ECON Paper 1 (Micro)
1/129
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
price controls
setting a min. or max. price by gov. so equilibrium price can’t be adjusted.
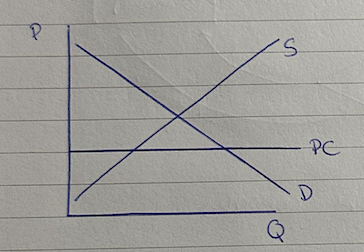
price ceiling
max price set by gov below equilibrium price
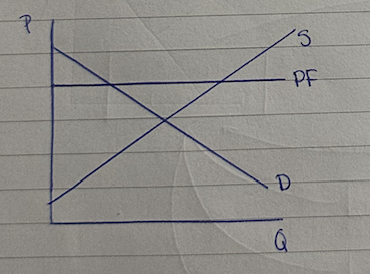
price floor
min price set by gov above equilibrium price
indirect taxes
payments made to gov by producers but partly consumers
excise taxes
placed on demerit goods
sales or value added tax (vat)
placed on almost all goods/services
specific tax
per unit amount added to good/service
ad valorem
fixed percentage of the price of a good/service
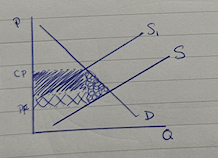
consumer burden (tax)
what the consumer pays
producer burden (tax)
what the producer pays
consumer + producer burden
= gov. revenue
welfare loss
societies loss during poor resource allocation
Producers pay more tax when demand is…
elastic
Consumers pay more tax when demand is…
inelastic
producer subsidy
payment by the gov. to producers, generally fixed for a per unit output; producers make more, consumers pay less.
market failure
when a market fails to efficiently allocate resources = allocative inefficiency.
externality
when actions of producers/consumers affect a third party
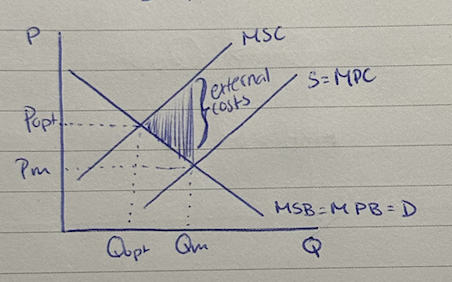
marginal private cost (MPC)
cost to producers for producing one more unit of a good.
marginal social cost (MSC)
cost to society for producing one more unit of a good
marginal private benefit (MPB)
benefits to consumers for consuming one more unit of a good.
marginal social benefit (MSB)
benefits to society for consuming one more unit of a good
MSB = MSC
allocative efficiency
markets
arrangement where buyers and sellers of goods/services are linked to make an exchange
competitive markets
large quantity of independent buyers and sellers, so no one can control price of product.
demand
the individual consumers willingness and ability to buy goods/services at different prices during a specific period of time (all else being equal)
the law of demand
there is a negative causal relationship between a goods price and its quantity demand in a specific time period (all else being equal)
the law of diminishing marginal marginal utility
consumers want benefit (utility) from purchasing goods/services. but the more they buy, the less additional (marginal) benefit they get (will only buy for a lower price).
scarcity
demand for a good or service is unlimited but the resources to make it are limited.
opportunity cost
the loss of other alternatives when one alternative is chosen.
the substitution effect
consumers will purchase the substitute good if price falls
the income effect
real income is income that adjusts to change in price - as price decreases, consumers will buy more.
non price determinants of demand
changes in income
tastes and pref.
future price expectations
price of related goods
size of market.
supply
the individual firms willingness and ability to produce different quantities of goods/services at different prices during a specific time period (all else being equal)
the law of supply
there is a positive causal relationship between a goods price and its quantity supplied in a particular time period.
short run
at least one FoP is fixed (usually capital)
long run
all FoP can be changed
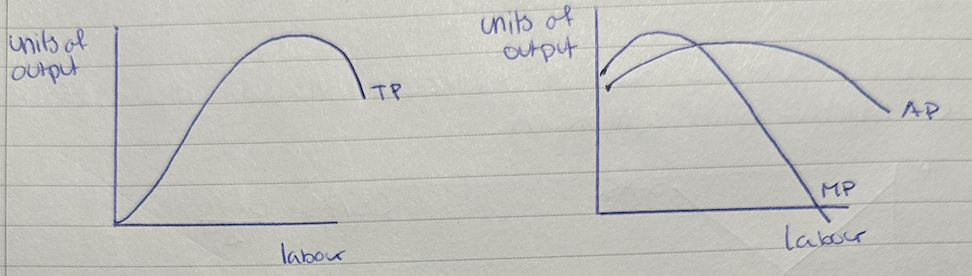
total product (TP)
total amount of output produced by a firm
marginal product (MP)
the additional output produced by a firm from one additional unit of variable input (labour)
average product (AP)
total quantity of output per unit of variable input
marginal cost (MC)
cost of producing an additional unit of output
non price determinants of supply
subsidies and taxes
tech advancements
other related goods prices
resource costs
future price expectations
size of market
the law of diminishing marginal returns
as more units of variable inputs (labour) are added to fixed inputs (capital), the marginal product of the variable input will increase, but at a certain point, decrease.
equilibrium
market quantity supplied = market quantity demand and there is no incentive for the price to change.
disequilibrium
surplus or shortage
signals
price changes are signals to producers/consumers when market circumstances change
rationing
price alleviates problems or scarce resources
incentive
if there is a surplus or shortage, it signals to producers to lower/higher price
allocative efficency
producing the combination of goods most wanted by society
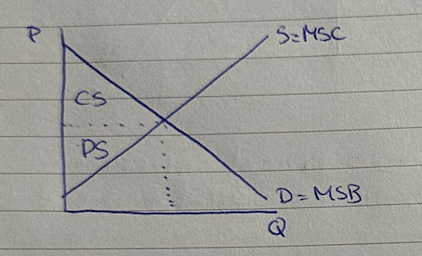
consumer surplus
benefit consumers get form paying less than what they were willing to pay
producer surplus
benefit producers get from selling at higher price than willing to
social surplus
sum of producer and consumer surplus, reached when market is in equilibrium
elasticities
measures the responsiveness of a variable to change in price or any of the variables determinants.
Price elasticity of demand (PED)
measures the responsiveness of consumers of a good/service to a change in price of that good/service
PED=0
perfectly inelastic demand
Qd is not responsive to change in price.
0 < PED < 1
inelastic demand
Qd is relatively unresponsive to change in price.
PED = 1
unit elastic demand
Qd is proportionally responsive to change in price.
1 < PED < infinity
elastic demand
Qd is relatively responsive to change in price.
PED = infinity
perfectly elastic demand
Qd is infinitely responsive to change in price.
determinants of PED
substitutes
proportion of income
luxury/necessity
addictiveness
time .
primary sector
raw materials
secondary sector
manufactured goods
tertiary sector
services
income elasticity of demand (YED)
measures the responsiveness of demand to change in income
YED > 0
normal good
YED > 1
luxury
YED < 0
inferior good
YED < 1
necessity
price elasticity of supply (PES)
measurement of responsiveness of the quantity of a good supplied to changes in that goods price.
0 < PES < 1
inelastic supply
Qs is relatively unresponsive to a change in price
PES = 0
perfectly inelastic supply
Qs is not responsive to a change in price
1 < PES < infinity
elastic supply
Qs is relatively responsive to a change in price
PES = 1
unit elastic supply
Qs is proportionally responsive to a change in price
PES = infinity
perfectly elastic supply
Qs is infinitely responsive to a change in price
determinants of PES
time
mobility of resources
ability to store stocks
unused capacity
rate of cost of production.
negative externality of production
external costs created by producers
tradable permits
market based policy where gov. sets amount of permits that can be bought and sold by polluters.
limitations of gov. intervention
size of externality
amount of tradable permits allowed
difficulty of enforcing regulations
externality remains with regulations
regulations
age restrictions,
where you product can be used
gov. interventions
subsidies
taxes
price controls
negative externality of consumption
the external costs created by consumers
demerit goods
goods that have harmful effects on the consumer and creates negative spill over effects on society
positive externalities of production
the external benefits created by producers
positive externalities of consumption
the external benefits that are created by consumers
merit goods
goods that are beneficial to consumer and created positive spill over effects on society
public goods;
non rivalrous and non excludable
non rivalrous
consumption by one person does not limit consumption by other person.
non excludable
no one is excluded from using the product
direct gov. provision
gov fully funds goods (public)
contracting out
gov. asks private company to do a task for them
asymmetric information
buyers and sellers don’t have equal access to information
adverse selection
one party has more info on quality of product than the other party
moral hazard
one pary takes risks but the other party faces the effects of those risks.
price ceiling diagram
price floor diagram
burden diagram
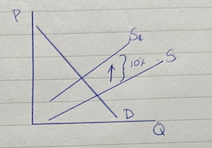
specific tax diagram
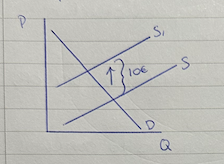
ad valorem tax diagram
diminishing marginal returns diagram(s)
consumer and producer surplus diagram
negative production externality diagram
MSC > MPC