
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
Trend in electronegativity
Decreases down the group, as the distance between the nucleus and outer shell increases is shielding increases and the ability of an atom to attract a shared pair of electrons to the nucleus decreases
Trend in boiling point
Increases down the group, as the size of the molecule increases so there are stronger van de wall forces between the molecules, which need more energy to overcome
Trend in reducing ability of halide ions
Reducing power increases as you go down the group, the ability ti lose an electron depends on shielding and atomic radius: atomic radius increases and the electrons are further away from the nucleus so it is easier for the ion to lose an electron and reduce another substance
How do sodium fluoride and chloride react with sulphuric acid?
HF or HCl gas forms- misty white fumes
Not strong enough to reduce H2SO4
How does sodium bromide react with sulphuric acid?
Redox reaction
Steamy brown fumes of hydrogen bromide
Sulphur dioxide: colourless gas
Bromide ions reduce sulphuric acid to sulphur dioxide
Bromine ions are themselves oxidises to bromine gas
H2SO4 + 2H+ + 2Br-
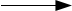
Br2 + SO2 + 2H2O
How does sodium iodide react with sulphuric acid?
Iodide ions are a very strong reducing agent, and will reduce the sulphuric acid to sulphur dioxide, then sulphur and then hydrogen sulfide
Iodide ions are oxidised to iodine
Steamy fumes of hydrogen iodide
Hydrogen sulphide is toxic and has a bad smell
How can acidified silver nitrate solution be used to identify halide ions?
Precipitate of silver halide will form, and the colour helps us distinguish the halide ion present
Why must the silver nitrate solution be acidified?
Removes any excess ions which mask the results e.g. also form a coloured precipitate
What colour precipitate does silver fluoride form?
no ppt
What colour precipitate does silver chloride form?
white ppt
What colour precipitate does silver bromide form?
cream ppt
What colour precipitate does silver iodide form?
yellow ppt
why is ammonia solution added?
each silver halide has a different solubility in the ammonia solution, so can help with identification
trend in solubility of the silver halides in ammonia
Decreases down group
what does silver chloride do in ammonia?
white ppt dissolves in dilute ammonia
what does silver bromide do in ammonia?
cream ppt dissolves in concentrated ammonia
what does silver iodide do in ammonia?
insoluble in concentrated ammonia
What is the reaction of chlorine with water?
Cl2 + H2O turns to 2H + Cl- + ClO- (chloride and chlorate ions form)
What happens when chlorine reacts with water in sunlight?
2Cl2 + 2H2O turns to 4H + 4Cl- + O2
Chlorine in water treatment
Chlorate ions kill bacteria/ pathogens in water so it is swimable and drinkable
Advantage of chlorine use in water
Kills bacteria and pathogens
Inhibits algal growth and removes smells/ tastes
Remains in water so no reinfection
Disadvantages of chlorine in water
toxic and harmful: can cause respiratory problems if inhales
can cause chemical burns
chlorinated hydrocarbons cause cancer
Reaction of chlorine with cold, dilute, aqueous Na
Cl2 + 2NaOH turns to NaClO + NaCl + H2O
Used to kill bacteria in houses and water