Bacillus Anthrax & Clostridium
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Bacillus Anthracis
First pathogenic bacteria which was:
Seen under microscope
To have Live attenuated vaccine
Isolated in culture media.
It is the largest pathogenic bacterium
Category (A) Bioterrorism agent
virulence factor
Plasmid Coded
Pxo1 plasmid
Anthrax toxin (Tripartite)
(only toxin which has 3 parts)
Edema factor: increases cAMP (MOA)
Protective factor: attachment of bacteria
Lethal factor: cause death of cells
Pxo2 plasmid
Capsule
Polypeptide made of polyglutamate
(all other capsules are polysaccharides)
Loss of plasmid → Loss of virulence → Useful in making vaccine (Sterne vaccine)
C/F & Pathogenesis
It is a zoonotic disease by : Cutaneous (M/C) , Inhalation , Ingestion
Infectious forms: Spores
Cutaneous Anthrax
Hide Porter's disease
Lesions seen on neck.
Referred to as Malignant Eschar (black color)
Pulmonary Anthrax
Wool Sorter's disease
Results in Hemorrhagic mediastinitis
Complications
Pericarditis
Septicemia
Form associated with Bioterrorism.
Intestinal Anthrax
Caused by eating undercooked meat.
Hemorrhagic enteritis
Complications
CNS/ Meningitis/ Meningoencephalitis
Hemorrhagic CSF
Hemorrhagic mediastinitis
Hemorrhagic enteritis
Diagnosis
Specimen
Skin
Blood
CSF
Sputum
Stool
Autopsy never performed in an animal with anthrax; alternatively blood sample/ cut one ear, taken and kept in biosafety cabinets (BSL II/III cabinets).
Microscopy
Bamboo stick appearance or box car appearance
There are holes inside which are spores (Gram poor)
For spores: Schaeffer & Fulton stain is used
McFadyean Reaction
Smear purple material around organism (indicates capsular material).
Blood culture morphologies
1.Blood agar
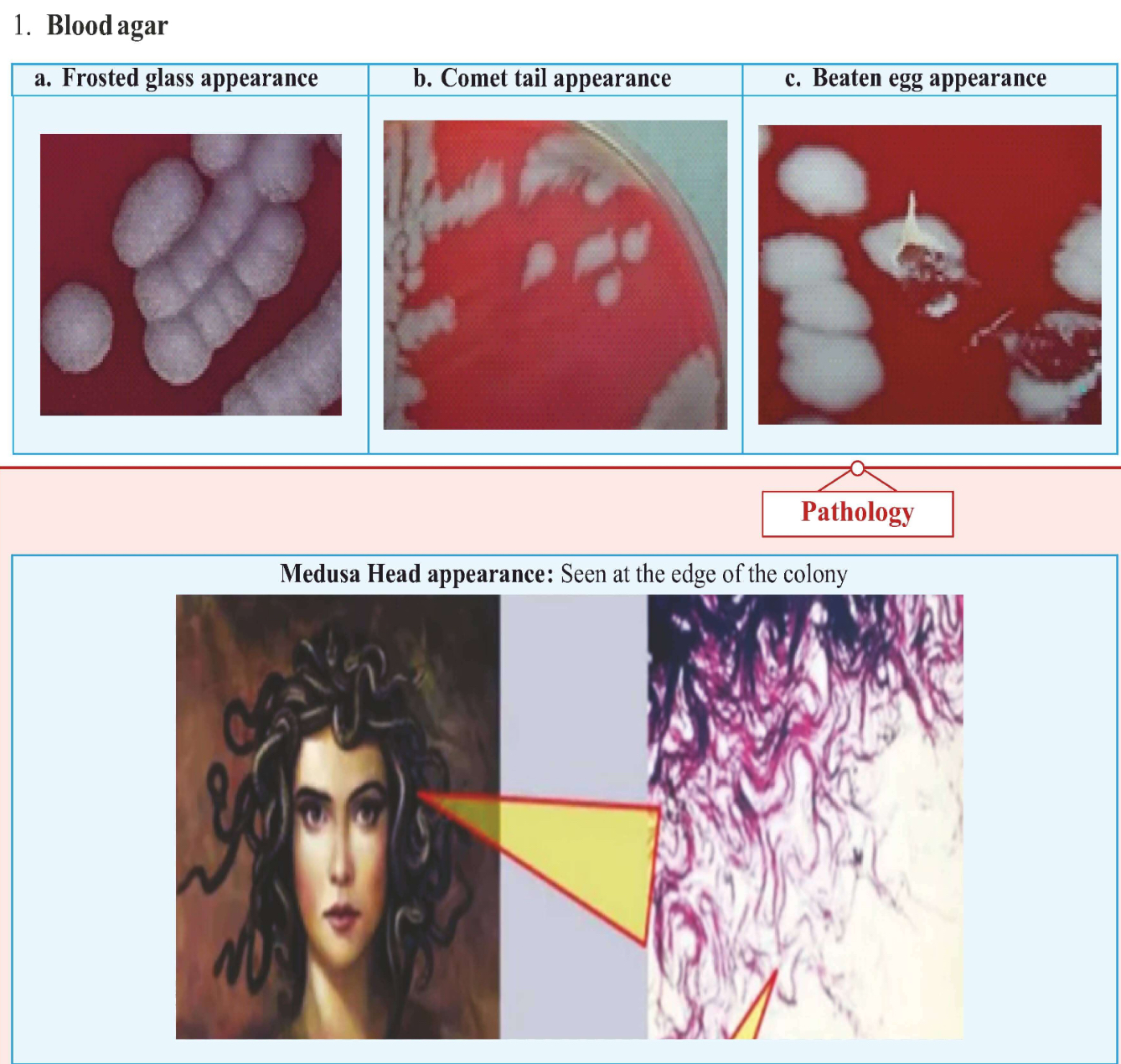
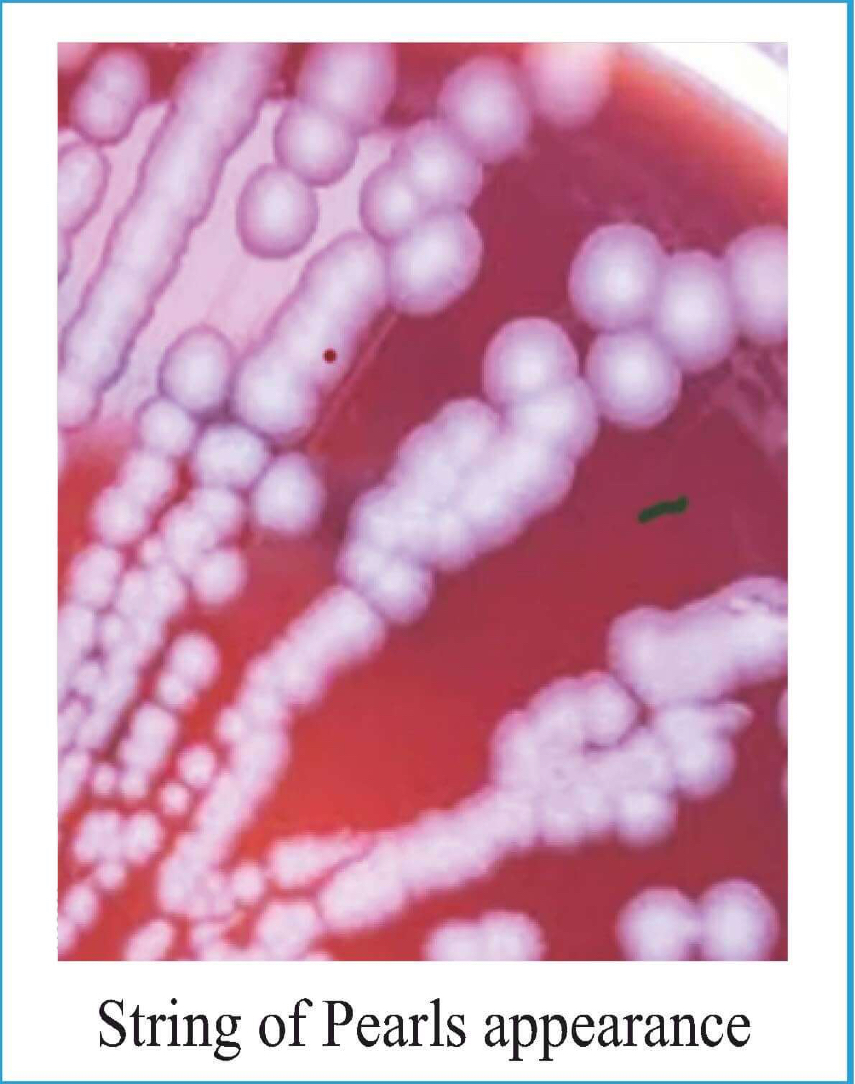
Blood agar + Penicillin
String of Pearls appearance
Agar + 0.5 - 0.50 u/ml of Penicillin
Cells: Spherical
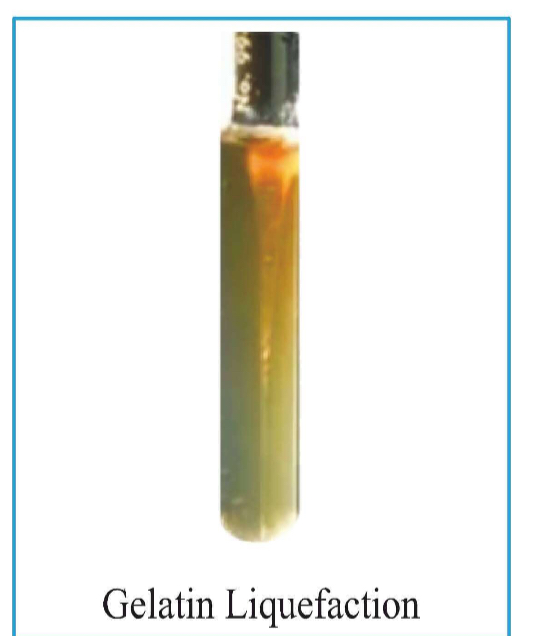
Gelatin Liquefaction
B. anthrax are obligate aerobes (require oxygen)
At surface of tube there is more oxygen than bottom, so it will have more energy at surface
Gelatin liquefaction occurs maximally at surface and keep on diminishing as moving down.
Shows inverted fir tree appearance.

PLET
PLET
• Selective media
• Polymyxin Lysozyme EDTA Thallous acetate.
Serology
Ascoli's ring thermo precipitin test
ELISA (used commonly)
CDC guidelines
Any Gram +ve bacillus,
Non-Motile,
Non-Hemolytic,
Catalase +ve.
Gives presumptive diagnosis of Anthrax
Precautions
Biosafety
Sanitization of factory
No autopsy for anthrax died animals.
Buried deep in quicklime / cremated to prevent soil contamination.
Duckering: Disinfection of wool is done by: 2% formaldehyde at 30-40° C for 20 minutes.
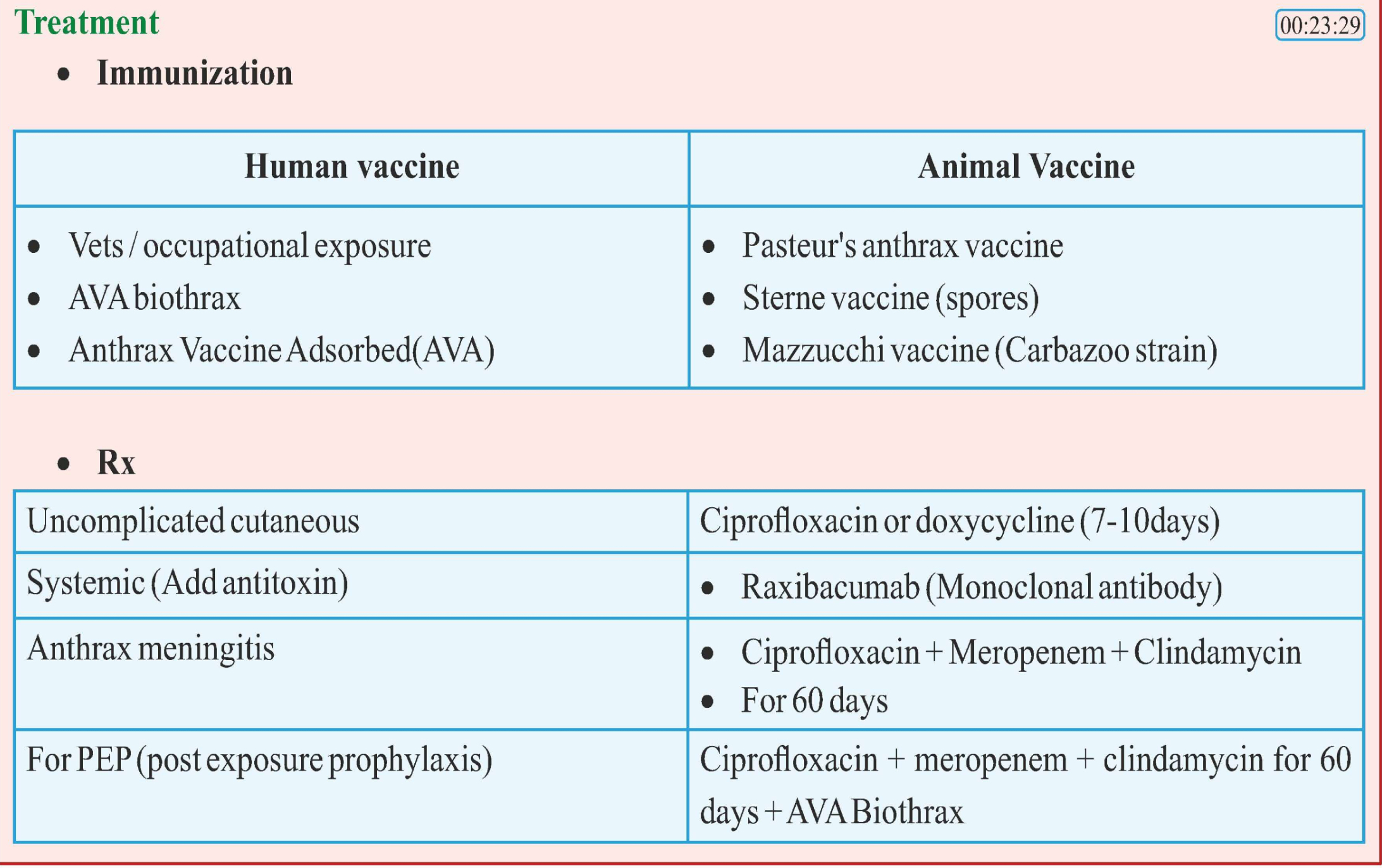
Treatment
Vaccination
Rx
Bacillus cerus
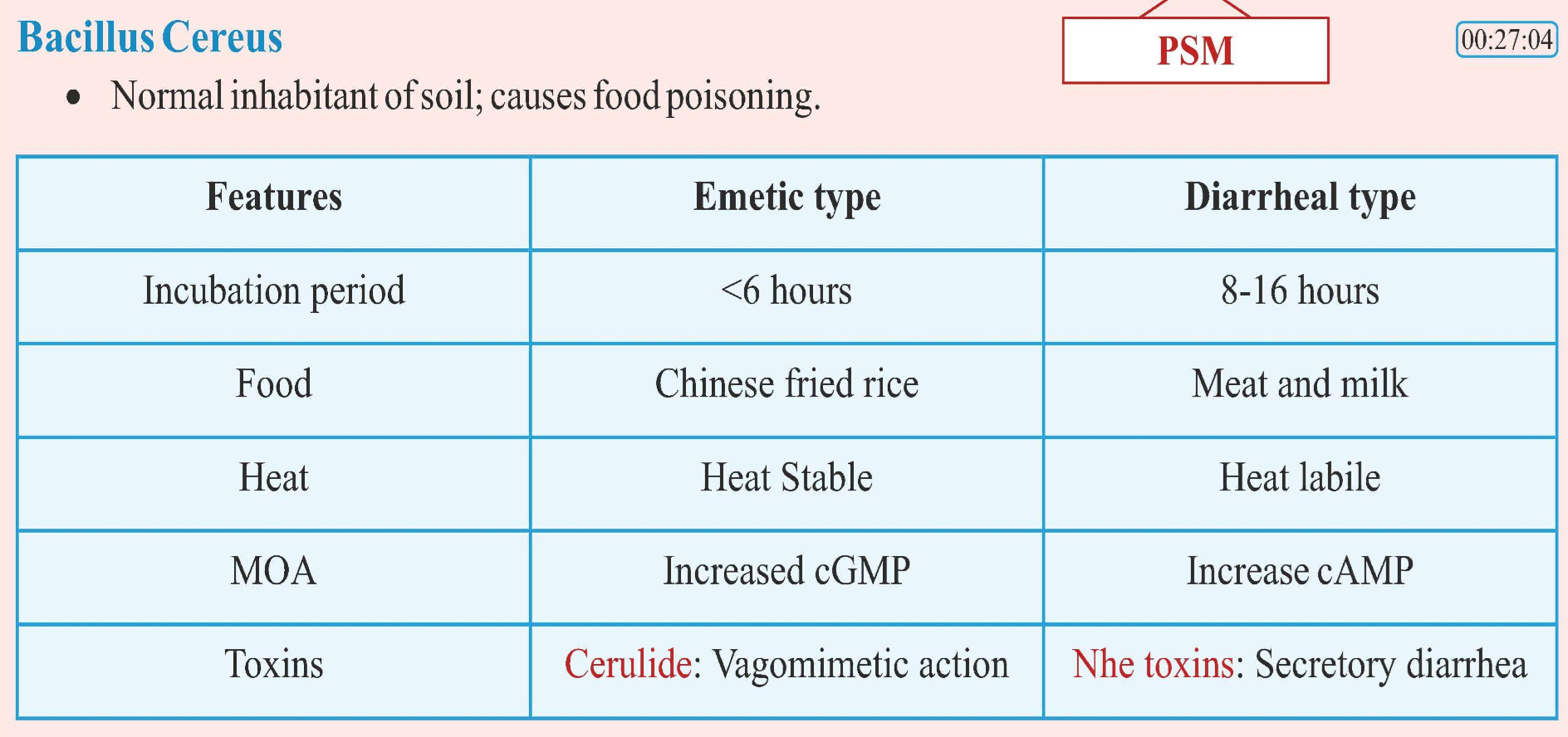
Lab Diagnosis
Motile, Hemolytic
Non encapsulated
Selective media
MYPA: Mannitol, Yolk Polymyxin, Agar
PEMBA: Polymyxin, Mannitol, Bromothymol blue, Agar
C. Perfringens
Non-motile
Encapsulated
Gram +ve Bacilli
Subterminal spores
Earlier known as C. Welchii
virulence factor
Invasive + Toxigenic
4 major toxins:
Beta (P)
Epsilon (8)
Iota (I)
Alpha (a) or Lecithinase or Phospholipase C
8 minor toxins:
Gamma (v),
Delta (0),
Theta (0) ,
Кара (к),
Lambda (2),
Eta (n),
Meu (M),
Veu (v)
Enzymes:
Histaminase,
Neuraminidase
Features of Gas Gangrene
Foul smelling, black, dirty looking tissues
Pain
Discharge
Gas bubbles (Crepitus)
Shock
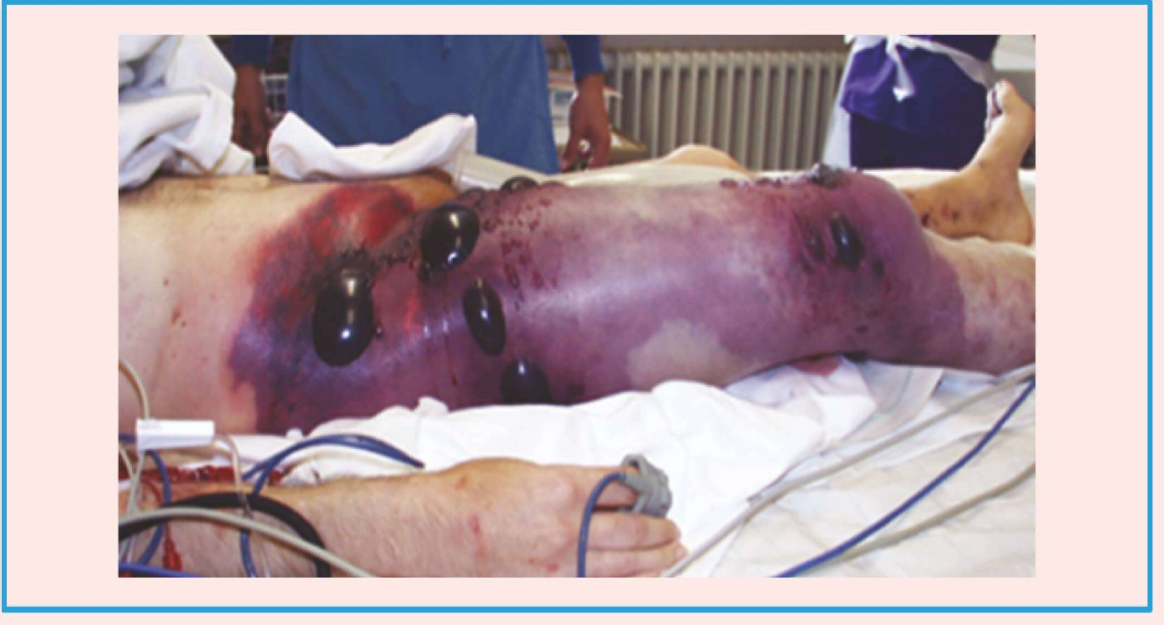
Incubation Period of Organisms causing Gas Gangrene
C. perfringens: 10-48 hrs
C. septicum: 2-3 days
C. novyi: 5-6 days
Treatment of Gas Gangrene
Surgical Debridement - Removal of Dead muscles
IV Penicillin + Clindamycin for 10-14 days
Hyperbaric oxygen
Passive Immunization can be given in some cases: Anti- gangrene serum
Others clinical features
2. Food Poisoning
Because of heat resistant Spores
Can be caused due to cold/ warmed up meat.
3. Gangrenous appendicitis
Caused by Type A
4. Necrotizing enteritis
Caused by Type C
5. PIGBEL
Common in European countries.
Abdominal pain & diarrhea
Caused by consumption of pork and sweet potato together.
Sweet potato has trypsin inhibitors which prevents the breakdown of beta toxin of pork in the intestine.
Rx: IV Penicillin + Metronidazole
Lab Diagnosis
Specimen: For gangrene case, we will take dead tissues such as-
Necrotic tissue
Muscle fragments
Microscopically
C. Perfringens shows: Subterminal spores.
C. Septicum shows: Citron body
Media: Robertson Cooked meat broth (Red/ Saccharolytic)
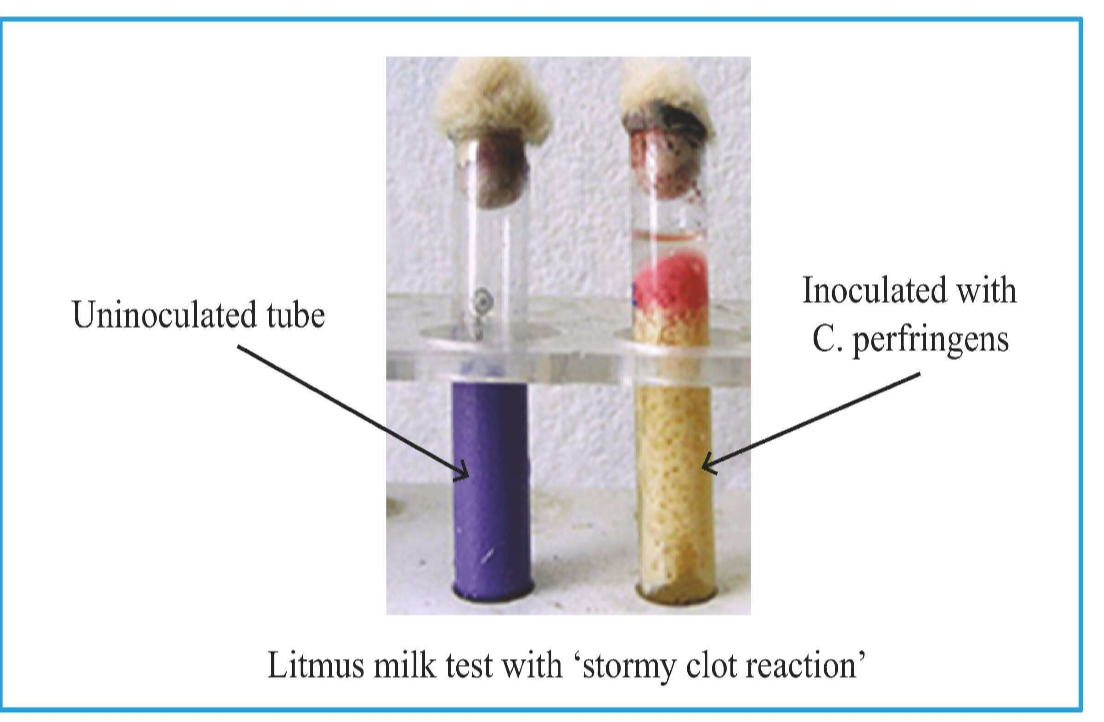
Litmus Milk: Stormy clot formation on litmus milk.
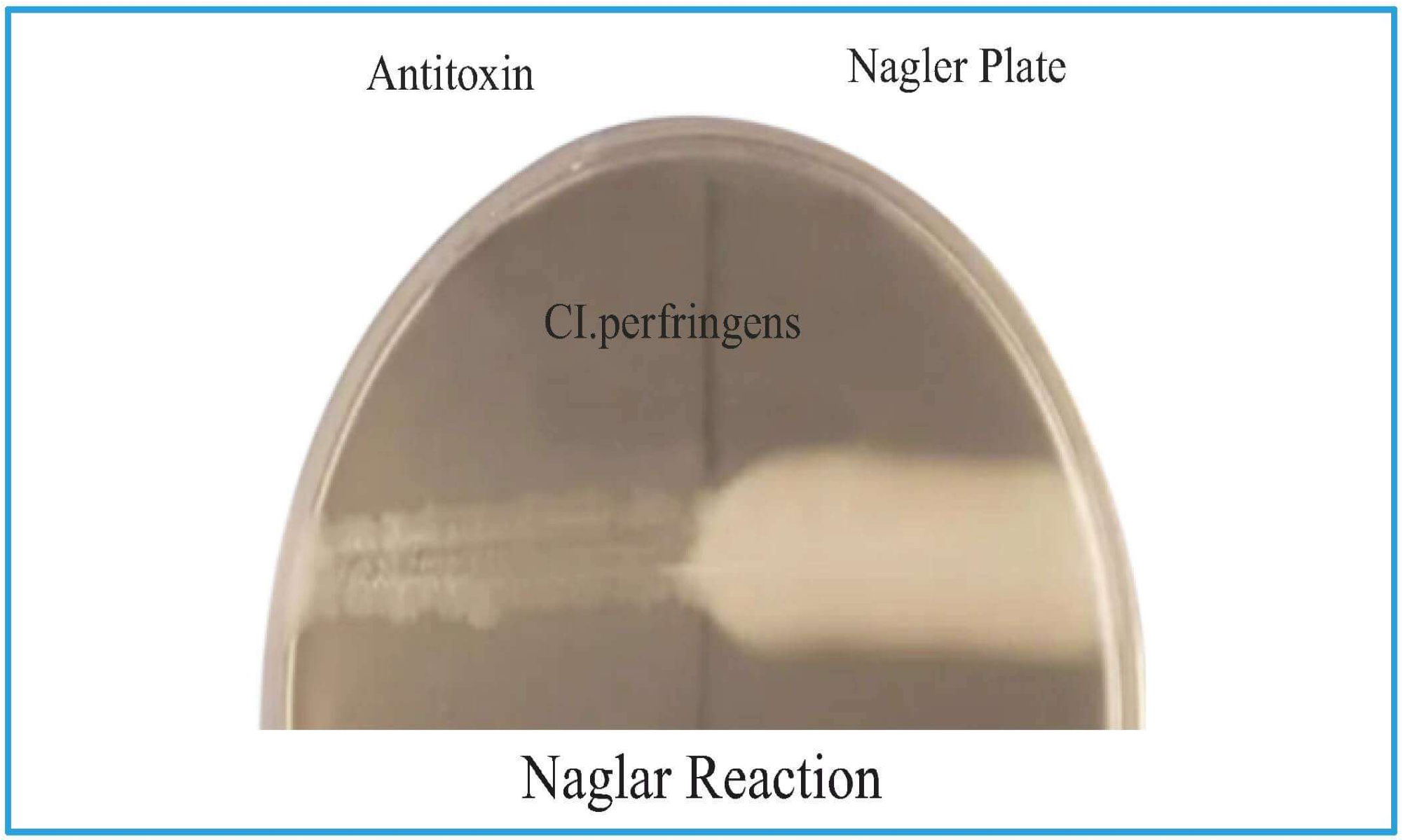
Naglar Reaction
Nagler plate has Egg yolk (lecithin) based agar
Medium is divided into two parts and patient's serum is put
C. perfringens has Lecithinase & egg yolk has lecithin which will break and opaque area is seen
On the other side, no opacification is seen as there is antitoxin which neutralizes.
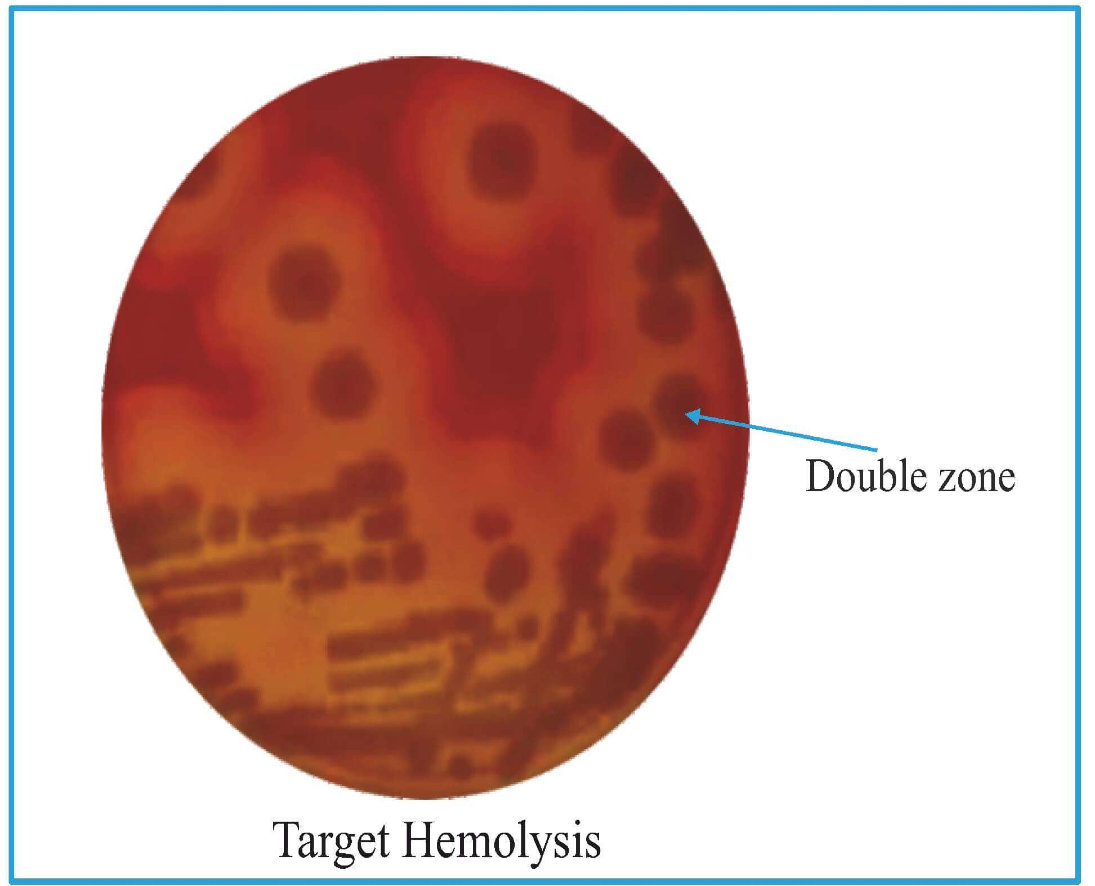
Target Hemolysis
Double zone of hemolysis.
Inner complete part is due to theta toxin
Outer incomplete part is due to alpha toxin
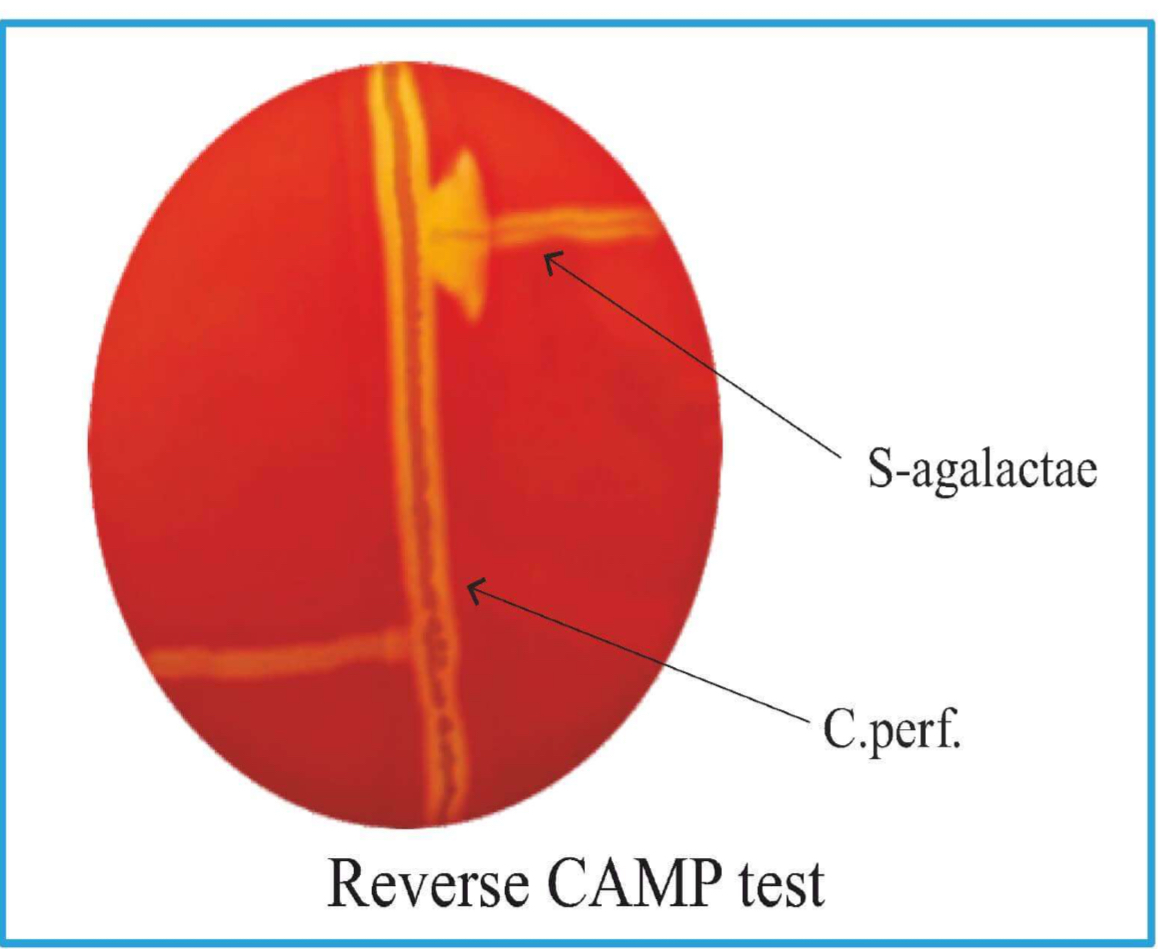
Reverse Camp Test +ve
Horizontal line: C. perfringes.
Arrow head formation at junction: S. agalactae.
Clostridium tetani
Causes: Tetanus (muscle spasm)
has terminal spore (drumstick appearance)
Transmission
By Injury: Unsterile RTA
No person to person transmission
Incubation Period- 6-10 days (shorter IP → worse)
Tetanus is also known as 8th day disease
Clinical features
symptom is increased tone of masseter muscle → Lockjaw / Trismus
With progression of disease:
Limb Spasm
Descending spastic paralysis
Deep tendon reflexes exaggerated.
Autonomous disturbance (2nd week; Increased BP, PR, Sweating)
M/c cause of death- Respiratory failure
Complications
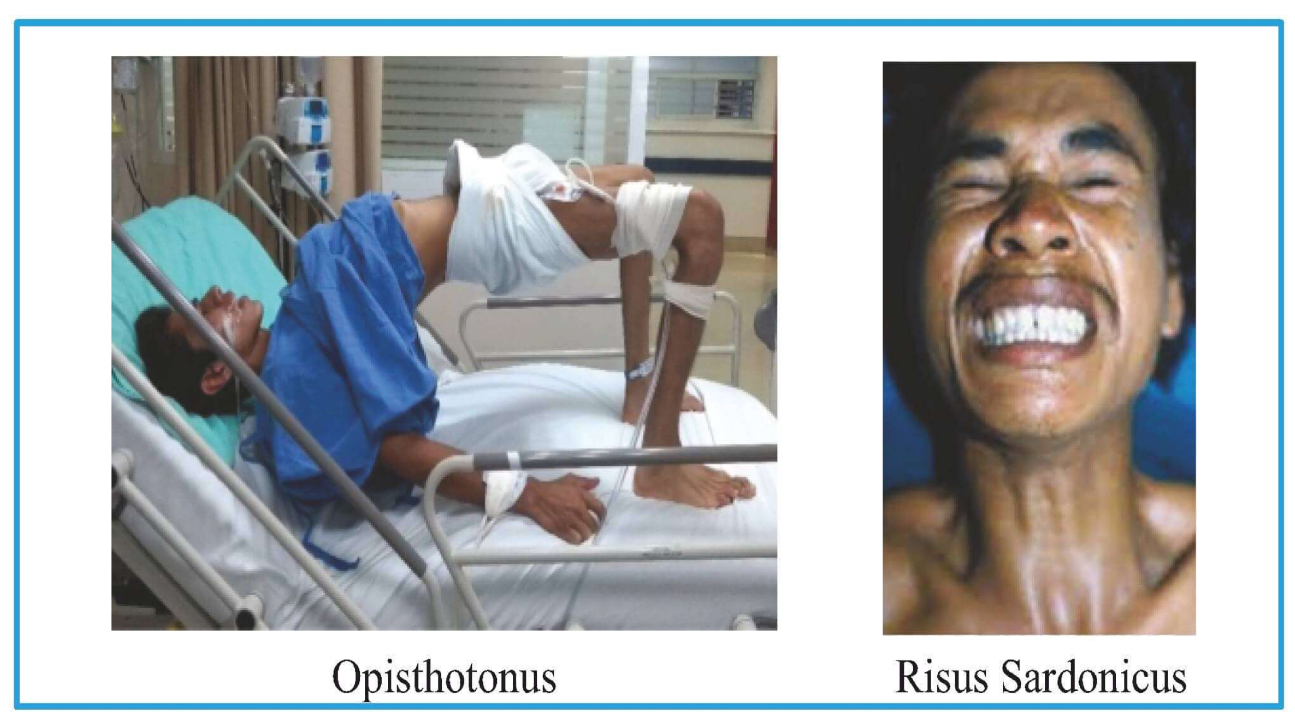
Risus Sardonicus (looks like patient is smiling but it's muscle contraction)
Opisthotonos
Specimen: Necrotic Tissue
Microscope examination
Gram +ve Bacilli
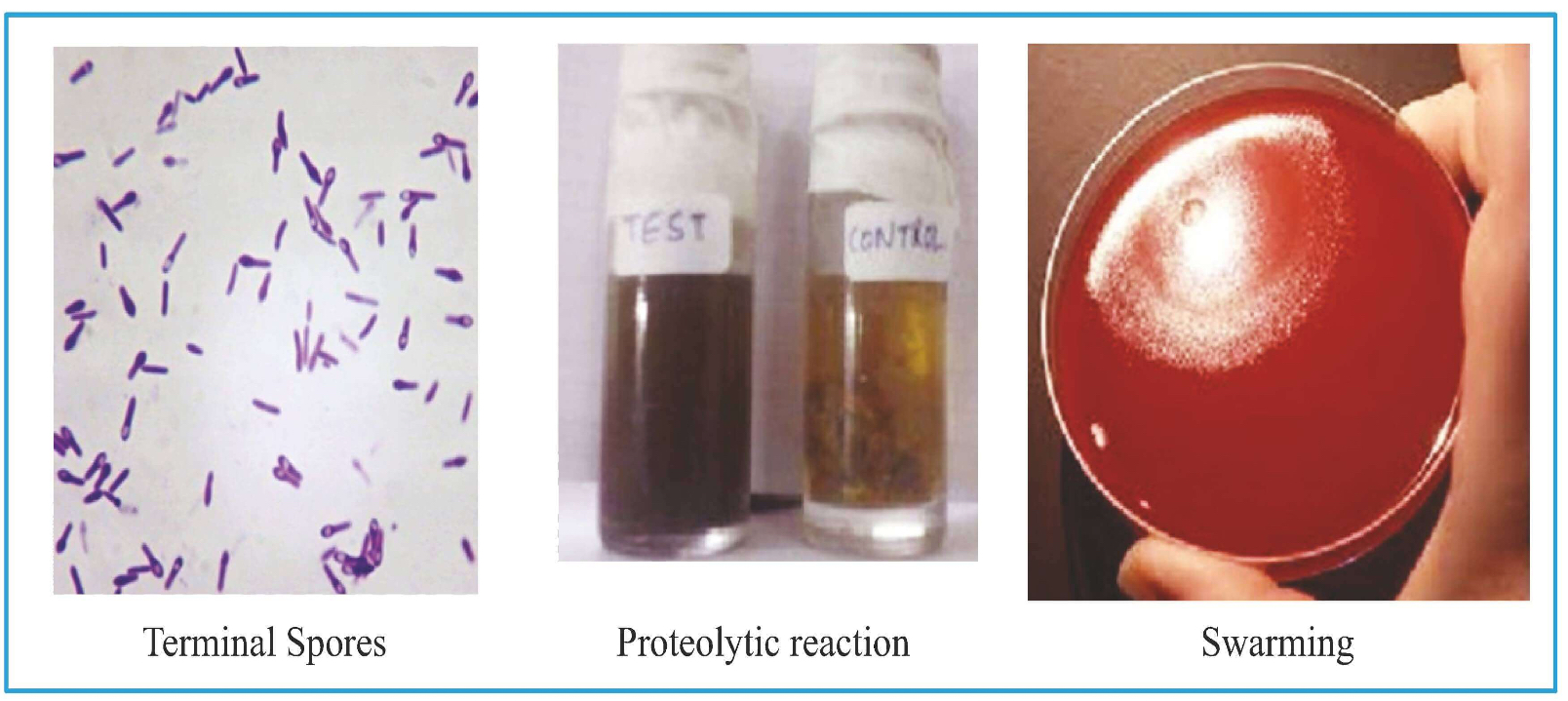
Spores: Terminal (drumstick appearance)
On blood agar: Concentric movement is seen- Swarming
Gelatin Stab: Fir tree appearance(as organism will work maximally at the bottom).
Robertson's Cooked Meat Broth: Black color; proteolytic reaction.
Virulence Factors of botulism toxin
Botulinum toxin: Produced intracellularly appears in medium only after cell death.
Serotype: 9 (A,B,C1,C2,D,E,F,G,FA hybrid)
0 A, B, E- cause infections in humans
• A- most severe
• All are chromosomal mediated
All are chromosomally coded except C1, C2, D which is phage coded exception: C2 is an enterotoxin
Clinical manifestations
No contraction of muscle (floppy muscles) → flaccidity is noted.
Types of botulism
Food borne botulism
Bottled and canned food (Heat labile toxins)
IP: 12-36 hrs
Results in
• Diplopia
• Dysphagia
• Dysarthria
• Descending flaccid paralysis.
• Dilated pupils.
• GI symptoms are also present.
Wound botulism
IP: 7-10 days
No GI symptoms
Infant botulism
Bottle fed / honey / baby food
IP: 1-2 days
First symptom: Constipation.
Floppy baby syndrome → flaccid muscles
Surgeries
Iatrogenic botulism
Lab diagnosis & Treatment of C. botulinum
Lab diagnosis
• Gram +ve Bacillus
• Spores seen
• Subterminal
• Oval
• Bulging
• Anaerobe
Treatment
• Toxoid Antiserum
Clostridium difficale
Normally present in the gut
Causes: pseudomembranous enterocolitis.
Virulence factors
• ToxinA: Enterotoxin (gut attached)
• Toxin B: Cytotoxin
mechanism
Toxin A & B entering the system → attack the GTP binding proteins (Rho, Rac, CDC 42) - damage to actin cytoskeletal → cell death.
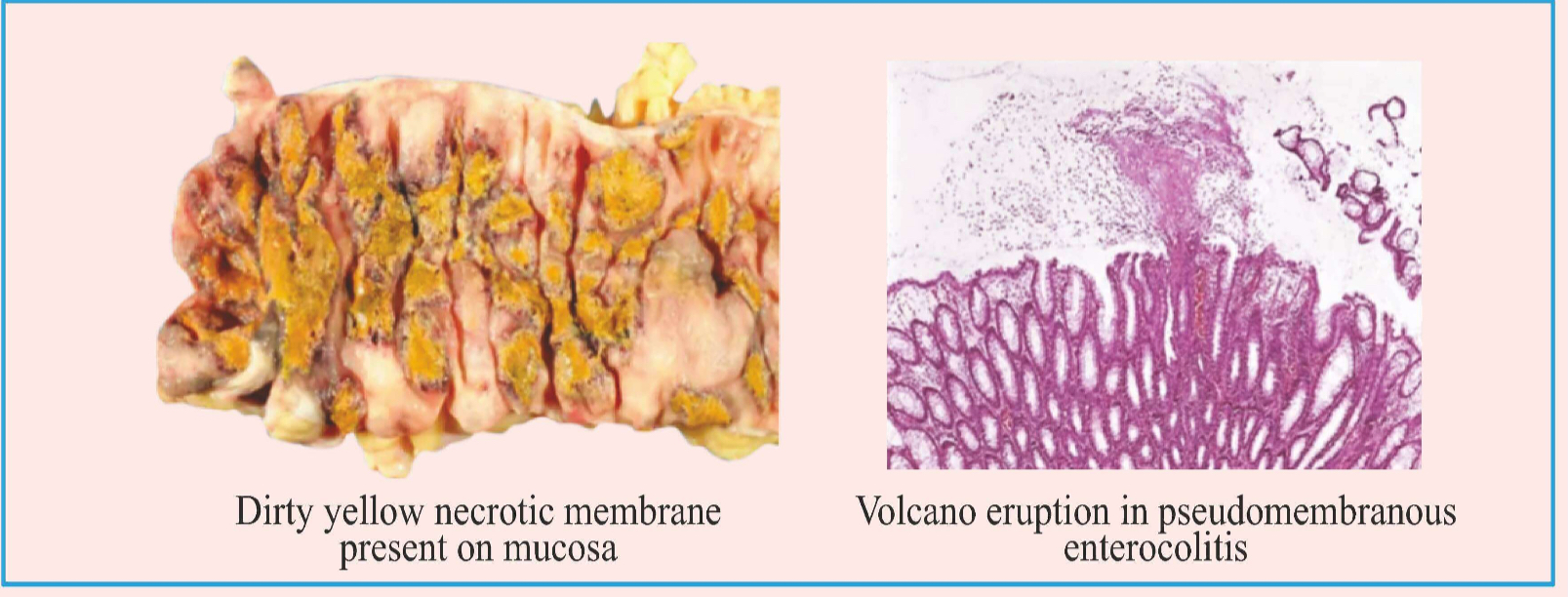
Toxins will stimulate ILS production → neutrophils recruitment → form dirty yellow necrotic membrane present on mucosa.
The dead cells will burst out like a volcano eruption (in microscopic vision)
Pseudomembranous Enterocolitis
Risk factor: Long term usage of antibiotics (3rd generation cephalosporins)
Clinical feature: Watery diarrhea
diagnosis
Colonoscopy: 100% specificity, 50% sensitivity.
Toxin: Tissue culture Assay; ELISA; PCR.
Media:
• CCFA: Cefoxitin Cycloserine Fructose Agar
• CCYA: Cefoxitin Cysteine Yeast Extract Agar
HPE: Volcano like eruption is seen.
treatment
Earlier oral vancomycin was used but now Fidaxomycin is used.
Recommended treatment: Oral vancomycin (500 mg four times daily) + intravenous metronidazole and rectal vancomycin enemas in cases of severe ileus (Fulminant CDI).