Ultrasound
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
DPT 5025 Practical
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Ultrasound
Type of sound and consists of waves that transmit energy by alternately compressing and rarefying material. used for thermal and non-thermal effects. high-frequency wave that can be described by its intensity, frequency, duty cycle, effective radiating area, and beam nonuniformity ratio.
Frequency
between 1-3 megahertz (1-3MHz)
Method of Action
US passes through tissue
Produces molecular motion/vibration as it is absorbed in the tissue
Causes friction between the particles/tissues which produces heat
Non-thermal happens are at the cellular level and changes membrane permeability
Conversion
converts electrical energy to mechanical (vibration/sound) energy through the use of a crystal in the transducer (soundhead) of the ultrasound unit.
Property of Conversion
these sound waves can penetrate tissues, promoting healing and reducing pain through thermal and non-thermal effects. the mechanical energy from the ultrasound waves interacts with the tissues, enhancing circulation and tissue repair.
Attenuation
the intensity (energy; heating ability) of ultrasound waves DECREASING as the waves travel through tissue.
What happens to the energy?
Absorption (accounts for 50% of attenuation)
Reflection (bouncing back of sound waves)
Refraction (bending sound waves)
Attenuation– Absorption
to achieve heating, tissue must ABSORB the ultrasound energy. absorption coefficients (attenuation coefficients) are HIGHER in tissues with more collagen content and lower in tissue with more water content.
Which heats faster: Bone or Blood?
Bone
Which heats faster: Cartilage or Fat?
Cartilage
Which heats faster: Tendon or Muscle?
Tendon
Indications for Ultrasound
as a deep heating modality (thermal- compromised tissue extensibility/joint contraction, muscular pain)
to facilitate healing (non-thermal- open wounds, chronic inflammation of soft tissue)
Thermal (Heating) Effects of Ultrasound
increased metabolic rate
increased circulation
increased soft tissue extensibility
decrease pain
decrease muscle spasm
decrease nerve conduction velocity
Non-Thermal (non-heating) Effects of Ultrasound
increase intracellular calcium
increase skin permeability (phonoph)
increase cell membrane permeability
increase protein synthesis (for soft tissue healing)
and more all of which impact activity and tissue repair
Ultrasound: Phonophoresis
the use of non-thermal ultrasound to enhance the delivery of topically applied medications; utilizes ultrasounds ability to enhance skin/tissue (cellular) permeability to facilitate drug phoresis (hydrocortisone cream)
therapeutic medication is mixed within the US gel
or the medication placed between two layers of US gel and will mix during application
Contraindications for Biophysical Agents
malignancy
pregnancy
pacemaker
impaired sensation
impaired mentation
Contraindications Specific to Ultrasound
malignancy
pregnancy
CNS tissue
joint cement
plastic components
pacemaker
thrombophlebitis
eyes
reproductive organs
Precautions for Ultrasound
acute inflammation
epiphyseal plates
fractures
breast implants
Ultrasound Adverse Effects
Ultrasound rapidly heats plastic and cement, which can cause damage to the material in the patient. Metal, however, is known to be fine.
What are 3 potential adverse effects of ultrasound?
Burn (superficial bone)
Cross Contamination (spreading of infection from transducer head)
Blood cell stasis due to standing waves (endothelial damage)
Ultrasound: Application Parameter: Soundhead
available in variety of sizes
US is produced by a crystal’s (quartz or synthetic ceramic) vibration when subjected to a high frequency alternating electrical current
sounded (transducer) produces a high frequency alternating current form from 0.75mHz to 3.3mHz.
Effective Radiating Area (ERA)
Can be found on the US unit or on the tag on the cord. The area of the face that is transmitting the ultrasound waves and influences the treatment. It determines the size of the area that can be treated.
General Rule of ERA
Treat the area equal to twice the ERA of the soundhead.
Beam Nonuniformity Ratio (BNR)
the ratio of the highest intensity to the average intensity emitted
beam emitted from soundhead is not uniform; varying intensities (w/cm²)
found on soundhead or transducer handle
best are between 3:1 and 6:1
the greater the BNR value, the less homogenous the sound beam and the greater risk for “hot spots” in treatment area
this is another reason to keep the soundhead continuously moving during treatment
Ultrasound: Mode of Delivery
Establish the desired effect of your treatment to determine the wave type.
Determine Frequency (MHz) based on depth of penetration desired.
Select Intensity (w/cm²) based on desired effects (thermal vs. non-thermal)
Select duration of treatment (minutes)
Continuous Wave at Higher Intensity
Thermal Effect (104-113℉)
Continuous Wave at Lower Intensity
Non-Thermal Effect (less than 104℉)
Pulsed Wave
Non-Thermal Effect (less than 104℉)
Duty Cycle
By setting the ultrasound parameters of “duty cycle” to either Pulsed or Continuous waves, either thermal or non-thermal effects can be produced. Remember that the “duty cycle” impacts the amount of heating– even with non-thermal ultrasound, some thermal effects still occur, though the effects are minimized, and vice-versa.
Continuous Ultrasound
Used when heating/thermal effects are desired.
Pulsed Ultrasound
Used when minimal heat/non-thermal effects are desired.
For thermal effects, what is the “duty cycle” set at?
100% (continuous)
For non-thermal effects, what is the “duty cycle” set at?
20% (pulsed)
Greater Frequency
less depth of penetration
more (even) tissue heating
greater rate of US absorption
Depth of Penetration
1.0MHz= approximately 5.0cm
2.0MH= approximately 2.6cm
3.0MHz= approximately 1.5 cm
General Principles of Intensity
greater intensity= greater heating
tissues with higher collagen content require lower intensities than tissues with lower collagen content (muscles, fat)
bone reflects sound waves; decrease the intensity of tissue if directly next to bone (periosteal pain)
increase intensity by 0.5w/cm² if water is used as a coupling agent.
Duration General Rule
more time= more heating
less time= less heating
3 Methods of Ultrasound Application
Direct Contact
Cushion Contact
Water Immersion
Coupling Medium
air is a poor transmitter
medium must be placed between pts skin and the US soundhead
this ensures effective US transmission to pt
types of coupling media are: commercial gel (direct contact method), commercial gel pad (cushion contact method), and tap water (water immersion method)
Cooler Coupling agents are most effective for what type of tissues?
Deeper tissues (64℉)
Cooling the soundhead may assist with what?
Deeper Penetration
What type of water is best for superficial lesions?
Room Temperature
What happens if skin temperature exceeds 85 degrees?
It is difficult to achieve vigorous deep tissue healing. Cooler skin results in deeper penetration.
Motion of the Soundhead
Should be moved throughout the treatment in a circular pattern or a back and forth pattern.
Speed of Soundhead
Approximately 4cm/second. Sufficient to maintain constant contact and motion; avoid increasing the size of the treatment.
Frequency/Duration
If no progress in 3 sessions, then re-evaluate.
Generally no more than 8-12 sessions.
Acute injury: non thermal US have 3 days between treatments.
Subacute and chronic conditions: daily to every other day.
Decision Making Tree
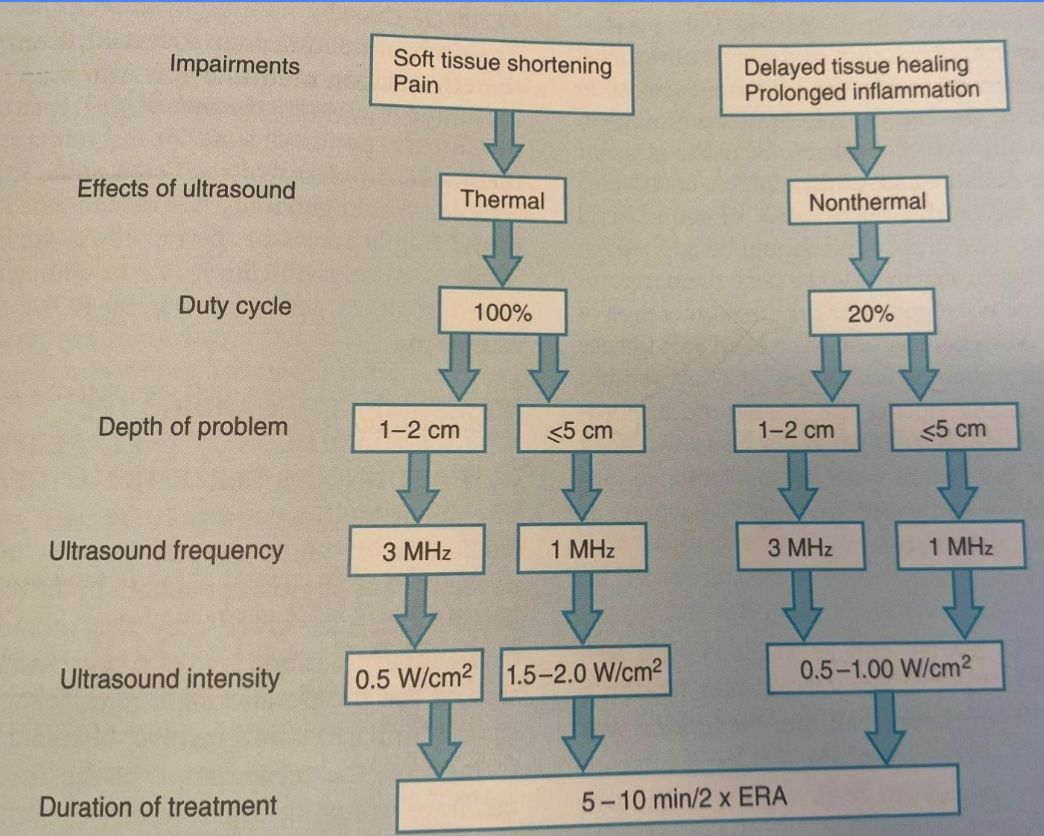
Ultrasound: Billing
timed code, 8 minute minimum treatment
If 5 minutes of US is clinically indicated, can it be billed?
Yes, you are not just billing for time of Ultrasound delivery, but entire time involved including set up, patient, education, screening, etc.
The intensity (energy; heating ability) of ultrasound waves decrease as the wave travel through tissue. Why? What happens to the energy?
It is absorbed, refracted, and reflected.