Microeconomics Unit 2-3
1/51
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Accounting Profit
The difference between total revenues and explicit costs only (Net Income)
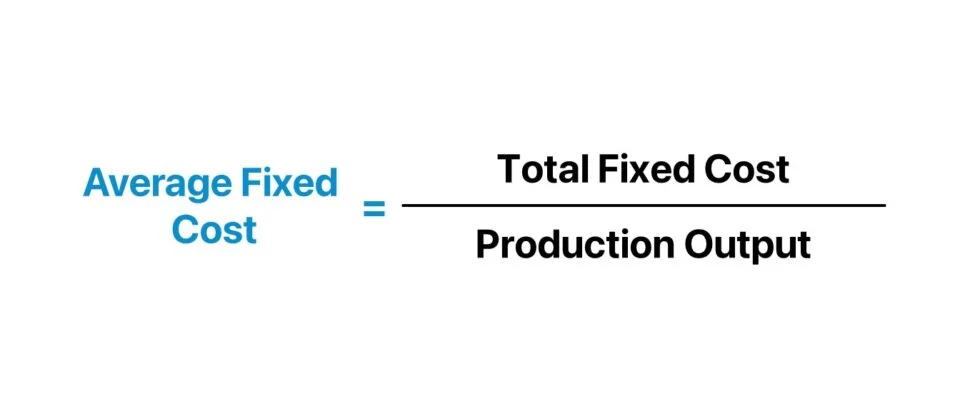
Average Fixed Cost
A firm's total fixed cost divided by total output (Cost that does not change with the change in the number of goods and services produced)
Average Fixed Cost (Formula)
Average Product
Total product divided by the variable input used in production (Average outputs produced by each input)
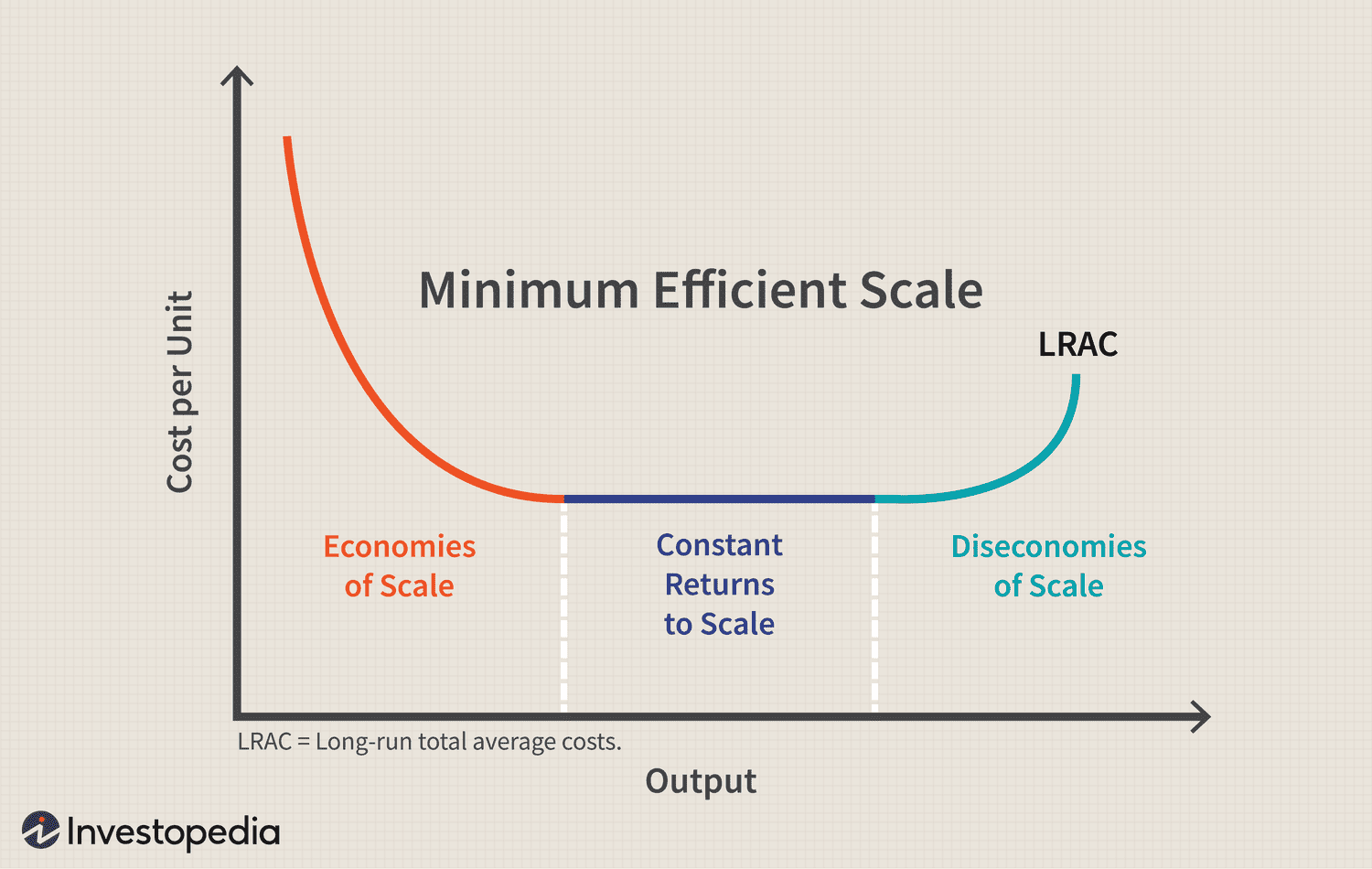
Diseconomies of Scale
As a firm's output increases, its LRATC curve increases. (When a company or business grows so large that the costs per unit increase)
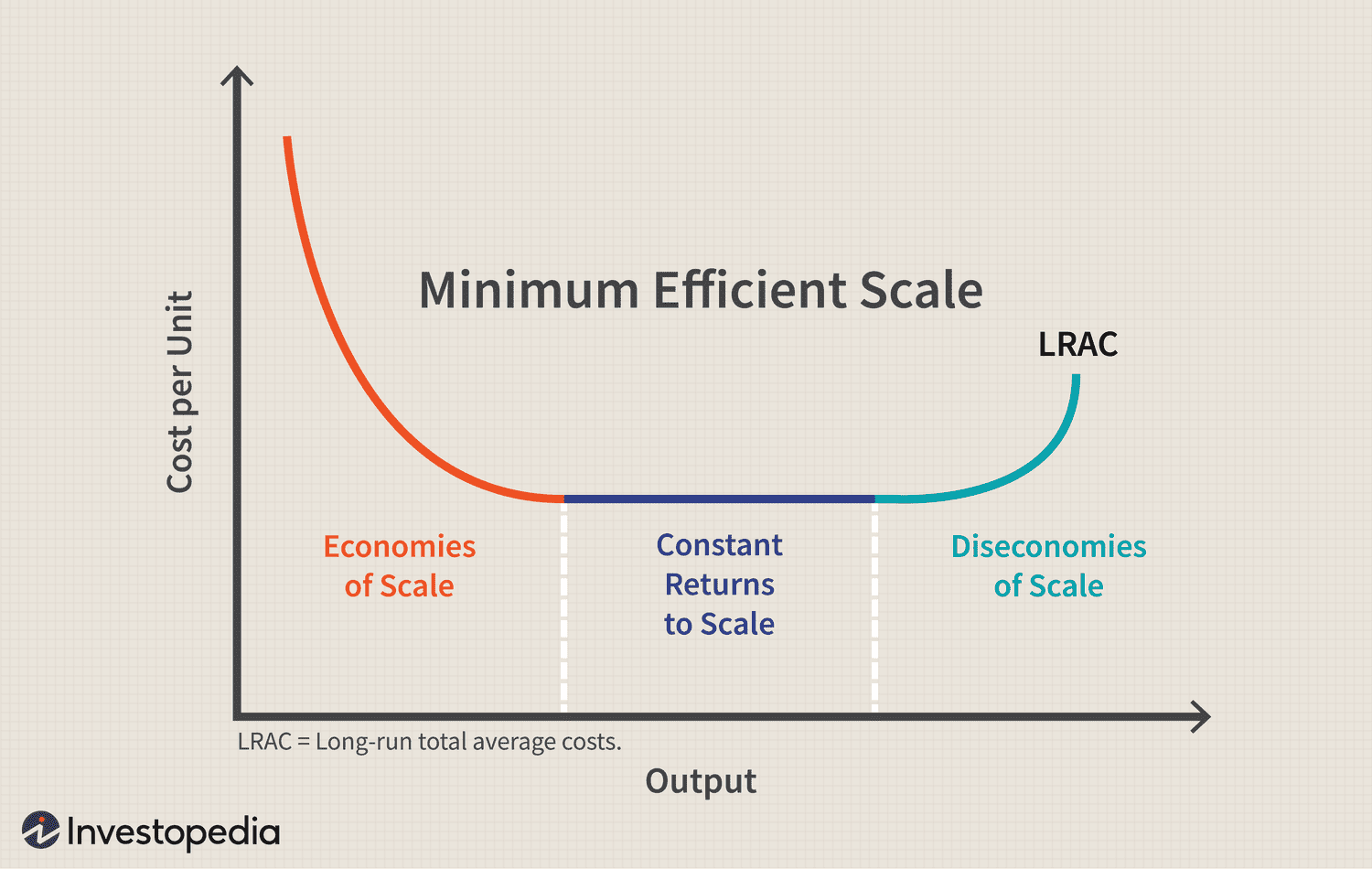
LRATC
Long-Run Average Total Cost
Economies of Scale
The cost advantages companies gain from increasing their output
Economic Profit
Total revenues subtracted by both explicit and implicit costs; this is the type of profit referred to in Economics (Net Profit)
Excise Tax
A per-unit tax placed on the sales of a specific product
Fixed Costs
These costs do not change when quantity changes in the short run, but can change in the long run (costs that are independent of volume)
Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns
The range of output over which smaller and smaller additional units of output are produced as successive equal increments of variable input are added to fixed quantities of other inputs in the short run. (Simplify This)
Long Run
Period of time over which supply can fully adjust to changes in demand (in the long run)
Lump-Sum Tax
A fixed tax on producers regardless of the amount produced [affects average fixed cost and average total cost]
Marginal Cost
What is costs to produce an additional unit of output
Marginal Product
How much additional output is produced when an input is added by a firm
Normal Profit
Zero economic profit [where an entrepreneur will not be better off in any other venture] (Company's total costs are equal to its total revenue)
Per-Unit Tax
A tax on each additional unit produced [affects variable costs: marginal cost, average total cost, and average variable cost]
Short Run
Period of time over which supply cannot fully adjust to changes in demand due to fixed resources
Total Costs
The total fixed and variable costs
Variable Costs
These costs change as production increases
TC (Formula)
TVC + TFC
ATC (Formula)
AVC + AFC or TC/Q
MC (Formula)
ΔTC/ΔQ
AVC
Average Variable Costs
AFC
Average Fixed Costs
TVC
Total Variable Costs
ATC
Average Total Cost
TC
Total Cost
TFC
Total Fixed Costs
Q
Quantity or Quantity Demanded
MC
Marginal Cost
AFC (Formula)
TFC/Q
AVC (Formula)
TVC/Q
Monopolistic Competition
Market structure characterized by many medium-sized firms who need to be innovative and differentiate their products in price and nonprice ways (Companies need to be innovative and appeal to buyers in order to stand out from competitors)
Monopoly
one firm constitutes the market selling a product for which there are no close substitutes (One company has total control over an industry)
Oligopoly
Market structure characterized by relatively few sellers who act interdependently and/or collusively to be price-makers and to control markets (Where an industry is dominated by a small group of influential companies)
Perfect Competition
Market structure characterized by a large number of sellers with a homogenous product, infinitely elastic demand for firms, and no barriers to entrty or exit
Economic Efficiency
The allocation of resources to most productive and desired uses
Profit-Maximizing (Loss-Minimizing) Criterion
the level of output at which MR = MC
MR
Marginal Revenue
Shut-Down Point
In the short run, the firm should shut down when price is less than AVC
Shut-down Point (Formula)
P < AVC
P
Price
Perfectly Competitive Firm's Demand Function (Formula)
P = MR
Profit Maximizing Criterion (Formula)
MR = MC
Socially Optimal Price [under perfect competition in the long run] (Formula)
P = MC
In the Long Run for a Perfectly Competitive Firm (Formula)
P = minimum average cost
Profit or Loss (Formula)
(P - ATC)*q
Herfindahl Index
the sum of the square of market shares of firms in a particular market or industry [used to measure the level of concentrated power of firms in an industry]
Natural Monopolies
Monopolies that have extensive economies of scale and can provide a product at a lower cost than can several firms (a type of monopoly in an industry with high barriers to entry and start-up costs that prevent any rivals from competing)
Price-Discrimination
This practice charges different customers with different prices for the same products
Fair-Pricing Return [In A Regulated Monopoly]
P = ATC (at intersection of demand curve and average total cost curve)