transdermal drug delivery2
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
hat does TDD (Total Daily Dose) depend on in transdermal drug delivery?
tDD depends on the area of contact between the patch and the skin.
How does TDD relate to drug loading in a patch?
TDD is less sensitive to drug loading when the skin controls the drug absorption, meaning patch size and design are more important than how much drug is loaded.
How does oral drug delivery differ from transdermal delivery in terms of absorption?
Oral delivery depends on drug solubility and bioavailability through the gastrointestinal system, whereas transdermal delivery is controlled by the skin’s permeability and the patch’s design.
Does the patch design automatically control the drug delivery rate?
: No, patch design does not automatically predetermine the rate of delivery; factors like skin condition and permeability affect the rate of absorption.
Why are drug loading and release mechanism not appropriate measures for bioequivalence in patches?
: Because bioequivalence should be measured by the actual drug effect in the body, not just by the amount of drug in the patch or the release mechanism.
Why should the drug loading in a patch be close to the amount delivered?
: For safety and predictability, the drug loading should match the intended dose to avoid overdose or ineffective treatment.
example 2: Post-menopause hormone replacement therapy
What is the purpose of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) after menopause?
HRT is used to replace estrogen in post-menopausal women to manage symptoms and prevent bone loss.
What type of drug is typically used for post-menopause hormone replacement?
Conjugated equine estrogens are commonly used, which are potent, high-clearance drugs.
What is the half-life (t1/2) of the hormone used in post-menopause therapy?
The half-life of the drug is about 0.05 hours, meaning it is cleared very quickly from the body.
What happens when conjugated equine estrogens are taken orally?
Orally, there is a high hepatic 1st-pass effect, meaning the drug is extensively metabolized by the liver before reaching systemic circulation.
What is the result of the hepatic 1st-pass effect with oral estrogen therapy?
the effect of the drug is reduced, leading to an elevated estrone/estradiol ratio, usually around 1 (higher estrone compared to estradiol).
What is the advantage of transdermal delivery for post-menopausal hormone therapy?
: Transdermal delivery provides sustained plasma levels of estrogen, avoiding the first-pass effect and leading to more stable hormone levels.
What are the pharmacological benefits of hormone replacement therapy (HRT)?
HRT helps alleviate hot flushes, irritability, and liver toxicity, while improving mental acuity and sleep quality.
How does the first patch for HRT work?
The first patch is a reservoir system that is worn for 3-4 days, with the drug (such as estradiol) released gradually over that period.
What is in the reservoir of the first patch?
The reservoir contains ethanol, which is depleted gradually over the course of 3-4 days to release the drug.
What types of transdermal patch systems are available for HRT?
Adhesive systems and layered systems are now on the market for transdermal estrogen delivery.
What is a combination transdermal patch system for HRT?
A combination system delivers both estradiol (estrogen) and levonorgestrel (a progestin) for combined hormone therapy
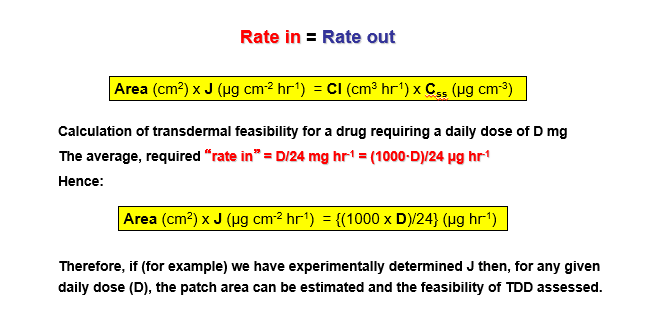
rate in rate out
Rate in is the amount of drug being delivered into the body from the patch (through the skin).
Rate out is the amount of drug being eliminated or metabolized by the body (related to clearance and steady-state concentration).
To deliver a specific daily dose (D) using a transdermal patch, you need to know how much drug the skin absorbs per area unit (J) and the required dose.Rate in = Rate out helps balance the delivery and absorption, so you can estimate the patch area based on the flux and the desired daily dose.
do i need to know this equation? check recording
hat is Buprenorphine?
Buprenorphine is an opioid drug with partial agonist and antagonist actions. It helps treat pain and opioid dependence.
What conditions is Buprenorphine used to treat?
Buprenorphine is used to treat:
Moderate to severe pain
Pain after surgery (peri-operative analgesia)
Opioid dependence
What is the half-life of Buprenorphine?
buprenorphine has a short half-life, meaning it is cleared from the body quickly.
Does Buprenorphine work well when taken orally?
No, Buprenorphine has zero oral bioavailability, meaning it doesn’t work well if taken by mouth.
How is Buprenorphine delivered transdermally?
Buprenorphine is delivered through the skin using transdermal patches with different dosing rates:
25, 50, or 75 μg/hour for general pain treatment.
5, 10, and 20 μg/hour patches are used for osteoarthritis pain.
how long is the Buprenorphine patch worn for osteoarthritis pain treatment?
he Buprenorphine patch for osteoarthritis pain is worn for 7 days.
What is the half-life (t1/2) of Nicotine?
Nicotine has a half-life of 2 hours and a high clearance (CL) rate, meaning it is removed quickly from the body.
How much Nicotine is delivered through chewing gum?
: Each stick of nicotine gum delivers about 1 mg of nicotine per hour.
What is the aim of transdermal nicotine delivery?
The aim is to deliver about 1 mg of nicotine per hour, which totals approximately 20 mg per day, gradually decreasing as the treatment progresses.
What types of transdermal nicotine patches are available?
Nicotine patches come in three types: adhesive, layered, and reservoir systems.
What is the patch size for nicotine transdermal systems?
The patch size is typically between 20 - 30 cm².
What is the loading dose of Nicotine in a patch?
The loading dose of Nicotine in a patch ranges from 25 mg to 100 mg.
Is Nicotine transdermal therapy available over-the-counter (OTC)?
Yes, Nicotine transdermal patches are available as over-the-counter (OTC) products.
What does occlusive mean in a transdermal drug delivery system?
Occlusive means the patch creates a seal over the skin to prevent air from getting through, which helps improve drug absorption.
What is meant by a static system in transdermal drug delivery?
A static system means the patch remains in place after application and doesn't require external activation—drug delivery happens continuously.
Why is the application area pre-determined in a transdermal patch?
The application area is fixed to ensure the correct amount of drug is delivered, based on the skin area the patch covers.
What does it mean that the site of application is pre-set?
The specific area of the body where the patch should be applied is pre-determined and labeled to ensure the drug is absorbed effectively.
What is meant by constant drug thermodynamic activity in transdermal systems?
Constant drug thermodynamic activity means the concentration gradient between the patch and skin is maintained, ensuring steady drug release.
What is zero-order delivery in transdermal drug delivery?
Zero-order delivery means the drug is released from the patch at a constant rate over time, regardless of the concentration remaining in the patch.
Why is adhesion reproducible in transdermal patches?
The adhesive used in transdermal patches is designed to stick securely and consistently, keeping the patch in place throughout the wear time.
How long can a transdermal patch provide sustained delivery of a drug?
A transdermal patch can provide sustained drug delivery for anywhere from 0.5 to 7 days.
Why is the removal time specified for transdermal patches?
The removal time is specified to ensure the patch delivers the proper dose of the drug and to stop delivery when needed.
What does the Cp-effect relationship mean in transdermal drug delivery?
he Cp-effect relationship means the drug's plasma concentration (Cp) is directly linked to its therapeutic effect, allowing for precise control.
How is bioequivalence determined for transdermal patches?
Bioequivalence is based on plasma drug concentrations (Cp), ensuring the patch provides the same effect as other drug forms.
What concerns are there with skin tissue levels of the drug in transdermal systems?
It's important to consider skin irritation or sensitization (allergic reactions) caused by the drug or patch formulation.
What are some key steps in the manufacturing process for oral drugs?
The manufacturing process for oral drugs involves powder filling, compression, and sometimes particle coating to ensure the drug is effectively delivered.
What is the barrier to drug absorption in transdermal delivery?
In transdermal delivery, the stratum corneum (SC) of the skin acts as the barrier, which is acidic and has a lipid barrier.
How does the skin's barrier resist transport in transdermal drug delivery?
The skin’s lipid barrier provides high resistance to transport, which makes it harder for drugs to pass through compared to the gastrointestinal epithelium.
What materials are typically used in transdermal patches?
Transdermal patches are made using polymers, solvents, and may involve processes like film-coating, web handling, and adhesives.
How much of the payload is delivered via oral administration?
Oral delivery can deliver 90-100% of the drug's payload to the body.
How much of the payload is delivered via transdermal administration?
Transdermal delivery typically delivers 25-75% of the drug’s payload.
How long does transdermal delivery typically last?
Transdermal delivery can provide drug delivery over 0.5 to 7 days, depending on the type of patch used.
How can Cp (plasma concentration) be manipulated with transdermal patches?
Cp can be controlled by adjusting the patch area, influencing the rate at which the drug is delivered to the body.