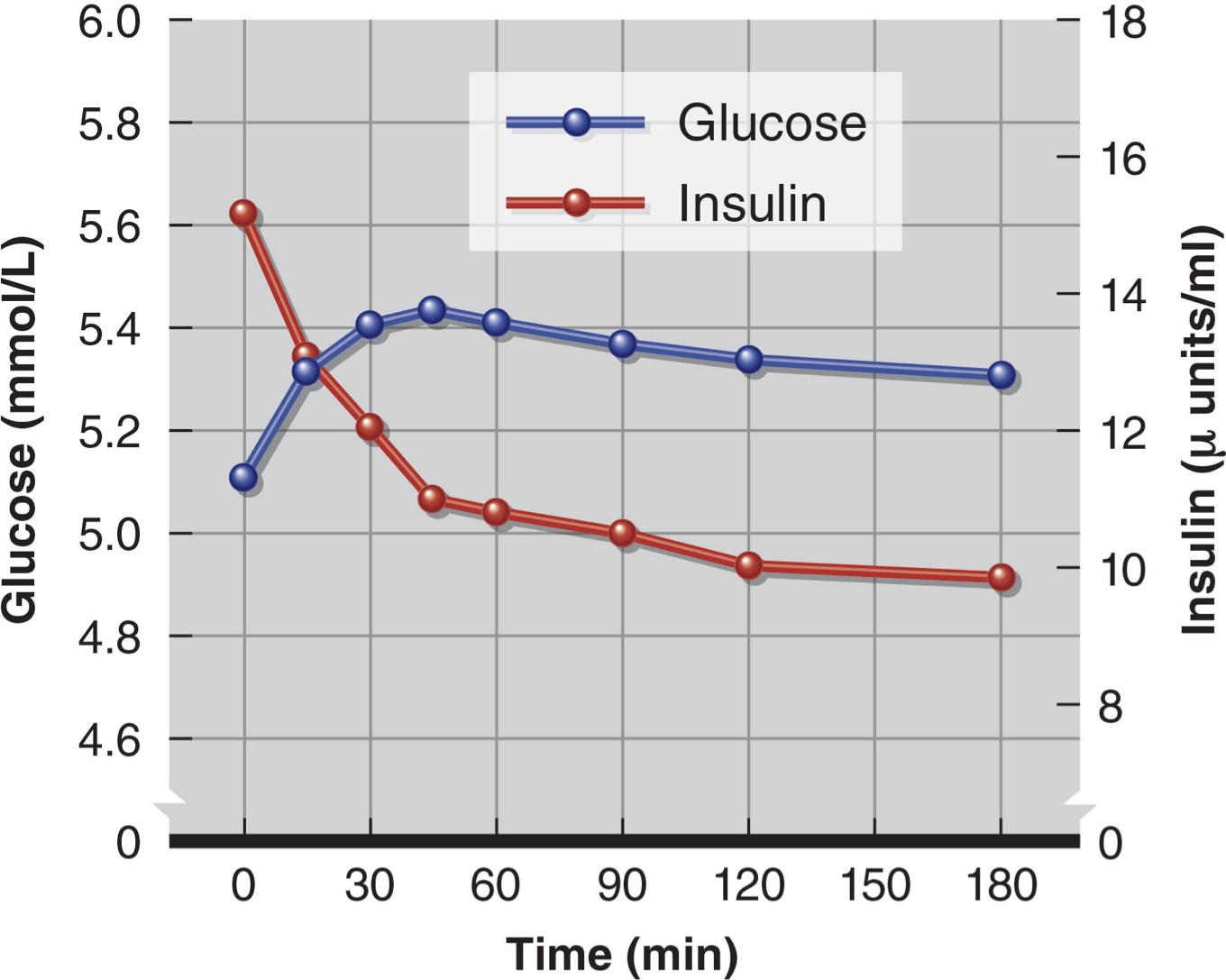
What causes the increase in glucose during this exercise?
Cortisol releases fat and protein that then gets converted into sugar
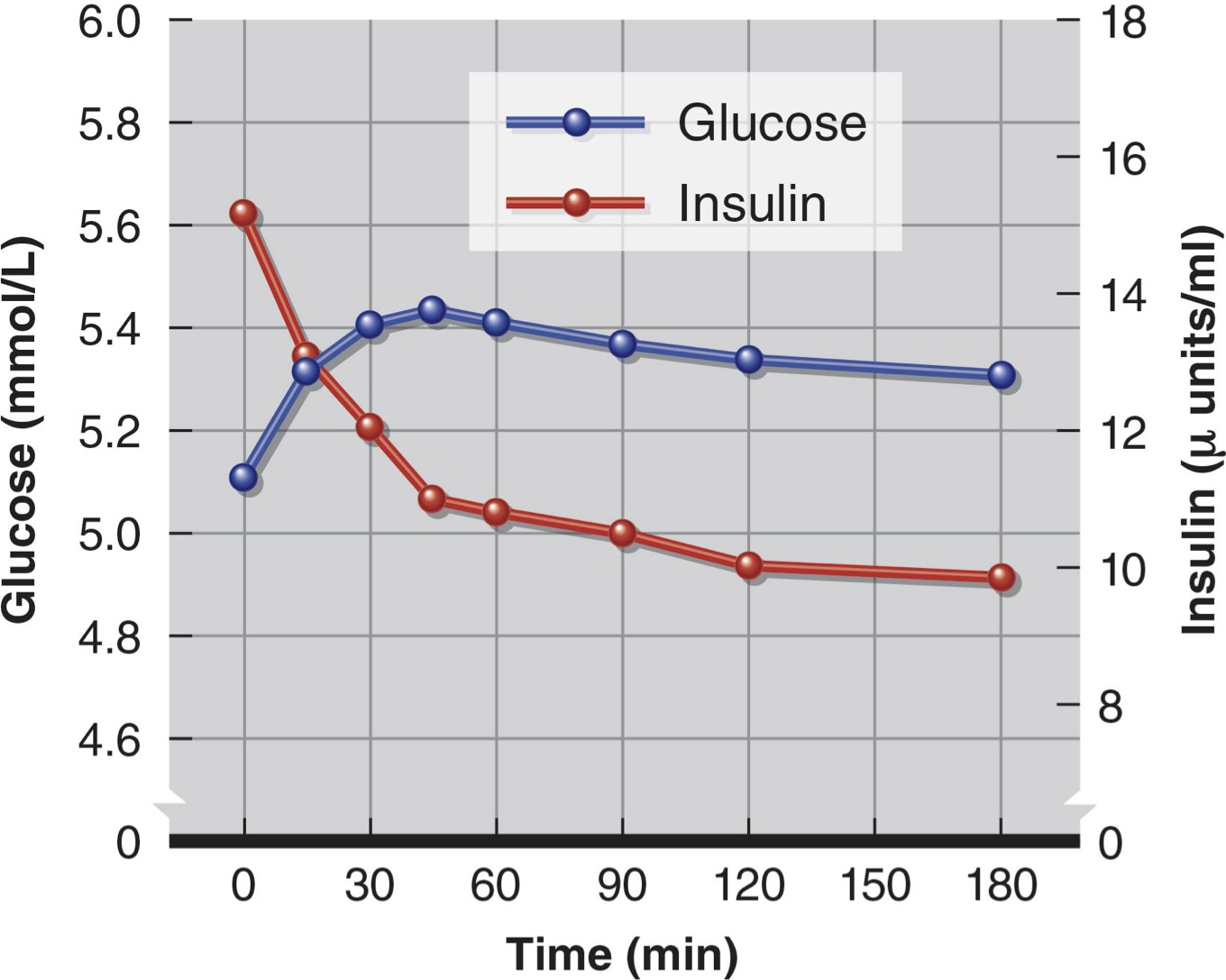
Why is insulin decreasing during while this person is working out?
The GLUT-4 exercise pathway is being used
When is ATP highest?
At rest
When is AMP highest?
While exercising
What does cAMP do?
Promotes sugar breakdown, stopping storage of glycogen
What does active synthase do?
Turns glucose into glycogen
What does active phosphorylase do?
Breaks down glycogen into glucose
How does adding a phosphate affect phosphorylase?
It actives it
How does adding a phosphate affect synthase?
It deactivates it
Do active synthase and phosphorylase run at the same time?
No
Why don’t active synthase and phosphorylase run at the same time?
It is not energy efficient
What hormone is made in the kidney?
Erythropoietin/EPO
Where does EPO go?
The red bone marrow in the epiphysis of bone
What does EPO do?
Stimulates RBC production to increase O2 transport
What stimulates EPO production?
A decrease in O2 in the blood
Why does EPO production occur in the kidney?
Kidneys filter all the blood so they constantly detect O2 levels
Why would someone train in high altitude, what affects would it have?
To increase EPO and have increase O2 transport at regular altitude
How often do all RBCs get cycled through?
Every 4 months
What are the four main hormones of exercise?
Epi/norepi, cortisol, and glucagon
What is not hormone of exercise?
Insulin
As exercise intensity increases what happens to hormonal response?
It increases
How would glycogen depletion affect the body?
Decreased ability to perform exercises
If glycogen falls too low what would be used to supplement it? And what hormone is would do it?
Fat and protein, cortisol
If you increase the rate of exercise intensity with low glycogen, how is RER affected and why?
RER increases because carbs are burning
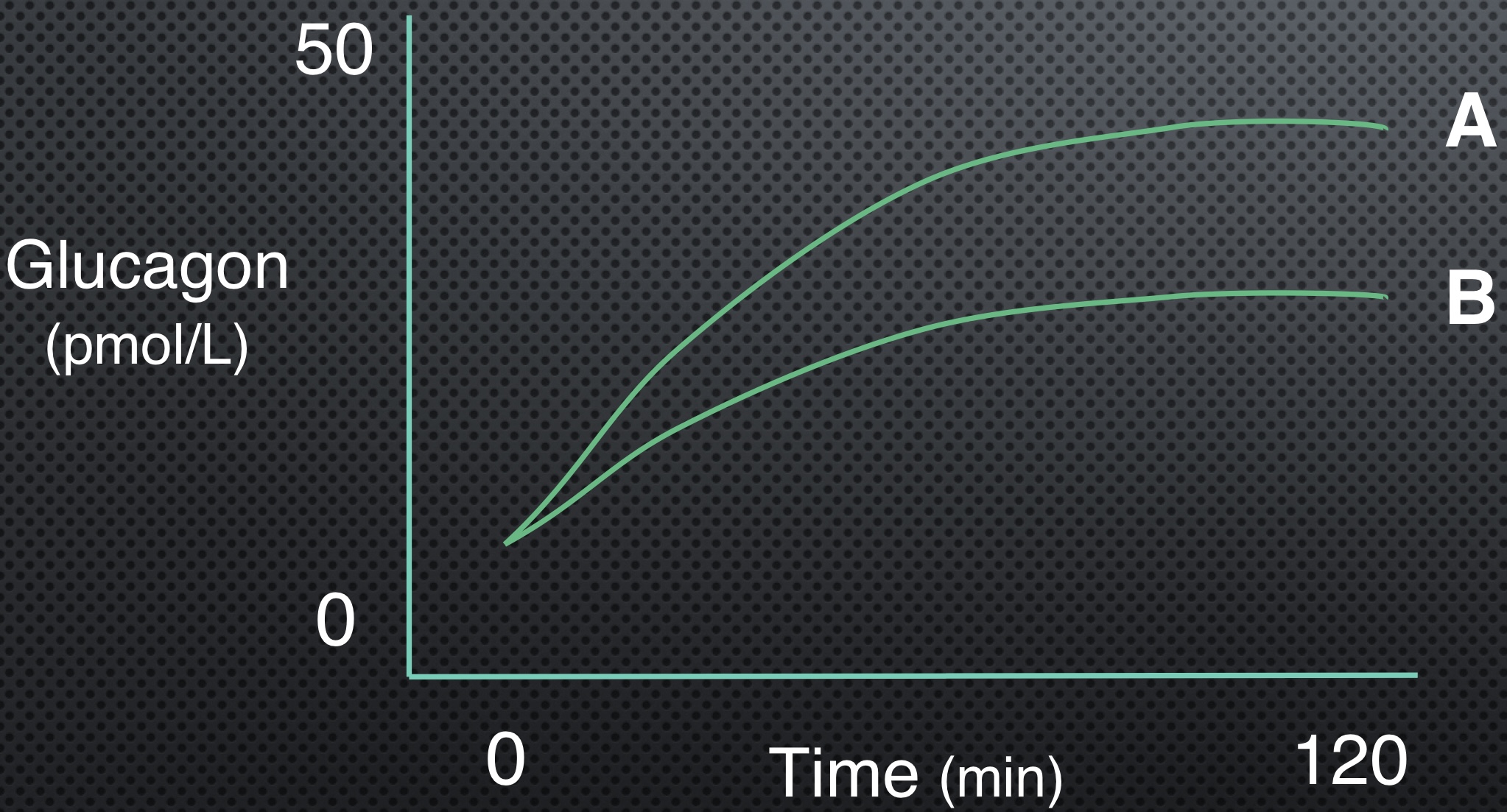
Which line has higher intensity?
A
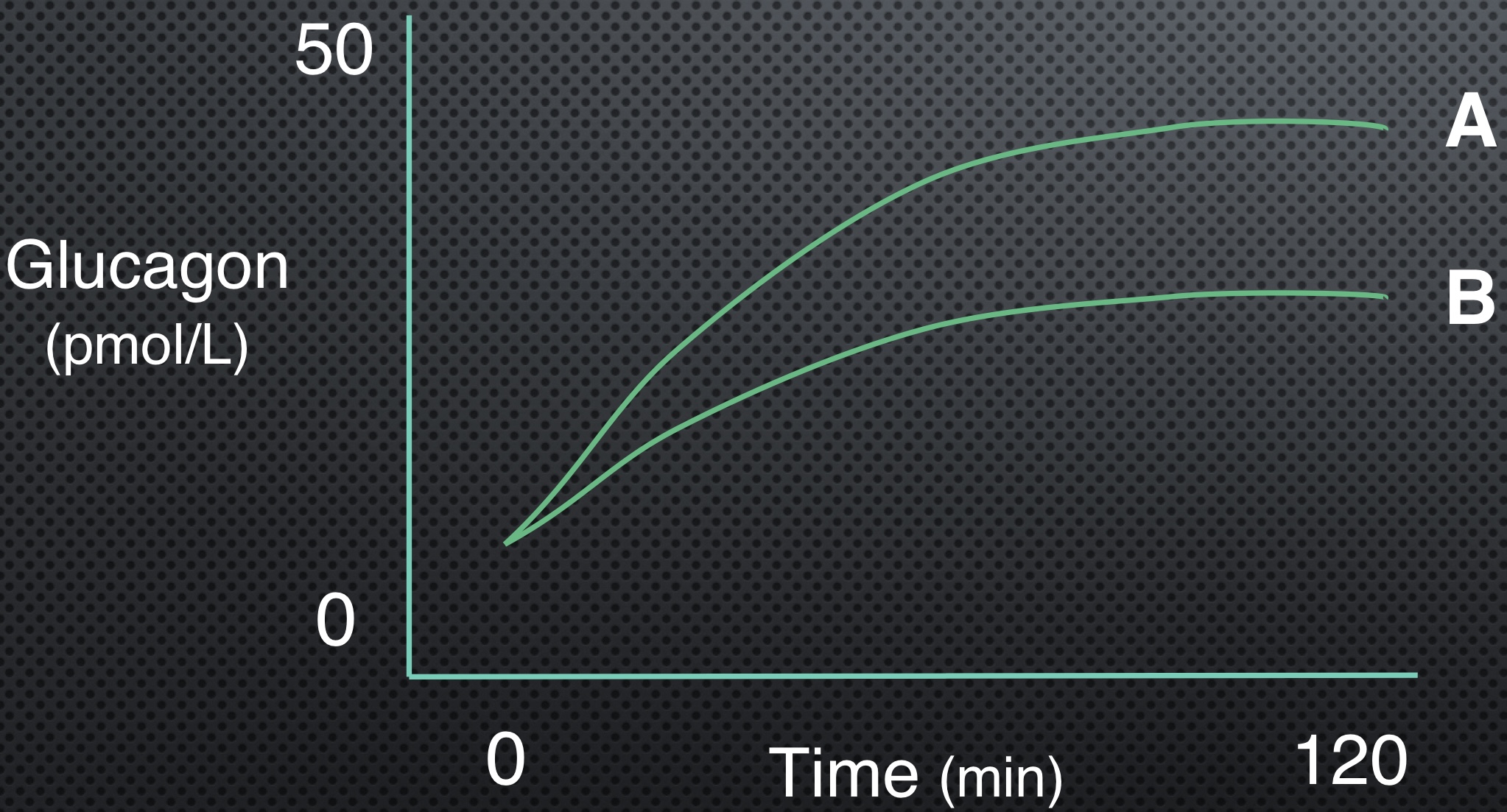
What is an estimated RPE for line A?
15 or more
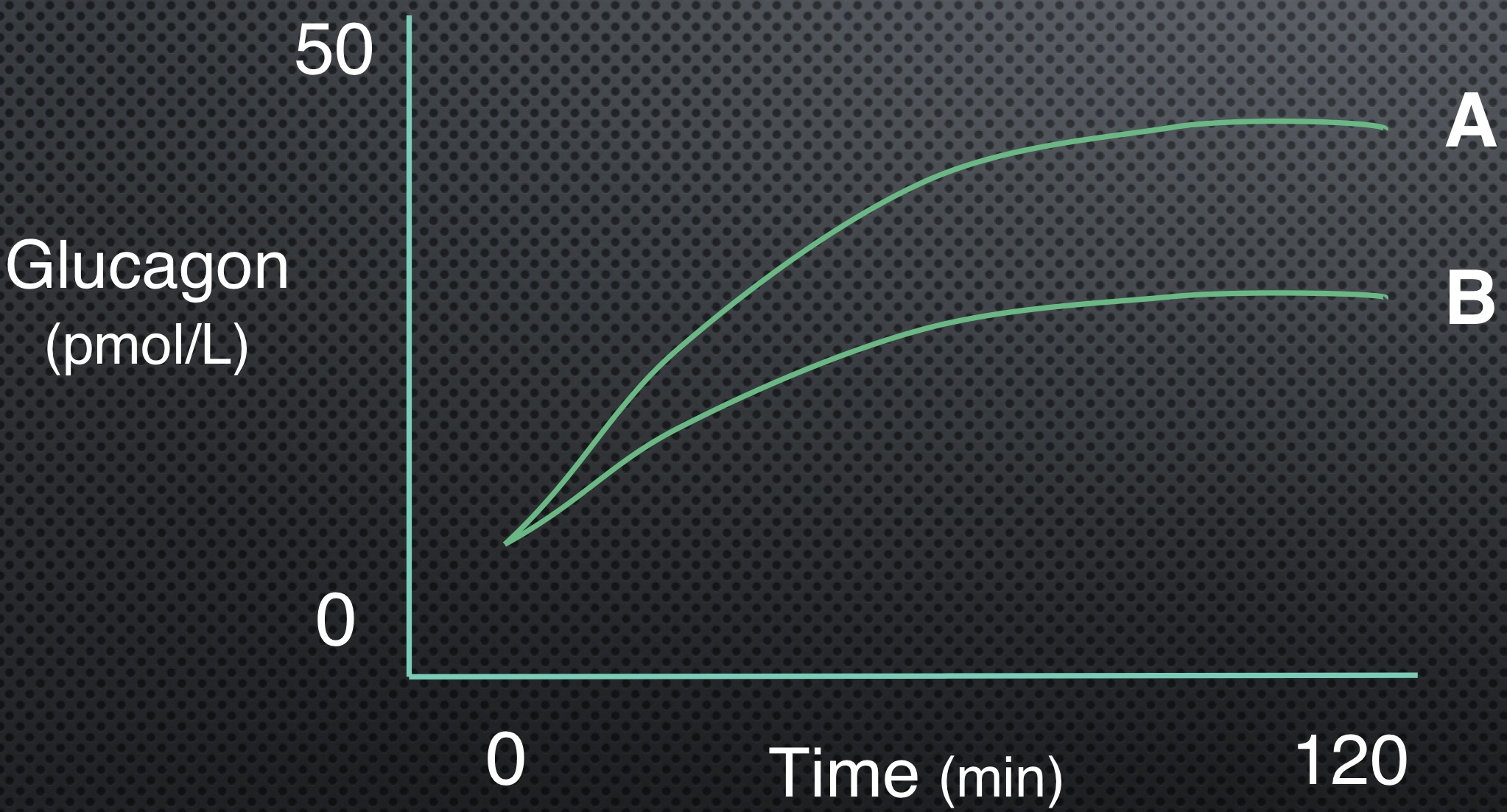
What is an estimated RPE for line B?
8-10
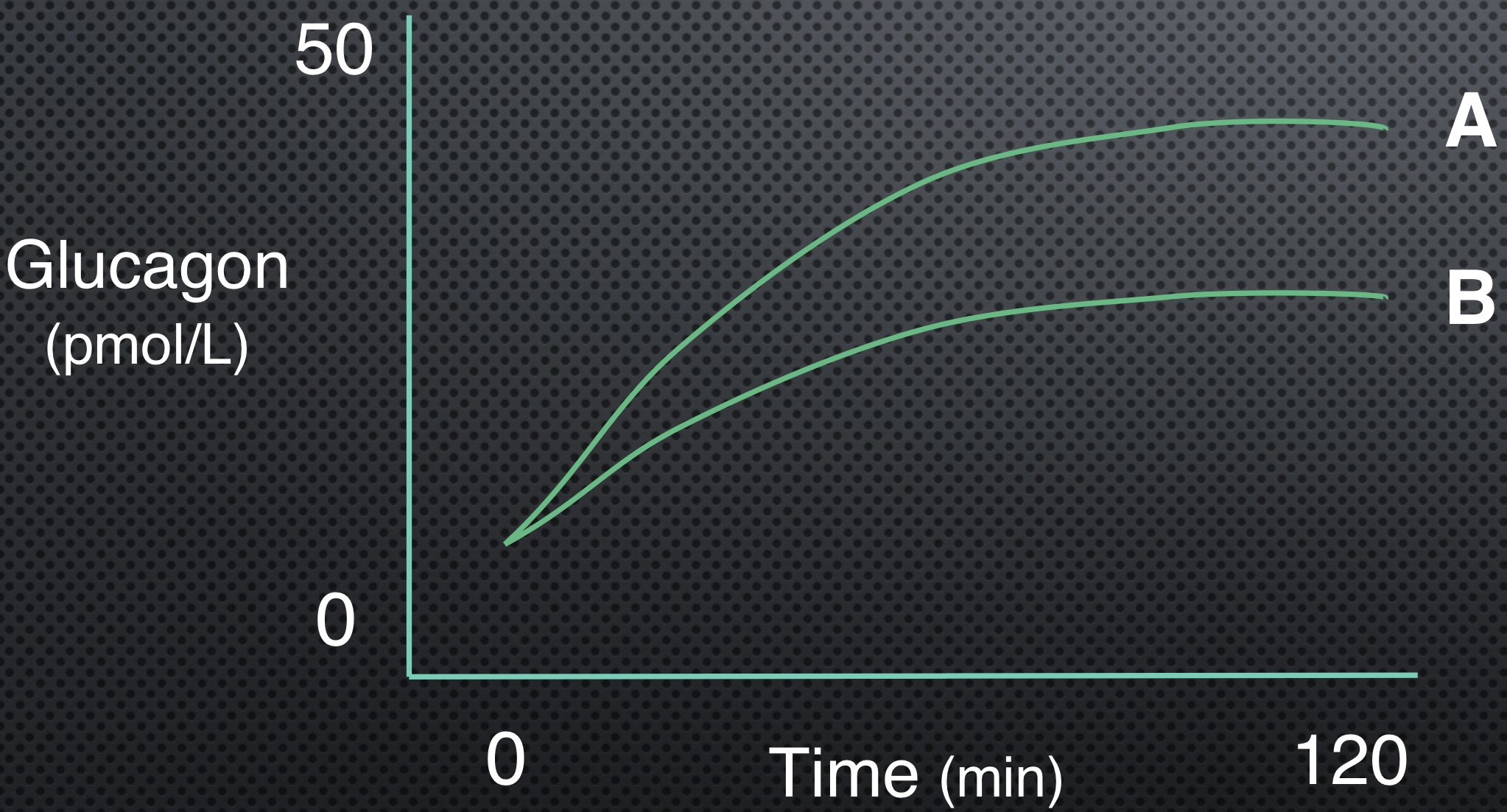
Which line is using more carbs?
A
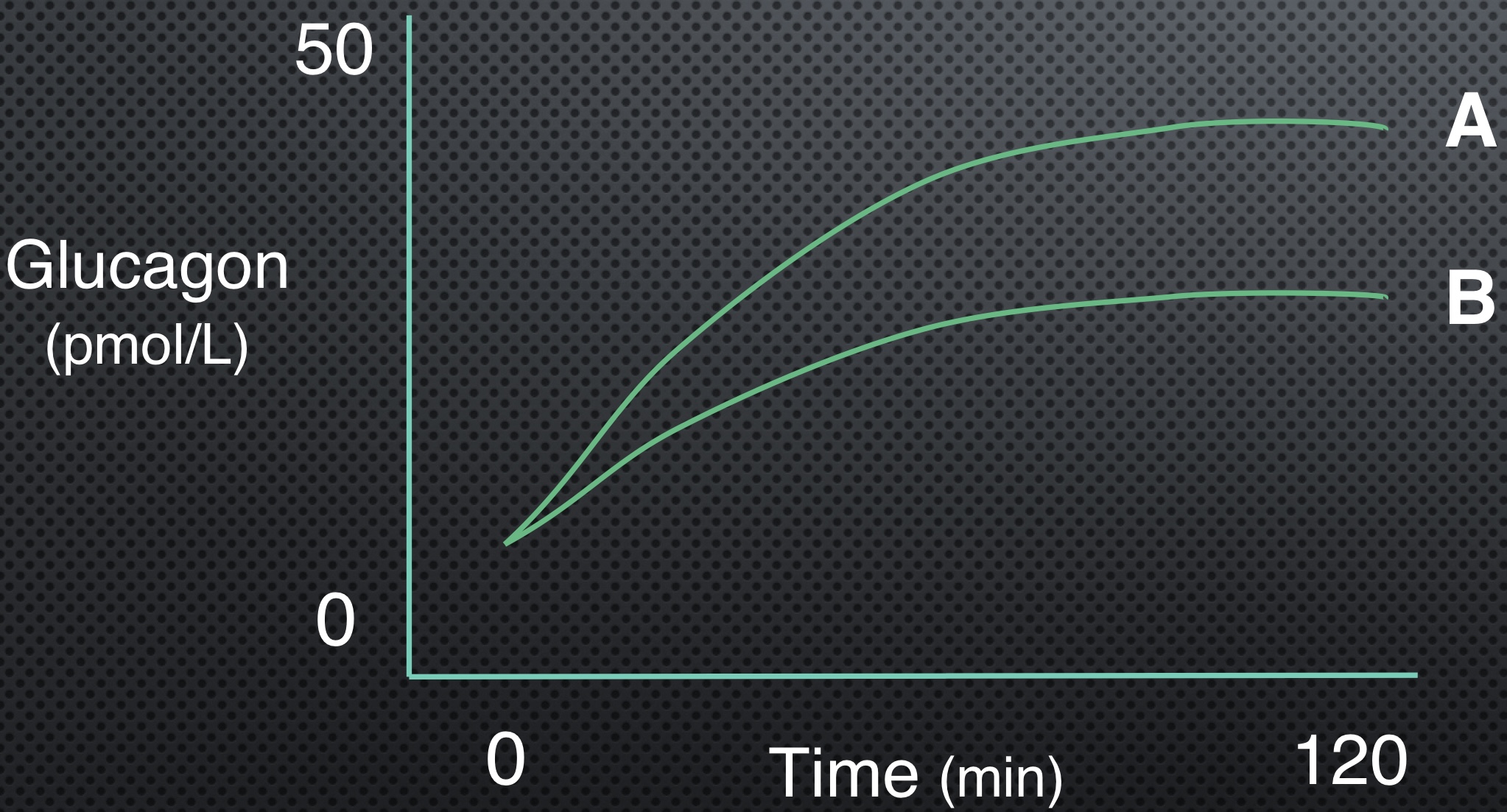
Which line has more epi/norepi?
A
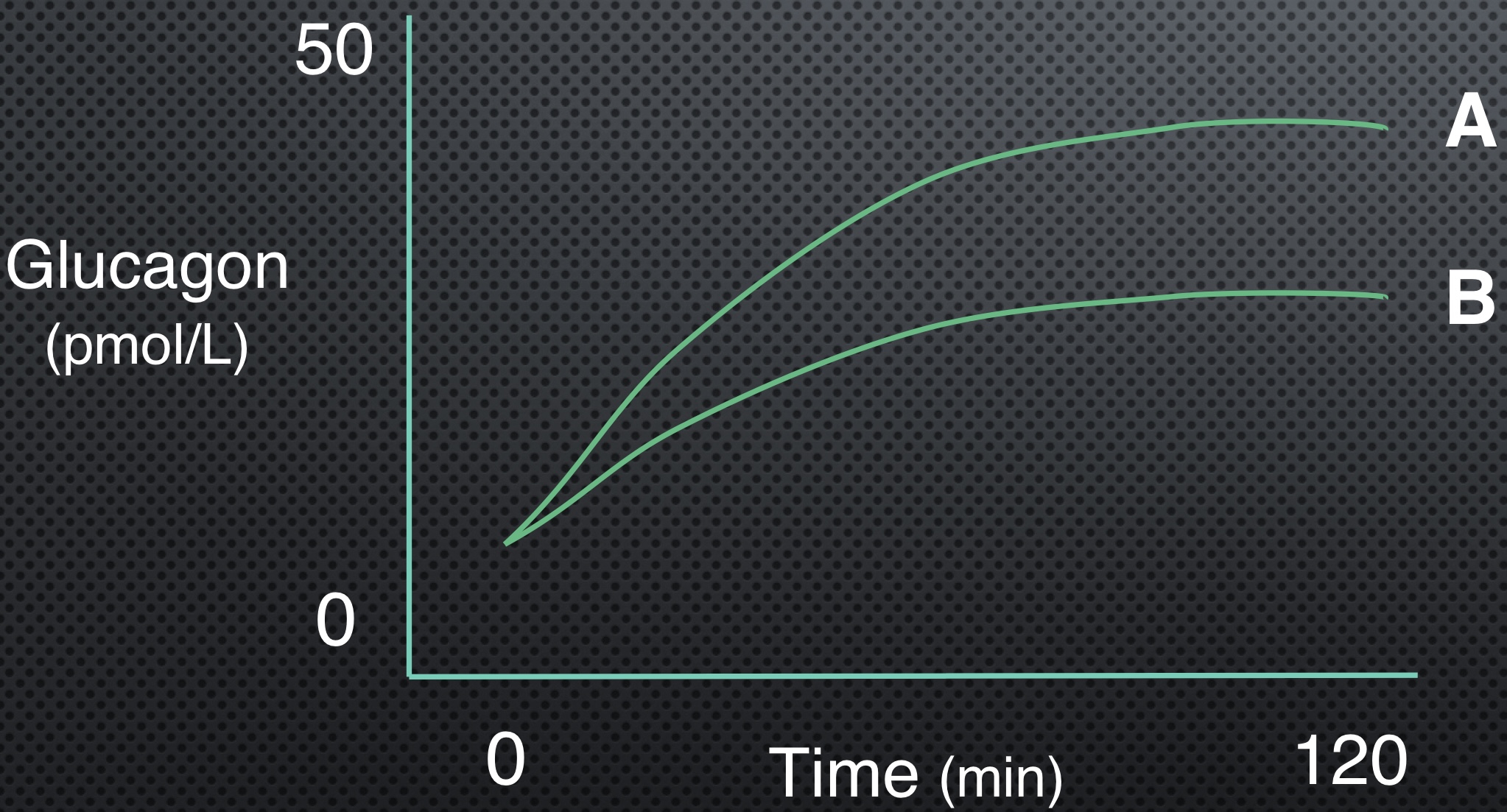
Which line has higher insulin levels?
B