chapter fourteen
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
transcriptional regulation
the means by which a cell regulates the conversion of information stored in DNA that of RNA
post transcriptional regulation
mechanisms controlling the processing, location, expression and half life of RNA
translational regulation
regulation of ribosome production, assembly, and localization of ER membranes
post translational regulation
mechanisms that influence the folding, function, location and half life of proteins
Scientists have discovered that the difference between blond and dark hair comes down in part to a single nucleotide difference in the DNA sequence of an enhancer that lies more than 350,000 base pairs away from the gene it controls. On average, blonds transcribe this gene less efficiently than people with dark hair. How can a tiny difference in a distant enhancer make a blond?
The functioning of enhancers is an example of _________________.
transcriptional control of gene expression
Scientists discovered that the difference between blond and dark hair comes down in part to a single nucleotide difference in the DNA sequence of an enhancer that lies more than 350,000 base pairs away from the gene it controls. On average, blonds transcribe this gene less efficiently than people with dark hair. How can a tiny difference in a distant enhancer make a blond?
Which of the following statements about an enhancer is correct?
An enhancer is a sequence associated with a protein to initiate transcription.
How is an enhancer that is thousands or tens of thousands of basepairs away from a gene able to regulate transcription of a gene that is so far away?
DNA looping with the help of a MEDIATOR could bring the enhancer bound by an activator (transcription factor) physically close to the promoter even if the enhancer is very far away.
Scientists discovered that the enhancer associated with hair color has a binding site for a particular transcription factor. One form of the binding site has the sequence CACTAAAG and is associated with dark hair, and the other form of the binding sequence has the nearly identical sequence CGCTAAG and is associated with blond hair. How could these two nearly identical enhancer-binding sites lead to different rates of initiating transcription of the regulated gene?
The transcription factor could bind to the enhancers with different affinities, with the sequence promoting stronger binding leading to higher rates of transcription.
The human gene controlled by the enhancer is called KITLG, and it encodes a signaling protein that binds to a cell-surface receptor. The signaling pathway activated by KITLG controls many phenotypes, including hair color.
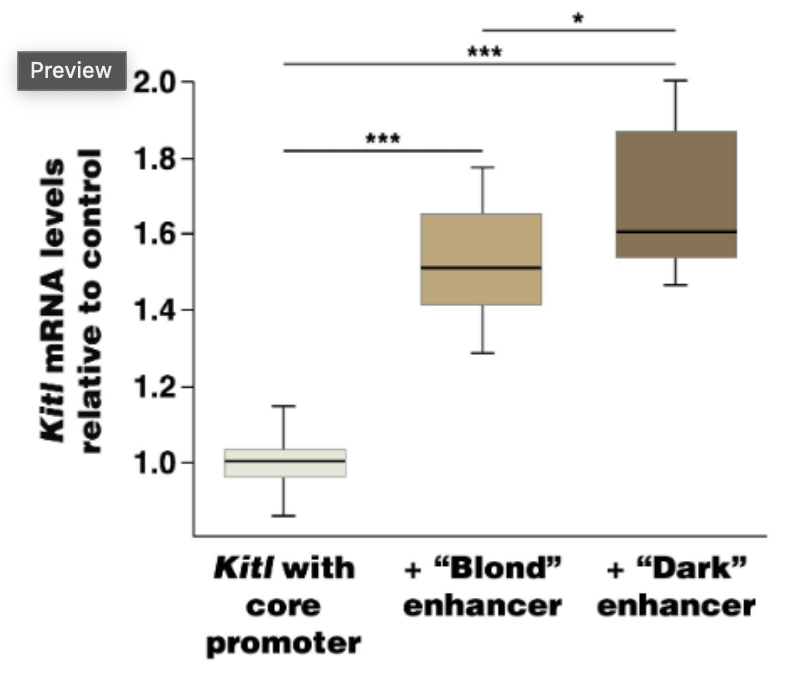
Scientists expressed the mouse version of the gene (Kitl) in mouse embryonic cells driven by its own promoter and with or without the human enhancer elements that are associated with blond or dark hair. They measured the amount of Kitl mRNA in embryonic mouse skin cells compared to untreated controls.
What can you conclude about the enhancers associated with either blond or dark hair driving the expression of Kitl mRNA?
Both enhancers drive much higher expression than the Kitl gene without the enhancer. The enhancer associated with dark hair drives higher levels of expression than the one associated with blond hair.
Alternative RNA splicing ________.
can allow the production of proteins of different sizes and functions from a single mRNA
Briefly define the term EPIGENETIC. Be sure to address whether the sequence of DNA is altered under epigenetic mechanisms
Surface-level covalent modifications that can be added to histones or directly to DNA sequences that influence the state (open or closed) of chromatin and thus the accessibility of genes. DNA sequences are not changed due to epigenetic modifications, thought their gene expression may be. Many epigenetic modifications are heritable.
whats a histone code
chemical modifications to histone proteins on their tails
Give four examples of covalent histone modifications (which functional chemical groups can be added to them):
acetyl, methyl, phosphate, ubiquitin, sumo