BIO 211-Lecture Test 2
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Capillaries
What are the smallest type of blood vessels?
Left atrium
Which chamber of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the lungs?
Oxygenated
The left atrium receives oxygenated or deoxygenated blood from the lungs?
4
How many veins carry oxygen rich blood from the lungs?
Pulmonary veins
What type of veins carry oxygen rich blood from the lungs?
4 pulmonary veins
What carries oxygen rich blood from the lungs?
Right ventricle
Which chamber of the heart pumps oxygen poor blood into the pulmonary trunk?
Left ventricle
Which chamber of the heart pumps oxygen rich blood into the aorta?
To pump blood throughout the body with greater distance with increased pressure
The left ventricle has to have a much thicker wall for what reason?
It has much thicker walls
What is special about the left ventricle?
Atrioventricular (AV) valves
What prevents backflow into the atria when the ventricles contract?
2
How many atrioventricular (AV) valves are there that prevent backflow into the atria when the ventricles contract?
To prevent backflow into the atria when the ventricles contract
What is the purpose of the atrioventricular (AV) valves?
The left internal carotid artery
What carries oxygenated blood to the brain?
To carry oxygenated blood to the brain
What is the purpose of the left internal carotid artery?
Coronary arteries
Coronary circulation happens via what?
Coronary circulation
What is the shortest circulation in the body?
Left ventricle
Within coronary circulation, which chamber of the heart receives most of the coronary blood supply?
Coronary circulation
What is the functional blood supply to the heart muscle itself?
Striated, short, branched, fat, and interconnected via intercalated discs
Cardiac muscle cells can be categorized as?
True
Cardiac muscle cells are synchronized in their contractions, true or false?
Depolarization of the atria
A P wave on an EKG signifies what?
Ventricular filling
Blood that passively flows from the atria through open AV valves into the ventricles is known as?
Volume of blood in each ventricle at the end of ventricular diastole
What does the end diastolic volume (EDV) mean?
End Diastolic Volume (EDV)
The volume of blood in each ventricle at the end of ventricular diastole is called what?
Volume of blood remaining in each ventricle after systole
What does the end systolic volume (ESV) mean?
End systolic volume (ESV)
The volume of blood remaining in each ventricle after systole is called what?
"Lub-dub"
What sounds are associated with the closing of heart valves?
EDV-ESV
How do you calculate stroke volume (SV)?
Stroke volume (SV)
EDV-ESV= what?
203 mL
If EDV=350 mL and ESV=147 mL, what is the stroke volume?
HR x SV (heart rate x stroke volume)
How do you calculate cardiac output (CO)
5.25 L/min
If HR=75 bpm and SV=70 mL, what is the CO?
Cardiac Output (CO)
HR X SV=what?
5.2 L/min
A patient has a HR of 80 bpm and a SV of 65 mL, what is their CO?
74 mL
A patient has an EDV of 200 mL and an ESV of 126 mL, what is their SV?
Blood flow to entire vascular system
What is proportional to CO?
Cardiac Output (CO)
Blood flow to the entire vascular system is proportional to what?
Skeletal muscle
Veins have less pressure to transport blood towards the heart so they are compressed by what to increase flow?
Skeletal muscle
What increases the flow of veins to move blood towards the heart?
Gas exchange
What takes place at the capillaries?
Resistance to blood flow
Blood viscosity can lead to what?
Increased resistance to blood flow
An increase in blood viscosity equals what?
Arterioles
What are the major determinants of peripheral resistance?
The smooth muscle in the walls of arterioles relaxes
Vasodilation occurs when?
Increase of the size of the lumen which decreases resistance
What is the result of vasodilation?
Decrease
Does vasodilation increase or decrease resistance?
Skeletal muscle, skin, and the heart
Blood flow is increased during exercise to what specific areas/structures of the body?
Kidneys and abdomen
Blood flow is decreased during exercise to what specific areas/structures/organs of the body?
Brain
Blood flow remains the same during exercise to what organ?
Alveoli
Where does gas exchange occur within the respiratory system?
Alveoli
What structure within the respiratory system have great surface area?
Elastic cartilage
The epiglottis consists of what type of tissue?
Hyaline cartilage
The epiglottis is not consisted of what type of tissue?
C-shaped cartilage rings
What maintains the trachea's patency?
Surfactant
Type 2 alveolar cells secrete what?
On the mediastinal surface of the lungs
Where is the Hilum found?
It is the site of entry & exit for blood vessels, bronchi, lymphatic vessels, and nerves
What is the purpose of the Hilum?
Intrapulmonary pressure (Ppul)
What is the air pressure within alveoli called?
The lung's natural tendency to recoil & the surface tension of alveolar fluid
There are two inward forces that promote lung collapse, what are they?
Tissue cells & blood in systemic/coronary capillaries
Internal respiration occurs between?
3
How many lobes does the right lung have?
Superior lobe, middle lobe, and inferior lobe
What are the lobes of the right lung?
2
How many lobes does the left lung have?
Superior lobe, inferior lobe
What are the lobes of the left lung?
Hilum
The left lung also contains a special feature to fit the heart, what is that feature called?
Type 2 alveolar cells
What secretes surfactant?
the process of taking air into the lungs
What does inspiration mean?
Inspiratory muscles
Inspiration is an active process involving what?
Diaphragm and external intercostals
Inspiratory muscles consist of what?
They contract
What happens to the inspiratory muscles during inspiration?
When the dome-shaped diaphragm contracts, it moves inferiorly and flattens out
Action of the diaphragm refers to what?
Increased thoracic cavity volume
What is a result of action of the diaphragm?
When the external intercostals contract, the rib cage is lifted up and out
Action of intercostal muscles refers to what?
Increased thoracic cavity volume
What is a result of action of intercostal muscles?
Elastic tissue in the stroma & alveolar surface tension
Lung compliance is normally high due to?
Blood flow reaching the pulmonary capillaries via arterioles
The perfusion portion of ventilation-perfusion coupling refers to what?
The amount of gas (air) reaching the alveoli via bronchioles
The ventilation portion of ventilation-perfusion coupling refers to what?
For optimal, efficient gas exchange
Ventilation & perfusion rates must be matched for what reason?
Ventilation & perfusion rates
For optimal & efficient gas exchange to occur, what must be matched?
A decline in blood pH which causes acidosis and increasing Pco2 which causes the hemoglobin-O2 bond to weaken which in turn causes O2 to unload off RBC's easier to meet the demands of cells.
As cells metabolize glucose, they us O2 causing?
Bicarbonate ions in plasma
CO2 is transported in the blood in what form?
70%
What is the % of bicarbonate ions?
Higher brain respiratory control centers
Respiratory rhythms are regulated by what?
Changing levels of Pco2, Po2, and pH in plasma
What are the most important chemical factors that influence breathing rate & depth?
Bohr effect
The decline in blood pH which causes acidosis and increasing Pco2 which causes the hemoglobin-O2 bond to weaken which in turn causes O2 to unload off RBC's easier to meet the demands of cells is referred to as what?
Flow of gases to equalize pressure
Pressure changes within pulmonary ventilation lead to what?
Nose & nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, and the pharynx
What are the major organs associated with the upper respiratory tract?
Larynx, trachea, bronchi & branches, and the lungs & alveoli
What are the major organs associated with the lower respiratory tract?
Ppul (pulmonary pressure)= Patm (atmospheric pressure)
During expiration, Ppul (pulmonary pressure) is greater than Patm (atmospheric pressure) which causes air to flow out of the lungs down its pressure gradient until what occurs?
How much stretch the lung has
Lung compliance is a measure of what?
Tidal volume
What respiratory volume signifies the normal daily breathing?
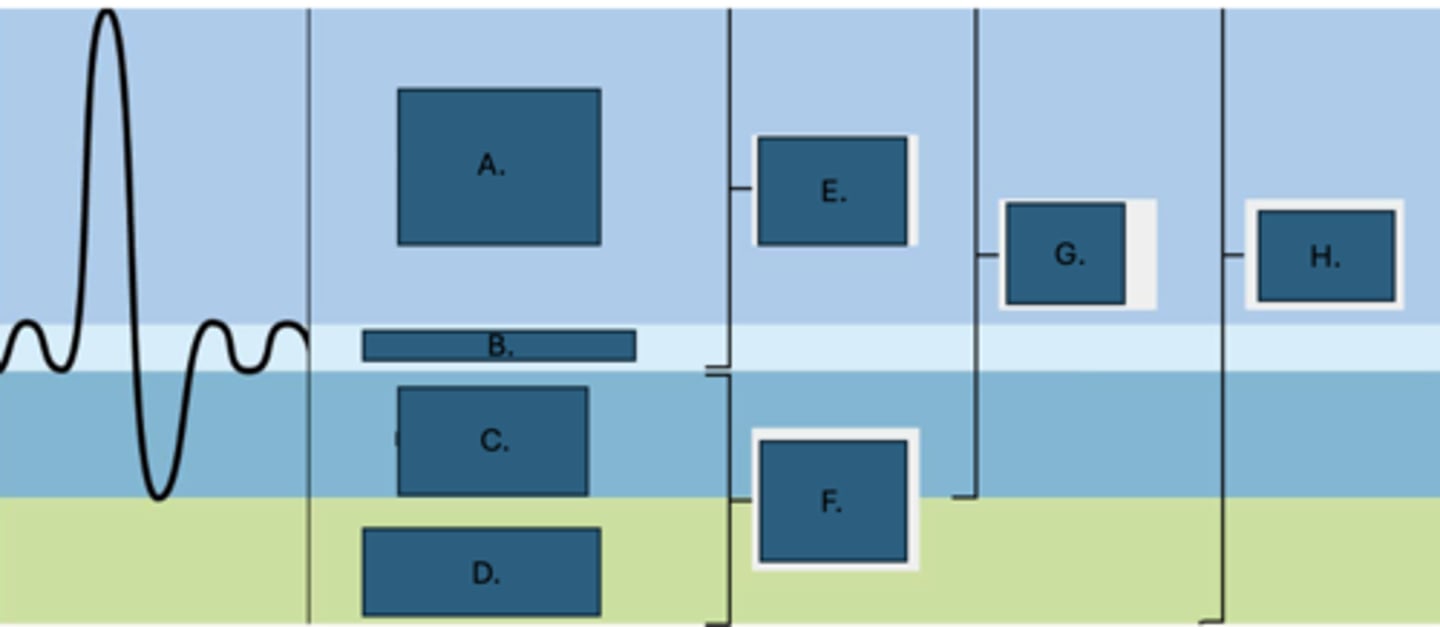
Inspiratory reserve volume
What is A?
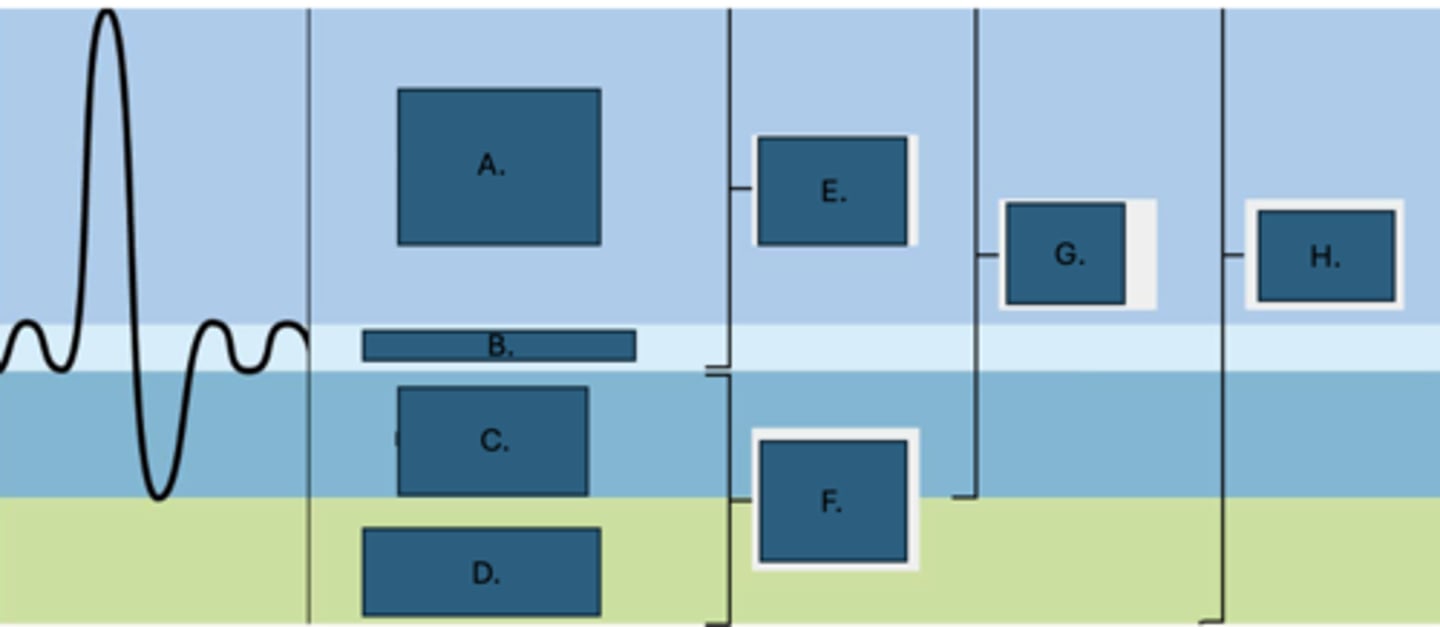
Tidal volume
What is B?
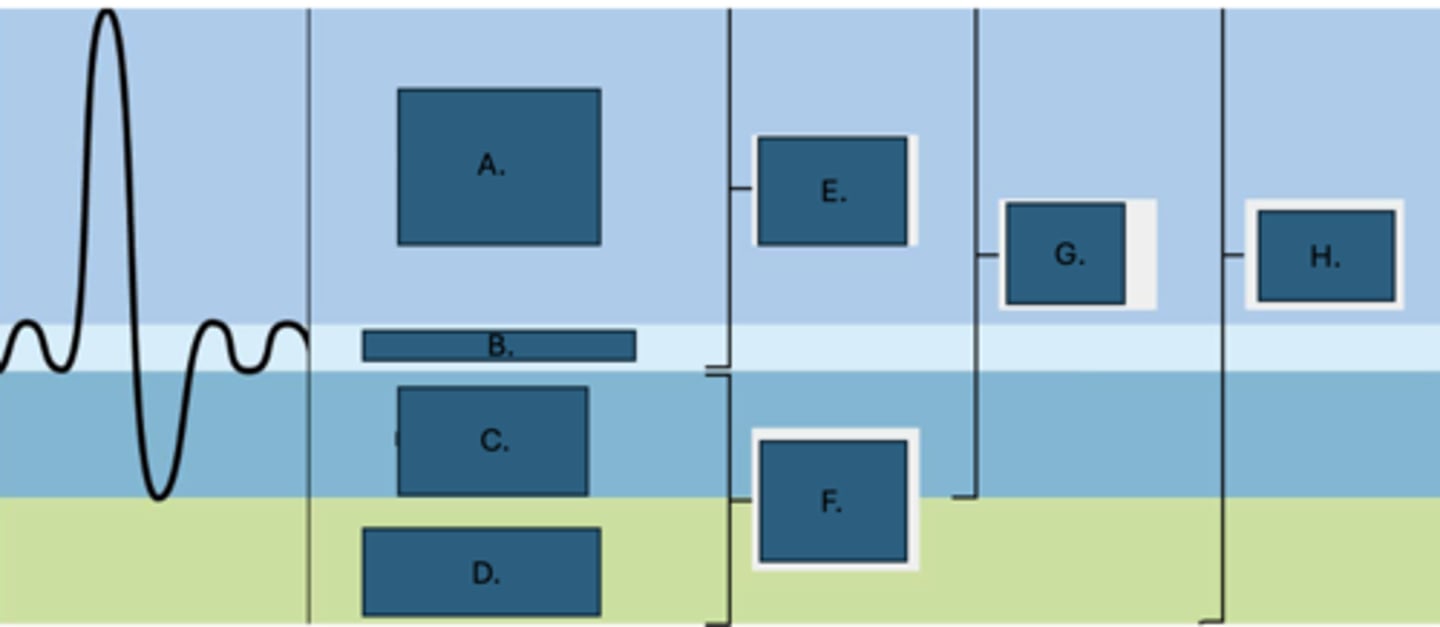
Expiratory reserve volume
What is C?
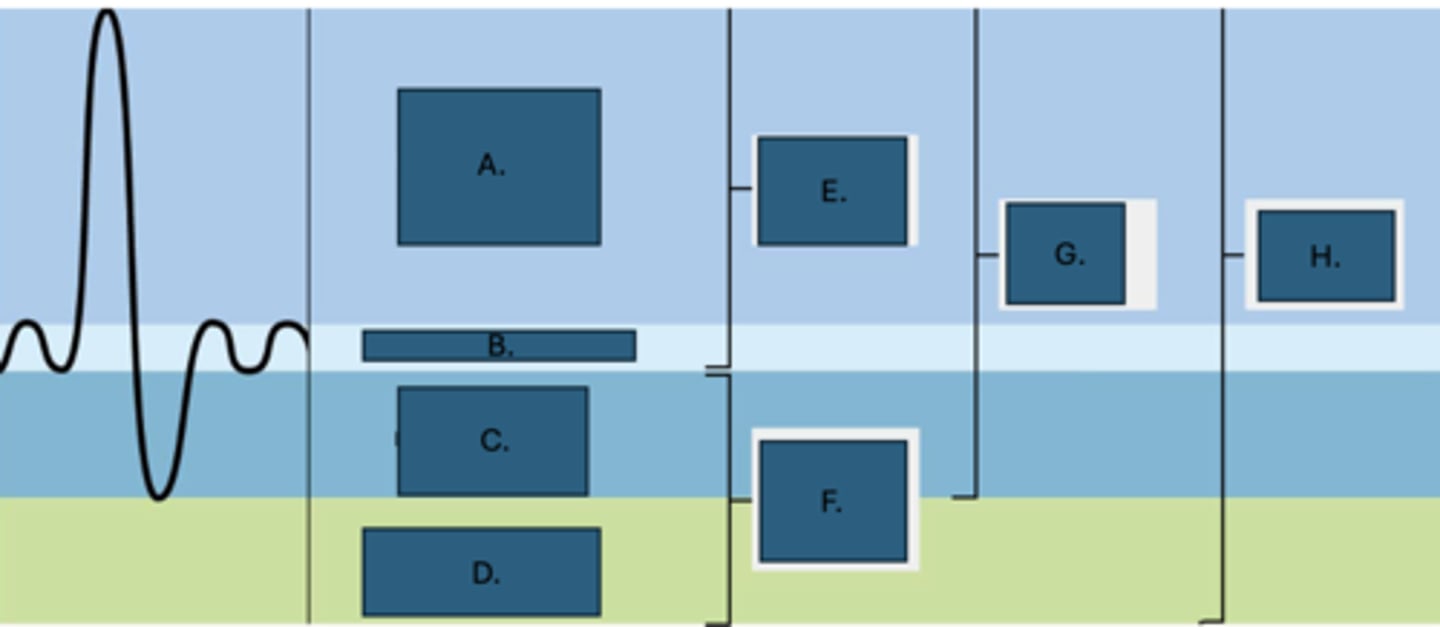
Residual volume
What is D?
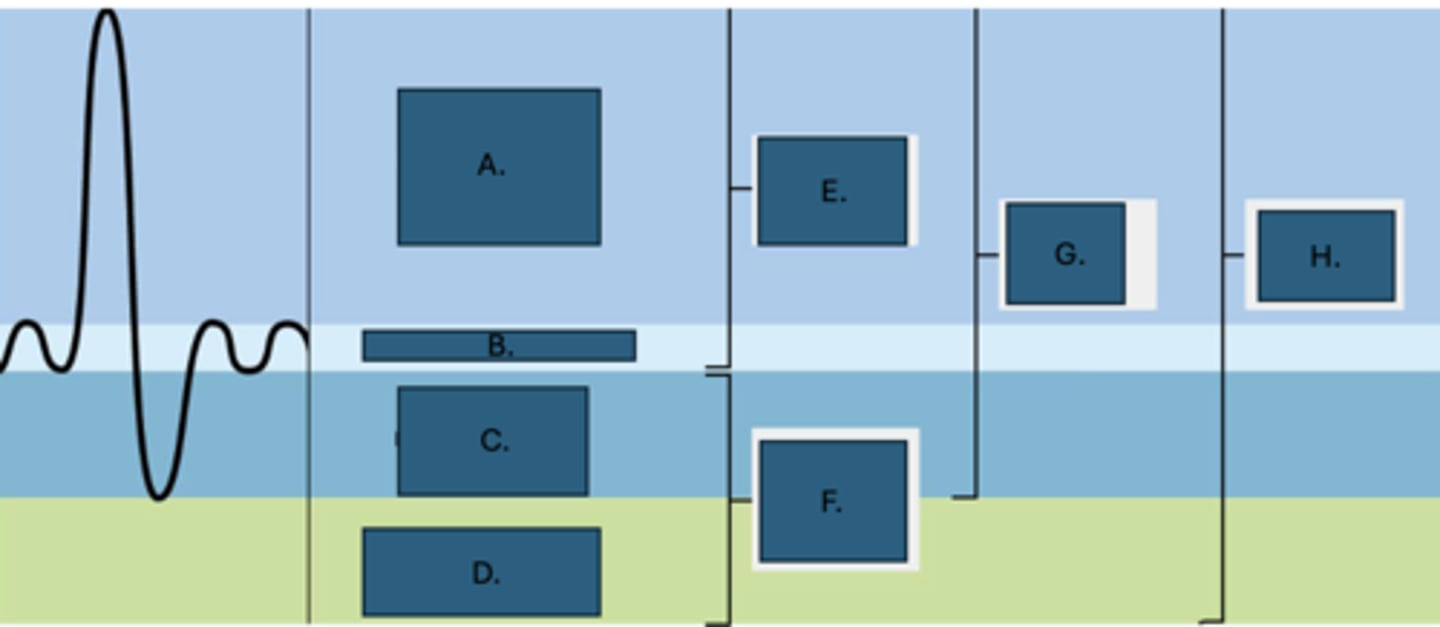
Inspiratory capacity
What is E?
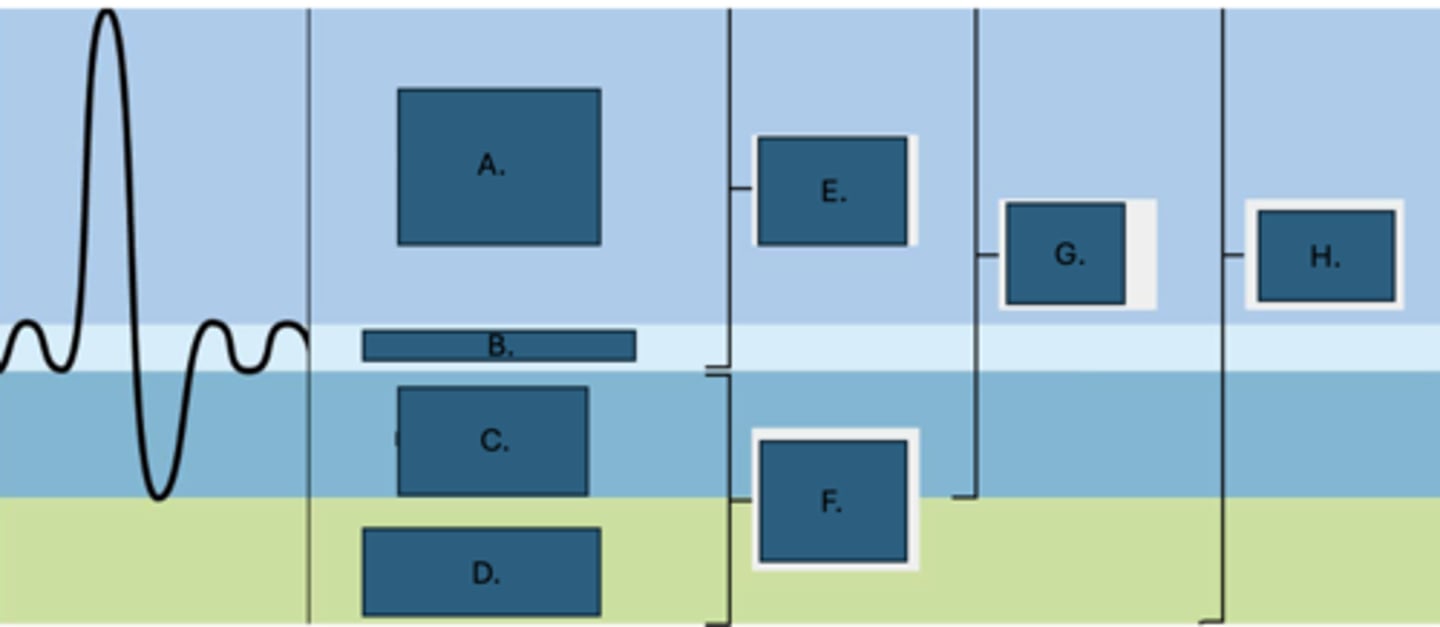
Functional residual capacity
What is F?
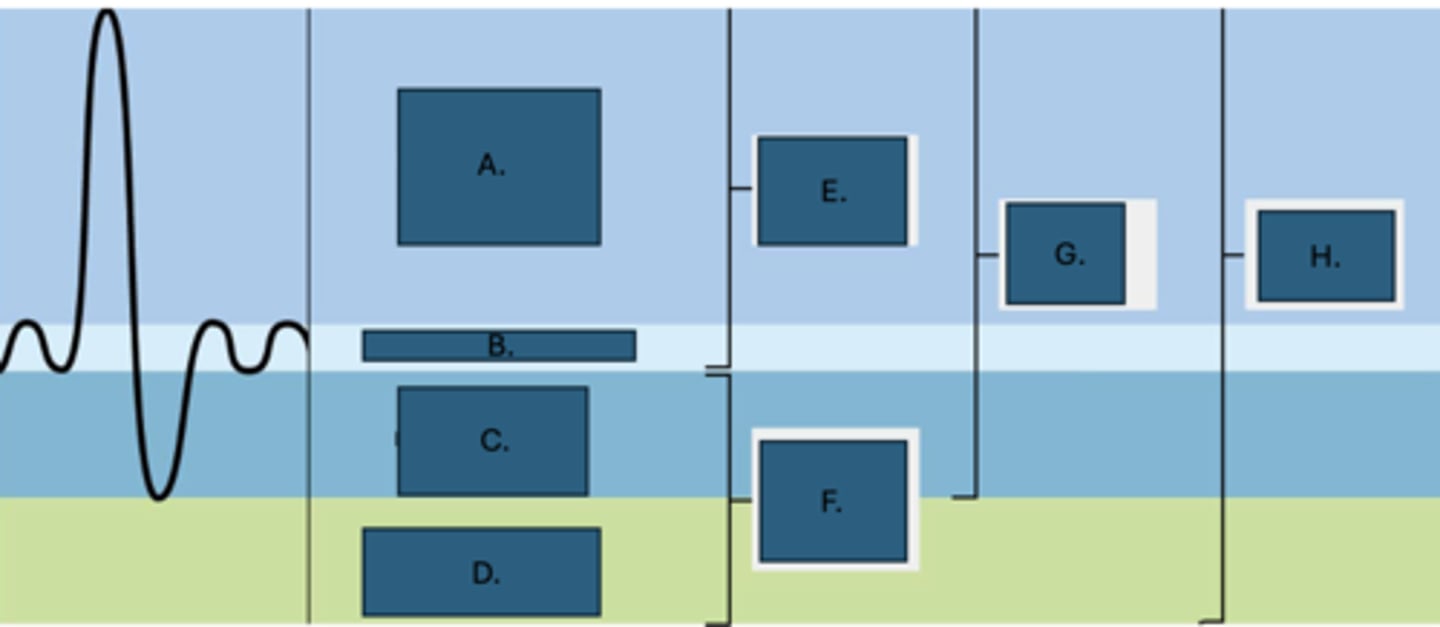
Vital capacity
What is G?
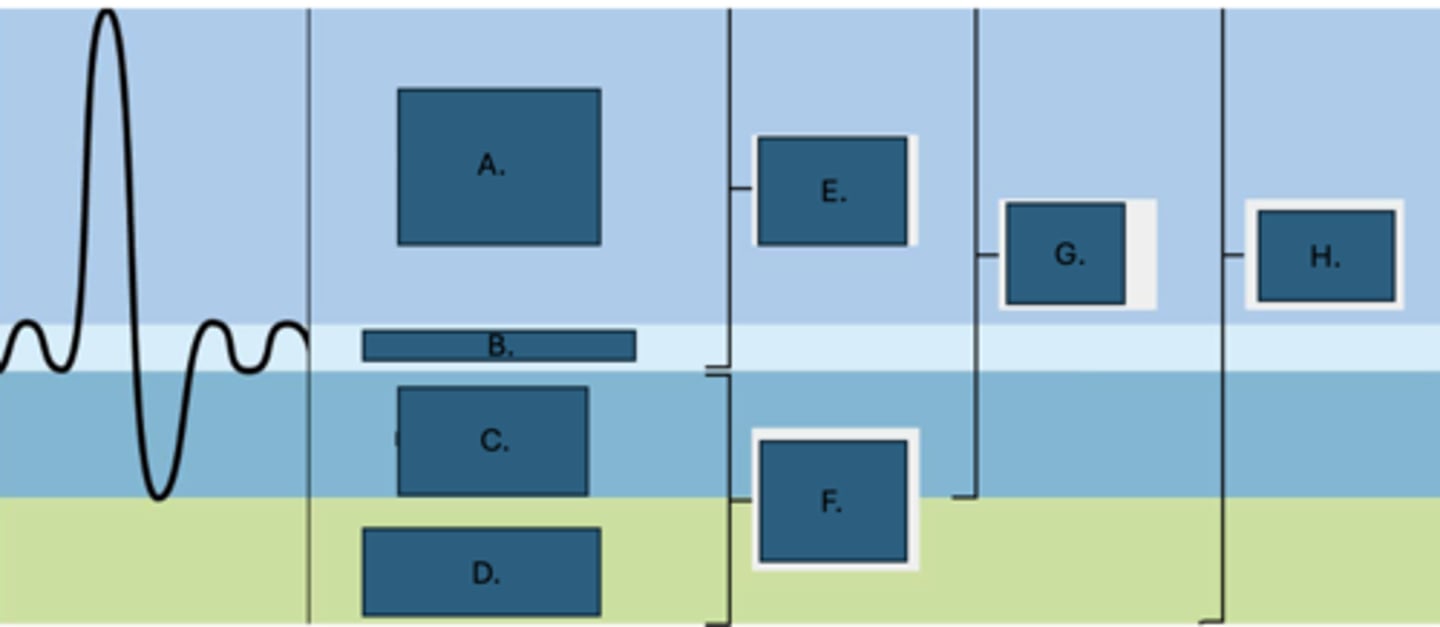
Total lung capacity
What is H?