Histology and Epithelial Tissue: Key Concepts and Classifications
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Histology
The scientific study of the microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues of plants and animals.
Epithelial Tissue
A sheet of cells that covers body surfaces or lines body cavities.
Connective Tissue
A diverse group of tissues that binds, supports, and protects other tissues, composed of cells and a large amount of extracellular matrix.
Muscle Tissue
Specialized tissue capable of contraction, which produces movement.
Nervous Tissue
Specialized tissue that generates and transmits electrical signals to coordinate body functions.
Cellularity
The density of cells in a tissue; high in epithelial, muscle, and nervous tissues, and low in connective tissue.
Extracellular Matrix
The non-cellular component present in connective tissue, abundant in connective tissue and very little in epithelial, muscle, and nervous tissues.
Vascularity
The presence of blood vessels; avascular in epithelial tissue and highly vascular in connective, muscle, and nervous tissues.
Main Function of Epithelial Tissue
Covering/Lining, Absorption, Secretion, Protection.
Main Function of Connective Tissue
Binding, Support, Protection, Transport.
Main Function of Muscle Tissue
Contraction to produce movement.
Main Function of Nervous Tissue
Communication and control.
Cell Junctions
Points of contact between cells that hold them together and allow for communication.
Tight Junctions
A series of integral proteins that fuse the outer surfaces of adjacent cell membranes, acting as a barrier to prevent substances from passing between cells.
Desmosomes
Protein complexes that act like 'spot welds' or rivets, linking adjacent cells and providing strong mechanical support.
Gap Junctions
Channels formed by connexon proteins that connect the cytoplasm of adjacent cells, allowing for the rapid passage of ions and small molecules.
Polarity in Epithelial Cells
Epithelial cells have a top (apical surface) and a bottom (basal surface), with specialized structures like cilia or microvilli on the apical surface.
Specialized Contacts in Epithelia
Cells are held together by tight junctions and desmosomes, forming continuous sheets.
Supported by Connective Tissue
All epithelial tissues rest on and are supported by an underlying layer of connective tissue.
Avascular but Innervated
Epithelia have no blood vessels but do have a nerve supply.
Regeneration
Epithelial tissue has a high capacity to regenerate, replacing cells lost to damage or friction.
Exocrine Glands
Have ducts that carry secretions to a surface; secretions are released onto a body surface or into a body cavity.
Endocrine Glands
Are ductless; secretions (hormones) are released directly into the bloodstream.
Merocrine Secretion
The gland secretes its product via exocytosis; the cell remains intact and healthy.
Apocrine Secretion
A portion of the cell's apical surface, containing the secretory product, pinches off and is released; the cell repairs itself.
Holocrine Secretion
The entire cell accumulates the secretory product and then ruptures, releasing the product and the cell's contents; the cell dies and is replaced.
Simple Epithelial Tissue
A single layer of cells.
Stratified Epithelial Tissue
Two or more layers of cells.
Pseudostratified Epithelial Tissue
A single layer of cells that appears to be multiple layers because the cell nuclei are at different levels.
Squamous Cells
Flat, scale-like cells.
Cuboidal Cells
Cube-shaped cells.
Columnar Cells
Tall, column-shaped cells.
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Simple, flat; located in alveoli of lungs and lining of blood vessels; function is rapid diffusion and filtration.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Simple, cube-shaped; located in kidney tubules and ducts of small glands; function is secretion and absorption.
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Simple, column-shaped; located in lining of the small intestine, stomach, and gallbladder; function is absorption and secretion of mucus and enzymes.
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Pseudostratified, column-shaped; located in lining of the trachea and upper respiratory tract; function is secretion (of mucus) and propulsion (by cilia).
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Stratified, flat; located in outer layer of skin (keratinized) and lining of the mouth and esophagus (non-keratinized); function is protection against abrasion.
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Stratified, cube-shaped; located in ducts of sweat glands and mammary glands; function is protection.
Transitional Epithelium
Stratified, varied shapes; located in lining of the urinary bladder and ureters; function is to stretch to allow for distension of the organ.
Bone
Bone is a type of connective tissue, not a primary tissue type itself.
Desmosome
Prevents cells from being pulled apart.
Gap Junction
Allows electrical stimulation to pass from cell to cell.
Tight Junction
Makes sure substances do not pass between the intestinal cells.
Capsule
Most glands are enclosed in a fibrous capsule.
Lobes
The glands are divided into lobes by connective tissue septa.
Stroma
The glandular tissue is supported and organized by the stroma, made of connective tissue.
Parenchyma
The parenchyma, typically made of epithelial tissue, carry out the functions of the gland.
Exocrine
The general term for glands that secrete their products directly into ducts is exocrine.
Endocrine
Glands that have lost contact with a body surface are called endocrine, and secrete their products into capillary rich interstitial spaces for quick distribution throughout the body.
Epithelial tissue classification
Epithelial tissue can be classified according to cell shape and number of layers.
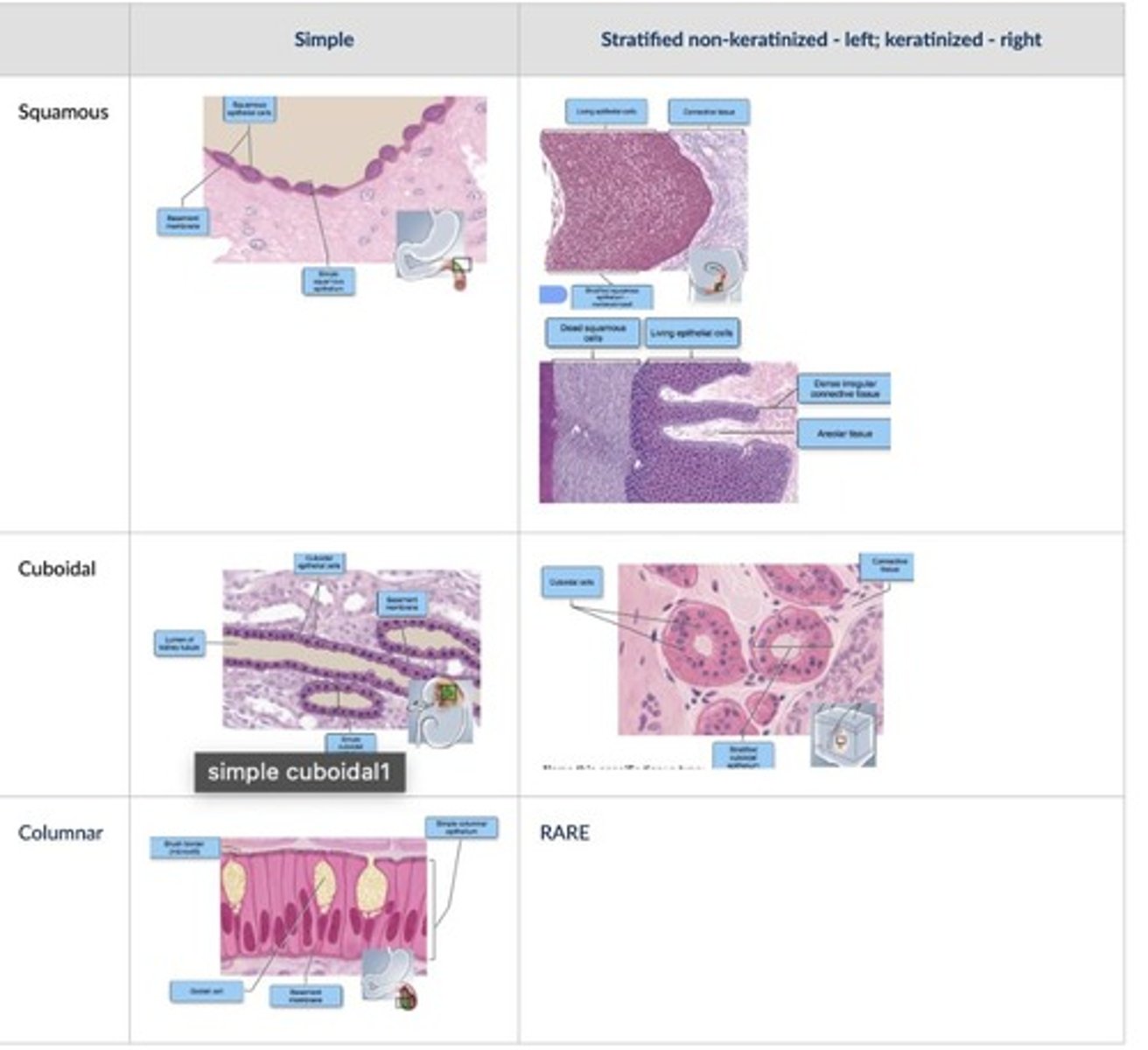
Simple
One layer of cells is called simple, and more than one layer is called stratified.
Squamous
Thin, flat, scaly cells are squamous.
Cuboidal
Cuboidal cells are cube in shape.
Columnar
Columnar cells are taller than they are wide.
Pseudostratified cells
Pseudostratified cells look like more than one layer because of the arrangements of the cells' nuclei.
Stratified columnar
Stratified columnar is the least widespread stratified epithelium in the body.
Stratified cuboidal
Stratified cuboidal lines the ducts of sweat glands.
Stratified squamous
Stratified squamous covers the surface of the skin.