Morphology of flowering plants
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Morphology is the study of external root , leaves , stem , fruits and flowers
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
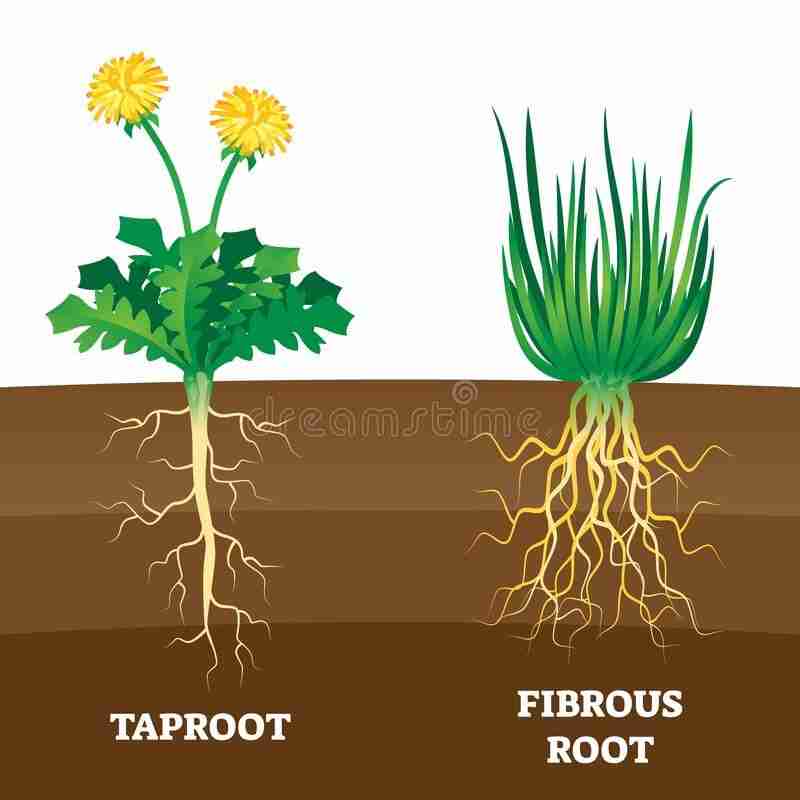
Types of roots
Tap root :1)Consist of roots , and lateral branches called secondary and tertiary etc
2) it is branched
3)Tap root is found in dicotyledons plant
4) example are mango and banana
Fibrous root:1) In fibrous root primary and lateral branches are absent, and roots emerges from the base of the stem
2) it is unbranched
3) it is found in monocotyledons plant
4) examples are cocounut and grass
Adventitious roots: 1) roots which arise from the parts of the plant other than the radicle
2) examples are grass and monestra
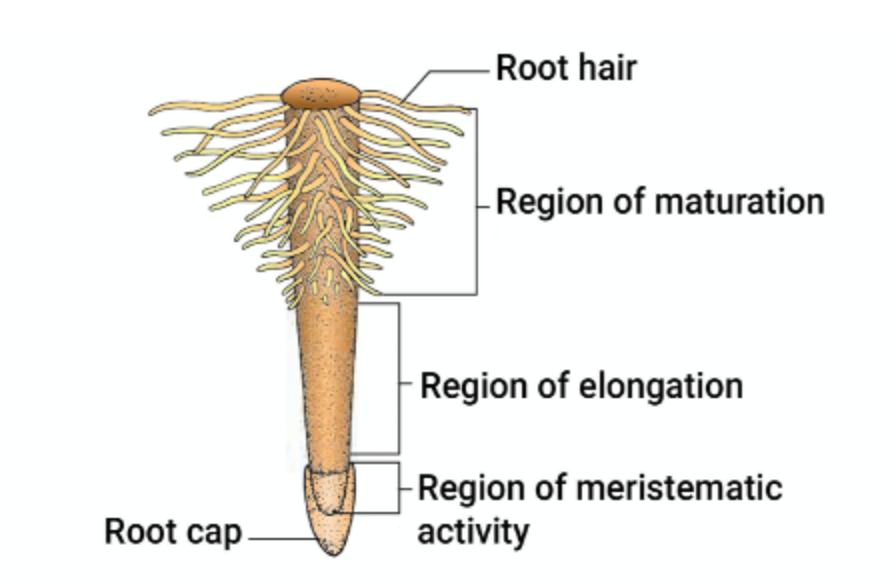
Regions of the root
Root cap: It covers the tip of the root and also protects it .
Region of meristematic activity: In which cells diivides rapidly,the cells of this region are small , thin walled and with dense protoplasm.
Region of elongation : they are responsible for the growth of the root in length as they undergo rapid elongation and enlargement
Region of maturation: it consists of matured cells and root hairs. Root hairs absorb water and minerals from the soil .
Functions of roots
1) absorption of water and minerals
2) provides anchorage
3) storage of reserved food particles
4) synthesis of plant growth regulators
Modification of roots A
Prop root: example BANYAN TREE
SStilt root : example MAIZE AND SUGARCANE
Modification of roots B
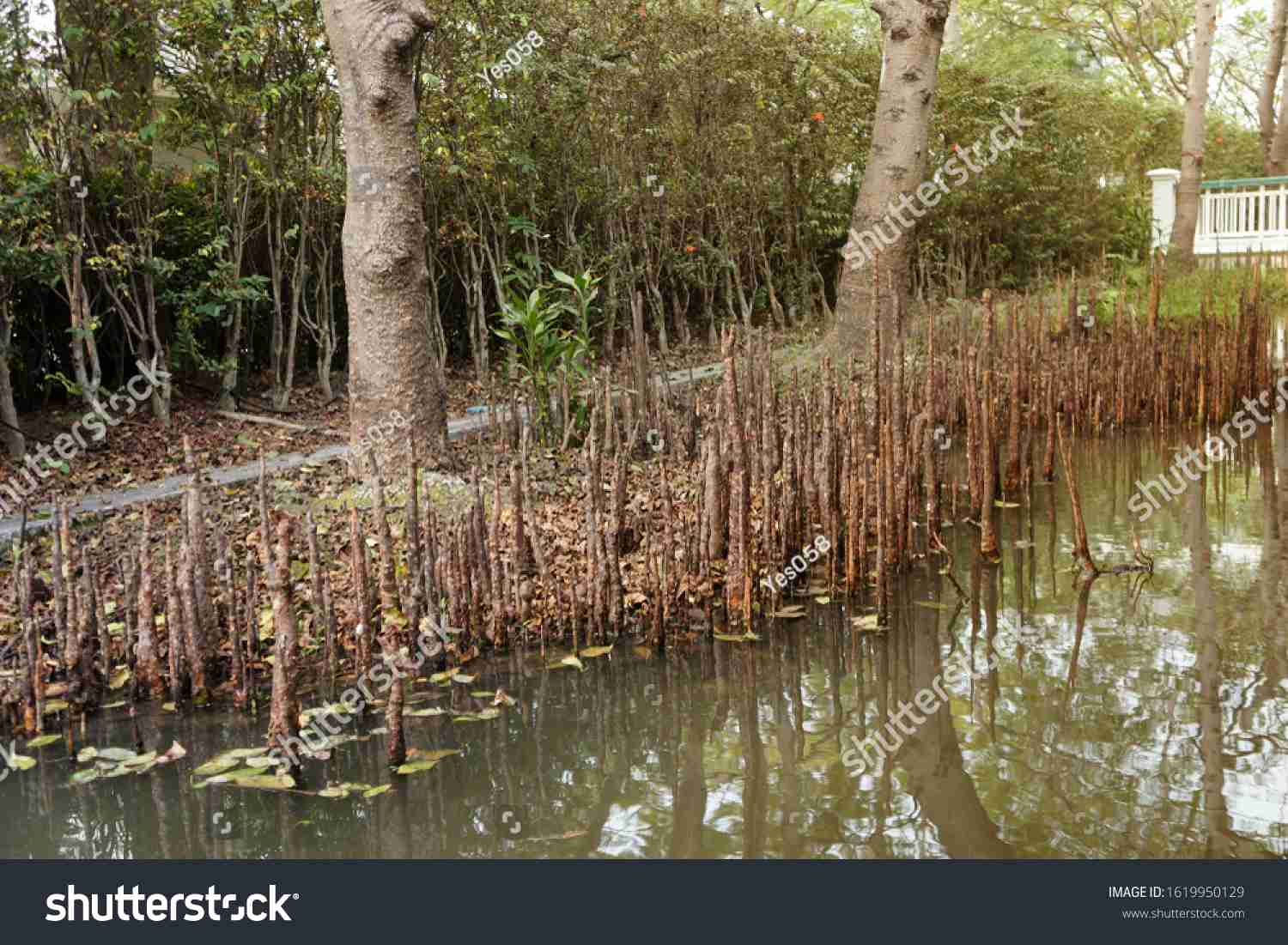
BREATHING ROOTS: Example is pneumatophora
They are found in rhizophora ,
This grows in swampy areas , many roots come out of the ground and grows vertically upward, this are called breathing roots , they have pneumatophora which helps to get oxygen.

Stem A
1)stem is a part of shoot system
2) It consists of branches leaves , fruits , flowers etc
3) it develops from plumule
4) stem bears nodes and internodes
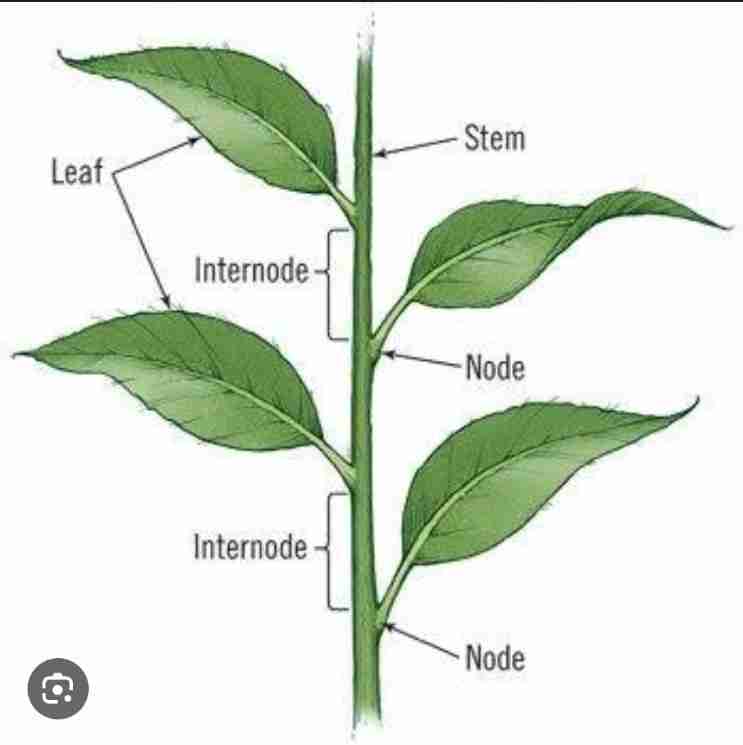
Stem B Nodes and Internodes
NODES: The region of stem where leaves are born
INTERNODE: The portion between 2 nodes
•Stems have terminal buds : apical bud and lateral bud.
Stem C functions of stem
1) Conduction of water and minerals
2) Conduction of food (photosynthates)
3) spreading out branches and bearing leaves flowers and fruits
3) storage of food , protection and vegetative propogation
Modification of stemA
Underground stem-stores food ,
Examples are : potato and ginger
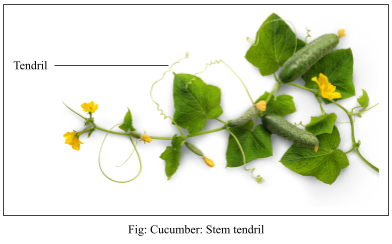
Stem tendril: develops from axillary bud , they are slender , spirally coiled and helps plants to climb
Examples are: cucumber and pumpkins
Thorns: develop from axillary buds, they are woody,straight and pointed , they protect plants from browsing animals.
Examples are: citrus and bougainvillea
Modification of stem B
Phylloclade
stems get modified into leaf like structure to perform photosynthesis and also storage
They are found in opuntia
Basal underground stem
Examples are banana and pineapple
Leaf A
Leaf is a lateral flattened structure borne on the stem
It develops from the auxiliary bud
It originates from the shoot apical meristems and are arranged in acropetal order
They are very important organs for photosynthesis.
Leaf consists of leaf base lamina and petiole

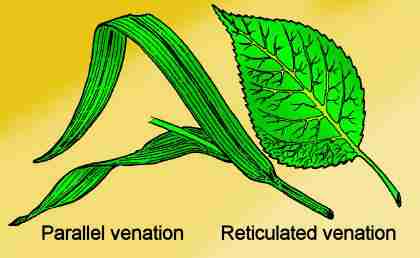
Leaf B venation
VENATION: Arrangement of veins and veinlets in the lamina of the leaf.
Venation are of 2 types
RETICULATE VENATION:when veinlets forms a network it is called as RETICULATE VENATION
It is found in dicotyledons
PARALLEL VENATION: Veins runs parallel to each other within the lamina it is called RETICULATE VENATION
It is found in monocotyledons
Types of leaves
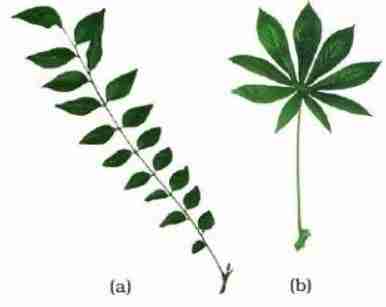
SIMPLE LEAF :when the lamina is incised the incision donot touch the midrib
COMPOUND LEAF: when the incision of the lamina reach upto the midrib breaking it to number of leaflets
Compound leaves are of two types
pinnately compound leaf: leaflets are present on the rachis in opposite manner .
Example is curry leaves
Palmately compound leaf : leaflets are attached on the rachis at a common point
Example is silk cotton
Diagram a: pinnately b: palmately
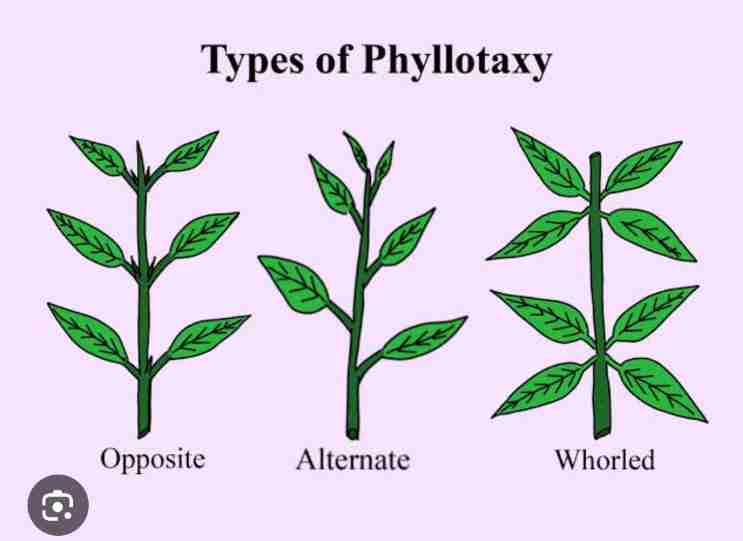
Phyllotaxy
Pattern of arrangement of the leaves on the stem
Alternate arrangement:single leaf arise at each node
Opposite arrangement: a pair of leaves arise at each node and lie opposite to each other
Whorled arrangement: more than two leaves arise at each node and forms a whorl
Modification of leaves
1) storage : onion
2) leaf tendril for climbing:peas
3) spines for defense : cacti
5) insectivorous plant : pitcher plant
Inflorescence A
It is the arrangement of flower in the floral axis
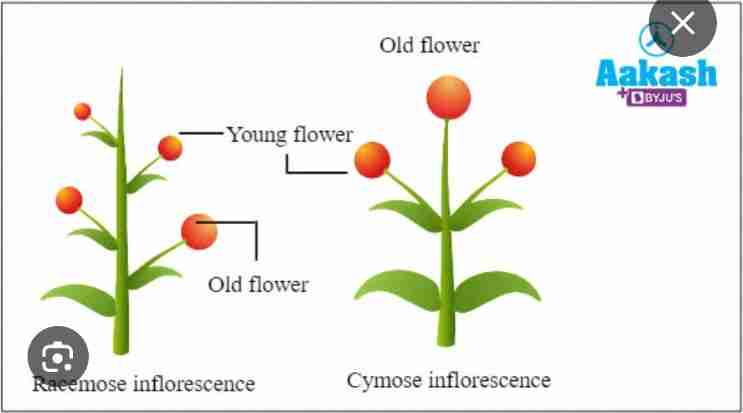
Inflorescence B types of inflorescence
RACEMOSE: younger flowers are present on the top and older flowers are present on the bottom
It is an acropetal succession
Main axis continues to grow
CYMOSE: older flowers are present on the top and younger flowers are present on the bottom
It is a basipetal succession
Main axis terminates into a flower
Flower
Flower is the reproductive unit of angiosperms.
It' is meant for sexual reproduction
Single flower is called as solitary flower
Group of flowers is called as inflorescence
Symmetry of a flower
ACTINOMORPHIC(RADIAL SYMMETRY)
When the flower can be divided into 2 equal half in any radial plane
ZYGOMORPHIC(BILATERAL SYMMETRY)
When the flower can be divided into 2 equal half in one particular plane
ASSYMETRIC
When a flower cannot be divided into any plane

Bract
Reduce leaf found at the base of pedicel
Bractate: flower with bract
Ebractate: flower without bract
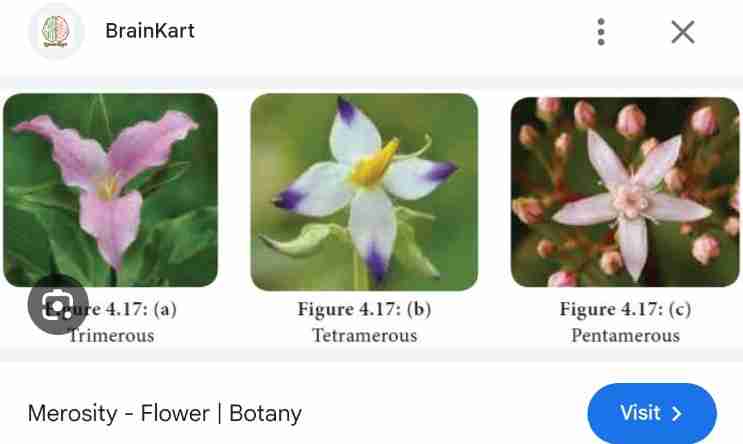
Merosity
No of floral appendages
Merosity is of three types : multiple of 3
2) tetramerous: multiple of 4
3) pentamerous: multiple of 5
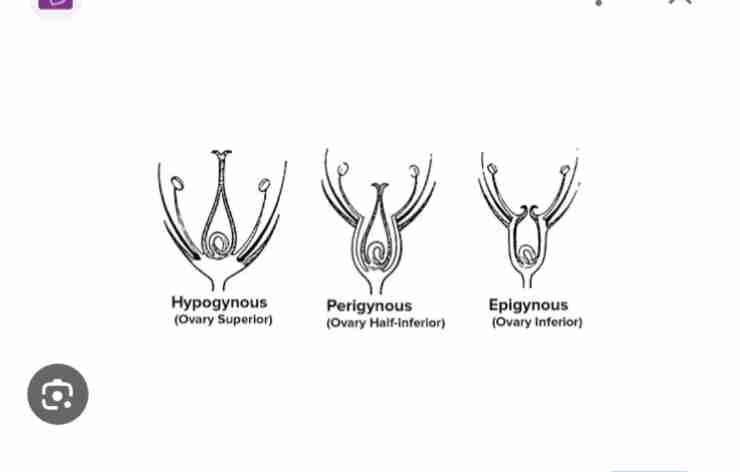
Based on the position of the calyx Corolla and androcium and ovary on the thalamus flower is divided into
Hypogynous : gynoecium occupies highest position and other Parts are located below it
Ovary is superior
Example is china rose
Perigynous: gynoecium is situated in the centre other parts are on the rim of the thallamus
Ovary is half inferior
Example is rose
Epigynous: margin of the thallamus grows upward enclosing the ovary completely and fuses with it
Ovary is inferior
Example is guavva
Flower( 4 floral whorls ) A
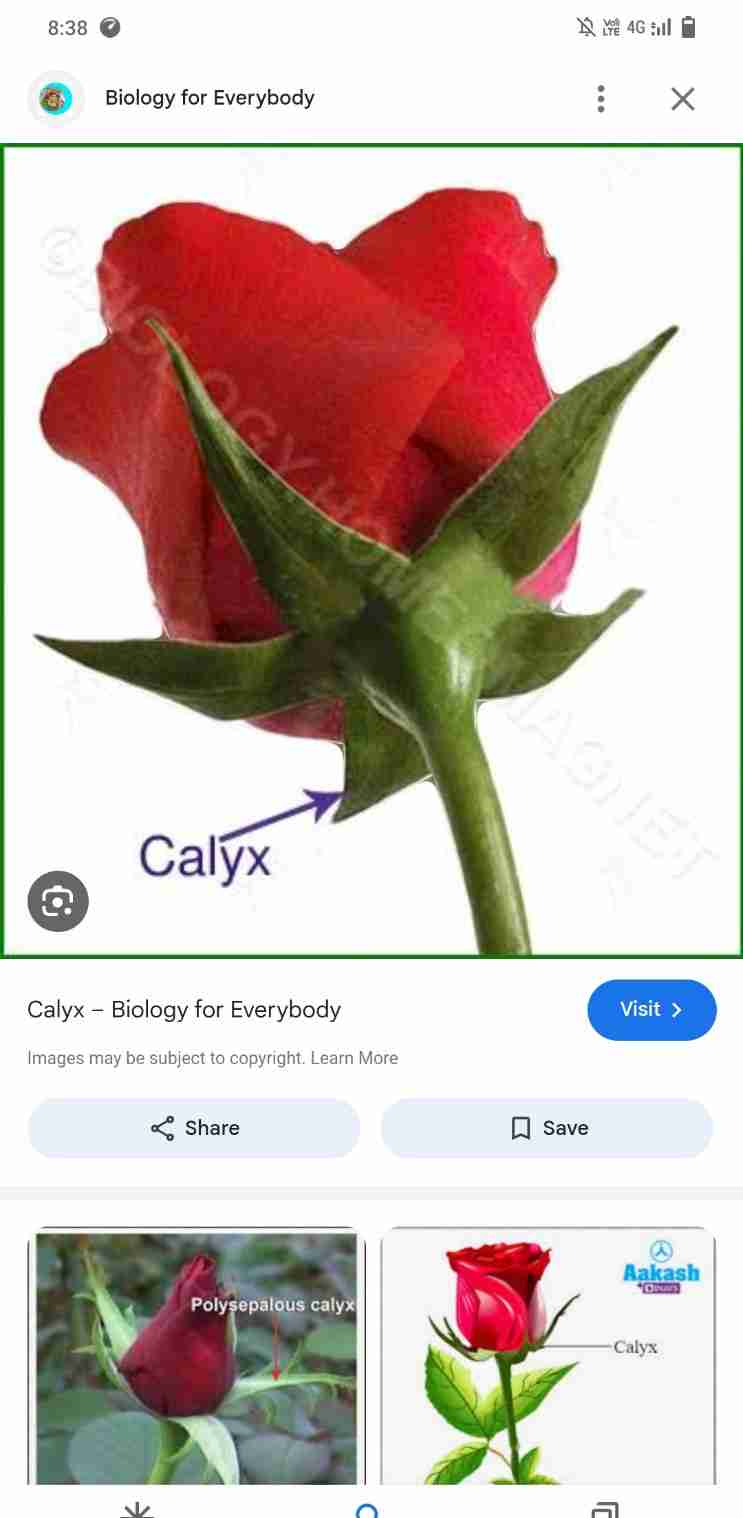
Calyx
Calyx is called sepals
It's is the outermost whorl
It is the green leaf like and protects the flower in the bud stage
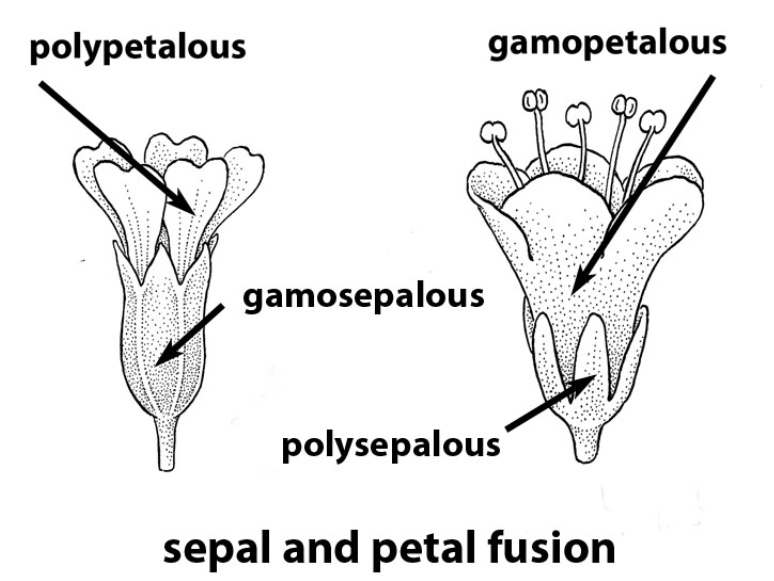
calyx can be divided into two types
1) polysepalous : free sepals
2)gamosepalous : United sepals

Flower B
Corolla
It's is bright coloured to attract the insects
Colour and shape varies
It' can be funnel tubular or bell shaped
Corolla can be divided into 2 types
1)polypetalous : free petals
2) gamosepalous: United petals

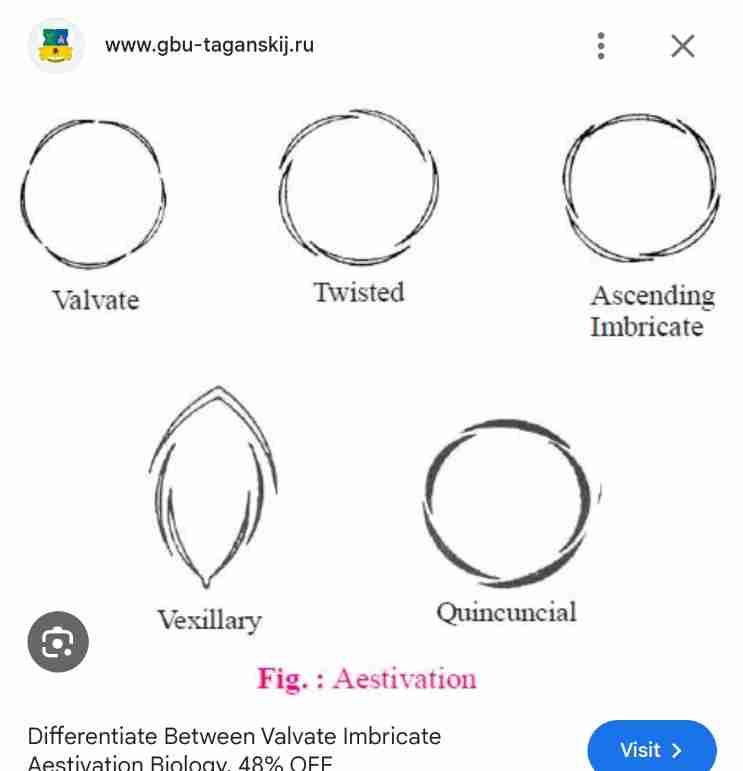
Aestivation A
Is the arrangement of sepals and petals in the floral bud with respect to the other members of the whorl
Aestivation B
Types of aestivation
Valvate
Twisted
Imbricate
Vexillary
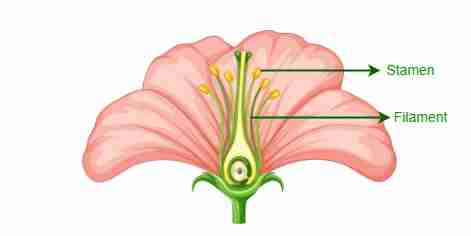
Androecium
It is called stamen
It is a male reproductive structure
Stamens can be divided into
1) anther
2) filament
Anther is a bilobed structure with two pollen sacs in each lobe
Stamens when attached to Corolla (petals)
They can be divided into two types
Epipetalous: stamen attached on petals
Example is brinjal
Epiphyllous : stamen attached on the perianth
Example is flowers of Lilly
Free stamens are called polyandrous
United stamens can be divided into 3 types
1)monodelphous: 1 group example is china rose
2)diadelphous: 2 groups example is pea
3) polydelpus: 3 or more groups example is citrus
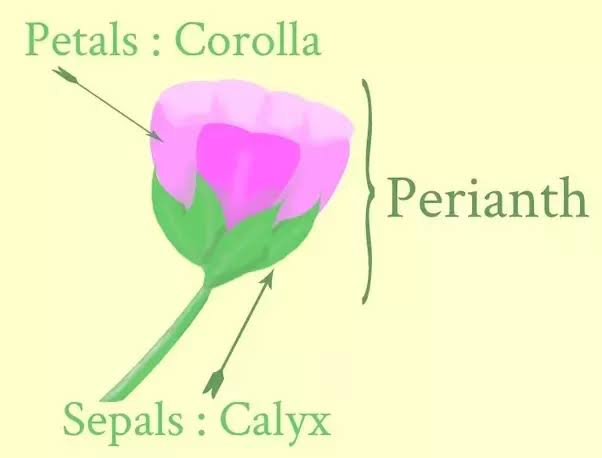
Perianth
In some flowers calyx and Corolla are not distinct and are termed as perianth
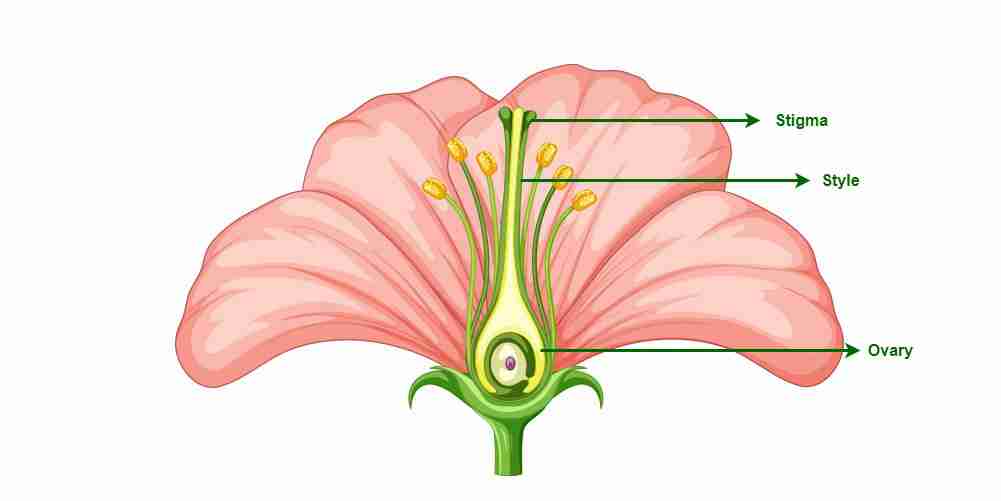
Gynoecium
It is called as carpel
Carpel consists of 3 parts
1) stigma: present on the tip , and it receives the pollen grain
2)style : connects stigma and ovary
3) ovary: swollen basal part , it consists of one or more ovules connected to the inner wall of ovary and is called placenta
Placentation
Arrangement of ovules within the ovary
Types of placentation
1) marginal: ovules are arranged on the margin
Example is green peas
2) axile: ovules are present at the axis of carpel
Example is lemon
3) pariental : ovules are present at the inner wall
Example is papaya
4) free Central : ovules are present at the Central axis
Example is capsicum
5)basal : single ovule attached at the base
Example is avacado