Unit One AP Gov Videos (1.5-1.9)
==1.5 Daily Video 2==
^^Amendment Process^^
Steps to ratify a Constitutional amendment.
- Propose through either the U.S. Congress or the National Convention. (Most go through Congress)
- Amendment has to have a 2/3 positive vote for it to be considered proposed.
- The amendment is handed to the Chief Archivist who drafts instructions from Congress and delivers this to each of the governors around the country.
- Now the Governors follow the instructions and must have a 3/4 positive vote from all states for the Amendment to be ratified.
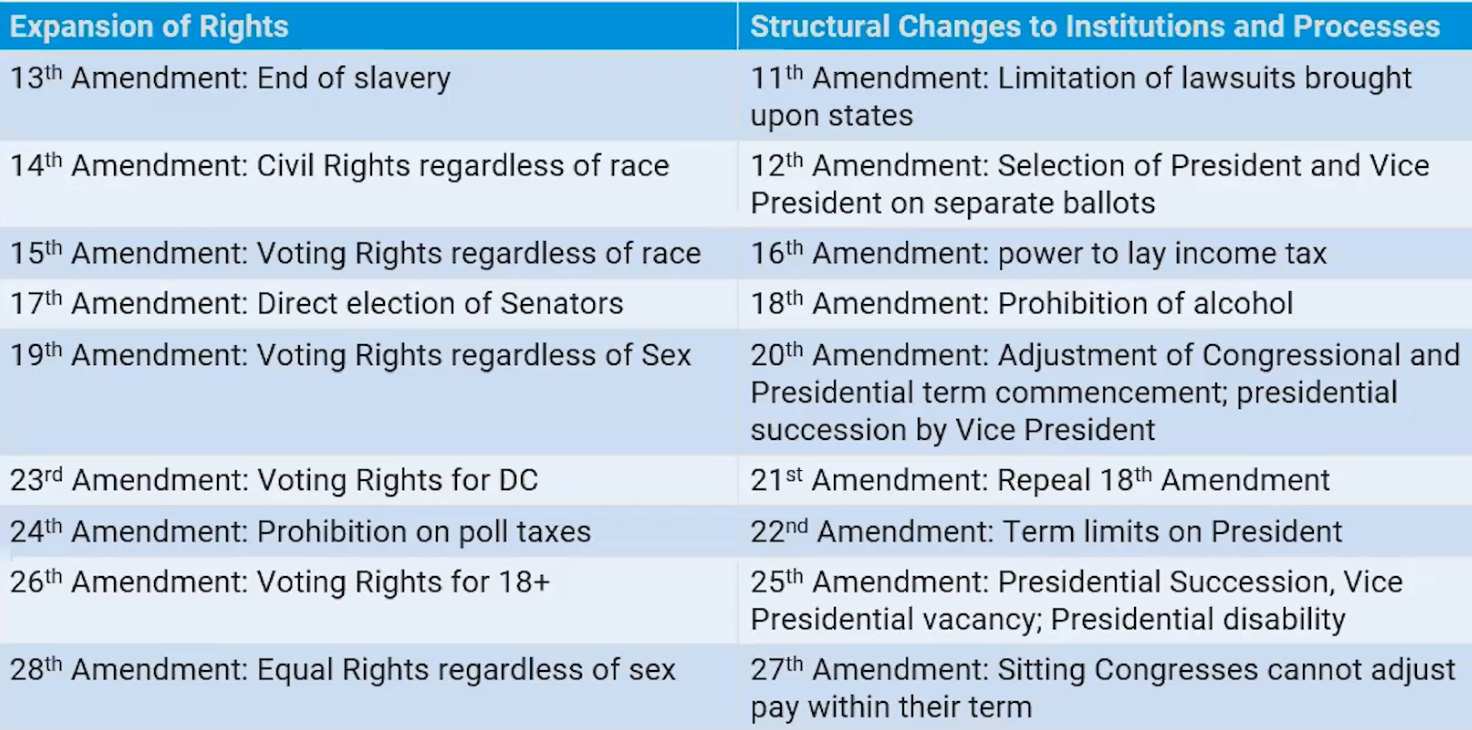
The Constitution only satisfied the 55 people behind the closed doors of the convention.
Eight out of the Twelve ratifying states proposed 210 amendments
The compromise for this was the Bill of Rights which ratified ten amendments 8 of which were rights-bearing for individuals while the other two were reservations of power for states and individuals.
==1.5 Daily Video 3==
^^FRQ Skills^^
- Identify - Means to name.
- Define - means to set the meaning of a term
- Describe - means to give a representation of the subject in words
- Explain - means to make known how or why something connects to something else
==1.6 Daily Video 1==
^^Federalist 51^^
- Explains the underlying principles of the Constitution that provide safeguards against abuse of power.
- Three Branches of gvmt = Maddison model
- Maddison states the separation of powers is essential to preserving liberty.
- Maddison states that giving each branch administrator, a constitutional method and personal motivation will resist the intrusion of other departments.
- Since men don't do the right thing on their own, and the government is run by men it needs to be set up to control itself.
- Maddison states that government dependence on people for control is ideal but there should always be a backup or additional method to control government.
- Maddison says that the legislative branch will be the most powerful so it needs to be split into two branches.
- Maddison also states that the executive branch will be the weakest so the power can be boosted by having constitutional veto power.
^^Brutus 1^^
- Maddison expresses concerns that the constitution has created a too powerful government.
^^Separation of Powers^^
- Legislative Branch - all of the powers of the legislative branch should be vested in a congress and should consist of a senate and a house - Article 1, Section 1
- Executive Branch - The executive power should be held by the President of the United States - Article 2, Section 1
- Judicial Branch - The power of the Judicial Branch shall be vested in one supreme court. - Article 3, Section 1
^^Powers for each Branch^^
- Legislative - make laws, declare war, collect taxes, regulate commerce
- Executive - make treaties, commander in chief of armed forces, grant pardons
- Judicial - The court has the authority to hear all cases in law arising under this constitution.
==1.6 Daily Video 2==
^^U.S. Constitution Checks and Balences^^
- House - the sole power of impeachment
- Senate - the power to try any impeachment (interbranch check), may approve/ disapprove presidents nominations for Fed Offices, may approve/ disapprove treaties the the president has negotiated
- Congress - countering the executive branch, can overide a presidential veto with a 2/3 vote in both houses.
- The President - Counter the legislative branch, can veto legislation that was approved by both houses of congress, control in operations of the armed forces as a counter to congresses ability to declare war.
- The Judiciary - can determine laws of Congress are unconstitutional, and determine actions of the president are unconstitutional.
^^Implications of Seperation of Powers and Checks and Balences^^
- Many positives are accosiated to multiple access points
- Access Points - stakeholders and institutions can interact with parts of the government.
Stakeholders and institutions can interact with governments by:
- meeting with a member to discuss impacts of congress on groups and people.
- Elect members of congress who share your intrests
- Donate money to the realection campaign to a member of congress or president.
- Meeting with your president one on one to express your concerns
- Submit amicus curiae briefs to influence courts decisions
- state protests infront of supreme court building
- Good Things - people have several avenues to attempt to influence policy making,
- Bad things - sometimes a branch disagrees with another which causes gridlock,
==1.6 Daily Video 3==
- 4.A - Describes authors claims, perspective, evidence, and reasoning
- 4.B - Explain how authors argument relates to political principles
- 4.C -
- 4.D - Explain how visual elements compare to political pricaples
==1.7 Daily Video 1==
- Federalism - describes the relationship between the state and national goverments.
- 10th Ammendment - the Federal Government only has those powers delegated in the Constitution. If it isn't listed, it belongs to the states or to the people.
^^Powers Left to States^^
matters of education,
health,
marriage,
issues regarding mortality,
police powers
Legal age to consume alc,
legal age to gamble both go under Mortality which means it is controled by the state
^^Concurrent Powers (shared powers)^^
levy taxes
maintain roads
create courts
borrow money

^^Obligations Of the States to the fed government and each other^^
- Full Faith and Credit - offical doccuments are valid in all states.
- Privliges and Immunites - prevents states from discriminating aginst citizens of other states.
- Extradition - commit a crime in another state, that state is required to return you to the state you commited the crime in.
==1.7 Daily Video 2==
- Fed Government collects taxes and distributes some of the money back to the states. This is called revenue sharing or cooperative federalism.
- Devolution - based on a presidents agenda, revenue sharing has been expanded, consolidated, or given back to states to control
- Revenue sharing gives the fed government more control over the state government.
- Mandates - fed governments telling states they must do something or the fed government wont give them what they want.
^^State and Fed relationship shifts over the past^^
- Dual Federalism was the norm until the mid to late 1800’s
- Once states had transportation, manufactoring, and buisness the fed government wanted to regulate commerce.
- 16th ammendment gave power to tax fed govvernment which caused more involvement w states.
- Interstate transportation of goods and bad buisness practices led to fed regulations for the workplace
- Once commerce came along congross decided to regulate it
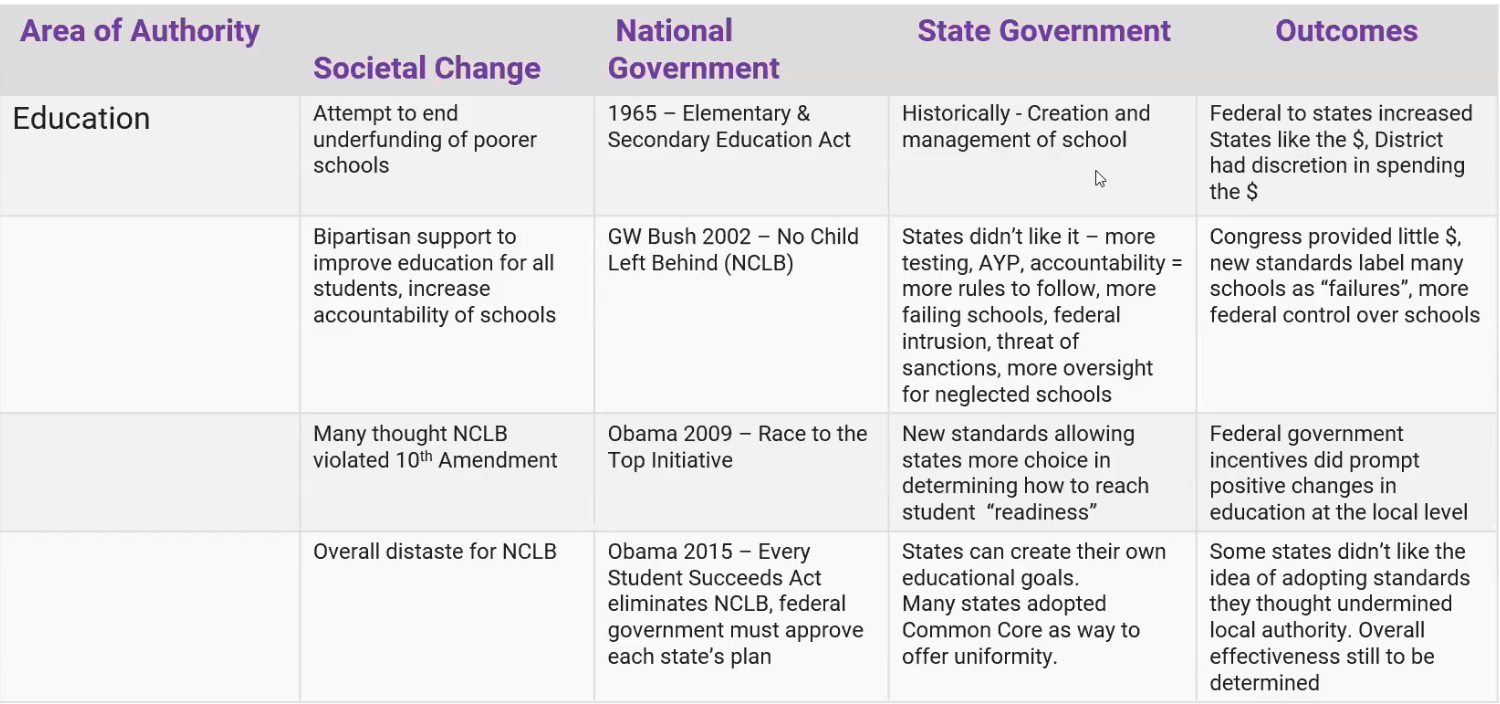
^^Examples of Sociental Changes^^
- Population Growth
- Groups demading protections - labor, businesses, civil rights
- National Concerns - Disaster readiness, increased 10th crimne rate
- Presidents with their own different agendas
- Urbanazation
- Bureucratic expertise
- Civil Rights Era
==1.7 Daily Video 3==
==1.8 Daily Video 1==
- Article 1, Section 8, Clause 3 - the U.S. have power to regulate commerce with foreign nations, among the states, and with indian tribes.
- Article 1, Section 8, Clause 18 - Elastic Clause
- Article VI - constitution laws take priority over any conflicting state laws.
- 10th ammendment - Powers that are not restricted by fed gvmt or state are reserved to the people or the states. Also called reserved powers.
- 14th ammendment - no state shall make laws the inflict the immunites of citizens or that harm life liberty and property or that harm equal protection of its laws.
- \

^^Debate over Fed and State Power^^
- The debate over the balence of power have been going on since the founding
- Courts have invoked the 10th and 14th ammendments differently at different points in timee.
- States have handeled most of the affairs of their people but this has slowly been shifting over to fed intervention
- There have also been shifts back to state power and control.
- right to privacy
- Freedom of Speech
- Fed protections on voting rights
==1.8 Daily Video 2==
- In McCulloh v Maryland, the feds needing somewhere to put their money and the gvmt can put. abank anywhere w/o getting taxed by the state because it is not a buisness it is apart of the gvmt.
- McCulloch v Maryland
- Clauses of constitution - Article VI, Article 1, section 8 clause 18
- Background - Congress passes law to create national bank branches in states, Maryland taxes Bank of U.S., Maryland sues McCulloch for refusing to collect and pay taxes in his bank.
- Holding - U.S. can use commerce, currency, tax powers, and Article VI, Article 1, section 8 clause 18 to create Bank of U.S., state cannot tax Bank of U.S. because it will destroy the bank.
- Effect - Precedant for judicial review, President, States when in violation with supremacy clause
- US v Lopez
- Clauses of constitution - Article VI, Article 1, Section 8, Commerce clause
- Background - Congress passed Gun Free School Zones Act making it illigal to have a gun within 1000 ft of a school. Lopez violates law. is tried, and appels.
- Holding - Gun ownership in schools cannot be properly regulated under constitutional reasoning found in Gun Free School Zones Act.
- Effect - law re legislated to focus on guns over state lines in school zones as it affects interstate commerce. Commerce clause can be used to reach reserved powers.
==1.9 Daily Video 1==
==1.9 Daily Video 2==
- \