7. Vascular Disorders & Thrombosis: Anatomy/Microanatomy
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
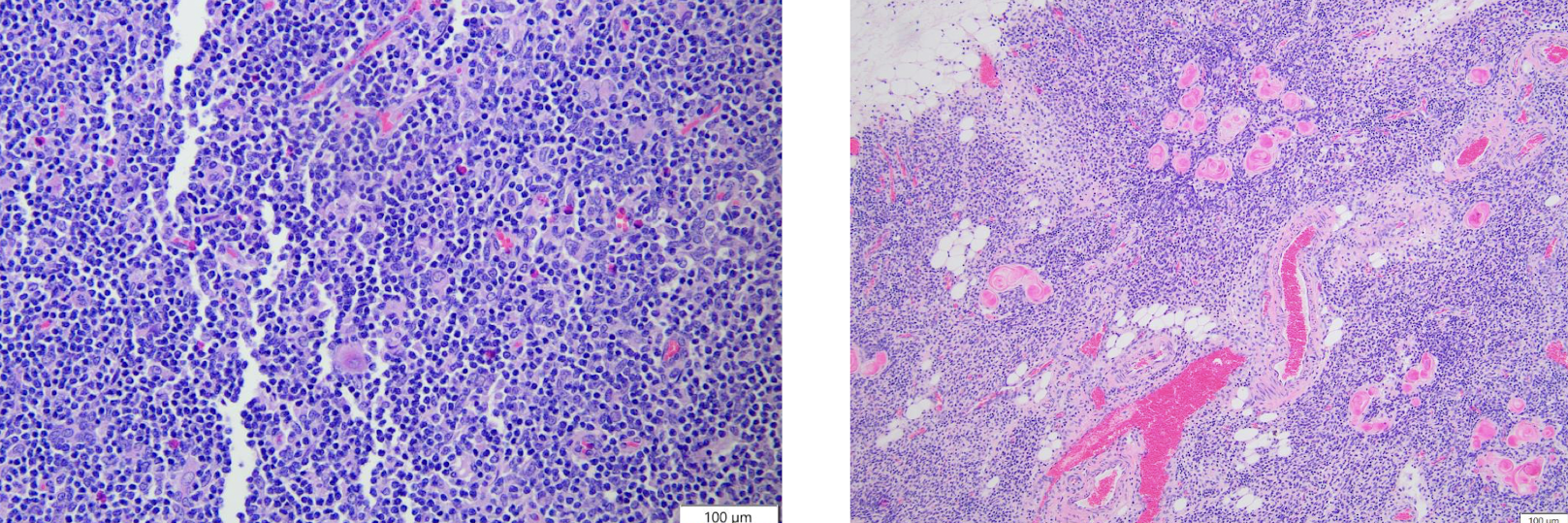
What is this showing?
severely atrophied thymus, which is largely devoid of lymphocytes
What is the main function of the circulatory system?
deliver nutrients and remove waste products from cells
True or false: The circulatory system is composed of blood, a central pump, and driving force to distribute blood through the system, most often known as the heart, and a vascular network which exchanges the nutrients and waste.
true
Arteries are under ________ pressure and move blood ________ from the heart.
high; away
Veins are under ________ and move blood ________ the heart.
low; towards
second network of vessels which drain the extracellular space that most, but not all, multicellular organisms have
lymphatics
Lymphatics ________ the veins and empty back into the blood via the ________ ________. That empties into the ________ ________.
parallel; thoracic duct; vena cava
largest vein of all that goes to the right side of the heart
vena cava
The walls of both arteries and arterioles will appear ________, both grossly and histologically. They can be identified based on the ________ and number of ________ fibers distributed throughout the wall.
thicker; thickness; elastin
often the closest to the heart, as they must withstand large pressures from the pump and be able to stretch (elastin fibers) and recoil to keep a continuous flow of blood
arteries
Arteries have a ________ lumen and ________ resistance. This facilitates ________ blood flow.
large; minimal
Arteries have a ________ vessel wall. It is made up of ________ muscle and ________ fibers.
thick; smooth; elastic
What is the purpose of the smooth muscle and elastic fibers?
tensile strength and elasticity
What is the main function of the arterioles?
provide resistance to the circulatory system as the blood moves further and further away from the heart and pressure will drop
What type of lumen do arterioles have?
narrow
What do arterioles respond to? What does this cause? What does this help maintain?
sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation; constriction and relaxation of vessels; blood pressure
All vessels have what layers?
tunica intima
tunica media
tunica adventitia
single layer around the lumen
tunica intima
deep to tunica media that allows the vessel to be dynamic
tunica media
supplies blood to arteries
tunica adventitia
What is the function of capillaries?
site of nutrient and waste exchange between the blood and surrounding tissue (extracellular/extravascular compartment)
What are the 3 types of capillaries?
continuous
fenestrated
discontinuous
What are the types of capillaries named for?
type of endothelial lining and basement membrane
What will differences in the lining allow for?
different substances to pass through and are present in different tissues
most numerous vessel of the circulatory system, but only contain 5% of the total blood volume at one time
capillaries
What is the velocity of blood flow through capillaries? How are the lamina? What does this do? What does this allow for?
slow; small; RBCs move through capillaries in a single file fashion; allows for time for exchange of nutrients and waste
The wall of the capillary is very ________, which also helps to facilitate the movement.
facilitate
In most cases, there is no more than what amount of space between a capillary and a cell?
1 mm of space
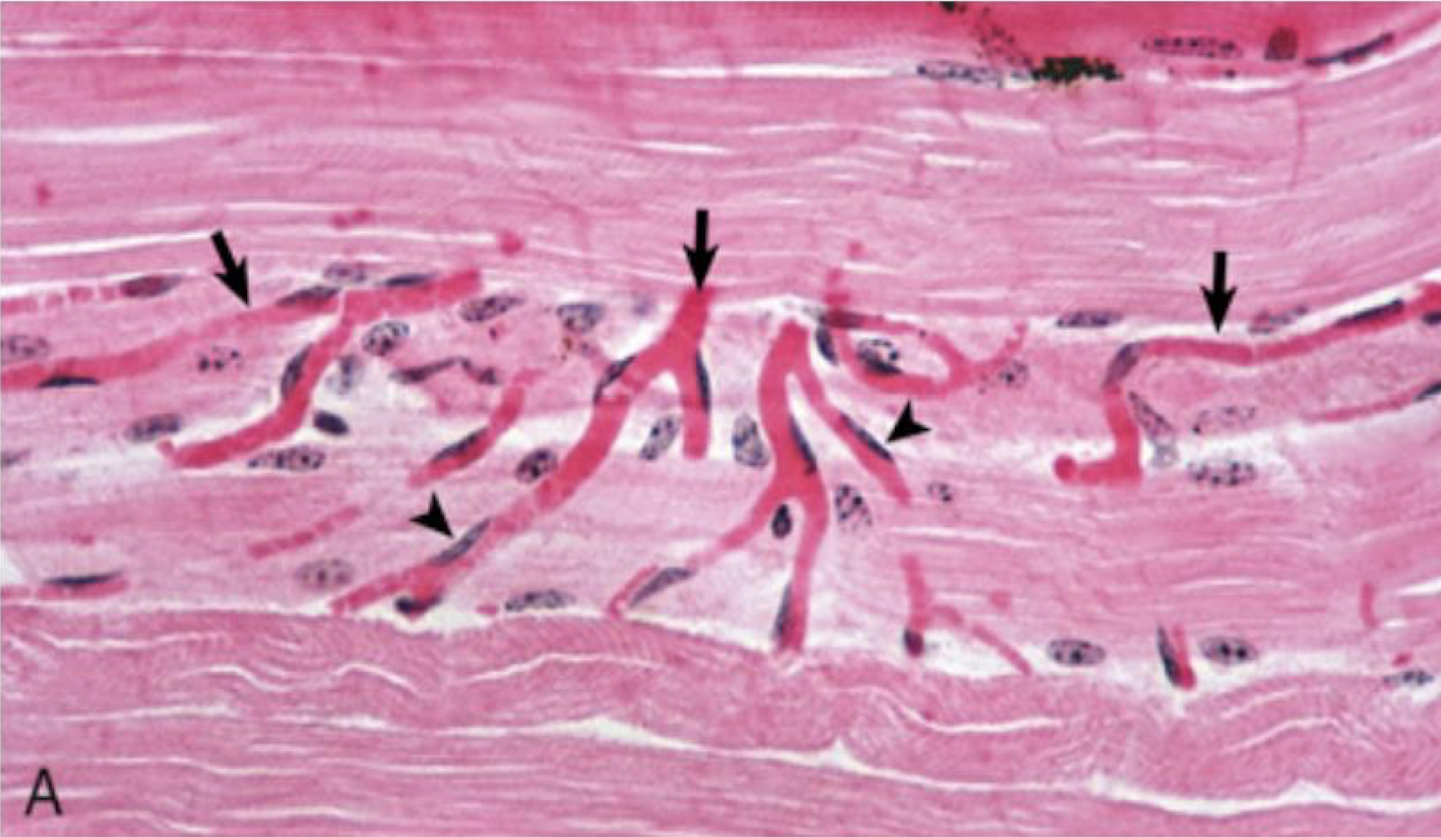
What is this?
capillary
What are the characteristics of continuous capillaries?
continuous endothelium
continuous basement membrane
Which type of capillary is the least leaky?
continuous
What is the only type of capillary that the brain has?
continuous
Continuous capillaries allow for the passage of only ________ molecules, as well as the exchange of ________ and ________, which can exchange through ________ of the endothelial cell. These capillaries are present in tissues which do not require or necessarily want the exchange of ________ products.
small; O2; CO2; microvesicles; larger
In what tissues can continuous capillaries be found?
B
M
L
B
brain (blood brain barrier)
muscle
lung
bone
What are the characteristics of fenestrated capillaries?
specialized spaces between endothelial cells (discontinuous endothelium)
continuous basement membrane
What is significant about the continuous basement membrane in fenestrated capillaries?
helps in keeping certain products within the lumen of the capillaries because it is negatively charged and will repel negatively charged items like albumin
What is significant about the discontinuous endothelium in fenestrated capillaries?
allows for the exchange of slightly large products and is selective about what passes through
In what tissues are fenestrated capillaries present int?
R
I
E
C
C
renal glomeruli
intestinal villi
endocrine glands
chroid plexuses
ciliary processes of the eye
Which type of capillary are the most leaky?
discontinuous
What are the characteristics of discontinuous capillaries?
endothelial cells don’t overlap
discontinuous basement membrane
Discontinuous capillaries allow for ________ passage of molecules from the ________ lumen into the ________ space.
maximum; vascular; extracellular
In what tissues are discontinuous capillaries found?
L
S
B
L
liver sinusoids
spleen sinusoids
bone marrow
lymph nodes
What are veins and venuoles mostly composed of? What does this allow for?
collagen; distention more than contraction
Veins and venuoles have little ________ ________ and ________, unlike arteries.
smooth muscle; elastin
Veins and venuoles can hold up to what percent of total blood volume?
65%
The vascular wall is ________ both grossly and histologically.
thinner
What does blood passage in veins and venuoles depend on?
O
C
I
one way valves to present back flow
contraction of skeletal muscles
increased pressure gradient due to increased pressure in the heart (cardiac suction effect)
What contributes to the most venous flow and helps with the movement of blood?
contraction of skeletal muscles
Why are one way values important for vein and venuoles?
because the pressure within the vein is relatively low
The return trip to the heart begins with the ________ ________ ________. It has a composition similar to ________, but will develop thin layers of ________ ________ the further away from the ________ they are.
post capillary venule; capillaries; smooth muscle; capillary
gives elasticity to vessels
elastin
What stain is used to highlight the elastin in vessels?
verhoff’s elastin stain
What is the microanatomy of elastin?
tunica intima (endothelium, elastin)
tunica media (smooth muscle)
tunica adventitia (connective tissue)
Lymphatics surround ________ and always run in concert with ________. They begin as ________ ________ lymphatic capillaries. They have ________ endothelial cells and large ________ ________, which can accommodate ________ particles into their lumen.
microcirculation; vasculature; blind ended; overlapping; interendothelial gaps; larger
What moves lymph forward towards the heart?
valves and contraction of skeletal muscles
Lymphatic vessels are ________ and a ________ pressure system like ________. Therefore, they have ________ and require ________ of ________ for movement of lymph.
distensible; low; veins; valves; contraction; muscle
Lymphatic vessels drain into ________ lymphatic vessels, pass through ________ ________, and eventually lead to the ________ ________, which drains into the ________ ________, returning lymph into circulation.
larger; lymph nodes; thoracic duct; vena cava
True or false: The pressure within the lumen of the lymphatic vessel acts as a bit of a valve closing these gaps and preventing escape of the flow of lymph from the lumen, meaning it can get it but it can’t get out.
true
What lines all the components of the circulatory system?
endothelium
What are the functions of the endothelium?
F
I
I
A
H
fluid distribution
inflammation
immunity
angiogenesis
hemostasis
Normal endothelium is ________, which helps to regulate ________ and prevent ________ formation, and ________, which helps break down the complexing of ________ into ________.
antithrombic; hemostasis; clot; profibrinolytic; fibrinogen; fibrin
specialized vascular networks formed by arterial blood vessels through the center of large venous sinuses
rete mirabile
What is the overall function of the rete mirabile? How does it do that?
R
I
O
E
countercurrent exchangers
regulating temperature
ionic contraction gradients
O2/CO2 exchange
equalized blood pressure in arteries before reaching the brain
A rete mirabile is predominant in ________, is located at the ________ of the ________, and is ________.
ruminants; base; brain; bilateral
True or false: As arterial blood travels through the rete mirabile, the venous blood surrounding allows for it to cool through countercurrent exchange. Located around the right and left internal carotid arteries as they pass by the pituitary gland, as well as along the cranial floor.
true
space between parenchymal and stromal cells and microcirculation
interstitium (extravascular compartment)
What are the functions of the interstitium?
P
M
G
S
provide pathways used by the microvasculature (vascular adventitia), lymphatic vessels, nerves, and trafficking leukocytes
module systematic physiologic properties exerted by parenchymal cells
general fluid pool/reservoir providing cushioning effects for organs, water/ion reserves
structural framework for cell survival
structural, adhesive, and absorptive components within the interstitium
extracellular matrix
What is the extracellular matrix predominantly composed of and provides most of the structural support?
type I collagen
What else is the extracellular matrix composed of?
T
G
G
P
type I collagen
glycoproteins
glycosaminoglycans
proteoglycans
provide sites of attachment for the structural proteins, as well as a site of adhesion for transmigrating leukocytes
glycoproteins
absorptive dissacharide complexes
glycosaminoglycans
hydrophilic and can bind large amounts of water and other soluble molecules
proteoglycans
What are the components of the extracellular matrix produced by?
P
F
G
M
T
parenchymal cells
fibroblasts
glial cells (CNS only)
macrophages
trafficking leukocytes