Circulation
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
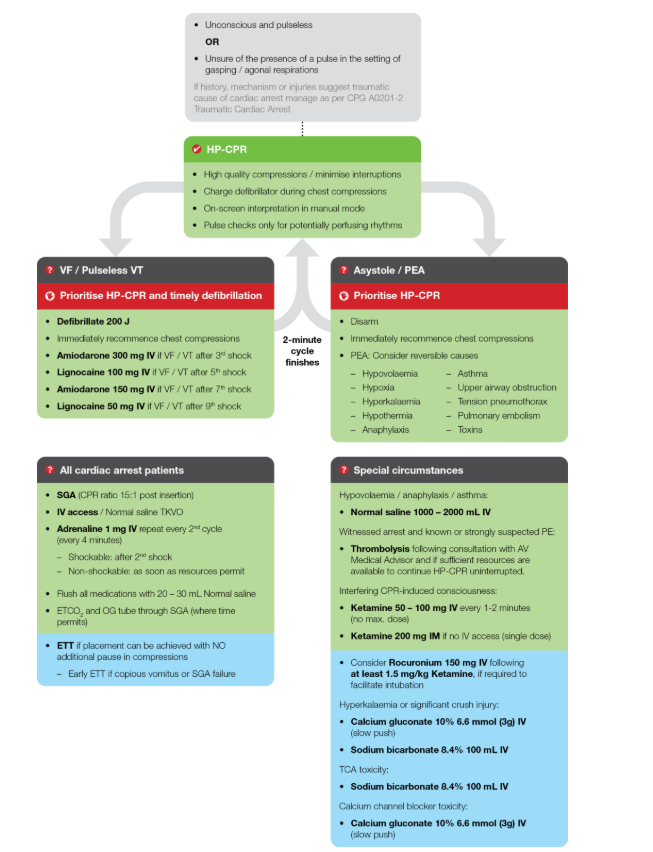
When to start CPR (CPG)
Unconscious & pulseless, or unsure of the presence of a pulse in the setting of gasping/agonal respirations
What is high quality CPR
Compressions 1/3rd of chest, allowing for recoil. 100-120 per minute.
Charge the defib during compressions
on-screen interpretation in manual mode
pulse checks only for potentially perfusing rhytmns
Drug order for Cardiac Arrest
Amiodarone 300mg after 3rd shock
Lignocaine 100mg after 5th shock
Amiodarone 150mg after 7th shock
Lignocaine 50mg after 9th shock
Reversible causes of arrest (4Hs and 4Ts + others)
Hypovolemia
Hypoxia
Hyperkalemia
Hypothermia
Anaphalaxis
Asthma
Upper airway obstruction
Tension pnemothorax
Tamponade
Thrombosis
Pulmonary embolism
Toxins
What do you do for all cardiac arrest patients?
SGA insertion, at a CPR ratio of 15:1
IV access with normal saline TKVO
Adrenaline 1mg every second cycle
Flush with 20-30mL saline
What do you do if the patient is interfering with CPR?
Ketamine 50-100mg every 1-2, no MAX OR 200mg IM
High Performance CPR Notes

Compression/Ventilation ratios
NO SGA/ETT - 30:2, w pause for ventilations
SGA IN SITU: 15:1, 6-8 per minute, NO PAUSE
Pad placement
Sternal: Right side of the chest, under the clavicle & above the nipple.
Apex: Left mid-axilliary line, 6th intercostal space
When is a patient in REFRACTORY VT/VF
When they remain in a shockable state after 3 defib attempts
How to ‘stack shocks’
Deliver first shock within 20 seconds of arrest occuring. Aim for 10 seconds between each shock with interpretation. THREE SHOCKS!
HP CPR SCRIPT
Approaching the end of the two minute cycle, this looks like (heart pattern) do you agree?
Continue compressions, everyone else clear
Charing to (X) joules
(SLAP) stop compressions, clear?
Still in (heart pattern), shocking/disarming
Medical Cardiac Arrest Guideline
ROSC Management

VACAR Report Facts
78% of cardiac arrest occured at home
65% were male
7830 OOH cardiac arrests
12% survived on bystander CPR
53% survived when shocked by public AED
83% if survivors were dispatched to their homes
118 per 100K people
3 Components of Cardiac Arrest
Unconscious, Apnoeic, Pulseless
What is actually happening during a cardiac arrest?
Lack of blood circulation causing lack of oxygen to the body
Lack of O2 causes loss of consciousness, abnormal or absent breathing - which can result in brain injury after 5 minutes
O2 lack causes organs to start dying, anearobic metab, cellular receptors stop resonding, acidosis, etc..
3 Phase Model of Cardiopulmonary CPR
Electrical phase: onset of arrest to >4 minutes
Circulatory phase: from 4-10 minutes
Metabolic phase: beyond 10 minutes
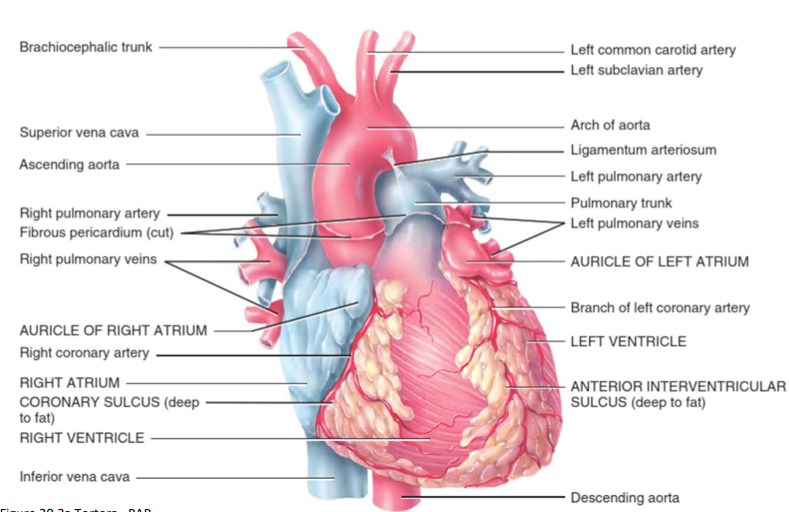
Where is the heart?
size of the fist
rests on the diaphragm in the mediastinum, 2/3rd of the midline
pointed end at the 5th IC space, MC line, broad portion is the base level of the 2nd rib
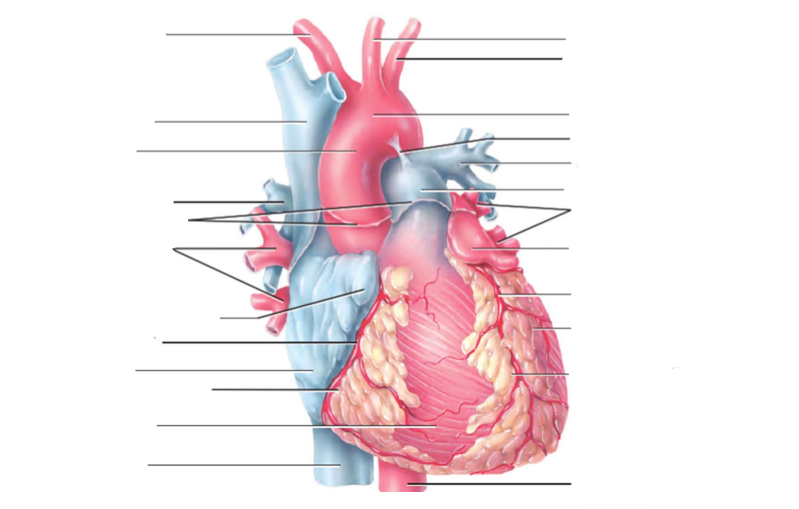
Heart Anatomy
3 layers of the heart wall
Epicardium (external), Myocardium (middle layer contraction), Endocardium (inner layer. layer of thin connecitve tissue)
How is the heart made up (chambers & valves)
four chambers - two atria & ventricles
four valves - two atrioventricular & semilunar
What is the purpose of CPR?
sufficent vital organ blood flow
preserves life until definitive procedures/interventions
compression & recoil generates a proportion of normal cardiac output
Cardiac pump Model
direct compression of heart between the sternum and veretbral body
blood is squeezed out of the heart with compression & fresh blood entering the heart during recoil
Thoracic pump Model
blood flow is a result of pressure changes within the thoracic cavity
heart is more passive
blood is forced out of the thorax when intrathoracic pressure is high
blood is drawn into the thoracic cavity due to sudden decrease in pressure (recoil)
Thoracic VS Cardiac Differences
Cardiac:
direct squeezing of the heart
works best in kids & young adults
blood is rejected from the heart
direct compression of the heart
Thoracic:
pressure changes in the chest
larger patients, more flexible chest walls
blood moves due to the pressure changes in the thotax
compression of the entire chest cavity
Good CPR?
Depth must be 1/3rd, more than 5cm in adults
Rate must be 100-120 pm
Allow for full recoil
Changes every 2 minutes to prevent fatigue
1 second per ventilation
Non shockable rhythm
Asystole (NO HEART FUNCTION)
PEA (electrical activity not coheisve with output - NO PULSE)
Ventricular Fibrillation
chaotic & bizzare originates in the ventricles
uncoordinated ineffective contraction of ventricles
quiver X contract
no effective ventricular contractions
SHOCKABLE
Ventricular Tachycardia
can be conscious
do not shock with pulse present
fast, wide, regular
LETHAL - can become VF or asys
SHOCKABLE
Defibrillation
An attempt to cause depolarisation of all the cardiac cells at once in the hope that the heart’s natural pacemakers will try and pace the heart in a more coordinated fashion, leading to uniform contraction of the heart & restoration of perfusion
What is ROSC?
Return of Spontaneous Circulation - evidence of perfusion. BP, improvement in colour, ETCO2 valuables better, increase in GCS & spont ventilations
What do do when ROSC is achieved?
return to primary survey
maintain management
continue your clinical assessment
reassume the clinical approach