ALL OF APHG VOCAB UNITS 1-7
1/348
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
349 Terms
spatial
relating to space
absolute location
the precise point where a place is located on Earth
cultural ecology
Geographic approach that emphasizes human-environment relationships.
relative location
where a place is located in relation to another place
geographic information system (GIS)
a computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data
place
specific human and physical characteristics of a location
region
a group of places on Earth with similar human and/or physical features
situation
the location of a place relative to other places and its surroundings
time-space compression
the shrinking of time distance between locations because of improved methods of transportation
distance decay
decline of activity or function with increasing distance from its point of origin
density
number of something in a specifically defined area
Ex: population density is the number of people per square mile or kilometer
human-environment interaction
connection and exchange between humans and the natural world
environmental determinism
the idea that human behavior is controlled by the physical environment
map scale
the relationship of the size of th emap to the size of the area it represents on Earth's surface
formal region
An area in which everyone shares in one or more distinctive characteristics
GPS
a system that determines accurately the precise position of something on Earth through satellites, tracking stations, and receivers
remote sensing
process of gathering data about Earth from instruments far above the planet's surface
spatial analysis
The analysis of geographic data about a certain place.
sense of place
The feeling that an area has a distinct and meaningful character
friction of distance
as distances increase, it requires more time, effort, and cost for interactions between places to occur; measures the degree to which distance affects the interaction between two places
distribution
The arrangement of something across Earth's surface.
landscape analysis
the task of defining and describing landscape
field observation
the act of physically visiting a location, place, or region and recording, firsthand, information there
built environment
part of the physical landscape that represents material culture; the landscape created by humans
ex: buildings, roads, signs, fences etc.
scale (relative scale)
the amount of territory that a map represents ex: global scale means the entire planet
reference maps
Maps designed for people to refer to for general information about places
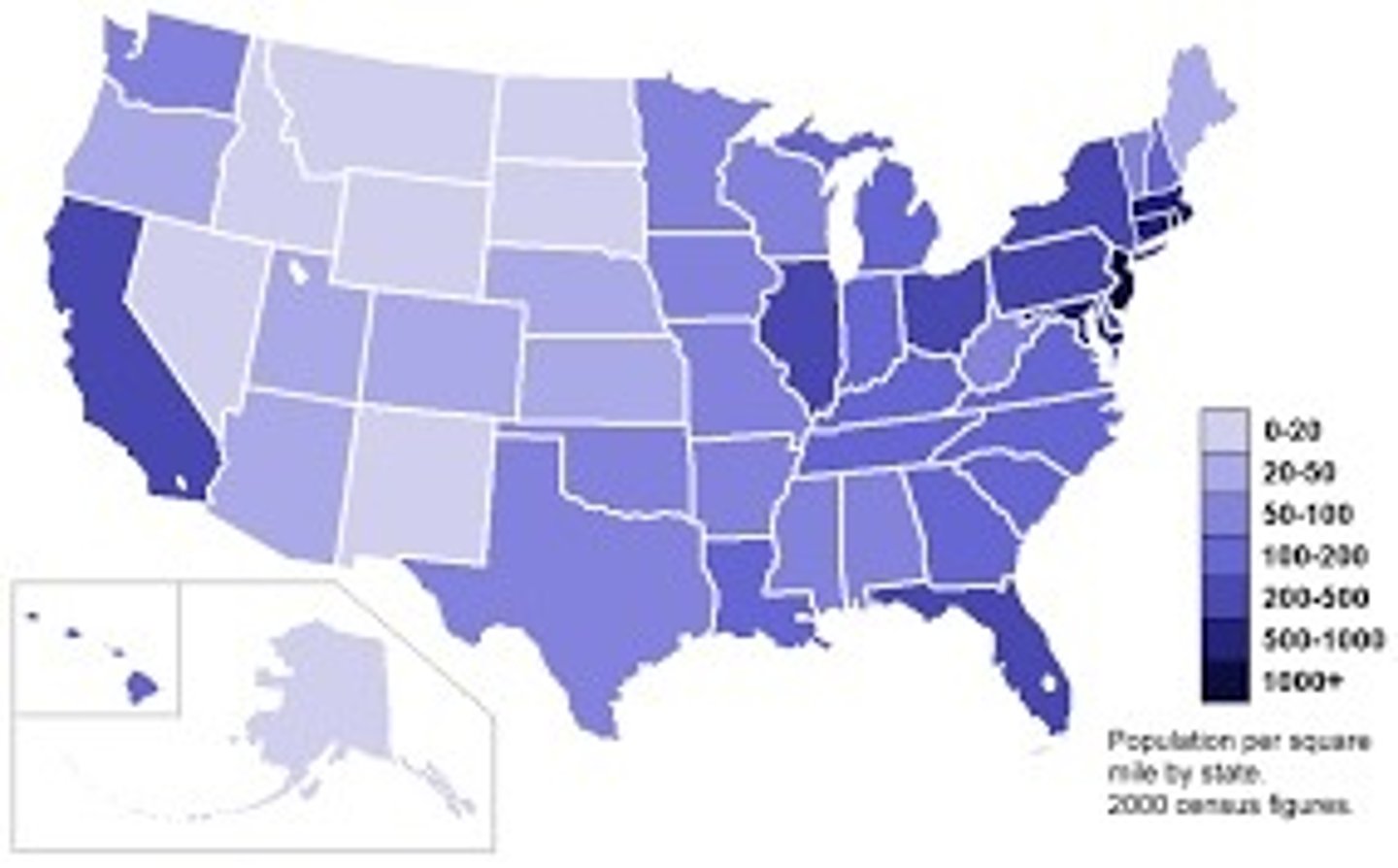
choropleth map (thematic)
uses various colors, shades of one color, or patterns to show the location and distribution of data
thematic map
a map that shows a particular theme, or topic
ex: choropleth, dot distribution, graduated symbol, isoline
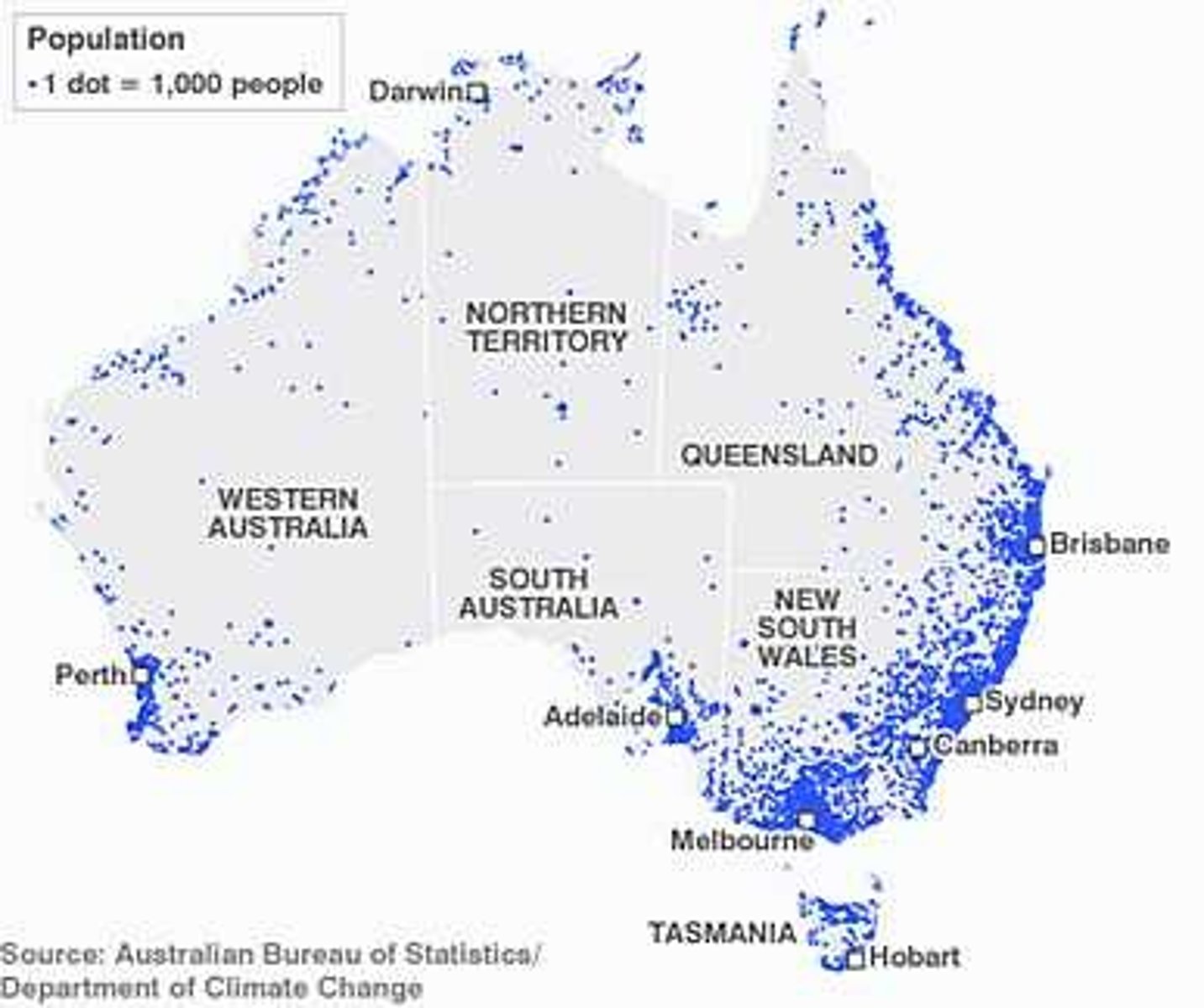
dot density map
A map where equal-size dots are used to demonstrate the frequency or intensity of a particular phenomena
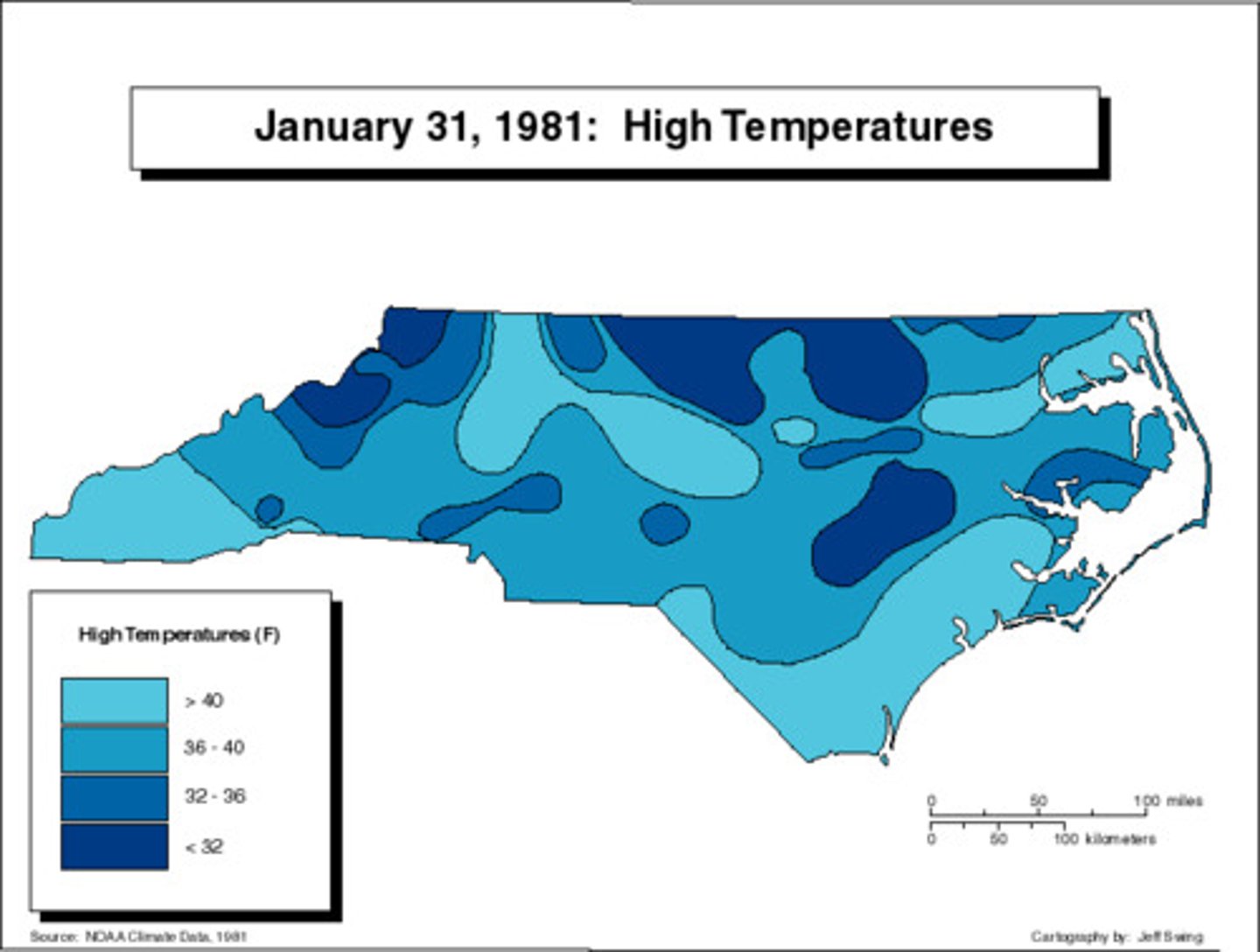
isoline map
A thematic map with lines that connect points of equal value.
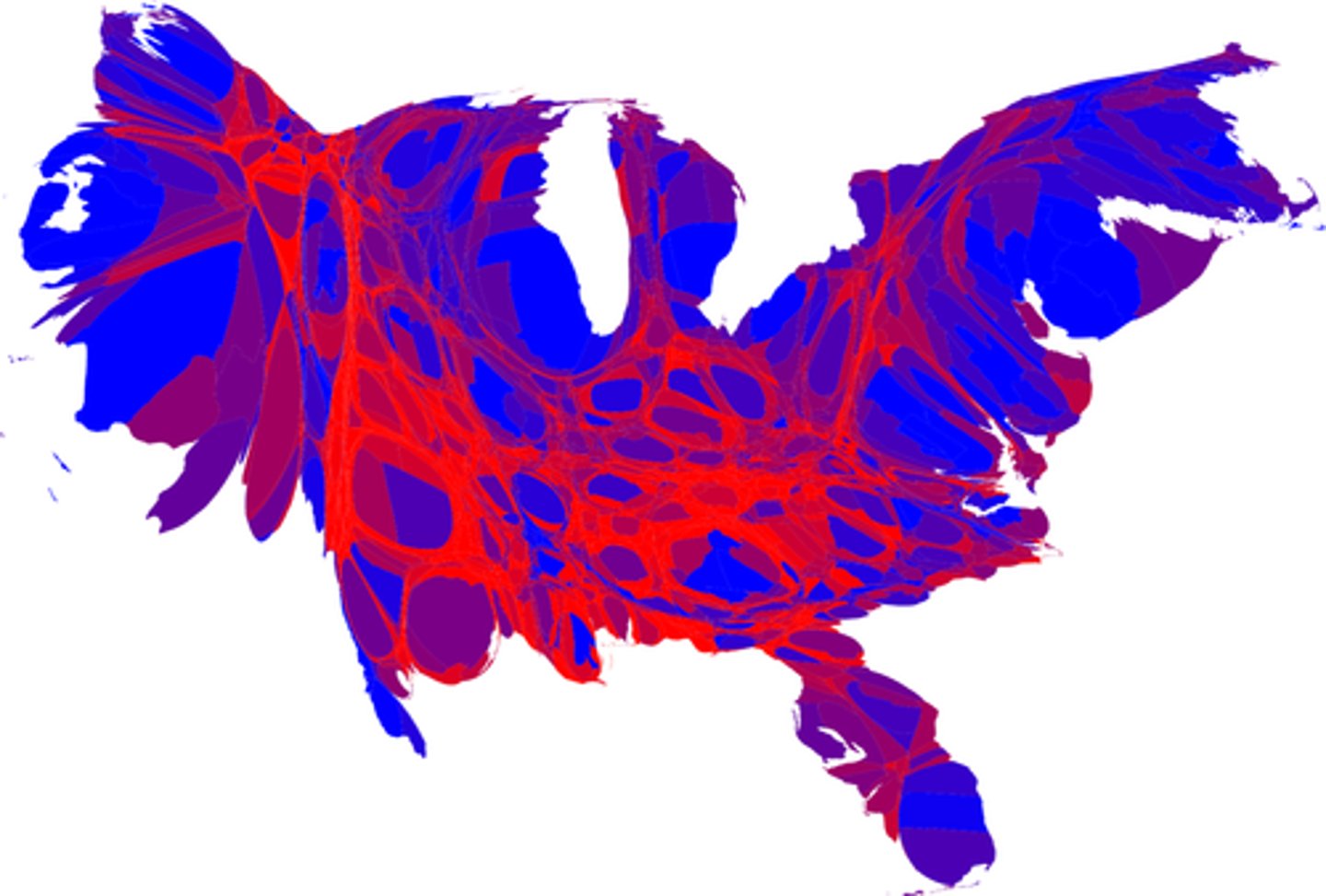
cartogram (thematic)
the sizes of countries are shown to some specific statistic
Mercator projection
a projection of a map of the world onto a cylinder in such a way that all the parallels of latitude have the same length as the equator
EX: used especially for marine charts and certain climatological maps.
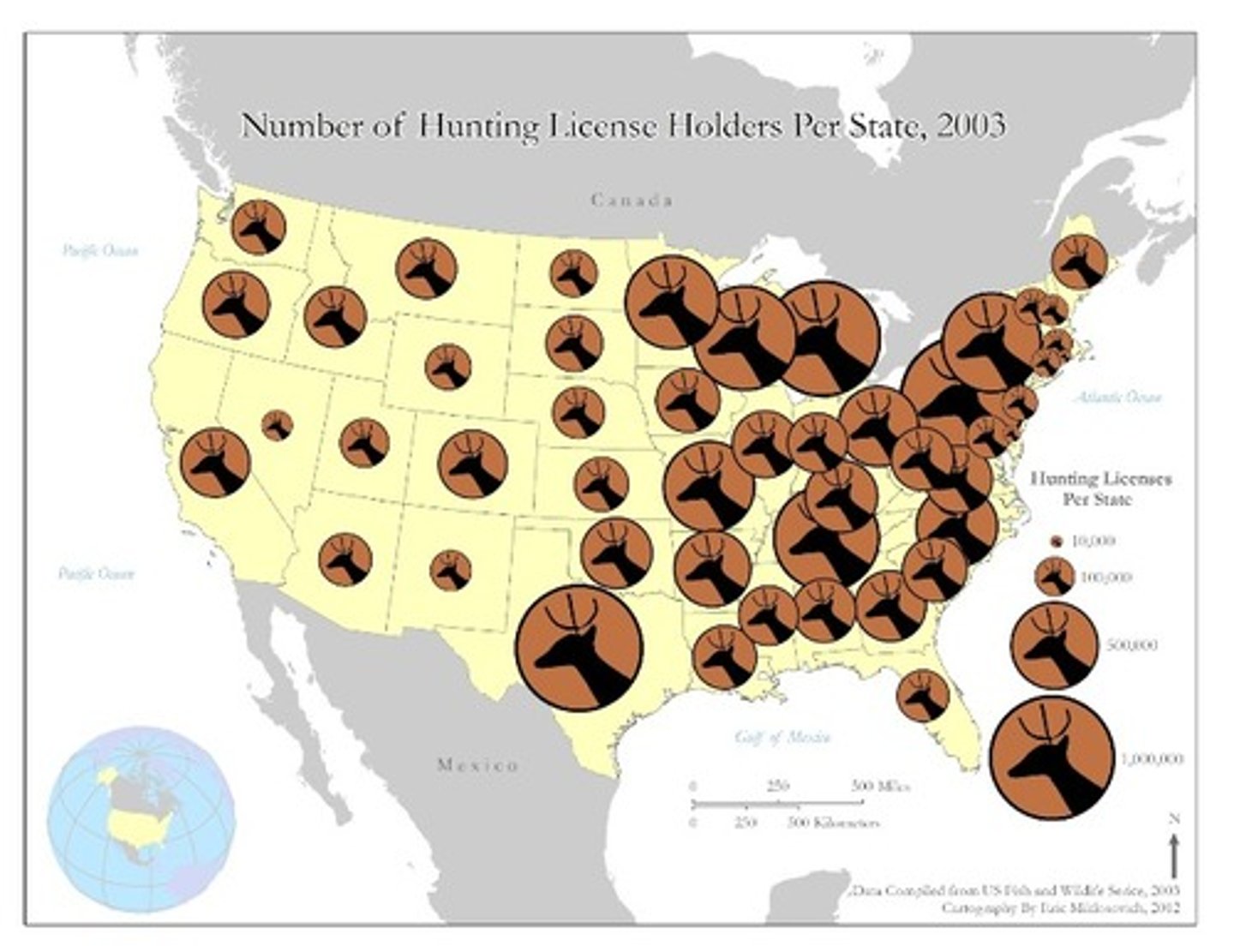
graduated/proportional symbol map
A map with symbols that change in size according to the value of the attribute they represent.
quantitative data
numerical data ex: distribution of people based on income
qualitative data
Data associated with a more humanistic approach to geography, often collected through interviews, empirical observations, or the interpretation of texts, artwork, old maps, and other archives.
scale of analysis
level at which the data is collected; global, regional, national, local (includes supranational and county)
spatial perspective
a way of thinking about how phenomena are positioned and arranged on Earth's surface. It focuses on "where" things are and why they are located there
absolute distance
The distance that can be measured with a standard unit length, such as a mile or kilometer.
absolute direction
the cardinal directions north, south, east, and west
census data
quantitative information collected through the official count of the number of people in defined area such as a state; conducted every 10 years
clustering
be or come into a cluster of close group; congregate
dispersal
process of distributing things or people over a wide area
elevation
height above sea level
flows
movement of people, goods, or information that has economic, social, political, or cultural effects ib societies
funtional region
an area organized by its function around a focal point, or the center of an interest or activity
global
relating to the whole world; worldwide
land use
the way humans manage and modify the natural environment to create built environments and semi-natural habitats
local
specific community, town, city or region
map projection
method for representing the Earth's curved surface on a flat surface
media reports
type of written account that can be used as a source of spatial information
national
distribution of phenomena over an entire country
natural resources
found within natural environment that is accessible and economically valuable to humans
pattern
the way in which things are arranged in a particular place
perceptual/vernacular region
type of region that reflects people's feelings and attitudes about a place
personal interviews
direct, face to face conversation between an interviewer and respondent
photographic interpretation
the process of examining photographs to identify objects and evaluate their significance
policy documents
communicate organizational policies and procedures
environmental possibilism
a theory of human-environment interaction that states humans have the ability to adapt the physical environment to their needs
satellite navigation system
satellite-based system for determining the absolute location of geographic features
space
the area between two or more things
sustainability
use of Earth's land and natural resources in ways that ensure they will continue to be available in the future
satellite imagery
collection of images of Earth taken by articial satellites that orbit the planet
travel narratives
travelers wrote accounts of what they obsereved in distant places
Are people concentrated evenly across the globe?
NO
What types of population density are there
Arithmetic
Physiological
Agricultural
Arithmetic population density
Total # of people divided by total land area.
Answers the “where” of population density, but not necessarily the “why?”
Physiological population density
# of people per unit area of arable land
The higher this is, the less resources that a country or region typically has available overall
High number = lots of good land
Agricultural population density
# of farmers per unit of arable land
The HIGH NUMBER IS BAD
High number= less available land per farmer
population composition
can predict population growth and decline, market trends for certain goods and services, and even political/voting trends!
we can make inform predictions about the economy and culture of places by studying this
potential/elderly support ratio
# of working age people (15-64) for the # of people 65 and older
dependency support ratio
# of people too young (under 15) or old (over 64) to work compared to # of people in their “productive” years
life expectancy
how long you will live
Typically higher for women than men
crude birth rate (CBR)
# of live births per year per 1000 people
total fertility rate (TFR)
total average # of live births per woman throughout her lifetime
Is this below or above the replacement rate of 2.1?
If a female is dropping under 2.1 then they are not replacing with females (only having males)
infant mortality rate (IMR)
# of deaths below 1 year of age compared to total # of births
crude death rate (CDR)
Total # of deaths per year per 1000 people
natural increase rate (NIR)
% by which a population grows in a year
“doubling time”
Rule of 70: A way to estimate the time it takes to double a number based on its growth rate.
formula: 70 divided by the growth rate.
The result is the number of years required to double.
demographic transition model
a tool demographers use to categorize countries' population growth rates and economic structures.
The model analyzes birth rates, death rates, and total population trends in a society at a given point of time
Epidemiologic Transition Model
typically includes four stages: the age of pestilence and famine, the age of receding pandemics, the age of degenerative diseases, and the age of delayed degenerative diseases.
Maternal Mortality Rate
the number of mothers who die in childbirth for every 1000th births
carrying capacity
the maximum number of people who can be realistically sustained by the geography of that area
preventative checks
In Malthusian theory, another way to stabilize human population includes all the factors that prevent human birth among which he advocated for 'moral restraint,' including late marriage and celibacy until a couple can afford to support children.
positive checks
Factors increasing mortality (War, Famine, Disease, etc…)
pro natalist
policies which are designed with the purpose of increasing the birth rate/fertility rate of an area
anti natalist
to encourage people to plan smaller families, lower fertility rates and reduce the number of births. These tend to be found in countries with high birth rates and rapidly growing populations.
immigration
the movement of people to another country for permanent settlement.
emigration
the process of leaving one's country of origin in order to settle in another country permanently.
voluntary migration
migration that is undertaken willingly by the group or individual involved.
forced migration
the involuntary movement of individuals or groups away from their home or country due to factors such as conflict, persecution, natural disasters, or economic hardship.
push factors
something that encourages an individual to migrate away from a certain place.
pull factors
positive factors that attract people to new areas from other areas.
Intraregional migration
the movement of people within the same region of a nation
WITHIN THE SAME COUNTRY
Interregional migration
Permanent movement from one region of a country to another
Transnational migration
the movement of people across international borders who maintain connections and ties to their home countries while establishing lives in new countries
Transhumance migration
the seasonal movement of livestock (herding) between mountains and lowland pastures
Counterurbanization
people leaving cities to go to rural areas
Guest workers
allowed to work in another country for a set amount of time
Chain migration
people follow the path of a previous migrant to a new area
Step migration
movement from one place to another in bursts.
this is often caused by intervening obstacles