Class 3 - Observations and Survey Research and Experimental Design
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
observational research methods
observational research is correlational, not causal
structured observation
occurs when what you’re observing is very defined, looking for certain things
unstructured observation
more exploratory, recording everything
disguised vs undisguised
participants behave more naturally when unaware of observation
natural/ contrived
personal observation
mechanical observation
an observational research strategy in which mechanical devices rather than human observers record the phenomenon being observed
eye tracking, facial expression analysis, GSR, heart rate, fMRI
observational methods pros and cons
pros:
actual behaviour is usually better than self report
no reporting bias
cons:
motives, attitudes, beliefs, preferences? unknown
selective perception
can’t infer underlying cause of behaviour
survey research
taps into variety of topics
many modes of delivery
structured and standardized
direct or indirect
question wording - can be a bias in how questions are phrased, do participants have the motivation/ ability to answer questions
procedure of a survey
starts with population, take sample from population, sample views product, sample answers questions about product
mode effect
difference in responses based on delivery method
primary vs recency effects
the way you deliver a survey needs to consistent with the type of answer you’re looking for
survey methods
telephone surveys
traditional, computer assisted (CAT)
personal surveys
in home, computer assisted (CAPI), mall intercept
mail surveys
mail, mail panel
electronic surveys
email, internet
mobile surveying
in app, SMS recruitment
personal surveys
very expensive
in-home survey
allows you to gather the most information possible about participant
mall intercept survey
computer assisted methods
mail surveys
require a lot of effort from participant
cover letter, questionnaire, incentive return envelope
requires valid mailing list, no verbal contact, can be panels
comparing survey methods
task factors
situational factors
respondent factors (such as anonymity)
the more contact the researcher has with the participant, the more data can be collected
external validity
the extent to which you can generalize the results of a study to the population
purpose is to make some sort of inference from the sample of the population you surveyed
procedure of an experiment
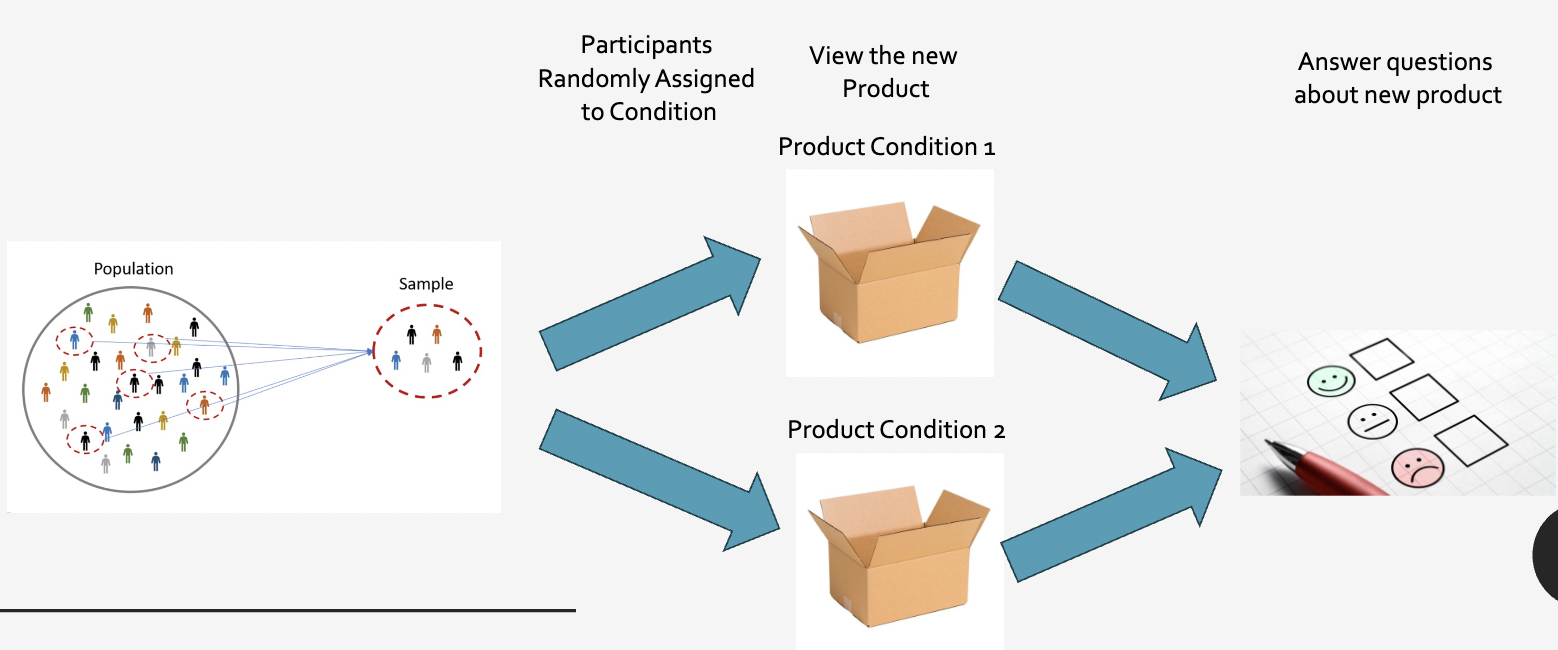
start with population, take sample from pop. participants are randomly assigned to condition (1 or 2, a or b, etc.). participants view the product with either condition they were assigned to. participants are asked the same questions about the product
requirements of causal inferences
determine whether X causes Y
concomitant variation (most important)
time of occurrence
elimination of confounds (alternate explanations)
concomitant variation
the extent to which X and Y vary together in the way predicted by the hypothesis. ie. when scores of X are low, scores of Y are also low.
time of occurence
the causing event must occur either before or simultaneously with the effect, it can’t occur afterwards. X must occur before Y
random assignment
participants are randomly assigned to one condition or another. best tool to establish causal relation. helps account for individual differences.
each individual differences / traits have an equal chance of being assigned to either condition
means that the difference in means of the two groups, can be attributed to the manipulation of X
concepts in experimental design
independent variables (IV) = X (predictor)
test units (ie. participants)
dependent variables (DV) = Y outcome
extraneous variables (random assignment helps rule these out
extraneous variables
history
maturation
testing effects
instrumentation
selection bias
attrition
ways to control extraneous variables
randomization
matching
statistical control
design control
purpose of an experiement
internal validity - is it causal?
and requires ecological validity - the extent to which an experiment uses stimuli that are realistic. are the material reflective of real life?
tradeoff between internal and external validity
hard to have high levels of both
the more contrived/artificial the study is, the harder it is to generalize findings to the greater population. but the more natural an experiment is, there is a greater threat of external / extraneous variables that you can’t control
between-subjects factorial design
tests different, independent groups of participants, with each group only exposed to one unique condition or independent variable
within-subjects design
tests the same participants under all conditions of the experiment, comparing their responses to measure changes caused by different levels of the independent variable
same people doing something twice
need less people to detect same effect
but signals to participants '“this is what we’re studying”
mixed design
combines between-subjects and within-subjects in one experiment to analyze effectiveness of different interventions (between-subjects) over time (within-subjects)
quasi-experimental design
designs that apply part of the procedures of true experimentation but lack full experimental control
one variables is manipulated, one is measured
lab vs field environment
laboratory: controlled, but artificial. researcher constructs the desired conditions. more control, higher internal validity
field: natural, real-world setting. set in actual market conditions.
demand artifacts
the respondents attempt to guess the purpose of the experiment and respond accordingly. common in lab environments
limitations of experimentation
time consuming (especially if researcher wants to measure long term effects)
expensive
difficult to administer