child maltreatment
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
what can child maltreatment include?
Physical
Sexual
Emotional
Exposure to dv
Neglect
Fabricated or induced illness
uk definition of child maltreatment
includes any abuse or neglect of a young person/child,
caused by inflicting harm or by failing to act to prevent harm,
classified as physical, sexual or emotional abuse; neglect; and fabricated illness
WHO definition of child maltreatment
all forms of physical and or emotional ill-treatment,
sexual abuse, neglect or negligent treatment or commercial or other exploitation,
resulting in actual or potential harm to the child, in the context of a relationship or trust of power
areas of uncertainity in defining
Do all forms of violence count as CM
Is CM only perpetrated by caregivers?
Is power differential necessary?
uk prevelance of CM
29% of adults (18-74) experienced CM before 18 years
44% of adults who experience abuse before age 16, experienced multiple types of abuse
however- not acceptable survey tool
outcomes across the lifespan due to CM
physical- neurological, metabolic etc
mental- PTSD, anxiety etc
psychosocial functioning- self-harm, school attainment etc
variation in outcomes due to the type of maltreatment
assumed:
Sexual and physical abuse is more harmful
Found:
Equivalence in the type of severity of outcomes across different types of abuse
risk and protective factors- risk
increase the probability of a poor outcome,
probability vs deterministic
cumulative impact
risk and protective factors- protective
Act as buffer in context of risk
Lessens the impact of harm
Still no guarantees
River analogy- risk and protective factors
Rain is the risk factor- increases river flow, leading to rougher conditions
Rocks, leaves, etc, are the protective factors- slow the flow and can lead to a stream( less harmful pathway)
Bronfenbrenner's ecological systems theory
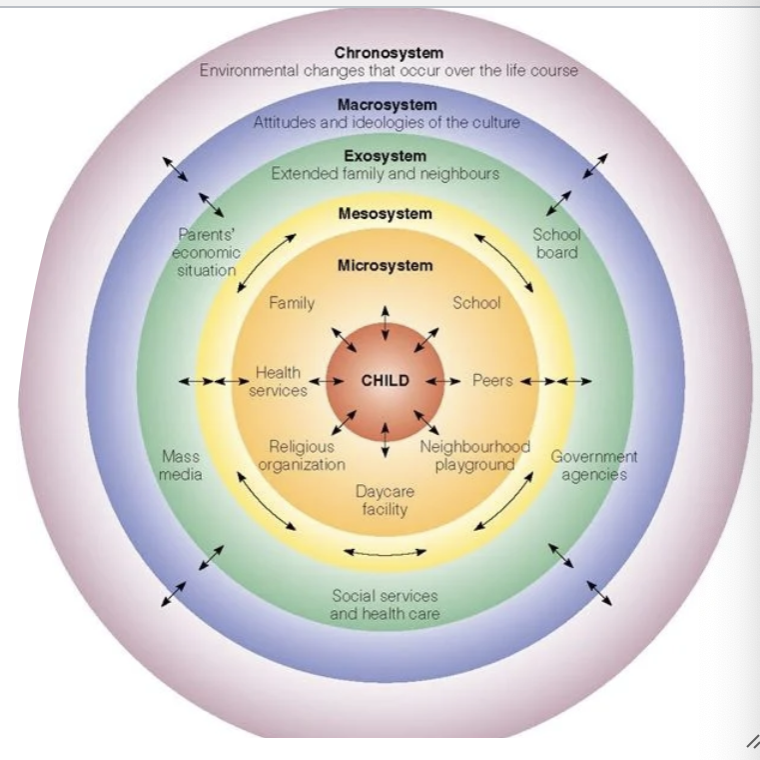
biopsychsocial model

latent vulnerability
how CM causes subtle brain changes that help a child survive in a dangerous environment
but creates a hidden, long-term risk for future mental health problems in adulthood, even if the child seems fine initially
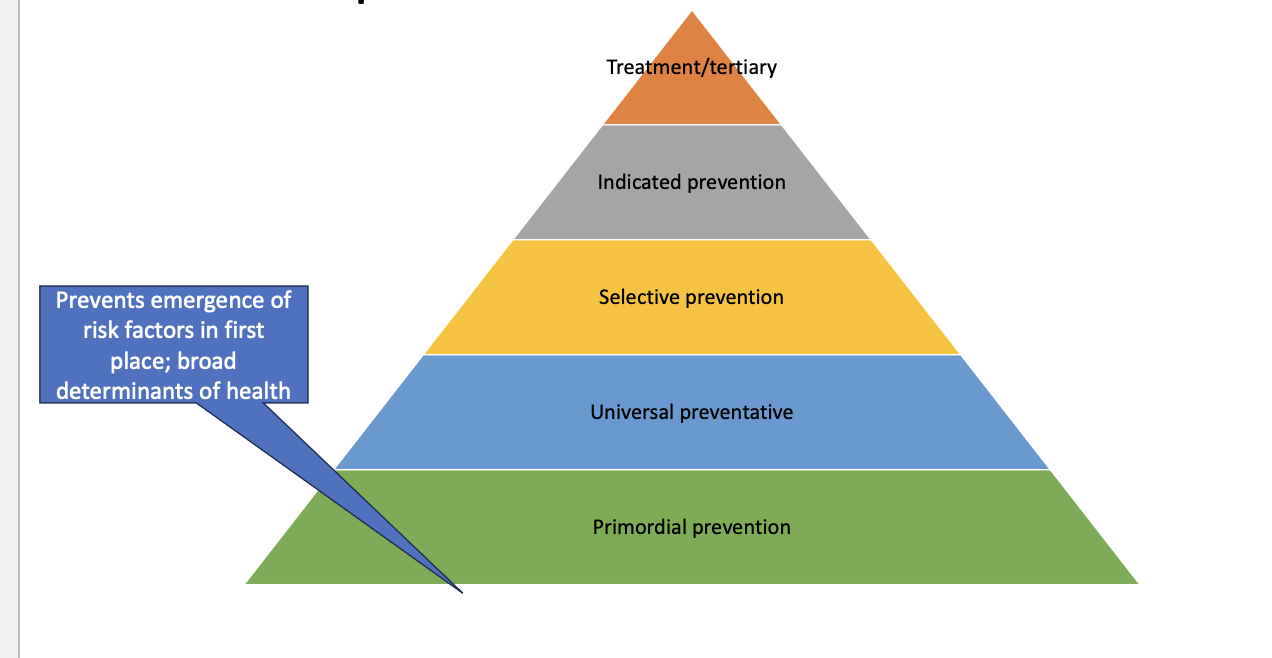
levels of prevention
top
treatment
indicated prevention
selective prevention
universal preventative
primordial prevention- prevents emergence of risk factors in 1st place