AORTIC STENOSIS DOPPLER ASSESSMENT unit 1
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
DOPPLER ECHO: AORTIC STENOSIS
ASSESSMENT
Severity of stenosis is determined by 5 steps what are they
1-Peak flow velocity
2 – Mean pressure gradient
3 – Aortic valve area
4 – Dimensionless index
5 – Simplified Continuity Equation
PEAK AORTIC FLOW VELOCITY ASSESSMENT
what does this measure, and how is this measured?
Antegrade systolic
velocity across the AV
• HIGHEST CW Doppler
jet
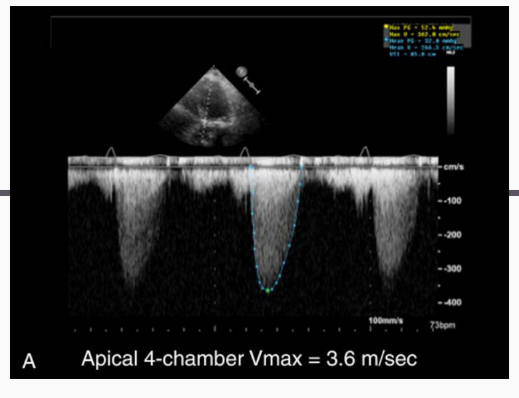
PEAK AORTIC
FLOW VELOCITY
Optimization how would you want to optimize the doppler signal
what will you do with the gains and wall fillter and the baseline and scale
what about the sweep speed where do you trace and what are the best views
Optimize Doppler signal
1- Decrease gains and increase
wall filter
2 – Adjust Baseline and scale
3 – Increase sweep speed
4- Trace TVI of outer edge of
signal (avoid noise and fine linear
signals)
B e s t V i ew s : A p i c a l 3 o r 5 C h am b e r,
Right Sternal Border, right
c l a v i c ul a r, and Suparsternal Notch
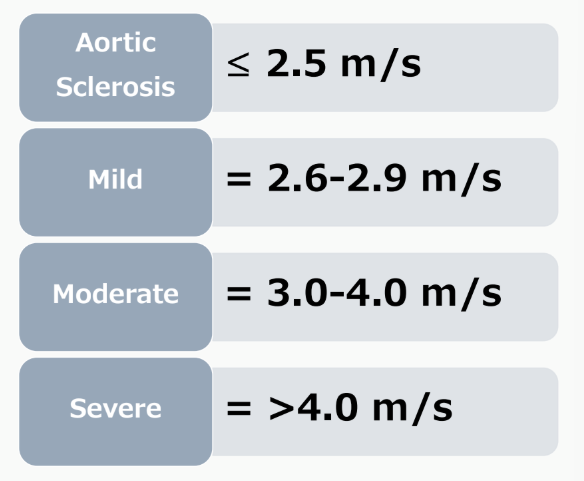
AS PEAK VELOCITY: SEVERITY SCALE
ASSUMES NORMAL CARDIAC
OUTPUT
Aortic sclerosis
mild
moderate
severe
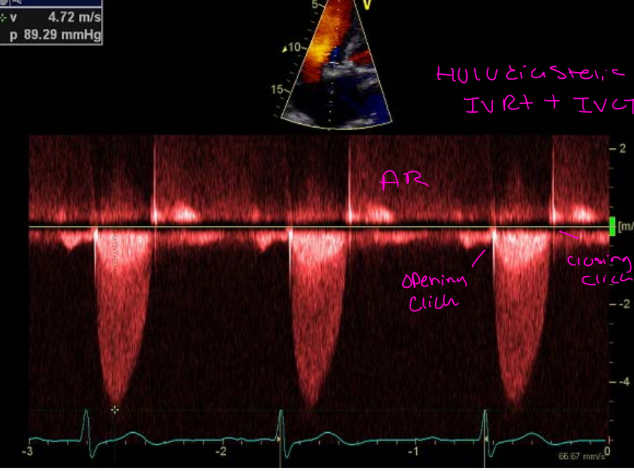
The mean pressure gradient is the difference in what?
Average Gradient across the? during what cardiac cycle
what equation is used at several velocity points and averaged
reported in what units
Difference in pressure between
the left ventricle and aorta in
systole
• Average gradient across the
aortic valve during entire systole
• Simplified Bernoulli equation is
used at several velocity points
and averaged
• Reported in mmHg
AS MEAN GRADIENT SEVERITY SCALE
what are the mild, moderate, severe numbers

A TVI tracing provides us with and what are they dependent on?
A TVI tracing provides both mean
gradients and peak
velocity/gradient
Both are flow dependent
(Check prior echos for the best
view and highest velocity)
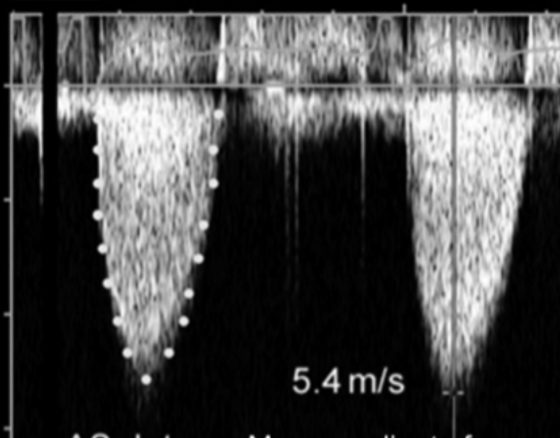
what are the Possible errors in measuring (3)
Incorrect identification of the flow
signal
• (e.g., mistaking the mitral regurgitation signal
or dynamic obstruction for AS)
• Respiratory motion
• Measurement variation among
sonographers
what calculation do we use for our AVA, what does it calculate using it…proximal…
•Continuity Equation for AVA
Volume flow proximal to and in
the stenotic orifice is equal
Continuity Equation AVA, independent of what can be used to calculate what
Independent of
flow, can be used
to calculate area
with AI, high or
low output states
Continuity Equation AVA, Measures
effective orifice
area what is this
Effective orifice area
(EOA) is the standard
parameter for the
clinical assessment of
aortic stenosis severity
AVA calculates solving for the-what is it finding out? / used for to determine
AVA calculates solving for the
narrowest area...aka EOA
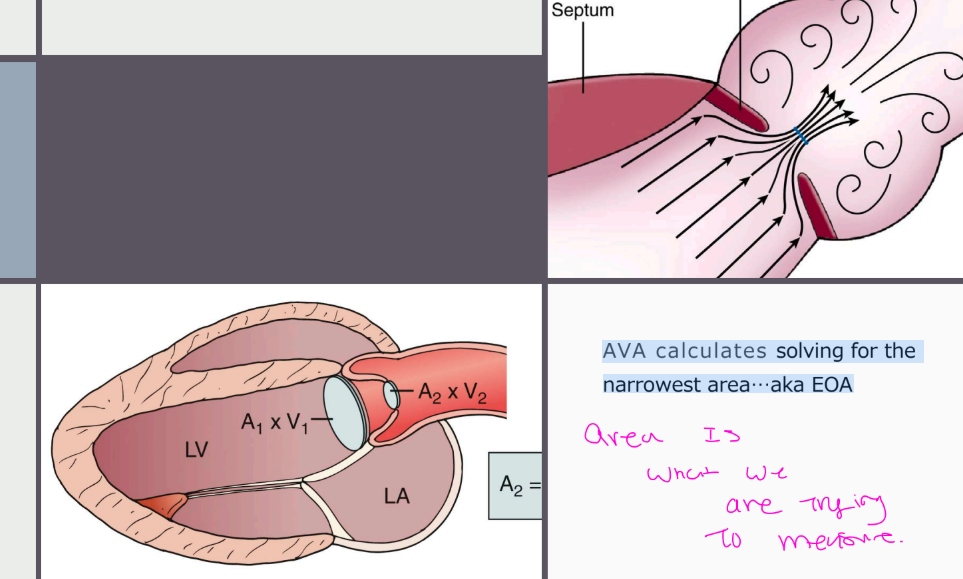
AS – continuity equation
Calculation of AVA Continuity equation
Measurements needed what are and what is the formula
LVOT diameter
LVOT velocity VTI (PW)
AV velocity VTI (CW)

Measurement of LVOT Diameter
in what view
measure in what cardiac cycle
what are the caliper placement
what are the normal values
what are the normal values between male and female
PLAX
Measure in early-mid systole
Caliper placement
• Insertion-to-insertion
Normal Values 1.8 – 2.4 cm
• Male 2.0-2.4
• Female 1.8-2.2
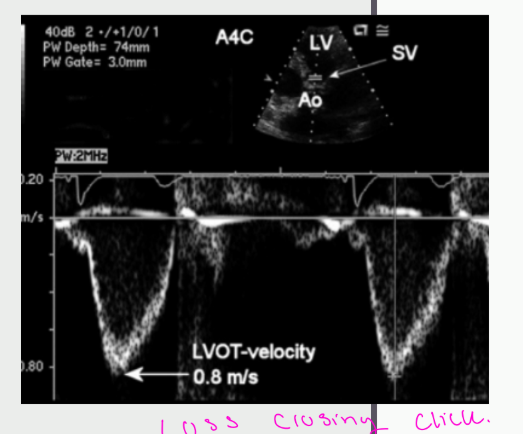
Measurement of LVOT TVI
you may lose what as stenosis increase
what is the normal LVOT TVI?
Heart rate takes at time of what measurement for accurate what assessment
•You may lose the valve click as
stenosis increases
•Normal LVOT TVI
• 18 – 22 cm
•Heart rate taken at time of SV
measurements for accurate CO
assessment
measurements of at least how many beats should be averaged for pt in normal sinus rhythm
3 beats
measurements of at least how many beats should be averaged for a pt with an arrhythmia like A-Fib
5 beats
LVOT spectral Doppler
you want to be what with flow?
Identify what velocity
what do you want to do with the doppler gain and compression
and how do you trace to obtain what
Choose the most parallel
to flow (PTF)
Identify modal velocity
Decrease Doppler gains
and lower compression
Trace outer edge of modal
velocity to obtain the TVI
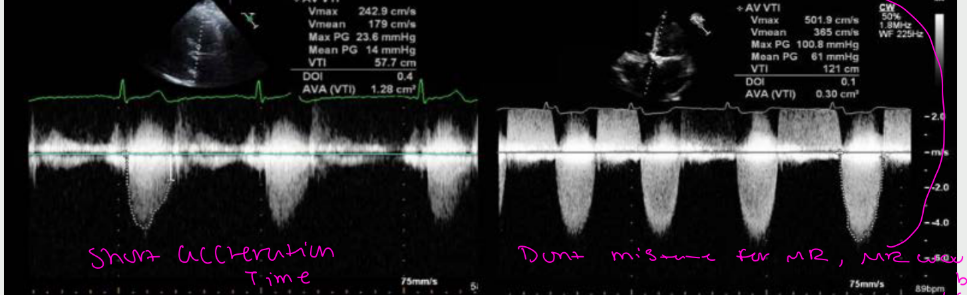
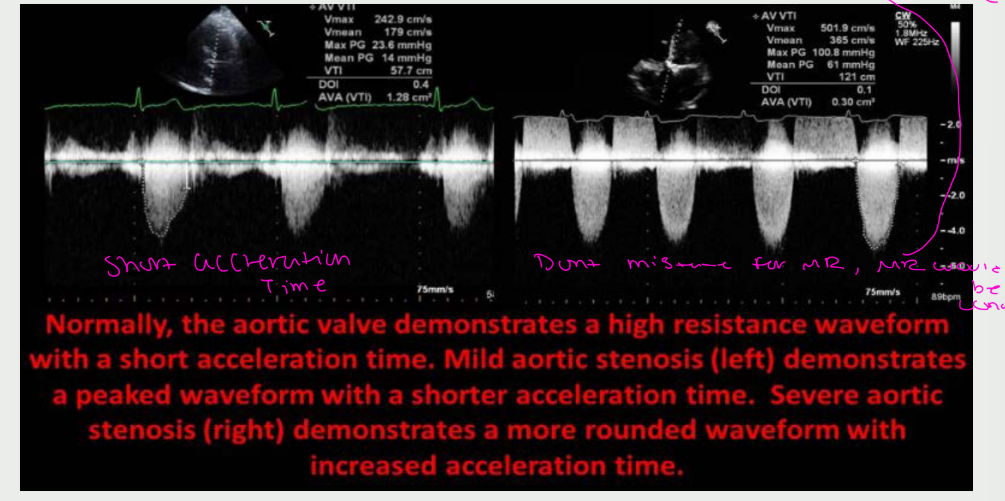
normally the AV demonstrates a what waveform with a what acceleration time. Mild AS left demonstrates a ____ waveform with a what acceleration time. sever AS on the right demonstrates a what waveform with what acceleration time
increased acceleration time” mean in AS?
👉 Blood takes longer to speed up because it’s pushing through a tight valve.
Why this happens in aortic stenosis
The valve opening is narrow
There is high resistance to flow
Blood cannot accelerate quickly
Peak velocity is delayed
📌 The tighter the valve → the longer the acceleration time.
What it looks like on Doppler
Rounded, delayed peak
Slow rise to max velocity
“Late-peaking” waveform
Increased acceleration time in aortic stenosis reflects delayed blood acceleration due to increased resistance across a severely narrowed aortic valve.”
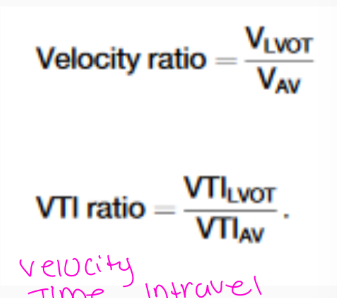
CONTINUITY EQUATION:
Limitations what are they?
Pitfalls…
1-Requires 3 measurements
2-LVOT diameter squared
3- Irregular rhythms
4-TDS
CONTINUITY EQUATION: (which one is the greatest potential source of error?
Limitations
Pitfalls
1-Requires 3 measurements
why
2-LVOT diameter squared
Calcification may result in what
LVOT is not circular which may cause what
3- Irregular rhythms
why
4-TDS
why
Pitfalls
1-Requires 3 measurements
– More room for error
2-LVOT diameter squared
– Greatest potential source of error
– Calcification may result in a small diameter
– LVOT is not circular which may cause underestimation in SV and AVA
3- Irregular rhythms
– Need to take multiple measurements
4-TDS
– Multiply errors
•Additional assessments recommended for
severity of aortic stenosis
•Simplified Continuity Equation (cm2)
•Indexed AVA (no units)
•Planimetry of aortic valve anatomic area
(cm2)
•Additional assessments recommended for
severity of aortic stenosis, describe each one
•Simplified Continuity Equation (cm2)
• The ratio of LVOT to aortic velocity is similar to the
ratio of VTIs with native aortic valve stenosis
•Indexed AVA (no units)
– Effective AVA expressed as a proportion of the LVOT
area
– Does not consider size of the LVOT
•Planimetry of aortic valve anatomic area
(cm2)
• Anatomic (geometric) CSA of the aortic valve orifice as
measured by 2D or
3D echo
AS
Measurements
/Equations

AS
Measurements
/Equations Dimensionless index
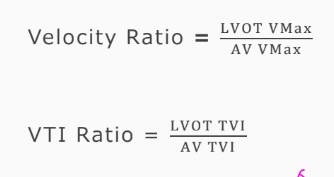
Dimensionless Index This measurement is available when? The dimensionless index expresses what?
This measurement is available when we
aren’t able to see or measure the LVOT
diameter in PLAX
The dimensionless index expresses the size
of effect orifice area and removes body size
Dimensionless Index limitations
Limitations: It removes body
size which varies from person
to person
Dimensionless Index
no stenosis = ratio will be what
as the stenosis gets more sever, what happens to the numbers
No stenosis = ratio will be 1
As the stenosis gets more severe, the numbers
decrease
Planimetry is difficult in
stenosis due to? Planimetry can used during what
Planimetry is difficult in
stenosis due to
calcification around the
valve with TTE
Planimetry can used
during TEE
Limitations to grading Aortic
Stenosis, when We cannot calculate AVA
With dynamic sub-aortic obstruction or a subaortic
membrane, SV calculations are not accurate
We cannot calculate AVA
what are other Limitations to grading Aortic
Stenosis (think of things that can overstimates mean gradient and alter the peak velocity/mean gradient
Significant Aortic Insufficiency with Aortic Stenosis
Creates high subaortic flow rates
Overestimates mean gradient
Hypertension can alter the peak velocity/mean gradient and
should therefore be recorded for every examination
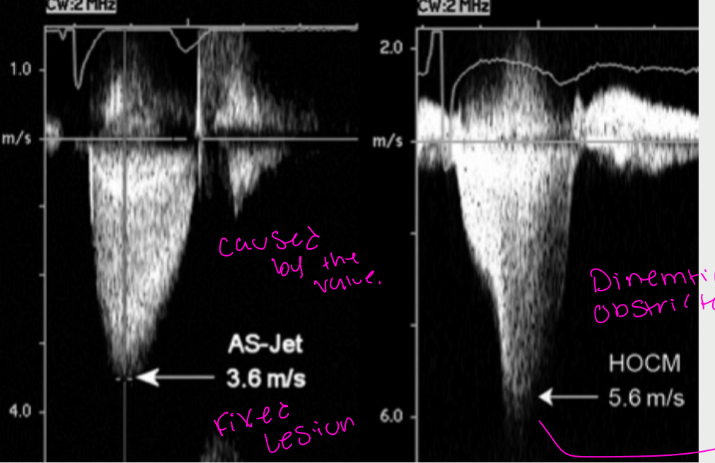
what is this showing
FIXED DOPPLER
SIGNAL VERSES
DYNAMIC
DOPPLER SIGNAL
What are the limitations to grading stenosis (5) (flow)
Abnormally high flow - High flow may be
reversible and should be addressed to see
the true severity of stenosis
• Anemia
• Hyperthyroidism
• Arterio-venous shunts
• Patients on hemodialysis that haven’t
gone through treatment
more limitations with MR, MS, how do these affect and when uncontrolled systemic blood pressure is
Mitral regurgitation may reduce the
cardiac output
Mitral Regurgitation signal may be
mistaken for AS signal
Mitral stenosis can also reduce cardiac
output
When uncontrolled systemic blood
pressure is present, it may reduce flow
and EF due to increase pressure
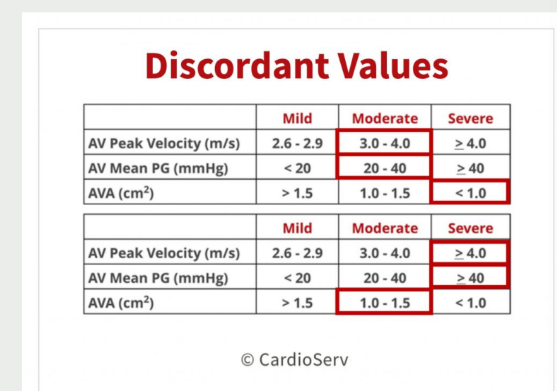
LOW FLOW LOW
GRADIENT
AORTIC STENOSIS what is showing with the numbers
This is a classic example
of when the numbers
don’t match
Pt’s AVA is less then 1.0
And Peak velocity and
mean PG are moderate
Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis
is a subset of pt who have what but do not meet to the classic echocardiographic criteria
can we visually see severe AS but what doesnt match due to what
LFLG severe AS is a subset of patients who
have severe valvular stenosis but do not meet
the classical echocardiographic criteria
• We can visually see severe AS but
numbers don’t match
• Due to insufficient flow across the
aortic valve
Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis
whats the #1, #2a, #2b
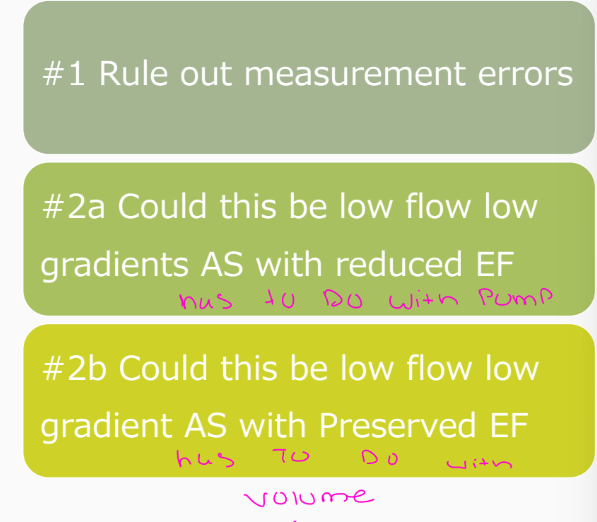
Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis
Velocity and gradients are dependant on?
Flow is determined by?
Flow status is equal to
Look at what
Velocity and gradients are dependant on flow!!!!
Flow is determined by flow status
• Flow status is equal to stroke vlume index
• Look at stroke volume index <35 ml/m2
Following conditions can result in
low-velocity/gradient severe AS
with _____EF including: what are they? (8)
hese conditions causing low flow low gradient AS ?% LV EF
Following conditions can result in
low-velocity/gradient severe AS
with preserved EF including:
Tachycardia
• Bradycardia
• Hypertension
• Small ventricular cavity
• Severe diastolic dysfunction
• Severe mitral or tricuspid valve disease
• Pulmonary hypertension
• Left or right ventricular dysfunction
these conditions causing low flow low gradient AS >50% LV EF
Low Flow Low Gradient AS <50% LV EF
If EF is decreased what will you also see be decreased?
What we will need to determine?
Reduced EF <50%
If EF is decreased velocities and gradients are
decreased
If the EF is reduced (<50%), then we need to
determine if the decrease in valve opening (AVA)
is due to true severe AS or LV dysfunction!
Low Flow Low Gradient AS <50% LV EF
Move forward to _________Stress Echo
The test tells us
Contractile Reverse- contractile response to
Dobutamine
Stroke Volume- Presence of flow reverse (> 20%
SVI from baseline)
More in Stress Echocardiography
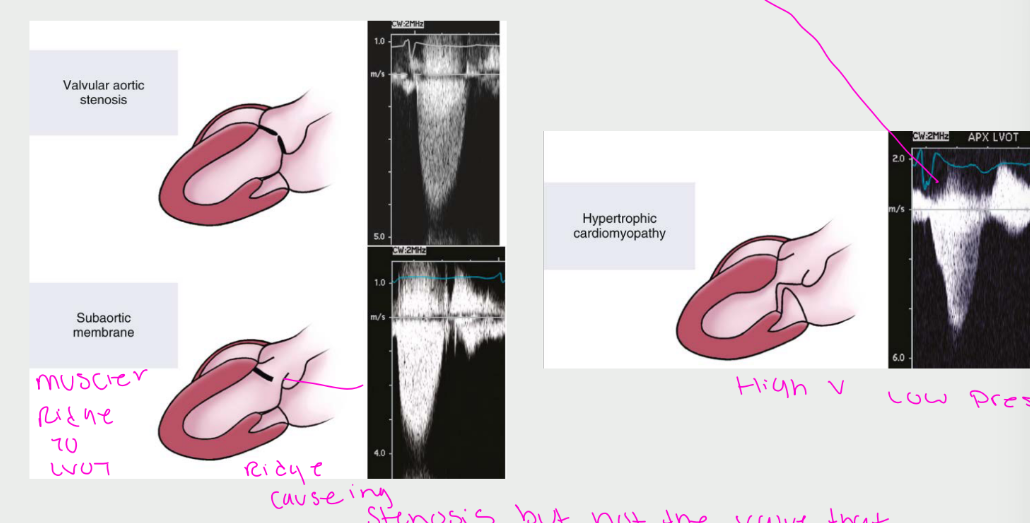
what are the Differentials
Left Ventricular Obstructions can be
caused by the following...(3)
Fixed subvalvular obstruction (a
subaortic membrane or a muscular
subaortic stenosis)
• Dynamic subaortic obstruction
(hypertrophic cardiomyopathy)
• Supravalvular stenosis
what is the medical treatment? (7)
Rheumatic Fever Prophylaxis
Diuretics
Ace inhibitors/Nitrates/Beta blockers
High cholesterol drugs
Cardioversion for Afib
Limitations on Activities an exercise in severe AS
Screening of first degree relative
what is the surgical treatment
SAVR (surgical aortic
valve replacement)
TAVR (transcatheter
aortic valve
replacement)
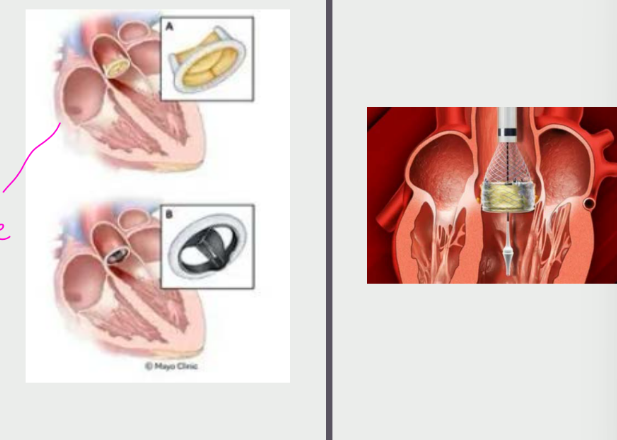
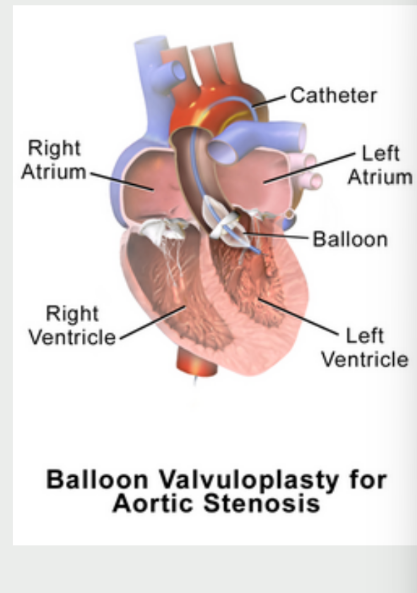
what are some other surgical treatments provides how many months of AS relief?
Aortic Balloon Valvuloplasty
Only provides < 6 months of AS
relief
Surgical
Treatment
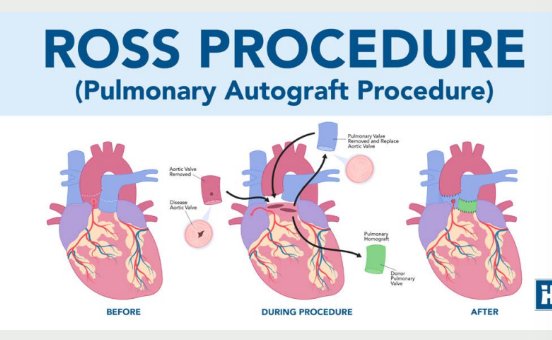
Ross procedure: what is it
Pulmonary valve
transplant to aortic
position, reimplantation
of the coronary arteries,
and placement of a
homograft in pulmonary
position