U3 Mendeleev Periodic Table Basics
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts from the Honors Chemistry Unit 3 lecture on Mendeleev and the organization of the Periodic Table.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Dmitri Mendeleev (1869) organized elements by increasing ___.
atomic mass
Mendeleev grouped elements with similar properties __.
together
Mendeleev's early periodic table had some ___ in its arrangement.
discrepancies
Mendeleev also ___ properties of undiscovered elements, like eka-aluminum.
predicted
Henry Moseley (1913) organized elements by increasing __.
atomic number
Moseley's arrangement resolved ___ found in Mendeleev's periodic table.
discrepancies
Glenn Seaborg contributed to the modern periodic table by moving the Lanthanides and Actinides to the __.
bottom
John Newlands created the ___, noting a repetition of properties every eighth element.
law of octaves
Lothar Meyer demonstrated a connection between atomic mass and ___.
elements' properties
Each entry on the modern periodic table includes the Chemical Name, ___ (number of protons), Chemical Symbol, and Average Atomic Mass.
Atomic Number
Metals are typically shiny, malleable, ductile, and able to ___ electricity.
conduct
___ donate electrons to become positively charged.
Metals
Transition metals are unique because they can lose ___ numbers of electrons.
different
Non-metals are generally not shiny, can be gases at room temperature, and are __.
brittle
Non-metals ___ electrons to become negatively charged.
accept
Non-metals are typically ___, meaning they do not conduct electricity.
insulators
Metalloids exhibit ___ metal and nonmetal characteristics.
some
Lanthanides and Actinides are mostly ___ and many are __.
synthetic, radioactive
___ go across the periodic table, and their elements are ___ as to characteristics.
Periods, unrelated
Dmitri Mendeleev (1869) organized elements by increasing ___.
atomic mass
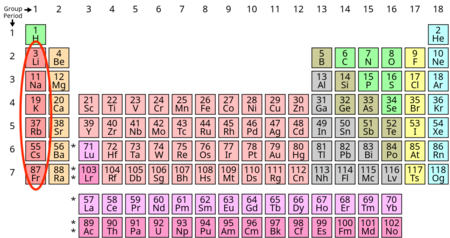
Alkalai metals
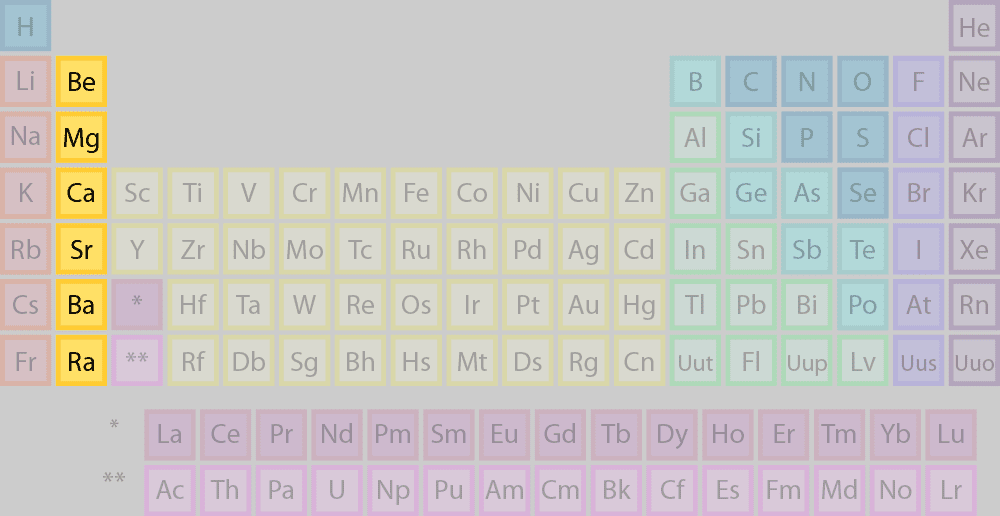
Alkaline earth metals
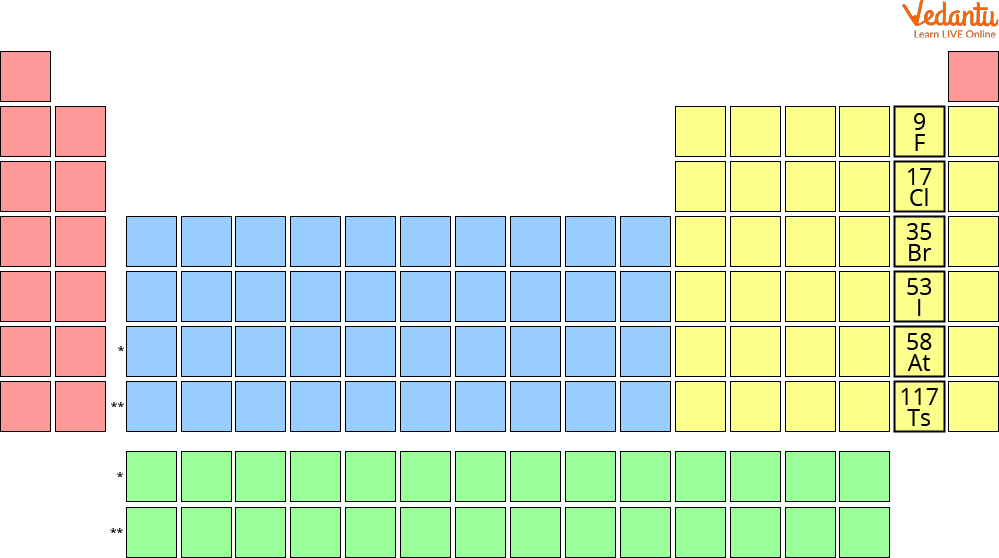
Halogens
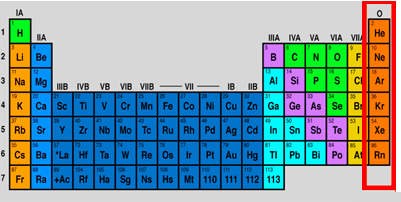
Nobel gases
What are valence electrons?
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom that are involved in chemical bonding.