K205 Module 2: Research In Kinesiology
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
FHV: Reflect on how evidence-based practice will inform someone’s work as a practitioner
Emma discusses how her applied practice and teaching is informed by research
She tries to balance the 3 key elements of EBP
Patient values and preferences
Research evidence
Clinical experience
Describe what research is
Gather and analyzing information.
It must contribute to NEW knowledge
Identify 9 dimensions of research
Topic
Novelty
Scope
Methodology
Mode of inquiry
Technology
Ideology
Politics
Utility
Describe the 9 dimensions of research
Topic:
biophysical to psychosocial
Novelty:
Distinction between past or new knowledge.
Generally research contributes to new knowledge; past knowledge would be a literature review
Scope:
Large or small sample size
Methodology:
Quantitative: main word is MEASURE
Qualitative: Data collection with researcher-as-instrument
Mixed methods:
Mode of inquiry:
Observation: no intervention. Gather info about the world as it is
Experimental: intervention and seeing if there is cause and effect of two or more variables
Technology:
Using an existing tech or developing a new method
Ideology:
Objective vs philosophy
Qual: researcher brings their own worldview/lens
Quant: try to be as objective as possible
Worldview?
Politics
Neutral or partisan approach?
Partisan = enacting social change or action research
Utility:
Basic: how does this work? in highly controlled setting such as lab. Used to find cause and effect
Applied: how can we use this knowledge to help people? less controlled settings such as field work. Understand change or impact health and behavior
Distinguish between literature reviews, systematic reviews, meta-synthesis and meta-analyses
Lit review:
No methods section
Can be qualitative or quantitative
Systematic review:
Has methods section
Qualitative or quantitative
Meta-syntheses
Has methods section
qualitative
Meta-analyses:
Has methods section
Bringing similar articles tgt and establishing an effect size
Identify topics of research in kinesiology
Biophysical: biology, physics, chemistry
Psychosocial: psychology, sociology
Understand the purpose of small and large sample sizes
Small:
Used for qualitative research
helps to spend more time with participants
gain in-depth understanding of the phenomenon interested in
Large:
Helpful to understand what generally happens
Distinguish between experimental and non-experimental/observational research
Experimental:
intervention
Non-experimental:
no intervention, just observing the world as it is
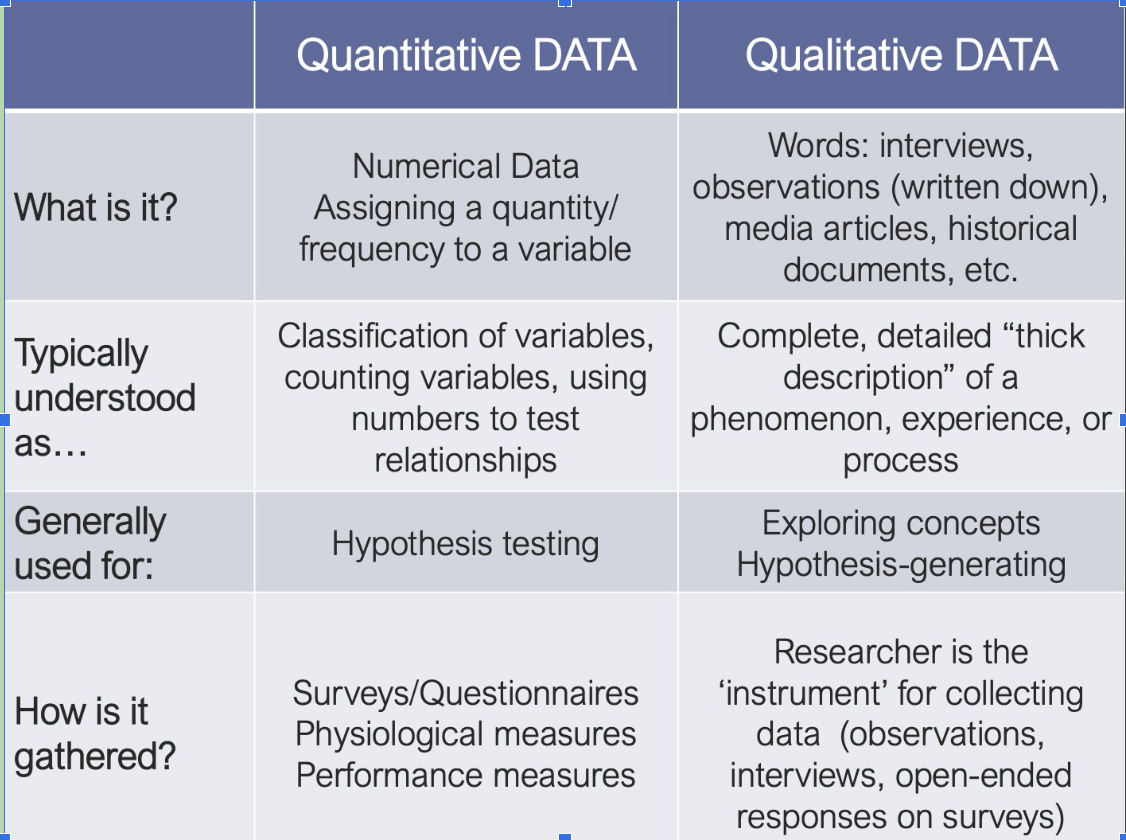
Identify characteristics of quantitative and qualitative research
What is it?
Typically understood as
Generally used for
How is it gathered?
What is assessed in each of them?
Quantitative: think numbers
dealing with numbers
assigning a quantity to a variable
Variables
Using numbers to test a relationship
Testing hypotheses
Data collection with an instrument
Surveys/questionnaires, performance and physiological measures
Assess validity and reliability, NOT credibility and trustworthiness
Qualitative: think words
Dealing with words
central phenomenon to be explored
Thematic analysis of data (inductively/deductively)
Hypothesis generating, exploring concepts
Data generation with “researcher as instrument”
Open ended surveys/questionnaires, interviews
Assess credibility and trustworthiness
Understand the relationship between basic and applied research
Basic:
How does this work?
Occurs in lab environment: highly controlled setting
Applied:
How can we use this knowledge to help people?
Occurs in the field: less controlled setting
What is effect size? How does meta analyses use ES?
How much or how strong
Takes the ES from multiple studies and does a super ES
What is validation in quantitative research
Test that the instrument is a good measure of the construct we are addressing
Validity vs Reliability
Validity: Accuracy
are we measuring what we think we are measuring
Reliability: Consistency
Is it going to be consistent across time