Rocks, the rock cycle, fossils, and the Geologic Time Scale
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
compaction & cementation
This happens when sediments become a solid rock. (example: sand becomes sandstone)
heat and pressure
These are two geological forces that change other rock types into metamorphic rock.
weathering, erosion & deposition
This happens when rocks are worn down, broken apart or when parts of rocks are relocated in a pile of sediments. These processes will eventually create new sedimentary rock.
magma
This is molten rock inside of a volcano.
lava
This is molten rock that flows out of volcano.
melting
This force happens when solid rock turns into a hot liquid.
crystallization
When molten rock cools sometimes this happens The slower it cools, the larger these become, the faster it cools, the smaller these become.
marble
This metamorphic rock is formed when limestone is subjected to tremendous heat and pressure.
slate
This metamorphic rock is formed when shale is subjected to tremendous heat and pressure.
basalt
This extrusive igneous rock is very common and makes up most of the seafloor.
granite
This intrusive igneous rock is very common and has 3 minerals in it: feldspar, quartz, and mica.
organic rocks
These sedimentary rocks are formed from the sediments of once living organisms. (Examples: coal and limestone.)
Igneous rocks are classified according to ...
their origin, texture, and mineral composition.
The process of the rock cycle forms a pattern of pathways. This results from ___________ , tremendous heat and pressure, and melting.
weathering, erosion, deposition, earthquakes, and volcanic activity
Earth's crust is broken up into masses called _______.
tectonic plates
Weathering, erosion, and deposition of rock on earth's surface leads to the formation of what type of rock?
sedimentary rock
Any rock that is melted then becomes what rock type?
igneous rock
Identify 2 types of sedimentary rock
possible answers: sandstone, limestone, coal, breccia, conglomerate, shale
Identify 2 types of igneous rock
possible answers: basalt, obsidian, pumice, granite
Identify 2 types of metamorphic rock
possible answers: slate, marble, schist, gneiss (nice!), metaconglomerate
What is the only rock type to contain fossils?
sedimentary
What are the cavities/holes in igneous porous rock called?
vesicles
What is Ms. Ryan's favorite rock sample (hint: it is a sedimentary rock)?
Conglomerate (sedimentary)
The Hawaiian islands are mostly composed of what rock type?
igneous
What are the two types of igneous rock?
intrusive and extrusive
Slow cooling magma and lava creates ____
larger grains and larger crystals
Rapid and fast cooling magma and lava creates_______
small grains and small crystals, like the rock granite
Describe extrusive rock:
A rock that forms outside the earth's crust; does contains few or no crystals...small, barely visible particles
Describe intrusive rock:
A rock that forms inside the earth's crust; often has crystals or visible particles
Variegation (rock)
Different colors present in the form of patches or bands
Abrasion
The grinding away of rock by other rock particles carried in water, ice, or wind. Example: Wind lifts and carries sediment in a sandstorm and carves/ smoothes rock formations.
geology
What is the study of Earth's layers and materials?
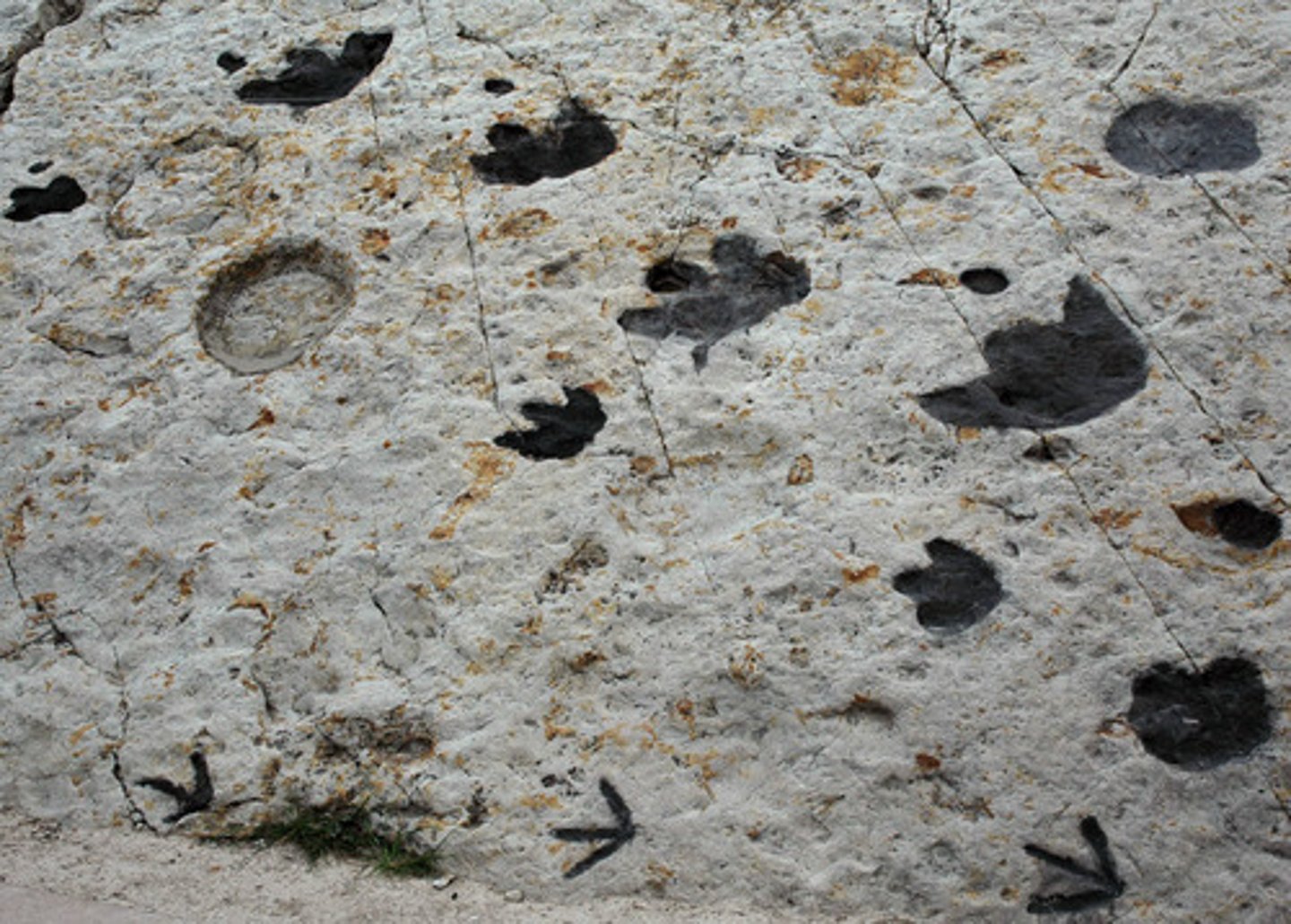
fossils
The physical remnants of an organism that lived more than 10,000 years ago.
sedimentary
What rock type can we find fossils?
body fossils, trace fossils
What are the two main types of fossils?
trace fossils
Foot prints, a nest, and animal dung (poo) are examples of what kind of fossil?

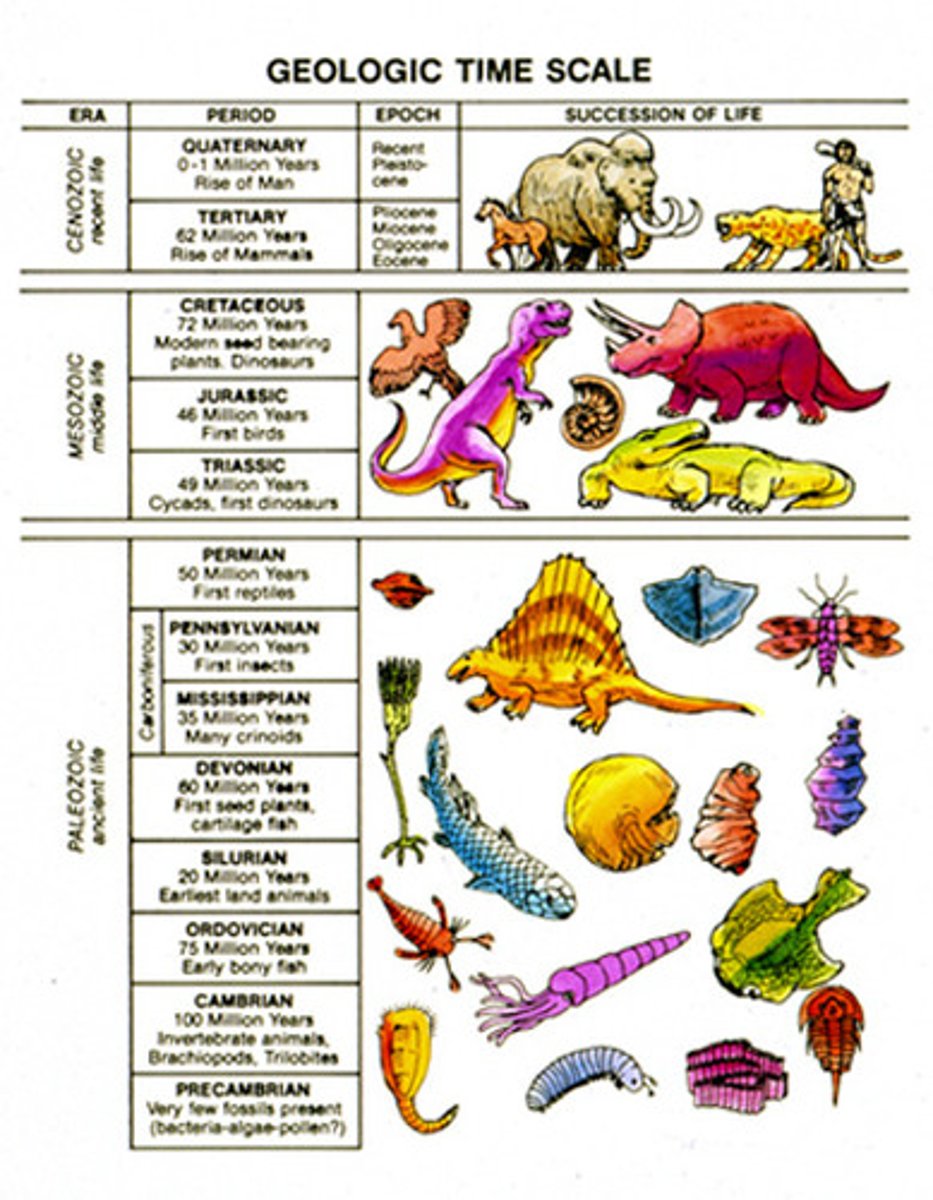
geologic time scale
A time scale established by geologists that reflects a consistent sequence of historical periods, grouped into four eras: Precambrian, Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic.

half life
What is the time it take for half of the atoms in a radioactive element to break down?
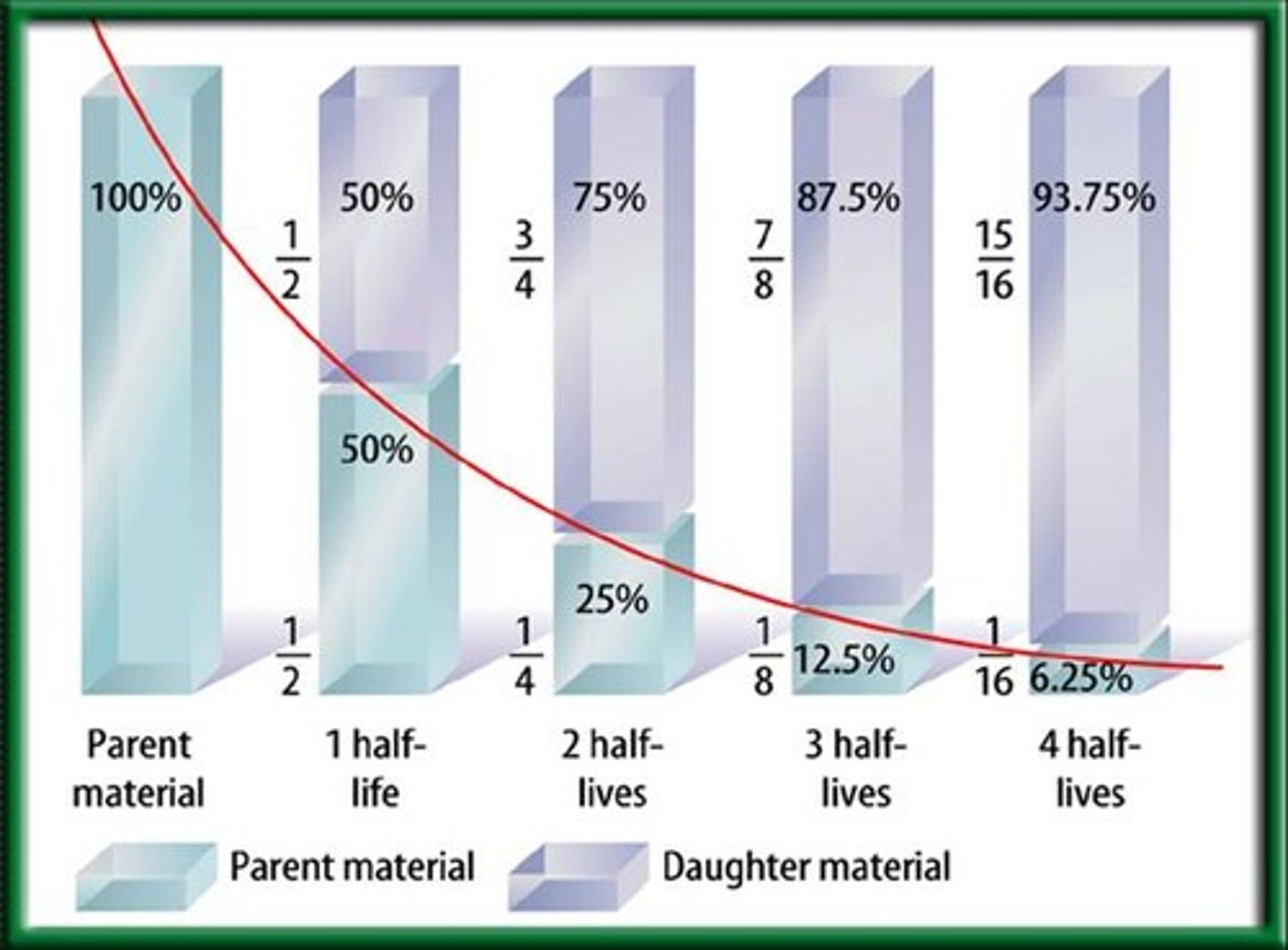
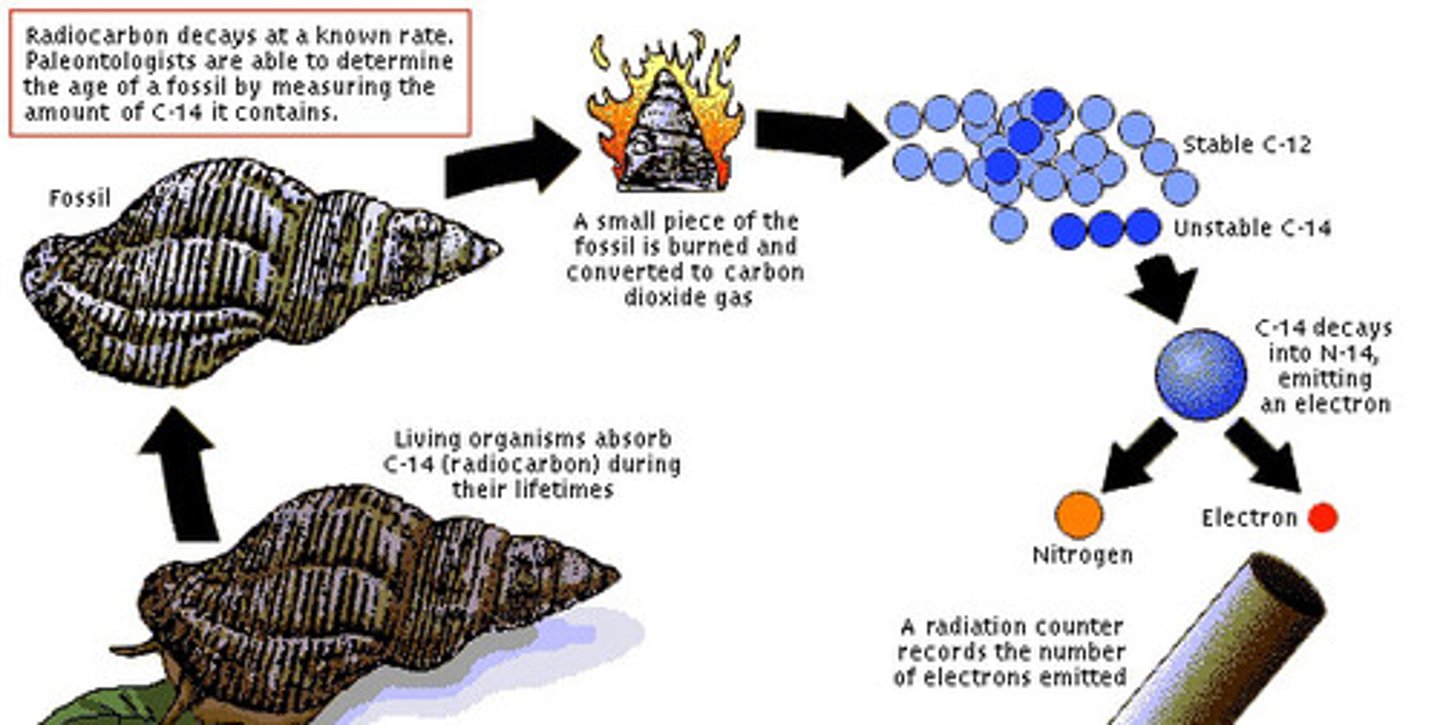
radiometric dating
the process of measuring the absolute age of geologic material by measuring the concentrations of radioactive isotopes and their decay products. This is also used to determine the absolute age of fossils and rock.
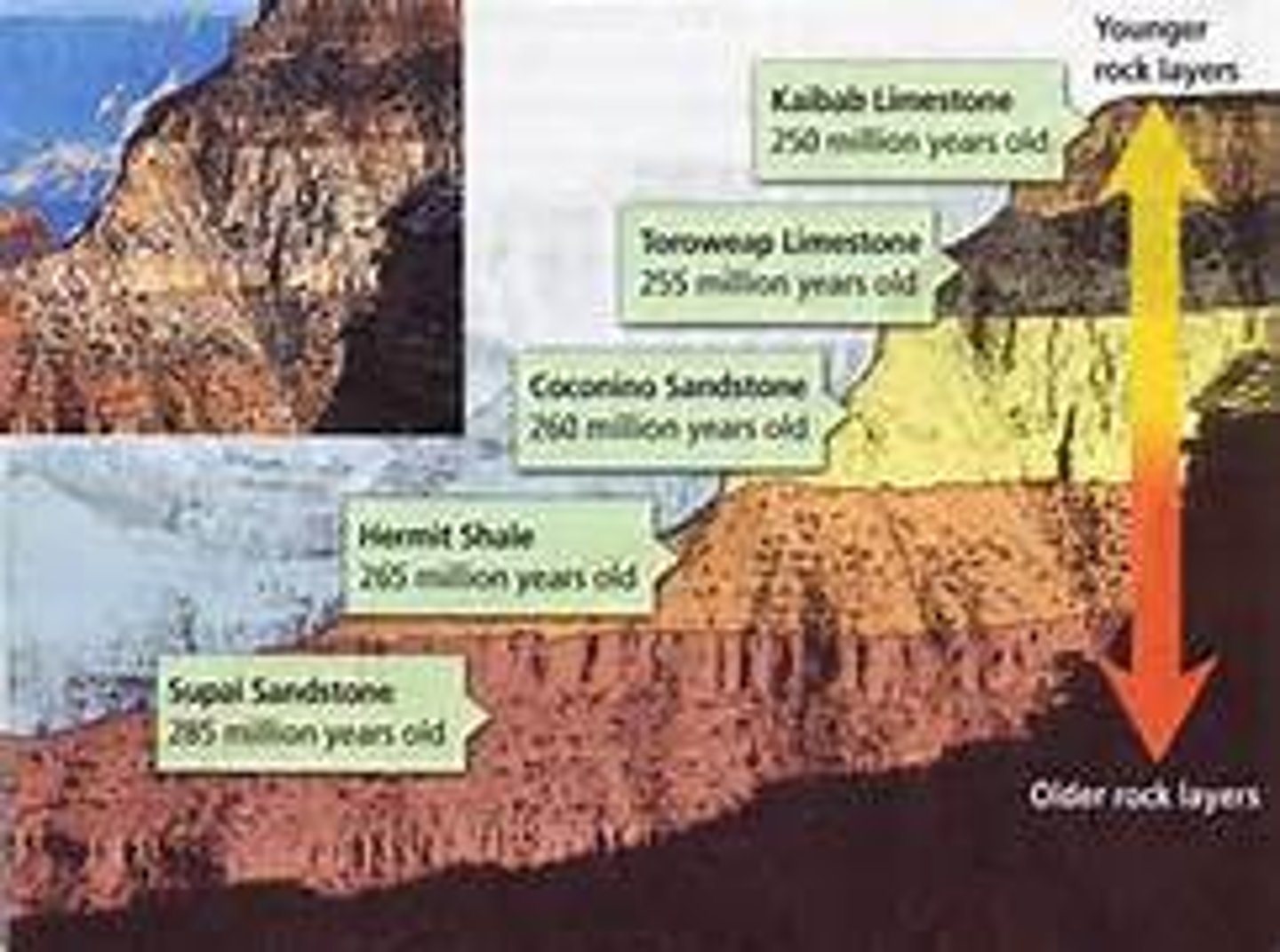
law of superposition
What is the principle that states younger rocks lie above older rocks if the layers have not been disturbed?
uniformitarism
What is the principle that states geologic processes that occurred in the past can be explained by current geological processes?
Eons
In the geological time scale which division of time is the largest? Hint: someone could exaggerate by saying that something happened a long time ago if it was ______ ago"
Cenozoic
What era do we currently live in right now? This is known as the age of mammals

period
Many epochs make up one...?
False, you need radiometric dating to determine absolute age.
We can determine the actual (absolute) age of a fossil using relative dating. True or False?
An ocean or coral reef
If many rocks were found in an area that were made of limestone (a type of sedimentary rock) what earth feature was in that particular location millions of years ago?
mass extinction
Many fossils or various plants and animals were found in one location, all in the same layer. What does this information tell us?
law of superposition
Which law of relative dating states that under "normal conditions" older layers will form toward the bottom and younger layers will form form toward the top?
Fault
What formation is at E?
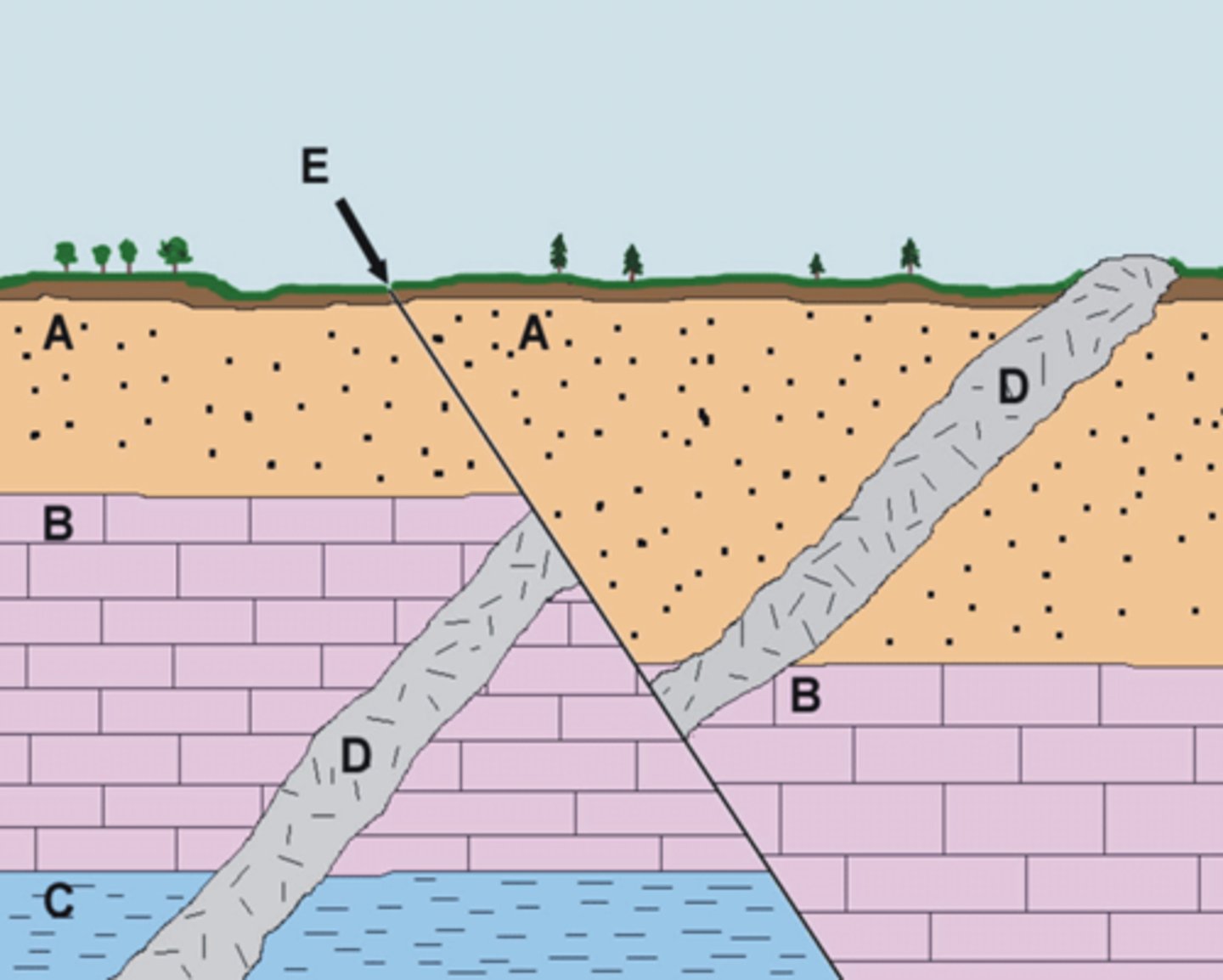
Layer C
What layer is the oldest
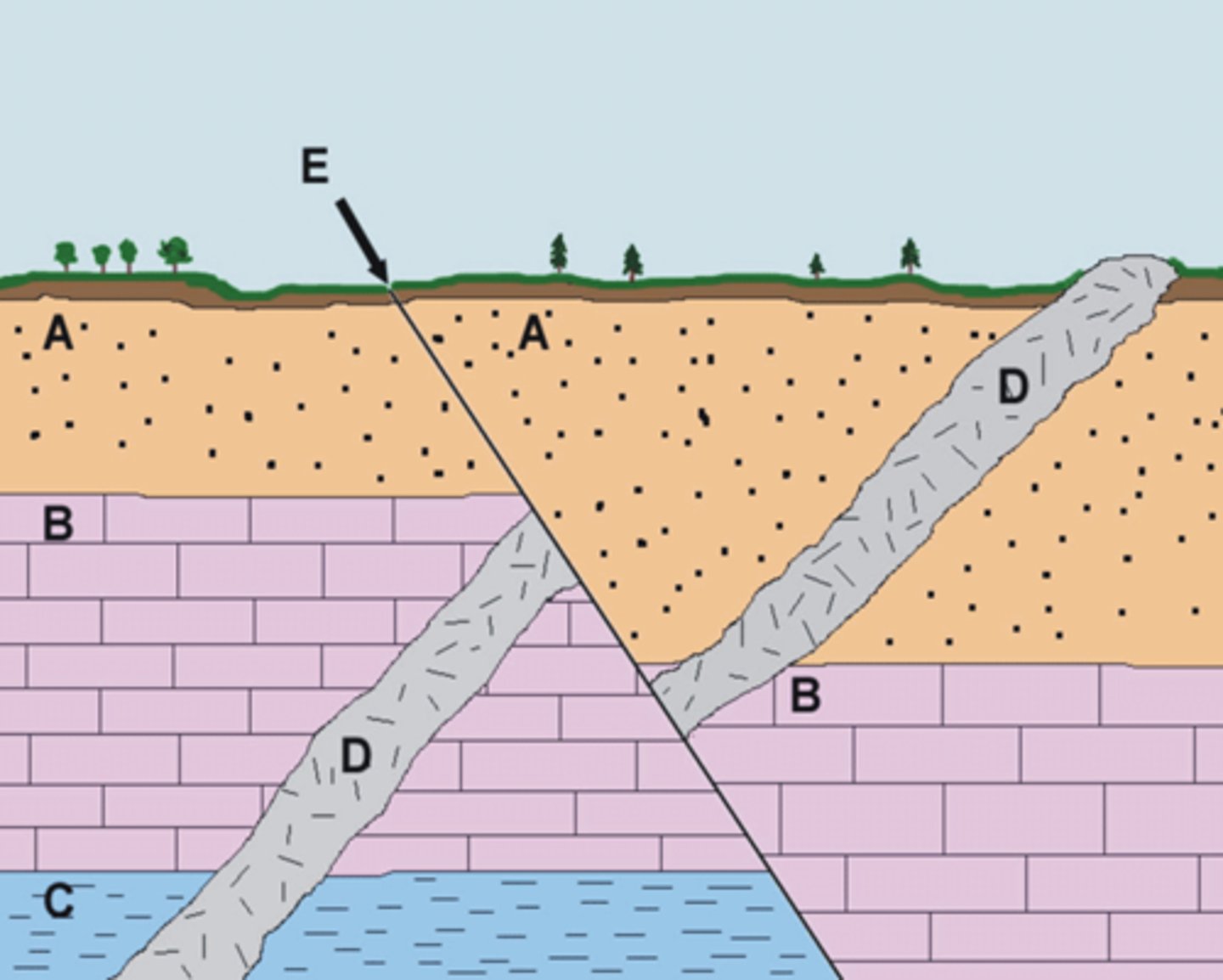
an intrusion of magma
What is labeled D?
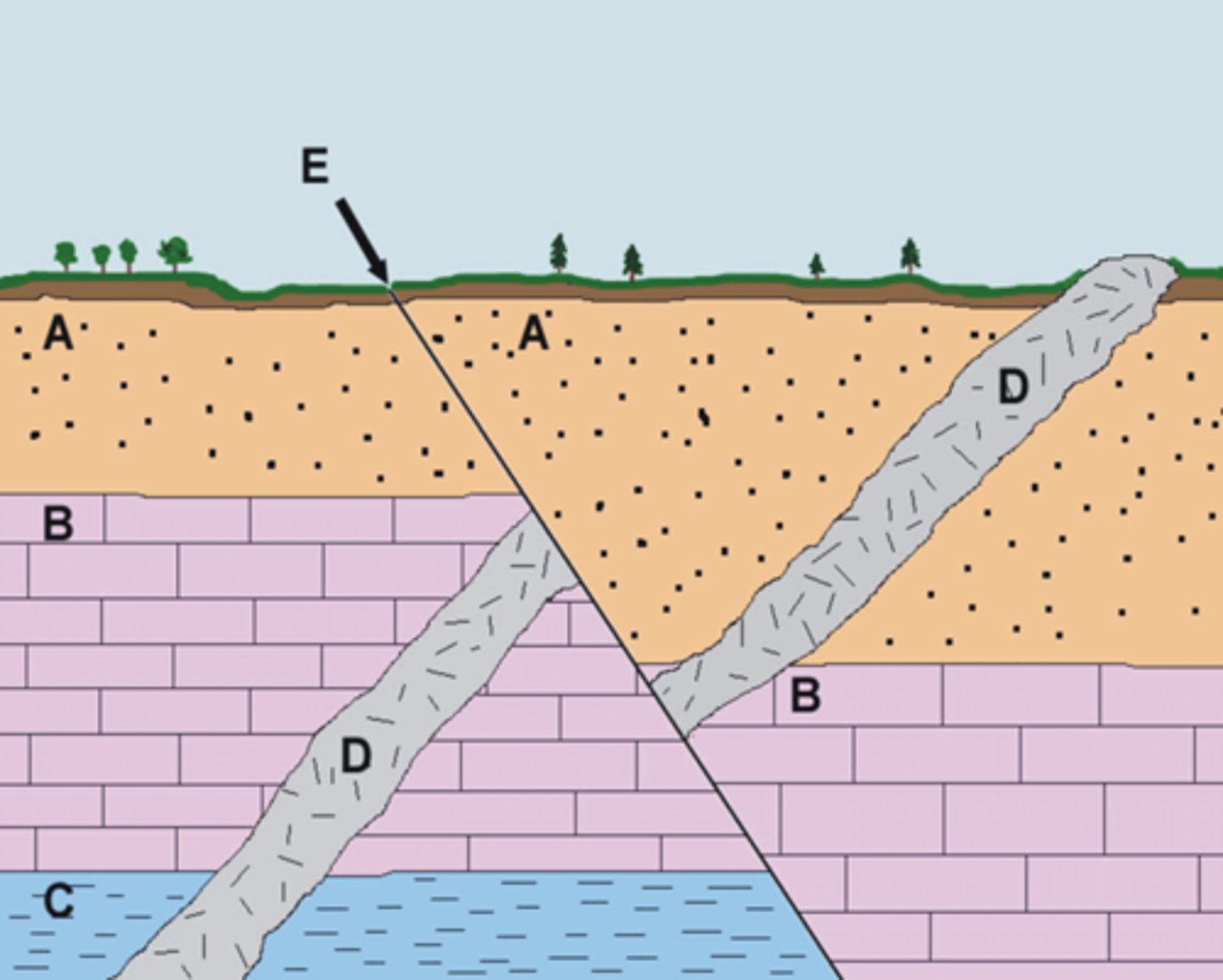
Quaternary
What period do we live in?
What layer of a rock is the oldest?
The bottom layer
The (blank) of a rock is the number of years that have passed since the rock was formed.
Absolute age
Relative age (rock)
the age of a rock compared with the ages of the other rocks
According to (blank) the oldest layer is at the bottom.
Law of superposition
Intrusion (rock)
a hardened layer of magma beneath earth's surface
Extrusion (rock)
a hardened layer of lava above earth's surface
index fossil
a fossil known to have lived in a particular geologic age that can be used to date the rock layer in which it is found

Precambrian Era
The oldest and longest Era. It covers 90% of Earth's history, life appears as basic single celled organisms and simple multicellular organisms evolve. Life exists only in the sea.
Strata
"layers" of rock, representing various periods of deposition

Weathering
The breaking down of rocks and other materials on the Earth's surface.

Erosion
The process by which wind, water, ice, or gravity transports soil and sediment from one location to another
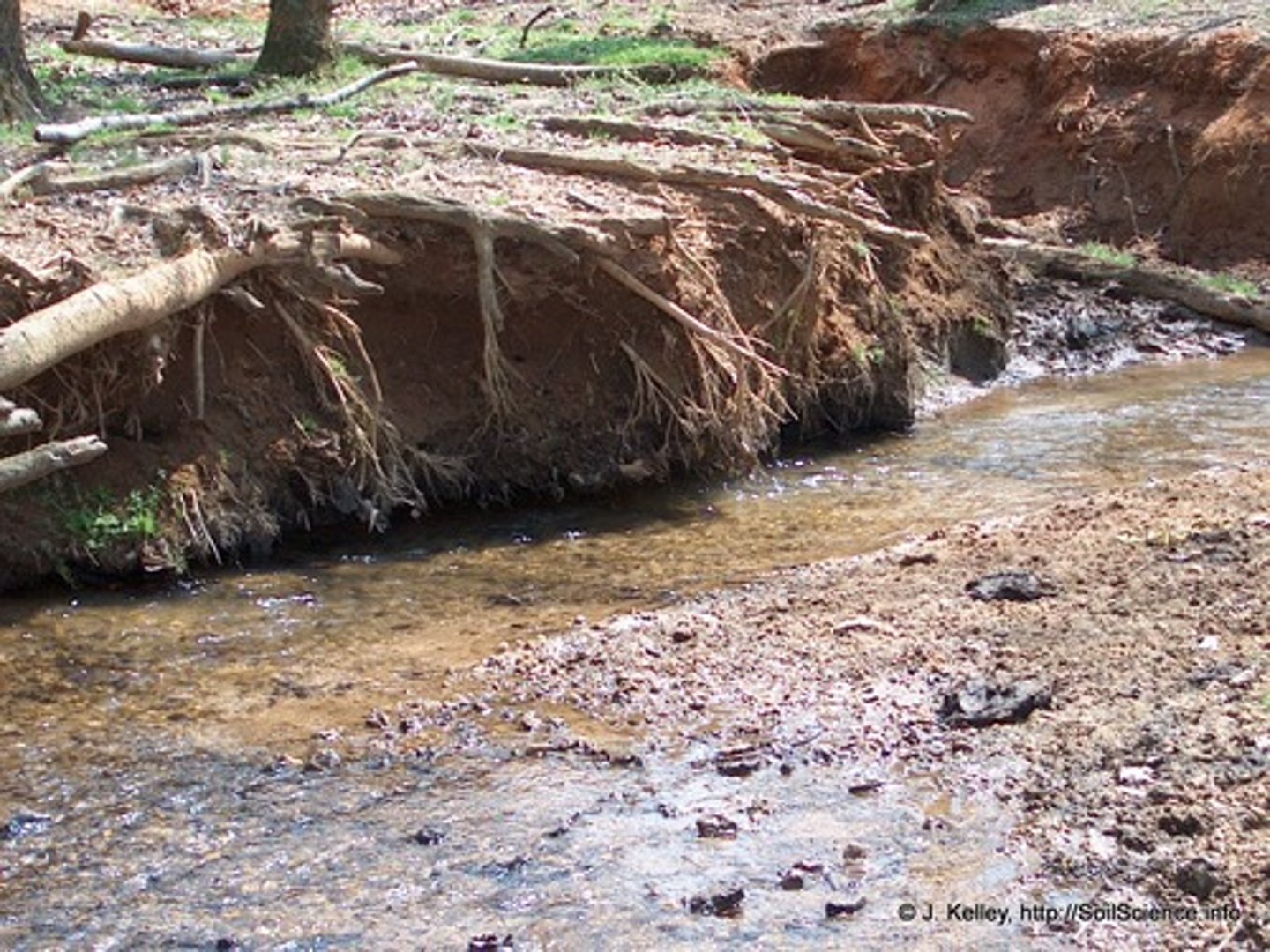

Deposition
Process in which sediment is laid down in new locations.

True or False: Most organisms in Earth's history have been preserved as fossils
False, there many gaps in the fossil record of organisms that we may never find fossils of. More than 99% of life on Earth does not get fossilized.
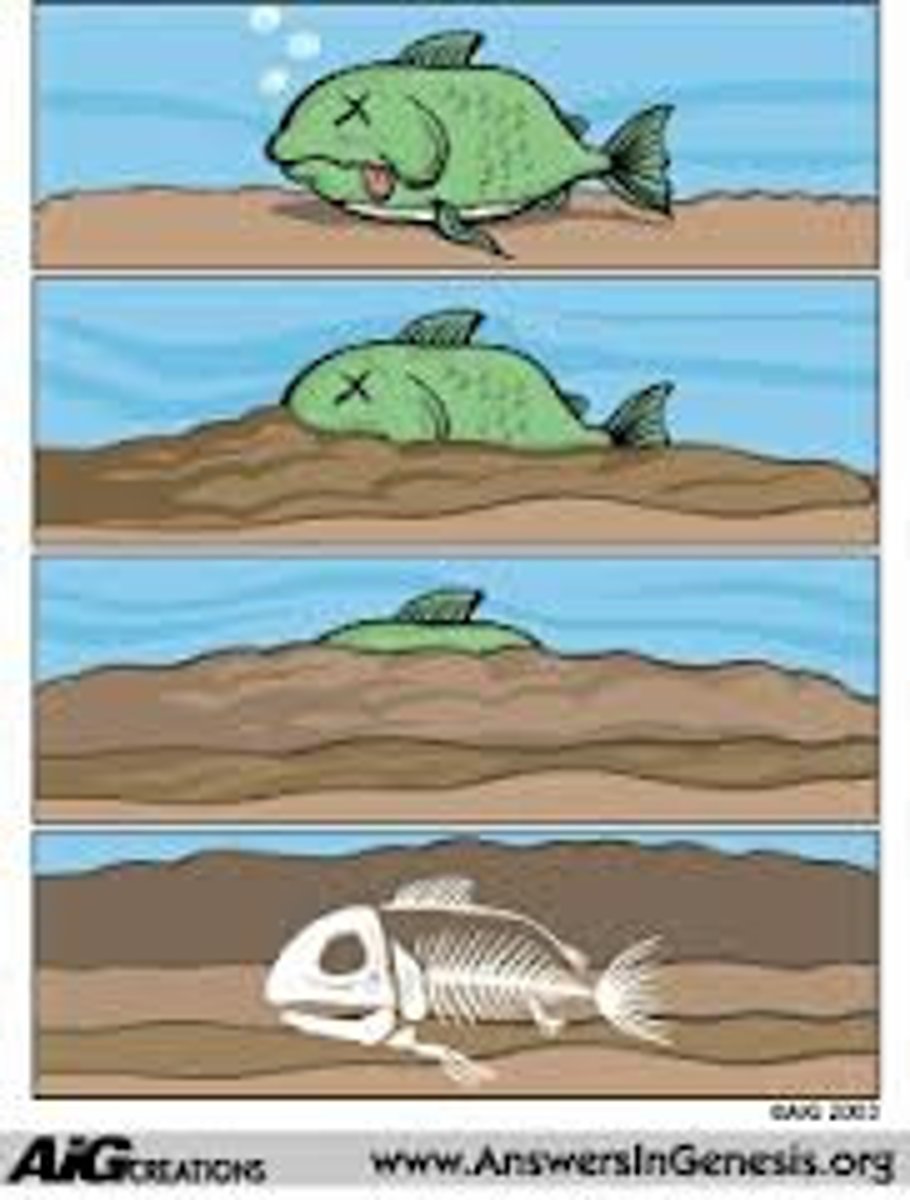

When did life first appear in the rock record?
The earliest life forms we know of were microscopic organisms (microbes) that left signals of their presence in rocks about 3.7 billion years old. This was during the Precambrian era.
Mineral
a naturally occurring, inorganic (abiotic) solid that has a crystal structure and a definite chemical composition

Law of Uniformitarianism
the idea that the same processes we see occurring now also occurred in the past
Chemical weathering
the process by which rocks break down as a result of chemical reactions
